Prediction Model of the Remaining Useful Life of the Drill Bit during Micro-Drilling of the Packaging Substrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
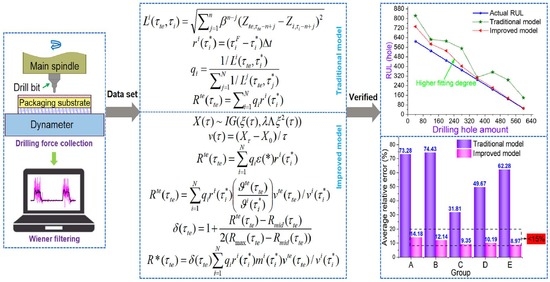
2. Establishment of the RUL Prediction Model
2.1. Traditional RUL Prediction Model
2.2. Improved RUL Prediction Model
3. Validation on the Improved RUL Prediction Model
3.1. Experiment on Collection of Axial Drilling Force
3.1.1. Micro-Drilling Experiment
3.1.2. Results of Drill Bit Failure and Signal Processing of Axial Drilling Force Signal
- (1)
- Calculating the periods of the axial drilling force signals through the cyclic stationary theory;
- (2)
- Based on accumulation theory in the time domain, if the axial drilling force signals are sliced according to the calculated periods and the average value of each signal segment is acquired after time domain superposition, the preliminary filtered signal would be obtained;
- (3)
- The signal accumulated in the time domain is used as the desired signal, and the original axial drilling force signals are filtered by the Wiener filter to obtain the final filtered signals.
3.2. Validation Results of the RUL Prediction Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kenny, S.; Baron, D.; Roelfs, B. A comprehensive packaging solution for next generation IC substrates. Microelectron. Packag. Conf. 2011, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.Y.; Chang, T.H.; Chang, T.C. An Investigation into the package and printed circuit board assembly solutions of an ultrathin coreless flip-chip substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 3855–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, D.; Gehin, D.; Gutierrez, M.E.; Girot, F. Modeling and tool wear in drilling of CFRP. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Shi, H.Y.; Huang, G.; Tao, S.; Gao, Z.S. Investigation on Drill Wear and Micro Hole Quality in High Speed Drilling of High Frequency Printed Circuit Board. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 825, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Fu, L.Y.; Yang, L.P.; Qu, Y.P.; Song, Y.X. Wear mechanisms of micro-drills during dry high speed drilling of PCB. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Gao, Z.S.; Huang, G.; Tao, S.; Fu, L.Y.; Liang, X. Micro hole drilling of high frequency printed circuit board containing hard fillers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Mativenga, P.T.; Withers, P.J. Assessment of machining performance using the wear map approach in micro-drilling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 59, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, J.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Liao, X. Tool wear state prediction based on feature-based transfer learning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 3283–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Lin, X.K.; Wang, Y. Characterization of drill bit breakage in pcb drilling process based on high speed video analysis. Circuit World 2017, 43, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Zheng, X.H.; An, Q.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, M. Tool breakage feature extraction in pcb micro-hole drilling using vibration signals. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 497, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, I.; Arkan, T.; Bao, W. Tool wear estimation in micro-machining: Part I: Tool usage–cutting force relationship. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2000, 40, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekian, M.; Park, S.; Jun, M. Tool wear monitoring of micro-milling operation. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2009, 209, 4903–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Song, F.M.; Fu, L.Y. Experimental study on drilling force in printed circuit board micro drilling process. Circuit World 2011, 37, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Xu, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, K.; Xu, Z.; Pei, H. Similarity-based prediction method for machinery remaining useful life: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 1501–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, Z. A Review: Prediction method for the remaining useful life of the mechanicalsystem. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2022, 22, 2119–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Xian, W.M.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Z. An improved autoregressive model by particle swarm optimization for prognostics of lithium-ion batteries. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wei, J.; Li, Z.H. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid deep learning model. Processes 2023, 11, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhan, Z.G.; Wen, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, S.; Pan, M. A hybrid model to assess the remaining useful life of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Processes 2023, 11, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Song, G. A deep attention residual neural network-based remaining useful life prediction of machinery. Measurement 2021, 181, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Tan, C.B.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, H.; Cui, B.; Zhang, X. A study of a domain-adaptive LSTM-DNN-based method for remaining useful life prediction of planetary gearbox. Processes 2023, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, O.F.; Camci, F.; Jennions, I.K. A Similarity-based prognostics approach for remaining useful life prediction. PHM Soc. Eur. Conf. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, H.; Cheng, N.; Li, Q. Remaining useful life prognostics of aircraft engines based on damage propagation modeling and data analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 12–13 December 2015; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Li, Z.X.; Qin, G.H.; Ding, K.; Lai, X.; Zhang, K. A novel prediction method based on bi-channel hierarchical vision transformer for rolling bearings’ remaining useful life. Processes 2023, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Pan, B.; Shi, L. A hybrid remaining useful life prediction method for cutting tool considering the wear state. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 3583–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarra, F.C.; Vargas-Machuca, J.; Coronado, A.M. Tool wear and remaining useful life (RUL) prediction based on reduced feature set and Bayesian hyperparameter optimization. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 2022, 16, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Liu, J.; Cao, J. Remaining useful life estimation using an inverse Gaussian degradation model. Neurocomputing 2016, 8, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.H. Research on Equipment Remaining Useful Life Prediction Methods Based on Limited Failure Historical Data. Master’s Thesis, Heifei University of Technology, Heifei, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Gao, Z.; Shi, H. Characterization of printed circuit board micro-holes drilling process by accurate analysis of drilling force signal. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 23, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Dai, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B. Remaining useful life prediction of cutting tools using an inverse Gaussian process model. Processes 2021, 11, 5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Hu, X.F.; Zhang, W.J. Remaining useful life prediction based on health index similarity. Reliab. Eng. Sys. Saf. 2019, 185, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Cao, S.C.; Mao, Z.J. Remaining useful life estimation of aircraft engines using a modified similarity and supporting vector machine (SVM) approach. Energies 2018, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Drill Diameter | Point Angle | Helix Angle | Flute Land Ratio | Overall Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.11 mm | 120° | 40° | 1:2 | 38.15 mm |
| Dielectric Constant | Dissipation Factor | Young’s Modulus | Density | Bending Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.4 | 0.008 | 32 Gpa | 2.0 g/cm3 | 510 Mpa |
| Spindle Speed | Repeatability | Movement Speed | Range of Drill Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 krpm | 5 μm | 85 m/min | 0.10–2.0 mm |
| Equipment | Dynameter | Amplifier | A/D Card | Software |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product model | Kistler 9256 CQ01 | 5080A108004 | 2855A5 | DynoWare 2825A-02-2 |
| Drill Bit Number | Failure (Hole Amount) | Drill Bit Number | Failure (Hole Amount) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-1 | 650 | C-4 | 1123 |
| A-2 | 652 | C-5 | 1440 |
| A-3 | 639 | D-1 | 1608 |
| A-4 | 642 | D-2 | 1795 |
| A-5 | 643 | D-3 | 1692 |
| B-1 | 799 | D-4 | 1769 |
| B-2 | 808 | E-1 | 1800 |
| B-3 | 804 | E-2 | 1800 |
| B-4 | 808 | E-3 | 1800 |
| B-5 | 803 | E-4 | 1800 |
| C-1 | 1154 | E-5 | 1800 |
| C-2 | 1436 | E-6 | 1800 |
| C-3 | 1389 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Tao, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H. Prediction Model of the Remaining Useful Life of the Drill Bit during Micro-Drilling of the Packaging Substrate. Processes 2023, 11, 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092653
Liu X, Tao S, Zhu T, Wang Z, Shi H. Prediction Model of the Remaining Useful Life of the Drill Bit during Micro-Drilling of the Packaging Substrate. Processes. 2023; 11(9):2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092653
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xianwen, Sha Tao, Tao Zhu, Zhaoguo Wang, and Hongyan Shi. 2023. "Prediction Model of the Remaining Useful Life of the Drill Bit during Micro-Drilling of the Packaging Substrate" Processes 11, no. 9: 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092653
APA StyleLiu, X., Tao, S., Zhu, T., Wang, Z., & Shi, H. (2023). Prediction Model of the Remaining Useful Life of the Drill Bit during Micro-Drilling of the Packaging Substrate. Processes, 11(9), 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092653