Hydrogen Compression Materials with Output Hydrogen Pressure in a Wide Range of Pressures Using a Low-Potential Heat-Transfer Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Material Composition Design and Preparation
2.2. X-ray Diffraction
2.3. PCT Test Analysis
2.4. Cyclic Performance Test
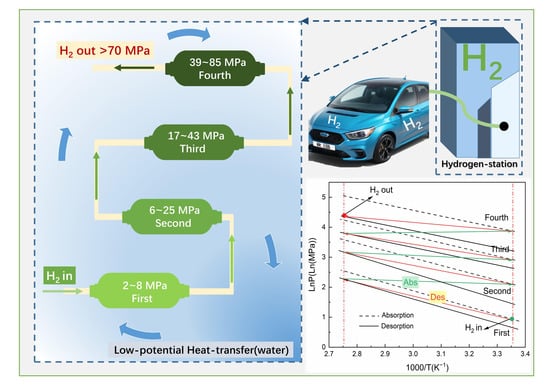
2.5. Application Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lototskyy, M.V.; Yartys, V.A.; Pollet, B.G.; Bowman, R.C., Jr. Metal hydride hydrogen compressors: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5818–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A. Hydrogen production from renewable and sustainable energy resources: Promising green energy carrier for clean development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-W.; Zhu, M.; Buckley, C.; Jensen, T.R. Functional Materials Based on Metal Hydrides. Inorganics 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Jiang, J.; Chen, K.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Z. Hydrogen production via hydrolysis and alcoholysis of light metal-based materials: A review. Nano Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Y.; Li, Q.; Ouyang, L.; Jiang, W.B.; Chen, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.W.; Li, Z.N.; Wang, S.M.; Zhu, M. Overview of hydrogen compression materials based on a three-stage metal hydride hydrogen compressor. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 895, 162465–162488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Cleaning the air and improving health with hydrogen fuel-cell Vehicles. Science 2005, 308, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debe, M.K. Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature 2012, 486, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdanghi, G.; Maranzana, G.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V. Review of the current technologies and performances of hydrogen compression for stationary and automotive applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 102, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Kondo, M.; Goto, S.; Ogami, N. Development of high-pressure hydrogen storage system for the Toyota “Mirai”. In Proceedings of the SAE 2015 World Congress & Exhibition, Detroit, MI, USA, 21–23 April 2021; pp. 1169–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, E.; Zoulias, E.; Tzamalis, G.; Massina, Z.; Analytis, V.; Christodoulou, C.; Stubos, A. Metal hydride hydrogen compressors: Current developments and early markets. Renew. Energy 2018, 127, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, K.; Kim, H.; Enoki, H.; Yoshimura, S.-I.; Ino, S.; Nakamura, Y. Development of TiZrMn Based Hydrogen Storage Alloys for a Soft Actuator. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkanas, E.I.; Christodoulou, C.N.; Tzamalis, G.; Stamatakis, E.; Chroneos, A.; Deligiannis, K.; Karagiorgis, G.; Stubos, A.K. Numerical investigation on the operation and energy demand of a seven-stage metal hydride hydrogen compression system for Hydrogen Refuelling Stations. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lototskyy, M.; Davids, M.W.; Swanepoel, D.; Louw, G.; Klochko, Y.; Smith, F.; Haji, F.; Tolj, I.; Chidziva, S.; Pasupathi, S.; et al. Hydrogen refuelling station with integrated metal hydride compressor: Layout features and experience of three year operation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 5415–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, H. A 70 MPa hydrogen-compression system using metal hydrides. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 9079–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrokhin, S.; Zotov, T.; Movlaev, E.; Verbetsky, V. Hydrogen interaction with Intermetallic compounds and alloys at high pressure. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 580, S90–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.M. Alloy selection for multistage metal-hydride hydrogen compressors: A thermodynamic model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 15702–15715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, M.; Wang, Q. Rare earth-nickel alloy for hydrogen compression. J. Alloy. Compd. 1993, 201, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lloyd, G.; Feldman Jr., K.; Razani, A. Thermal analysis of the Ca0.4Mm0.6Ni5 metal-hydride reactor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 1998, 18, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q. Hydrogen storage properties of (La-Ce-Ca)Ni5 alloys and application for hydrogen compression. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiya, M.M.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Hopkins, R.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.J. A high performance dual-stage hydrogen compressor system using Ca0.2Mm0.8Ni5 metal hydride. In Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, SMASIS, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 745–751. [Google Scholar]
- Odysseos, M.; De Rango, P.; Christodoulou, C.N.; Hlil, E.K.; Steriotis, T.; Karagiorgis, G.; Charalambopoulou, G.; Papapanagiotou, T.; Ampoumogli, A.; Psycharis, V.; et al. The effect of compositional changes on the structural and hydrogen storage properties of (La-Ce)Ni5 type intermetallics towards compounds suitable for metal hydride hydrogen compression. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 580, S268–S270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, H.; Yan, K.; Liu, J. Effects of Ce/Y on the cycle stability and anti-plateau splitting of La5-xCexNi4Co (x=0.4, 0.5) and La5-yYyNi4Co (y=0.1, 0.2) hydrogen storage alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 236, 121725–121735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipek, S.; Jacob, I.; Paul-Boncour, V.; Percheron-Guegan, A.; Marchuk, I.; Mogilyanski, D.; Pielaszek, J. Investigation of ZrFe2 and ZrCo2 under very high pressure of gaseous hydrogen and deuterium. Pol. J. Chem. 2001, 75, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar]
- Zotov, T.; Movlaev, E.; Mitrokhin, S.; Verbetsky, V. Interaction in (Ti,Sc)Fe2-H2 and (Zr,Sc)Fe2-H2 systems. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 459, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Lü, F.; Mi, J.; Hao, L.; Jiang, L. Laves phase hydrogen storage alloys for super-high-pressure metal hydride hydrogen compressors. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, M. Composition design of Ti-CrMn-Fe alloys for hybrid high-pressure metal hydride tanks. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 639, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Advanced high pressure metal hydride fabricated via Ti-Cr-Mn alloys for hybrid tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, S.; Huot, J. Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 Alloy with Addition of x wt %Zr (x = 0, 2, 4, 8, and 12). Inorganics 2017, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Sheng, P.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X. Overview of Ti-based laves phase hydrogen storage alloys for hydrogen compressor. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2019, 43, 754–764. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, G.; Li, X. Development of Ti1.02Cr2-x-yFexMny (0.6≤x≤0.75, y=0.25, 0.3) alloys for high hydrogen pressure metal hydride system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15087–15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, X. High-pressure hydrogen storage properties of TixCr1-yFeyMn1.0 alloys. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 5759–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Liu, J.W.; Zhu, M. Achieving high equilibrium pressure and low hysteresis of Zr-Fe based hydrogen storage alloy by Cr/V substitution. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 806, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, L. Investigation on Ti-Zr-Cr-Fe-V based alloys for metal hydride hydrogen compressor at moderate working temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 21580–21589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, Z.; Piao, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L. Studies on Ti-Zr-Cr-Mn-Fe-V based alloys for hydrogen compression under mild thermal conditions of water bath. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 892, 162145–162452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, K.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M. Ti-CrMn-Fe-based alloys optimized by orthogonal experiment for 85 MPa hydrogen compression materials. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 891, 161791–161816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, W.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Optimization of Ti-ZrCr-Fe alloys for 45 MPa metal hydride hydrogen compressors using orthogonal analysis. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 889, 161629–161636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, Y.H.; Huang, H.X.; Liu, B.G.; Lv, Y.J.; Zhang, B.; Lv, W.; Yuan, J.G.; Wu, Y. Effects of the different element substitution on hydrogen storage properties of Ti0.8Zr0.2Mn0.9Cr0.6V0.3M0.2 (M=Fe, Ni, Co). J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 908, 164605–164613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challet, S.; Latroche, M.; Heurtaux, F. Hydrogenation properties and crystal structure of the single BCC (Ti0.355V0.645)100-xMx alloys with M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni (x=7, 14 and 21). J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 439, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrokhin, S.V.; Tepanov, A.A.; Verbetsky, V.N. Hydrogen interaction with alloys of NdNi5-xAlx system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 22353–22357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lototskyy, M.V.; Yartys, V.A.; Tarasov, B.P.; Davids, M.W.; Denys, R.V.; Tai, S. Modelling of metal hydride hydrogen compressors from thermodynamics of hydrogen-metal interactions viewpoint: Part I. Assessment of the perfor mance of metal hydride materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, T.B.; Clewley, J.D. Hysteresis in metal hydrides. J. Less Common Met. 1982, 83, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, R. Hysteresis in metal-hydrogen systems. J. Alloy. Compd. 1997, 253, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L. Effect of rare earth doping on the hydrogen storage performance of Ti1.02Cr1.1Mn0.3Fe0.6 alloy for hybrid hydrogen storage application. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 731, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, J.; Mintz, M.H. Kinetics and mechanisms of metal hydrides formation-a review. J. Alloy. Compd. 1997, 253, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, S.; Nakamura, H.; Furukawa, A.; Nasako, K.; Satoh, K.; Imoto, T.; Saito, T.; Yonezu, I. A method for numerical expressions of PC isotherms of hydrogen absorbing alloys. Z. Phys. Chem. 1993, 179, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-N.; Luo, S.; Flanagan, T.B. Analysis of sloping plateaux in alloys and intermetallic hydrides. J. Alloy. Compd. 2004, 384, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Lototsky, M.V.; Davids, M.W.; Linkov, V.; Yartys, V.A.; Solberg, J.K. Chemical surface modification for the improvement of the hydrogenation kinetics and poisoning resistance of TiFe. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, S770–S774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modibane, K.D.; Williams, M.; Lototskyy, M.; Davids, M.W.; Klochko, Y.; Pollet, B.G. Poisoning-tolerant metal hydride materials and their application for hydrogen separation from CO2/CO containing gas mixtures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 9800–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosub, V.; Joubert, J.M.; Latroche, M.; Cerny, R.; Percheron-Guegan, A. Hydrogen cycling induced diffraction peak broadening in C14 and C15 Laves phases. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corgnale, C.; Sulic, M. High pressure thermal hydrogen compression employing Ti1.1CrMn metal hydride material. J. Phys. Energy 2019, 2, 014003–014015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corré, S.; Bououdina, M.; Fruchart, D.; Adachi, G.-Y. Stabilisation of high dissociation pressure hydrides of formula La1-xCexNi5 (x=0-0.3) with carbon monoxide. J. Alloy. Compd. 1998, 275–277, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Liautaud, F.; Pasturel, A.; Allibert, C.H.; Colinet, C. thermodynamic study of valence state of cerium and hydrogen storage in Ce(Ni1-xCux)5 compounds. J. Less-Common Met. 1985, 110, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Xiao, X.Z.; Chen, L.X.; Fan, X.L.; Liu, L.X.; Li, S.Q.; Ge, H.W.; Wang, Q.D. Development of Ti-Cr-Mn-Fe based alloys with high hydrogen desorption pressures for hybrid hydrogen storage vessel application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 12803–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Xu, L.; Jiang, X.J.; Li, X.G. Study on the hydrogen storage property of (TiZr0.1)xCr1.7-yFeyMn0.3 (1.05<x<1.2, 0.2<y<0.6) alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2018, 28, 470–477. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonnier, V.; Enoki, H.; Asano, K.; Kim, H.; Sakaki, K. Tuning the hydrogenation properties of Ti1+yCr2-xMnx laves phase compounds for high pressure metal hydride compressors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 36369–36380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbetsky, V.N.; Mitrokhin, S.V.; Zotov, T.A.; Movlaev, E.A. Intermetallic hydrides with high dissociation pressure. Mater. Matters 2007, 2, 9–12. [Google Scholar]






| Alloys | Compositions | La | Ce | Ca | Y | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-1 | Design | 19.84 | 5.00 | / | 5.29 | 69.86 |
| ICP | 19.20 | 5.04 | / | 5.02 | 70.74 | |
| First-2 | Design | 16.93 | 6.83 | 1.47 | 3.25 | 71.53 |
| ICP | 16.11 | 6.32 | 0.80 | 2.71 | 74.06 |
| Alloys | Compositions | Ti | Zr | Cr | Mn | Cu | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Second | Design | 30.89 | / | 36.91 | 24.82 | 4.10 | 3.29 | / |
| ICP | 29.90 | / | 37.44 | 25.72 | 4.22 | 2.72 | / | |
| Third | Design | 31.09 | / | 47.27 | 7.14 | / | / | 14.51 |
| ICP | 30.42 | / | 47.50 | 7.45 | / | / | 14.63 | |
| Fourth | Design | 22.96 | 10.94 | / | / | / | 9.16 | 56.93 |
| ICP | 23.03 | 10.45 | / | / | / | 9.96 | 56.56 |
| Alloys | Compositions | T (K) | Cmax (H/f.u.) | Pa (MPa) | Pd (MPa) | Sf | Hf | ΔH (kJ·mol−1 H2) | ΔS (J·mol−1·K−1 H2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-1 | La0.6Ce0.15 Y0.25Ni5.0 | 303 | 6.25 | 2.52 | 1.72 | 0.40 | 0.38 | −21.74 a −25.02 d | −98.69 a −106.25 d |
| 323 | 6.23 | 4.44 | 3.21 | 0.40 | 0.32 | ||||
| 363 | 6.24 | 10.55 | 8.90 | 0.42 | 0.17 | ||||
| First-2 | La0.5Ce0.2Y0.15Ca0.15Ni5.0 | 303 | 6.60 | 2.05 | 1.44 | 0.23 | 0.35 | −22.59 a −24.34 d | −99.81 a −102.63 d |
| 323 | 6.51 | 3.73 | 2.71 | 0.21 | 0.32 | ||||
| 363 | 6.09 | 9.08 | 7.15 | 0.25 | 0.24 | ||||
| Second | TiCr1.1Mn0.7 V0.1Cu0.1 | 298 | 2.55 | 5.90 | 4.72 | 1.46 | 0.22 | −20.28 a −22.19 d | −102.14 a −106.78 d |
| 323 | 2.49 | 11.93 | 11.52 | 1.05 | 0.03 | ||||
| 353 | 2.40 | 21.13 | 19.06 | 1.22 | 0.10 | ||||
| 363 | / | 26.13 c | 25.04 c | / | / | ||||
| Third | TiCr1.4Mn0.2 Fe0.4 | 293 | 2.65 | 16.07 | 15.86 | 0.74 | 0.01 | −14.51 a −12.337 d | −91.89 a −84.37 d |
| 323 | 2.58 | 29.64 | 27.06 | 0.94 | 0.09 | ||||
| 353 | 2.59 | 44.05 | 37.38 | 1.59 | 0.16 | ||||
| 298 | / | 17.85 | 17.60 | / | / | ||||
| 363 | / | 51.59 c | 42.97 c | / | / | ||||
| Fourth | Ti0.8Zr0.2Fe1.7V0.3 | 293 | 2.90 | 35.0 | 31.50 | 1.24 | 0.10 | −13.11 a −12.75 d | −93.61 a −91.18 d |
| 323 | 2.63 | 61.50 | 48.00 | 1.38 | 0.24 | ||||
| 353 | 2.58 | 87.13 | 77.36 | 1.33 | 0.12 | ||||
| 298 | / | 39.05 | 33.70 | / | / | ||||
| 363 | / | 100.75 c | 84.73 c | / | / |
| Elements | Capacity | Plateau Pressure | Hysteresis | Slope | Activation Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Ce | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
| Y | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Ca | ↑ | ↓ | - | - | ↑ |
| Elements | Capacity | Plateau Pressure | Hysteresis | Slope | Activation Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | - | - |
| Mn | - | - | ↑ | - | ↑ |
| V | ↑ | - | - | ↓ | - |
| Cu | ↓ | ↑ | - | ↓ | - |
| Fe | ↓ | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Elements | Capacity | Plateau Pressure | Hysteresis | Slope | Activation Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| V | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | - |
| Alloys | Phase | Abundance/wt.% | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | Parameters of Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-1 | CaCu5 | 100% | 4.9596(1) | 3.9885(1) | 84.96(1) | Rw = 4.20 Rp = 2.53 |
| First-2 | CaCu5 | 100% | 4.9610(1) | 3.9862(1) | 84.97(1) | Rw = 4.08 Rp = 2.57 |
| Second | C14 Laves | 91.85 | 4.8700(1) | 7.9880(2) | 164.07(1) | Rw = 5.23 Rp = 3.59 |
| Ti3Cr3O | 8.15 | 11.3090(7) | 11.3090(7) | 1446.46(8) | ||
| Third | C14 Laves | 93.35 | 4.8619(1) | 7.97338(1) | 163.22(1) | Rw = 4.06 Rp = 2.87 |
| Ti3Cr3O | 6.85 | 11.2823(2) | 11.2823(2) | 1436.14(8) | ||
| Fourth | C14 Laves | 100% | 4.8816(1) | 7.9482(2) | 164.03(1) | Rw = 3.57 Rp = 2.55 |
| Gas Composition | Standard Indicators | Measured Content |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H2) (%) | ≥99.99 | 99.99 |
| Oxygen (O2) (ppm) | ≤5 | 3 |
| Nitrogen (N2) (ppm) | ≤60 | 50 |
| Carbon monoxide (CO) (ppm) | ≤5 | 3 |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) (ppm) | ≤5 | 2 |
| Methane (CH4) (ppm) | ≤10 | 5 |
| Water vapor (H2O) (ppm) | ≤10 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Li, B.-Q.; Prokhorenkov, M.; Movlaev, E.; Xu, J.; Xiong, W.; Yan, H.-Z.; Mitrokhin, S. Hydrogen Compression Materials with Output Hydrogen Pressure in a Wide Range of Pressures Using a Low-Potential Heat-Transfer Agent. Inorganics 2023, 11, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050180
Zhang X, Zhao Y-Y, Li B-Q, Prokhorenkov M, Movlaev E, Xu J, Xiong W, Yan H-Z, Mitrokhin S. Hydrogen Compression Materials with Output Hydrogen Pressure in a Wide Range of Pressures Using a Low-Potential Heat-Transfer Agent. Inorganics. 2023; 11(5):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050180
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xu, Yu-Yuan Zhao, Bao-Quan Li, Mikhail Prokhorenkov, Elshad Movlaev, Jin Xu, Wei Xiong, Hui-Zhong Yan, and Sergey Mitrokhin. 2023. "Hydrogen Compression Materials with Output Hydrogen Pressure in a Wide Range of Pressures Using a Low-Potential Heat-Transfer Agent" Inorganics 11, no. 5: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050180
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhao, Y. -Y., Li, B. -Q., Prokhorenkov, M., Movlaev, E., Xu, J., Xiong, W., Yan, H. -Z., & Mitrokhin, S. (2023). Hydrogen Compression Materials with Output Hydrogen Pressure in a Wide Range of Pressures Using a Low-Potential Heat-Transfer Agent. Inorganics, 11(5), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050180