Multi-Mechanistic and Therapeutic Exploration of Nephroprotective Effect of Traditional Ayurvedic Polyherbal Formulation Using In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
Abstract
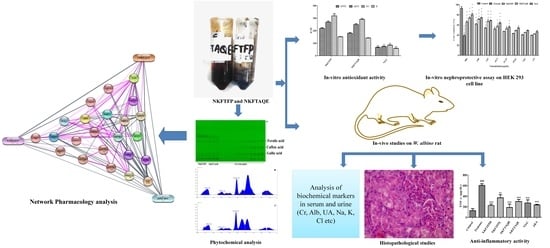
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Procurement of Sample
2.3. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents and Free-Radical Scavenging Activity of NKFTFP and NKFTAQE
2.4. HPTLC Profiling and Quantitative Estimation for Simultaneous Separation of Gallic Acid, Caffeic Acid and Ferulic Acid
2.5. Network Pharmacology Analysis
2.6. In Vitro Cell Line Studies for the Nephroprotective Effect of NEERI KFT
2.6.1. Determination of Nephroprotective Activity of NEERI KFT
2.6.2. Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA) of NEERI KFT
2.7. In Vivo Studies for the Nephroprotective Effect of NEERI KFT
2.7.1. Experimental Animal
2.7.2. Experimental Groups for Nephroprotective Studies
2.7.3. Estimation of Biochemical Markers in Serum and Urine
2.7.4. Assessment of Antioxidant Markers
2.7.5. Assessment of Inflammatory Markers
2.7.6. Histopathology
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Phenolic, Flavonoids and Free-Radical Scavenging Activity of NKFTFP and NKFTAQE
3.2. HPTLC Quantitative Estimation for Simultaneous Separation of Gallic Acid, Caffeic Acid and Ferulic Acid
3.3. Network Pharmacology Analysis
3.4. In Vitro Cell Line Studies
3.5. Cellular Antioxidant Activity
3.6. In Vivo Studies for the Nephroprotective Effect of NEERI KFT
3.6.1. Body Weight Changes
3.6.2. Estimation of Biochemical Markers in Serum and Urine
3.6.3. Assessment of Antioxidant Markers
3.6.4. Assessment of Inflammatory Markers
3.6.5. Histopathological Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acharya, V.; Olivero, J. The Kidney as an Endocrine Organ. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2018, 14, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, L. The kidney—An organ of critical importance in physiology. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 3953–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lote, C.J. Principles of renal physiology. In Principles of Renal Physiology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latcha, S.; Jaimes, E.A.; Patil, S.; Glezerman, I.G.; Mehta, S.; Flombaum, C.D. Long-term renal outcomes after cisplatin treatment. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xavier, S.; Haneefa, S.; Anand, D.; Polo, P.; Maheshwari, R.; Shreedhara, C.; Setty, M. Antioxidant and nephroprotective activities of the extract and fractions of Homonoia riparia Lour. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mahgoub, E.; Kumaraswamy, S.M.; Kader, K.H.; Venkataraman, B.; Ojha, S.; Adeghate, E.; Rajesh, M. Genipin attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by counteracting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kpemissi, M.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K.; Veerapur, V.P.; Negru, M.; Taulescu, M.; Chandramohan, V.; Hiriyan, J.; Banakar, S.M.; Nv, T.; Suhas, D.S.; et al. Nephroprotective activity of Combretum micranthum G. Don in cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats: In-vitro, in-vivo and in-silico experiments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiruddin, S.; Parveen, A.; Khan, W.; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, S. TLC-Based Metabolite Profiling and Bioactivity-Based Scientific Validation for Use of Water Extracts in AYUSH Formulations. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 2847440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, G.; Parveen, B.; Umar Khan, M.; Sharma, I.; Kumar Sharma, A.; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, S. A systematic review on nephron protective AYUSH drugs as constituents of NEERI-KFT (A traditional Indian polyherbal formulation) for the management of chronic kidney disease. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6441–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S.; Ansari, M.H.R.; Parveen, R.; Khan, W.; Ahmad, S.; Husain, S.A. Chromatography Based Metabolomics and in Silico Screening of Gymnema sylvestre Leaf Extract for Its Antidiabetic Potential. Evidence-based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 7523159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.U.; Gaurav; Zahiruddin, S.; Basist, P.; Krishnan, A.; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, S. Nephroprotective potential of Sharbat-e-Bazoori Motadil (sugar-free) in HEK-293 cells and Wistar rats against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekbbal, R.; Iqubal, A.; Ansari, M.; Ahmad, S.; Haque, S. Evaluation of cardioprotective potential of isolated swerchirin against the isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in wistar albino rats. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2022, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav; Zahiruddin, S.; Parveen, B.; Ibrahim, M.; Sharma, I.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, S. TLC-MS Bioautography-Based Identification of Free-Radical Scavenging, α-Amylase, and α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Compounds of Antidiabetic Tablet BGR-34. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29688–29697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaurav; Khan, M.U.; Basist, P.; Zahiruddin, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Parveen, R.; Krishnan, A.; Ahmad, S. Nephroprotective potential of Boerhaavia diffusa and Tinospora cordifolia herbal combination against diclofenac induced nephrotoxicity. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauzdytė, D.; Pukalskas, A.; Viranaicken, W.; El Kalamouni, C.; Venskutonis, P.R. Protective effects of Phyllanthus phillyreifolius extracts against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress in HEK293 cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabavi, S.M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Habtemariam, S.; Moghaddam, A.H.; Latifi, A.M. Ameliorative effects of quercetin on sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress in rat’s kidney. Ren. Fail. 2012, 34, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OECD/OECDE. Test No. 407: Repeated Dose 28-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents—OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.; Parveen, B.; Zahiruddin, S.; Gautam, G.; Parveen, R.; Ahmed, M.; Arun, K.; Sayeed, G. Analysis of polyphenols in Aegle marmelos leaf and ameliorative efficacy against diabetic mice through restoration of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory status. J Food Biochem. 2021, 46, e13852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpemissi, M.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K.; Veerapur, V.P.; Potârniche, A.V.; Adi, K.; Vijayakumar, S.; Banakar, S.M.; Thimmaiah, N.V.; Metowogo, K.; Aklikokou, K. Antioxidant and nephroprotection activities of Combretum micranthum: A phytochemical, in-vitro and ex-vivo studies. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, S.; Verma, K.; Khan, R. Nephroprotective efficacy of chrysin against cisplatin-induced toxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W.; Jia, N. Nephroprotective Effect of Gelsemine Against Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity is Mediated Via Attenuation of Oxidative Stress. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 71, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee-Khorasany, A.; Razavi, B.M.; Taghiabadi, E.; Yazdi, A.T.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Effect of crocin, an active saffron constituent, on ethanol toxicity in the rat: Histopathological and biochemical studies. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Baboota, S.; Amin, S.; Mir, S.R. Ameliorative effect of a standardized polyherbal combination in methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akomolafe, S.F.; Akinyemi, A.J.; Anadozie, S.O. Phenolic Acids (Gallic and Tannic Acids) Modulate Antioxidant Status and Cisplatin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 984709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özen, S.; Akyol, Ö.; Iraz, M.; Söǧüt, S.; Özuǧurlu, F.; Özyurt, H.; Odaci, E.; Yildirim, Z. Role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester, an active component of propolis, against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2004, 24, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bami, E.; Ozakpınar, O.B.; Ozdemir-Kumral, Z.N.; Köroglu, K.; Ercan, F.; Cirakli, Z.; Sekerler, T.; Izzettin, F.V.; Sancar, M.; Okuyan, B. Protective effect of ferulic acid on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 54, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, P.; Han, L.; Wang, T.; Chen, K.; Gao, Y. Gallic acid suppresses colon cancer proliferation by inhibiting SRC and EGFR phosphorylation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, A.; Heibati, F.; Heidarian, E. Gallic acid exerts anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and nephroprotective effects against paraquat-induced renal injury in male rats. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Ghosh, S.; Das, A.K.; Sil, P.C. Ferulic acid protects hyperglycemia-induced kidney damage by regulating oxidative insult, inflammation and autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gahlot, V.; Yadav, D.K. Phytochemical and Network Pharmacology Based Evaluation of Antiepileptic Potential of Identified Metabolites in Argimone mexicana. Pharmacogn. Res. 2021, 13, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, G. Network Pharmacology-Based Validation of Traditional Therapeutic Claim of Momordica Charantiain Alleviating Diabetic Nephropathy. J. CAM Res. Prog. 2022, 1, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Girard-Lalancette, K.; Pichette, A.; Legault, J. Sensitive cell-based assay using DCFH oxidation for the determination of pro- and antioxidant properties of compounds and mixtures: Analysis of fruit and vegetable juices. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basist, P.; Parveen, B.; Zahiruddin, S.; Gautam, G.; Parveen, R.; Khan, M.A.; Krishnan, A.; Shahid, M.; Ahmad, S. Potential nephroprotective phytochemicals: Mechanism and future prospects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Hassan, W.; Ahmad, F.U.D.; Jabeen, Q.; Ahmed, H.; Iqbal, O. Citrus aurantium Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8928306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, G.S.; Kim, H.J.; Shen, A.H.; Lee, S.B.; Khadka, D.; Pandit, A.; So, H.S. Cisplatin-induced kidney dysfunction and perspectives on improving treatment strategies. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2014, 12, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crona, D.J.; Faso, A.; Nishijima, T.F.; McGraw, K.A.; Galsky, M.D.; Milowsky, M.I. A Systematic Review of Strategies to Prevent Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Oncologist 2017, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perše, M.; Večerić-Haler, Ž. Cisplatin-induced rodent model of kidney injury: Characteristics and challenges. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1462802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lee, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C. The effect of ketoanalogues on chronic kidney disease deterioration: A meta-analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oronsky, B.; Caroen, S.; Oronsky, A.; Dobalian, V.E.; Oronsky, N.; Lybeck, M.; Reid, T.R.; Carter, C.A. Electrolyte disorders with platinum-based chemotherapy: Mechanisms, manifestations and management. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabas, K.; Milner, R.; Farese, J.; Baylis, C.; Croker, B.; Archer, L.; Adin, C. Hyperbilirubinemia’s protective effect against cisplatin nephrotoxicity in the Gunn rat. Anticancer Drugs 2008, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arunkumar, P.A.; Viswanatha, G.L.; Radheshyam, N.; Mukund, H.; Belliyappa, M.S. Science behind cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in humans: A clinical study. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, R.W.; Bailey, M.A. Hyperkalemia: Pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, iii2–iii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenini, G.; Lloret, A.; Cascella, R. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: From a mitochondrial point of view. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duni, A.; Liakopoulos, V.; Roumeliotis, S.; Peschos, D.; Dounousi, E. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and evolution of chronic kidney disease: Untangling ariadne’s thread. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holditch, S.J.; Brown, C.N.; Lombardi, A.M.; Nguyen, K.N.; Edelstein, C.L. Recent advances in models, mechanisms, biomarkers, and interventions in Cisplatin-Induced acute kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S.; Tang, S.; Wang, Y.P.; Xiao, S.Y.; Chen, C.; Li, W. Supplementation of American ginseng berry extract mitigated cisplatin-evoked nephrotoxicity by suppressing ROS-mediated activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S.; Maji, C.; Sarkar, P.K.; Sarkar, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Mandal, T.K. Ameliorative effect of two Ayurvedic herbs on experimentally induced arsenic toxicity in calves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 197, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, D.; Kumar, V.; Verma, A.; Gupta, P.S.; Kumar, H.; Dhingra, V.; Mishra, V.; Sharma, M. Antidiabetic, renal/hepatic/pancreas/cardiac protective and antioxidant potential of methanol/dichloromethane extract of Albizzia Lebbeck Benth. stem bark (ALEx) on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinrinde, A.S.; Oduwole, O.; Akinrinmade, F.J.; Bolaji-Alabi, F.B. Nephroprotective effect of methanol extract of moringa oleifera leaves on acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Afr. Health Sci. 2020, 20, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.A.; Javed, K.; Jafri, M.A. Effect of Rheum emodi (Revand Hindi) on renal functions in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuthan, A.; Chogtu, B.; Bairy, K.L.; Sudhakar; Prakash, M. Evaluation of diuretic activity of Amaranthus spinosus Linn. aqueous extract in Wistar rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarkish, F.; Hashemi, K.; Talebi, A.; Kamalinejad, M.; Soltani, N.; Pouladian, N. Effect of the administration of Solanum nigrum fruit on prevention of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017, 9, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, M.; Shahinfard, N.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Saki, K.; Shahsavari, S.; Taherikalani, M.; Ghafourian, S.; Baharvand-Ahmadi, B. Chicory: A review on ethnobotanical effects of Cichorium intybus L. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 8, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Bulle, S.; Reddy, V.D.; Hebbani, A.V.; Padmavathi, P.; Challa, C.; Puvvada, P.K.; Repalle, E.; Nayakanti, D.; Aluganti Narasimhulu, C.; Nallanchakravarthula, V. Nephro-protective action of P. santalinus against alcohol-induced biochemical alterations and oxidative damage in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Ghosh, S. Curcumin and chronic kidney disease (CKD): Major mode of action through stimulating endogenous intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Molecules 2014, 19, 20139–20156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushik, J.; Tandon, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kaur, T.; Singla, S.K.; Kumar, J.; Tandon, C. Delving into the Antiurolithiatic Potential of Tribulus terrestris Extract Through –In Vivo Efficacy and Preclinical Safety Investigations in Wistar Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakhera, A.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Bansal, D.; Dubey, N. Chemopreventive role of Coriandrum sativum against gentamicin-induced renal histopathological damage in rats. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Aeri, V.; Gaur, P.K.; Jachak, S.M. Phytochemical, therapeutic, and ethnopharmacological overview for a traditionally important herb: Boerhavia diffusa linn. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 808302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naggayi, M.; Mukiibi, N.; Iliya, E. The protective effects of aqueous extract of carica papaya seeds in paracetamol induced nephrotoxicity in male wistar rats. Afr. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 598–605. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Javed, F.; Asif, M.; Baig, M.K.; Arif, M. HPLC analysis and in vivo renoprotective evaluation of hydroalcoholic extract of cucumis melo seeds in gentamicin-induced renal damage. Medicina 2019, 55, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandeep, D.; Krishnan Nair, C.K. Amelioration of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by extracts of Hemidesmus indicus and Acorus calamus. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Singh, B.; Kishor, A.; Singh, S.; Bhat, M.N.; Surmal, O.; Musarella, C.M. Exploring plant-based ethnomedicine and quantitative ethnopharmacology: Medicinal plants utilized by the population of Jasrota Hill in Western Himalaya. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Chaudhuri, P.K. Chemistry and pharmacology of Tinospora cordifolia. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameters | Control | Toxicant | NKFTFPH | NKFTFPL | NKFTAQEH | NKFTAQEL | Vit-C | AKA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood urea (mg/dL) | 22.37 ± 1.732 | 63.83 ± 2.241 A | 30.4 ± 2.771 a | 34.89 ± 1.074 a | 28.73 ± 1.711 a | 31.04 ± 0.438 a | 30.85 ± 4.681 a | 27.31 ± 2.764 a |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.51 ± 0.009 | 1.61 ± 0.037 A | 0.58 ± 0.028 a | 0.63 ± 0.005 a | 0.52 ± 0.019 a | 0.55 ± 0.025 a | 0.69 ± 0.027 a | 0.47 ± 0.086 a |
| Total Protein (gm/dL) | 6.46 ± 0.547 | 9.83 ± 0.112 B | 6.52 ± 0.471 b | 6.76 ± 0.209 b | 6.59 ± 0.293 b | 7.17 ± 0.180 b | 7.55 ± 0. 424 b | 8.12 ± 1.03 c |
| Albumin (gm/dL) | 2.54 ± 0.341 | 5.03 ± 0.217 B | 3.07 ± 0.141 c | 3.10 ± 0.489 c | 2.60 ± 0.350 b | 3.34 ± 0.460 ns | 3.39 ± 0.350 ns | 2.93 ± 0.903 c |
| Globulin (gm/dL) | 3.61 ± 0.260 | 6.04 ± 0.167 B | 4.05 ± 0.101 b | 4.54 ± 0.405 c | 3.79 ± 0.521 b | 3.87 ± 0.103 b | 3.90 ± 0.350 b | 4.39 ± 0.530 c |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.12 ± 0.021 | 0.22 ± 0.016 B | 0.18 ± 0.012 c | 0.20 ± 0.018 ns | 0.18 ± 0.025 c | 0.19 ± 0.012 ns | 0.18 ± 0.016 c | 0.18 ± 0.026 ns |
| Bilirubin (direct) (mg/dL) | 0.04 ± 0.008 | 0.078 ± 0.005 C | 0.06 ± 0.006 c | 0.07 ± 0.004 ns | 0.06 ± 0.006 c | 0.06 ± 0.005 ns | 0.06 ± 0.003 ns | 0.05 ± 0.012 ns |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | 2.29 ± 0.246 | 4.14 ± 0.125 A | 2.37 ± 0.133 b | 2.87 ± 0.028 c | 2.24 ± 0.0165 a | 2.42 ± 0.004 b | 2.64 ± 0.280 b | 2.89 ± 0.545 c |
| ALT (U/L) | 21.54 ± 4.372 | 53.95 ± 2.828 A | 26.92 ± 0.180 a | 46.33 ± 3.660 ns | 18.13 ± 3.156 a | 40.98 ± 1.886 c | 35.81 ± 2.073 b | 24.49 ± 4.207 a |
| AST (U/L) | 150.05 ± 5.075 | 261.09 ± 3.477 A | 167.93 ± 5.045 a | 187.56 ± 5.389 a | 166.61 ± 1.059 a | 199.57 ± 2.575 b | 203.70 ± 16.623 b | 178.65 ± 5.338 a |
| ALP (U/L) | 137.57 ± 2.930 | 182.87 ± 3.503 A | 118.77 ± 3.920 a | 159.18 ± 2.591 b | 109.56 ± 2.981 a | 149.83 ± 3.166 a | 144.74 ± 3.368 a | 127.91 ± 5.593 a |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 5.74 ± 0.075 | 4.02 ± 0.338 C | 6.70 ± 0.185 c | 5.19 ± 0.068 ns | 6.26 ± 0.396 c | 5.73 ± 0.507 ns | 6.70 ± 0.454 c | 4.79 ± 1.159 ns |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 136.31 ± 1.506 | 161.40 ± 2.880 B | 139.31 ± 2.711 b | 147.99 ± 2.274 ns | 142.59 ± 3.615 b | 145.99 ± 4.798 c | 144.71 ± 3.772 c | 136.67 ± 4.398 b |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 5.09 ± 0.361 | 3.66 ± 0.362 C | 4.69 ± 0.507 ns | 4.60 ± 0.296 ns | 5.38 ± 0.450 c | 5.18 ± 0.246 ns | 4.87 ± 0.604 ns | 4.98 ± 0.292 ns |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 106.79 ± 1.760 | 94.36 ± 1.801 B | 104.47 ± 1.113 c | 100.16 ± 1.309 ns | 106.32 ± 1.261 b | 103.46 ± 1.733 c | 106.19 ± 2.903 b | 107.22 ± 3.49 bb |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 11.19 ± 0.775 | 8.18 ± 0.412 B | 10.71 ± 0.443 b | 9.26 ± 0.165 ns | 11.21 ± 0.236 b | 9.94 ± 0.151 c | 10.41 ± 0.591 c | 10.24 ± 0.318 c |
| Parameters | Control | Toxicant | NKFTFPH | NKFTFPL | NKFTAQEH | NKFTAQEL | Vit-C | AKA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine urea (mg/dL) | 61.28 ± 5.714 | 31.12 ± 2.325 A | 53.62 ± 1.922 b | 46.06 ± 1.731 c | 53.80 ± 2.164 b | 49.32 ± 2.892 c | 47.96 ± 6.327 c | 54.45 ± 2.347 b |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.02 ± 0.147 | 0.55 ± 0.175 A | 1.38 ± 0.15 b | 1.25 ± 0.055 c | 1.37 ± 0.039 b | 1.35 ± 0.077 b | 1.30 ± 0.218 c | 1.35 ± 0.233 b |
| Total Protein (gm/dL) | 5.28 ± 0.057 | 8.87 ± 0.856 B | 5.56 ± 0.392 b | 6.32 ± 0.621 c | 5.72 ± 0.501 b | 6.03 ± 0.608 b | 5.98 ± 0.671 b | 5.38 ± 0.028 b |
| Albumin (gm/dL) | 2.50 ± 0.167 | 8.66 ± 1.317 A | 2.32 ± 0.169 a | 3.04 ± 1.328 b | 2.43 ± 0.208 a | 2.33 ± 0.210 a | 2.81 ± 0.365 b | 2.48 ± 0.565 a |
| Globulin (gm/dL) | 1.66 ± 0.189 | 5.28 ± 0.471 A | 2.37 ± 0.268 a | 2.65 ± 0.395 a | 2.05 ± 0.114 a | 3.04 ± 0.198 b | 2.80 ± 0.208 a | 1.77 ± 0.332 a |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.16 ± 0.010 | 0.36 ± 0.029 A | 0.18 ± 0.019 a | 0.21 ± 0.021 a | 0.18 ± 0.015 a | 0.18 ± 0.024 a | 0.20 ± 0.014 a | 0.17 ± 0.010 a |
| Bilirubin (direct) (mg/dL) | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 0.17 ± 0.026 B | 0.08 ± 0.021 b | 0.10 ± 0.014 c | 0.08 ± 0.011 b | 0.10 ± 0.011 c | 0.09 ± 0.006 b | 0.09 ± 0.021 c |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | 2.79 ± 0.953 | 8.14 ± 0.125 A | 4.66 ± 0.965 b | 4.73 ± 0.142 b | 3.68 ± 0.367 b | 5.05 ± 0.103 c | 5.14 ± 0.987 b | 4.48 ± 0.324 b |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 1.38 ± 0.288 | 4.08 ± 0.410 B | 1.92 ± 0.220 c | 2.80 ± 0.790 ns | 2.27 ± 0.141 c | 2.60 ± 0.335 ns | 3.15 ± 0.256 ns | 3.21 ± 0.509 ns |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 83.31 ± 2.740 | 110.37 ± 2.812 A | 89.32 ± 2.749 a | 96.41 ± 2.764 c | 88.79 ± 1.187 a | 91.36 ± 2.685 b | 92.41 ± 4.151 b | 90.54 ± 1.520 b |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 2.61 ± 0.362 | 1.13± 0.209 B | 2.37 ± 0.290 b | 1.33 ± 0.072 ns | 2.71 ± 0.178 b | 2.15 ± 0.108 c | 2.11 ± 0.191 c | 2.45 ± 0.254 b |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 70.81 ± 4.878 | 50.29 ± 1.321 B | 65.82 ± 3.606 c | 60.39 ± 1.477 ns | 67.80 ± 0.798 c | 63.35 ± 5.649 ns | 66.35 ± 2.835 c | 65.40 ± 2.764 c |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 3.54 ± 0.574 | 7.23 ± 0.334 A | 4.13 ± 0.062 b | 5.66 ± 0.372 ns | 4.67 ± 0.566 b | 4.99 ± 0.234 b | 5.23 ± 0.557 c | 4.76 ± 0.318 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaurav; Sharma, I.; Khan, M.U.; Zahiruddin, S.; Basist, P.; Ahmad, S. Multi-Mechanistic and Therapeutic Exploration of Nephroprotective Effect of Traditional Ayurvedic Polyherbal Formulation Using In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010168
Gaurav, Sharma I, Khan MU, Zahiruddin S, Basist P, Ahmad S. Multi-Mechanistic and Therapeutic Exploration of Nephroprotective Effect of Traditional Ayurvedic Polyherbal Formulation Using In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010168
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaurav, Ikshit Sharma, Mohammad Umar Khan, Sultan Zahiruddin, Parakh Basist, and Sayeed Ahmad. 2023. "Multi-Mechanistic and Therapeutic Exploration of Nephroprotective Effect of Traditional Ayurvedic Polyherbal Formulation Using In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010168
APA StyleGaurav, Sharma, I., Khan, M. U., Zahiruddin, S., Basist, P., & Ahmad, S. (2023). Multi-Mechanistic and Therapeutic Exploration of Nephroprotective Effect of Traditional Ayurvedic Polyherbal Formulation Using In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Biomedicines, 11(1), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010168