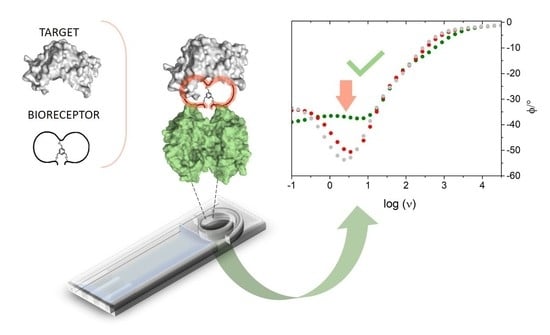
An Impedimetric Biosensing Strategy Based on BicyclicPeptides as Bioreceptors for Monitoring h-uPA Cancer Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Cancer Type | [h-uPA] Range | References |
|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | 0.21–16.06 ng mL−1 | [38] |
| Soft-Tissue Sarcoma (STS) | <4.76 ng mL−1 | [39] |
| Bladder cancer | <34.1 ng mL−1 | [40] |
| Colorectal cancer | 5.5–7.5 ng mL−1 | [41] |
| Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 0.21–1.92 ng mL−1 | [42] |
| Pancreas cancer | 1.2–7.6 ng mL−1 | [43] |
| Chronic pancreatitis | 0.9–5.4 ng mL−1 | [44] |
| Liver cancer | 0.2–14.7 ng mL−1 | [45] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Sandwich-Type Affinity Electrochemical Assay for h-uPA
2.3. Impedimetric Assay for h-uPA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparing P3 and P2 Performance in Voltammetric Assay
3.2. EIS-Based Sensor Design and Characterization
3.3. Impedimetric Detection Strategy: Preliminary Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| List of Abbreviations and Acronyms | |
| 1-NPP | 1-Naphtyl phosphate disodium salt |
| 4PL | Four parameters logistic |
| Ab1 | Urokinase polyclonal primary antibody |
| Ab2 | Anti-Rabbit IgG-Alkaline phosphatase secondary antibody |
| Cdl | Double-layer capacitance |
| CPE | Constant phase element |
| CPEPL | Constant phase element associated with the protein layer |
| DC | Direct current |
| DEA | Diethanolamine |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetry |
| EDTA | Ethylendiaminotetraacetic acid |
| EEC | Electric equivalent circuit |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| h-uPA | Human-urokinase plasminogen activator |
| Ki | Inhibitory affinity constant |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| NSA | Non-specific adsorption |
| P1 | Bicyclic peptide P1 |
| P2 | Bicyclic peptide P2 |
| P3 | Bicyclic peptide P3 |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PL | Protein layer |
| PoC | Point-of-care |
| Rct | Charge transfer resistance |
| RctPL | Charge transfer resistance associated with the protein layer |
| Rs | Solution resistance |
| SPCE | Screen-printed carbon electrode |
| SPE | Screen-printed electrode |
| Strep-SPCE | Streptavidin-modified screen-printed carbon electrode |
| Strep-MBs | Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads |
| tris-HCl or Trizma-HCl | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride |
| Tween 20 | Non-ionic polyoxyethylenesorbitan monolaurate |
| uPAR | Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor |
| UK18 | Bicyclic peptide UK18 |
| W | Warburg impedance element |
References
- Kurrikoff, K.; Aphkhazava, D.; Langel, Ü. The future of peptides in cancer treatment. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, D.; Salomé Veiga, A.; Castanho, M.A.R.B. From antimicrobial to anticancer peptides. A review. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sfragano, P.S.; Moro, G.; Polo, F.; Palchetti, I. The Role of Peptides in the Design of Electrochemical Biosensors for Clinical Diagnostics. Biosensors 2021, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, L. Peptide-based electrochemical biosensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Gooding, J.J. Peptide Modified Electrodes as Electrochemical Metal Ion Sensors. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stortini, A.M.; Baldo, M.A.; Moro, G.; Polo, F.; Moretto, L.M. Bio- and Biomimetic Receptors for Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metal Ions. Sensors 2020, 20, 6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Boyd, B.J. Peptide-based biosensors. Talanta 2015, 136, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimov, J.Y.; Lai, R.Y. An electrochemical peptide-based biosensing platform for HIV detection. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Xing, Y.; Liu, L. Design of electrochemical biosensors with peptide probes as the receptors of targets and the inducers of gold nanoparticles assembly on electrode surface. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; He, Y.; Mao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, G. Electrochemical assay of active prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using ferrocene-functionalized peptide probes. Electrochem. commun. 2010, 12, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Yun, J.W.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. Re-engineering of peptides with high binding affinity to develop an advanced electrochemical sensor for colon cancer diagnosis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1146, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.M.; Ryu, M.Y.; Yun, J.W.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. Electrochemical peptide sensor for diagnosing adenoma-carcinoma transition in colon cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, S.; Guo, L.; Shen, C.; Yang, M.; Rasooly, A. DNA Generated Electric Current Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, C.A.; Pei, D. Bicyclic Peptides as Next-Generation Therapeutics. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12690–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangarzadeh, S.; Kanafi, M.M.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Barati, M.; Ranjbari, J.; Tayebi, L. Bicyclic peptides: Types, synthesis and applications. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodbeen, R.; Paaske, B.; Jiang, L.; Jensen, J.K.; Christensen, A.; Nielsen, J.T.; Huang, M.; Mulder, F.A.A.; Nielsen, N.C.; Andreasen, P.A.; et al. Bicyclic Peptide Inhibitor of Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator: Mode of Action. ChemBioChem 2013, 14, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.; Wind, T.; Blouse, G.E.; Christensen, A.; Petersen, H.H.; Kjelgaard, S.; Mathiasen, L.; Holtet, T.L.; Andreasen, P.A. A Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator-inhibiting Cyclic Peptide with an Unusual P2 Residue and an Extended Protease Binding Surface Demonstrates New Modalities for Enzyme Inhibition *. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38424–38437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henneke, I.; Greschus, S.; Savai, R.; Korfei, M.; Markart, P.; Mahavadi, P.; Schermuly, R.T.; Wygrecka, M.; Stürzebecher, J.; Seeger, W.; et al. Inhibition of urokinase activity reduces primary tumor growth and metastasis formation in a murine lung carcinoma model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, A.; Cendron, L.; Chen, S.; Touati, J.; Winter, G.; Zanotti, G.; Heinis, C. Bicyclic Peptide Inhibitor Reveals Large Contact Interface with a Protease Target. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.P. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Han, X. The urokinase plasminogen activator system in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2013, 67, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouri, A.; Dekaken, A.; El Bairi, K.; Aissaoui, A.; Laabed, N.; Chefrour, M.; Ciccolini, J.; Milano, G.; Benharkat, S. Plasminogen activator system and breast cancer: Potential role in therapy decision making and precision medicine. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mekkawy, A.H.; Pourgholami, M.H.; Morris, D.L. Involvement of Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator System in Cancer: An Overview. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 918–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; O’Grady, P.; Devaney, D.; O’Siorain, L.; Fennelly, J.J.; Lijnen, H.J. Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a marker for aggressive breast carcinomas. Preliminary report. Cancer 1988, 62, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiping, X.; Guangde, Z.; Wenhua, X. Expression and significance of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in breast cancer. Chinese J. Cancer Res. 1999, 11, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänicke, F.; Prechtl, A.; Thomssen, C.; Harbeck, N.; Meisner, C.; Untch, M.; Sweep, C.G.J.F.; Selbmann, H.-K.; Graeff, H.; Schmitt, M.; et al. Randomized Adjuvant Chemotherapy Trial in High-Risk, Lymph Node-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Identified by Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type 1. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Look, M.P.; van Putten, W.L.J.; Duffy, M.J.; Harbeck, N.; Christensen, I.J.; Thomssen, C.; Kates, R.; Spyratos, F.; Fernö, M.; Eppenberger-Castori, S.; et al. Pooled Analysis of Prognostic Impact of Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator and Its Inhibitor PAI-1 in 8377 Breast Cancer Patients. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FEMTELLETM uPA/PAI-1 ELISA BioMedica Diagnostics. Available online: https://www.hct.group/product/femtelle-upa-pai-1-elisa/ (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Mahmood, N.; Mihalcioiu, C.; Rabbani, S.A. Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Its Receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-P.; Chen, J.-S.; Mao, C.; Niu, H.-L.; Song, J.-M.; Jin, B.-K. A label-free photoelectrochemical biosensor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator detection based on a g-C3N4/CdS nanocomposite. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1025, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Parajuli, P.; Podila, R. Rapid detection of urokinase plasminogen activator using flexible paper-based graphene-gold platform. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarczewska, M.; Kékedy-Nagy, L.; Nielsen, J.S.; Campos, R.; Kjems, J.; Malinowska, E.; Ferapontova, E.E. Electroanalysis of pM-levels of urokinase plasminogen activator in serum by phosphorothioated RNA aptamer. Analyst 2015, 140, 3794–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdeo, D.; Kesarwani, V.; Suhag, D.; Ahmed, J.; Alshehri, S.M.; Gandhi, S. Self-assembled chitosan polymer intercalating peptide functionalized gold nanoparticles as nanoprobe for efficient imaging of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in cancer diagnostics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Tripathi, P.P.; Gandhi, S. Graphene nanosheets as an electric mediator for ultrafast sensing of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor-A biomarker of cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trier, N.; Hansen, P.; Houen, G. Peptides, Antibodies, Peptide Antibodies and More. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moro, G.; Severin Sfragano, P.; Ghirardo, J.; Mazzocato, Y.; Angelini, A.; Palchetti, I.; Polo, F. Bicyclic peptide-based assay for uPA cancer biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocato, Y.; Frasson, N.; Laura, C.; Angelini, A. Inibitori Peptidici Biciclici Dell’attivatore Del Plasminogeno Di Tipo Urochinasi Umana (HuPA). 2022. Available online: https://iris.unive.it/handle/10278/5007900 (accessed on 3 April 2022).
- Banys-Paluchowski, M.; Witzel, I.; Aktas, B.; Fasching, P.A.; Hartkopf, A.; Janni, W.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Pantel, K.; Schön, G.; Rack, B.; et al. The prognostic relevance of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) in the blood of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taubert, H.; Würl, P.; Greither, T.; Kappler, M.; Bache, M.; Lautenschläger, C.; Füssel, S.; Meye, A.; Eckert, A.W.; Holzhausen, H.-J.; et al. Co-detection of members of the urokinase plasminogen activator system in tumour tissue and serum correlates with a poor prognosis for soft-tissue sarcoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casella, R.; Shariat, S.F.; Monoski, M.A.; Lerner, S.P. Urinary levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor in the detection of bladder carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 2494–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.; Kirchheimer, J.C.; Sedlmayer, A.; Bell, C.; Ermler, D.; Binder, B.R. Clinical value of determination of urokinase-type plasminogen activator antigen in plasma for detection of colorectal cancer: Comparison with circulating tumor-associated antigens CA 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Strojan, P.; Budihna, M.; Šmid, L.; Vrhovec, I.; Škrk, J. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) in tissue and serum of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Eur. J. Cancer 1998, 34, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, D.; Friess, H.; Deflorin, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Bründler, M.-A.; Riesle, E.; Korc, M.; Büchler, M.W. Enhanced expression of urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor in pancreatic carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, K.; Szcześniak, P.; Bulska, M.; Kumor-Kisielewska, A.; Durko, L.; Gąsiorowska, A.; Orszulak-Michalak, D.; Małecka Panas, E. Serum level of Urokinase Plasminogen Activator (uPA) Correlates with the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Pancreat. Disord. Ther. 2015, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Yen, Y.-H.; Chang, K.-C.; Hung, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, M.-T.; Hu, T.-H. Elevated levels of serum urokinase plasminogen activator predict poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravalli, A.; da Rocha, C.G.; Yamanaka, H.; Marrazza, G. A label-free electrochemical affisensor for cancer marker detection: The case of HER2. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 106, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, S.; Jin, H.; Bao, W.; Huang, S.; Wang, J. An electrochemical impedance sensor for the label-free ultrasensitive detection of interleukin-6 antigen. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibau, C.; Md Arshad, M.K.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Nuzaihan, M.; Fathil, M.F.M.; Estrela, P. Gold interdigitated triple-microelectrodes for label-free prognosticative aptasensing of prostate cancer biomarker in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Podder, P.S.; Russo, M.; Henry, C.; Cinti, S. Tailored point-of-care biosensors for liquid biopsy in the field of oncology. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Kolay, J.; Wang, R.; Wan, Z.; Wang, S. Label-free imaging and biomarker analysis of exosomes with plasmonic scattering microscopy. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 12760–12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong Hong Tsang, D.; Lieberthal, T.J.; Watts, C.; Dunlop, I.E.; Ramadan, S.; del Rio Hernandez, A.E.; Klein, N. Chemically Functionalised Graphene FET Biosensor for the Label-free Sensing of Exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tartaggia, S.; Meneghello, A.; Bellotto, O.; Poetto, A.S.; Zanchetta, M.; Posocco, B.; Bunka, D.; Polo, F.; Toffoli, G. An SPR investigation into the therapeutic drug monitoring of the anticancer drug imatinib with selective aptamers operating in human plasma. Analyst 2021, 146, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, L.-G.; Puiu, M.; Bala, C. Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection of Endocrine Disruptors. Sensors 2020, 20, 6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkova Gajdosova, V.; Lorencova, L.; Blsakova, A.; Kasak, P.; Bertok, T.; Tkac, J. Challenges for impedimetric affinity sensors targeting protein detection. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 28, 100717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, G.; Bottari, F.; Liberi, S.; Covaceuszach, S.; Cassetta, A.; Angelini, A.; De Wael, K.; Maria, L. Covalent immobilization of delipidated human serum albumin on poly (pyrrole-2-carboxylic) acid film for the impedimetric detection of perfluorooctanoic acid. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 134, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maso, L.; Trande, M.; Liberi, S.; Moro, G.; Daems, E.; Linciano, S.; Sobott, F.; Covaceuszach, S.; Cassetta, A.; Fasolato, S.; et al. Unveiling the binding mode of perfluorooctanoic acid to human serum albumin. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutiger, A.; Tanno, A.; Hwu, S.; Tiefenauer, R.F.; Vörös, J.; Nakatsuka, N. Nonspecific Binding—Fundamental Concepts and Consequences for Biosensing Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8095–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenberg, J.Y.; Ling, Y.; Kim, S. Non-Specific Adsorption Reduction Methods in Biosensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wael, E.D.A.-E.D.A.-G.M.A.-R.C.A.-K. De Mapping the gaps in chemical analysis for the characterisation of aptamer-target interactions. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, F.; Moro, G.; Sleegers, N.; Florea, A.; Cowen, T.; Piletsky, S.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Wael, K. Electropolymerized o-Phenylenediamine on Graphite Promoting the Electrochemical Detection of Nafcillin. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.A.; Belanger, B.A.; Haaland, P.D. Calibration and assay development using the four-parameter logistic model. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1993, 20, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kim, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Strouse, R.J.; Schenerman, M.; Jiang, X.-R. Implementation of Parallelism Testing for Four-Parameter Logistic Model in Bioassays. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Marcano, N.E.; Morales-Cruz, M.; Vega-Hernández, G.; Gómez-Moreno, R.; Binder, C.; Baerga-Ortiz, A.; Priest, C.; Cabrera, C.R. PCR-assisted impedimetric biosensor for colibactin-encoding pks genomic island detection in E. coli samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, E.; Kim, S.J.; Taguchi, T.; Izukura, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Furukawa, J.; Yayoi, E.; Shin, E.; Takatsuka, Y.; Koyama, H.; et al. A prospective study on the prognostic significance of urokinase-type plasminogen activator levels in breast cancer tissue. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 123, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borstnar, S.; Vrhovec, I.; Svetic, B.; Cufer, T. Prognostic Value of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator, and its Inhibitors and Receptor in Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Breast Cancer 2002, 3, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampelj, M.; Arko, D.; Cas-Sikosek, N.; Kavalar, R.; Ravnik, M.; Jezersek-Novakovic, B.; Dobnik, S.; Dovnik, N.F.; Takac, I. Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) in breast cancer-correlation with traditional prognostic factors. Radiol. Oncol. 2015, 49, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moro, G.; Ferrari, L.; Angelini, A.; Polo, F. An Impedimetric Biosensing Strategy Based on BicyclicPeptides as Bioreceptors for Monitoring h-uPA Cancer Biomarkers. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040234
Moro G, Ferrari L, Angelini A, Polo F. An Impedimetric Biosensing Strategy Based on BicyclicPeptides as Bioreceptors for Monitoring h-uPA Cancer Biomarkers. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(4):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040234
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoro, Giulia, Leonardo Ferrari, Alessandro Angelini, and Federico Polo. 2023. "An Impedimetric Biosensing Strategy Based on BicyclicPeptides as Bioreceptors for Monitoring h-uPA Cancer Biomarkers" Chemosensors 11, no. 4: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040234
APA StyleMoro, G., Ferrari, L., Angelini, A., & Polo, F. (2023). An Impedimetric Biosensing Strategy Based on BicyclicPeptides as Bioreceptors for Monitoring h-uPA Cancer Biomarkers. Chemosensors, 11(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040234