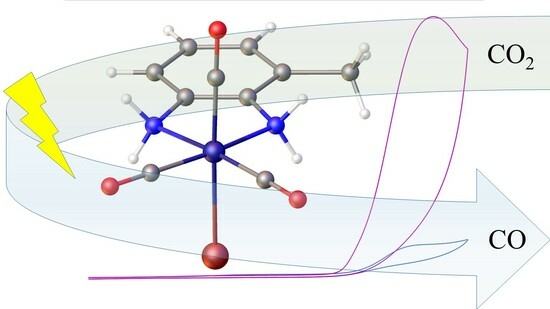
Manganese(I) Diamine Electrocatalysts: Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction to Carbon Monoxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
E°′ = −0.12 (−0.0592 pKa) V vs. Fc+/Fc
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Solid State Structure
2.3. Spectroscopy
2.4. Photochemistry
2.5. Electrochemistry
2.6. Electrocatalysis
3. Experiment/Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sick, V. Spiers memorial lecture: CO2 utilization: Why, why now, and how? Faraday Discuss. 2021, 230, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, A.M.; Bercaw, J.E.; Bocarsly, A.B.; Dobbek, H.; DuBois, H.D.L.; Dupuis, M.; Ferry, J.G.; Fujita, E.; Hille, R.; Kenis, P.J.; et al. Frontiers, opportunities, and challenges in biochemical and chemical catalysis of CO2 fixation. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6621–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.J.; Xie, M.; Sk, M.A.; Lee, J.; Fisher, A.; Wang, X.; Lim, K.H. A review on the electrochemical reduction of CO2 in fuel cells, metal electrodes and molecular catalysts. Catal. Today 2014, 233, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, D.L. Development of molecular electrocatalysts for energy storage. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 3935–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, E.E.; Kubiak, C.P.; Sathrum, A.J.; Smieja, J.M. Electrocatalytic and homogeneous approaches to conversion of CO2 to liquid fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, A. Industrial synthesis of hydrocarbons from hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1940, 32, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzel, N.W.; Werle, C.; Leitner, W. Transition metal complexes as catalysts for the electroconversion of CO2: An organometallic perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11628–11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, C.; Robert, M.; Saveant, J. Catalysis of the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2423–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, R.; Schille, B.; Roemelt, M. Homogeneously catalyzed electroreduction of carbon dioxide—Methods, mechanisms, and catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4631–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changcheng, C.; Nichola, A.W.; Machan, C.W. A look at periodic trends in d-block molecular electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 9454–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, K.A. Carbon dioxide reduction with homogenous early transition metal complexes: Opportunities and challenges for developing CO2 catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 336, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle, K.E.; Warnan, J.; Leung, J.J.; Reuillard, B.; Karmel, I.S.E. Reisner Electro- and solar-driven fuel synthesis with first row transition metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2752–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, B.J.; Eisenberg, R. Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide by using macrocycles of nickel and cobalt. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7361–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, C.; Drouet, S.; Robert, M.; Saveant, J. A local proton source enhances CO2 electroreduction to CO by a molecular Fe catalyst. Science 2012, 338, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberem, E.; Roesel, A.F.; Rosas-Hernaandez, A.; Kull, T.; Fischer, S.; Spannenberg, A.; Junge, H.; Beller, M.; Ludwig, R.; Roemelt, M.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the electrochemical reduction of CO2 catalyzed by iron cyclopentadienone complexes. Organometallics 2019, 38, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, J.D.; Kubiak, C.P. Homogeneous CO2 reduction by Ni(cyclam) at a glassy carbon electrode. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 3932–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mash, B.L.; Raghavan, A.; Ren, T. NiII complexes of C-substituted cyclam as efficient catalysts for reduction of CO2 to CO. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem 2019, 2019, 2065–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, D.C.; McCrory, C.C.L.; Peters, J.C. Studies of cobalt-mediated electrocatalytic CO2 reduction using a redox-active ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 4980–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapovetsky, A.; Do, T.H.; Haiges, R.; Takase, M.K.; Marinescu, S.C. Proton-assisted reduction of CO2 by cobalt aminopyridine macrocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5765–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valyaev, D.A.; Lavigne, G.; Lugan, N. Manganese organometallic compounds in homogeneous catalysis: Past, present, and prospects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 308, 191–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawecker, J.; Lehn, J.; Ziessel, R.R. Photochemical and electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide mediated by (2,2′-Bipyridine)tricarbonylchlororhenium(I) and related complexes as homogeneous catalysts. Helv. Chim. Acta 1986, 69, 1990–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrez, M.; Molton, F.; Chardon-Noblat, S.; Deronzier, A. [Mn(bipyridyl)(CO)3Br]: An abundant metal carbonyl complex as efficient electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9903–9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smieja, J.M.; Sampson, M.D.; Grice, K.A.; Benson, E.E.; Froehlich, J.D.; Kubiak, C.P. Manganese as a substitute for rhenium in CO2 reduction catalysts: The Importance of acids. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 2484–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grills, D.C.; Ertem, M.Z.; McKinnon, M.; Ngo, K.T.; Rochford, J. Mechanistic aspects of CO2 reduction catalysis with manganese-based molecular catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 374, 173–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinopoli; Porte, N.T.L.; Martinez, J.F.; Wasielewski, M.R.; Sohail, M. Manganese carbonyl complexes for CO2 reduction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 365, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanbury, M.; Compain, J.-D.; Chardon-Noblat, S. Electro and photoreduction of CO2 driven by manganese-carbonyl molecular catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 361, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, J.; Shaw, T.W.; Stanton, C.J.; Majetich, G.F.; Bocarsly, A.B.; Schaefer, H.F. NHC-Containing manganese(I) electrocatalysts for the two-electron reduction of CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5152–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friães, S.; Realista, S.; Mourão, H.; Royo, B. N-Heterocyclic and mesoionic carbenes of manganese and rhenium in catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Tory, J.; Hartl, F. Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide with a manganese(I) tricarbonyl complex containing a nonaromatic alpha-diimine ligand. Organometallics 2014, 33, 5002–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.A.; Myren, T.H.T.; Luca, O.R. Redox-active manganese pincers for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Inorganics 2020, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.K.; Pell, W.; Korobkova, I.; Richeson, D. Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 using Mn complexes with unconventional coordination environments. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8010–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siritanaratkul, B.; Eagle, C.; Cowan, A.J. Manganese carbonyl complexes as selective electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction in water and organic solvents. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherpf, T.; Carr, C.R.; Donnelly, L.J.; Durawski, Z.S.; Gelfand, B.S.; Piers, W.E. A mesoionic carbene–pyridine bidentate ligand that improves stability in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction by a molecular manganese catalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 13644–13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Luthra, M.; Jakobsen, J.B.; Madsen, M.R.; Castro, A.C.; Hammershøj, H.C.D.; Pedersen, S.U.; Balcells, D.; Skrydstrup, T.; Daasbjerg, K.; et al. Exploring the parameters controlling product selectivity in electrochemical CO2 reduction in competition with hydrogen evolution employing manganese bipyridine complexes. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Gerke, C.S.; Saund, S.S.; Zito, A.M.; Siegler, M.A.; Thoi, V.S. CO2 activation with manganese tricarbonyl complexes by an H-atom responsive benzimidazole ligand. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2023, e202300796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.Y.; Evans, R.; Bocarsly, A.B. Extending the π-system in MnI diimine tricarbonyl complexes: Impacts on photochemistry, electrochemistry, and CO2 catalytic reduction activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2023, e202300435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, J.; Cole, J.M. Analyzing structure–Activity variations for Mn–carbonyl complexes in the reduction of CO2 to CO. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.; Franco, F.; Belmonte, M.M.; Friães, S.; Royo, B.; Luis, J.M.; Lloret-Fillol, J. Decoding the CO2 reduction mechanism of a highly active organometallic manganese electrocatlysts: Direct observation of a hydride intermediate and its implications. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 10375–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, C.; Neri, G.; Piercy, V.L.; Younis, K.; Siritanaratkul, B.; Cowan, A.J. A manganese complex on a gas diffusion electrode for selective CO2 to CO reduction. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieber, W.; Beck, W.; Zietler, G. Neuere anschauungen über reaktionsweisen der metallcarbonyle, insbesondere des mangancarbonyls. Angew. Chem. 1961, 73, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knor, G.; Leirer, M.; Synthesis, A.V. characterization and spectroscopic properties of 1,2-diiminetricarbonylrhenium(I)chloride complexes with o-benzoquinone diimines as ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 610, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonell, S.; Miller, A.J.M. Carbon dioxide electroreduction catalyzed by organometallic complexes. Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 70, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, M.; Belkina, V.; Ngo, K.T.; Ertem, M.Z.; Grills, D.C.J. Rochford An investigation of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction using a manganese tricarbonyl biquinoline complex. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakes, B.M.; Dempsey, J.L.; Miller, A.J.M. Determining the overpotential of electrochemical fuel synthesis mediated by molecular catalysts: Recommended practices, standard reduction potentials, and challenges. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 4161–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, T.I.A.; Betz, R.; Booysen, I.N.; Potgieter, K.; Mayer, P. Coordination of bidentate aniline derivatives to the fac-[Re(CO)3]+ core. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, E.; Lucarini, F.; Crochet, A.; Ruggi, A.; Zobi, F. Correlation of MLCTs of group 7 fac-[M(CO)3]+ complexes (M = Mn, Re) with bipyridine, pyridinylpyrazine, azopyridine, and pyridin-2-ylmethanimine type ligands for rational photoCORM design. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3758–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.A.; Dhakal, B.; Hulme, R.J.; Nichol, G.S.; Felton, G.A.N. Correlations between photophysical and electrochemical properties for a series of new Mn carbonyl complexes containing substituted phenanthroline ligands. Inorg. Chim Acta 2015, 427, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.A.; Dhakal, B.; Donovan, E.S.; Nichol, G.S.; Felton, G.A.N. Non-photochemical synthesis of Re (diimine)(CO)2(L)Cl (L = phosphine or phosphite) compounds. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2015, 59, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.A.; Brereton, K.R.; Ruoff, K.P.; Tang, H.M.; Felton, G.A.N.; Miller, A.J.M.; Dempsey, J.L. Bathochromic shifts in rhenium carbonyl dyes induced through destabilization of occupied orbitals. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 5389–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkely, H.; Vogler, A. Absorption spectra and CT transitions of compounds containing ReI(CO)3Cl, S2+ and Se2+ as donors and o-benzoquinone diimine as acceptor. Inorg. Chem. Comm. 2007, 10, 1236–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIndoe, J.S.; Vikse, K.L. Assigning the ESI mass spectra of organometallic and coordination compounds. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 54, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, F.H.; Kennard, O.; Watson, D.G.; Brammer, L.; Orpen, A.G.; Taylor, R. Tables of bond lengths determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Part 1. Bond lengths in organic compounds. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. II 1987, 2, S1–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, E.; Fabio, Z. Visible Light-activated PhotoCORMs. Inorganics 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, E.S.; McCormick, J.J.; Nichol, G.S.; Felton, G.A.N. Cyclic voltammetric studies of chlorine-substituted benzenedithiolato-diiron hexacarbonyl electrocatalysts inspired by the [FeFe]-hydrogenase active site. Organometallics 2012, 31, 8067–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.A.; Dhakal, B.; McDonald, L.T.; Nichol, G.S.; Felton, G.A.N. Inter-ligand intramolecular through-space anisotropic shielding in a series of manganese carbonyl phosphorous compounds. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 14296–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, F.; Cometto, C.; Vallana, F.F.; Sordello, F.; Priola, E.; Minero, C.; Nervi, C.; Gobetto, R. A local proton source in a [Mn(bpy-R)(CO)3Br]-type redox catalyst enables CO2 reduction even in the absence of Bronsted acids. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14670–14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.; Chung, W.; Lau, C. The effect of weak Brønsted acids on the electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide by a rhenium tricarbonyl bipyridyl complex. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 453, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riplinger, C.; Carter, E.A. Influence of weak Brønsted acids on electrocatalytic CO2 reduction by manganese and rhenium bipyridine catalysts. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountree, E.S.; McCarthy, B.D.; Eisenhart, T.T.; Dempsey, J.L. Evaluation of homogeneous electrocatalysts by cyclic voltammetry. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9983–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, M.; Iwasaki, M. Voltammetric Study on CO2 reduction electrocatalyzed by cobalt tetraphenylporphrine in DMF solution. Chem. Lett. 1993, 22, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrez, M.; Orio, M.; Molton, F.; Vezin, H.; Duboc, C.; Deronzier, A.; Chardon-Noblat, S. Pulsed-EPR evidence of a manganese(II) hydroxycarbonyl intermediate in the electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide by a manganese bipyridyl derivative. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.; McCrory, C.C.L. Strategies for breaking molecular scaling relationships for the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 6993–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Nielsen, R.J.; Gray, H.B.; Goddard, W.A. A Mn bipyrimidine catalyst predicted to reduce CO2 at lower overpotential. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2521–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.A.; Miller, C.J.; Kubiak, C.P. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 using group VII metal catalysts. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.A.N.; Glass, R.S.; Lichtenberger, D.L.; Evans, D.H. Iron-only hydrogenase mimics. Thermodynamic aspects of the use of electrochemistry to evaluate catalytic efficiency for hydrogen generation. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 9181–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, B.D.; Martin, D.J.; Rountree, E.S.; Ullman, A.C.; Dempsey, J.L. Electrochemical reduction of Brønsted acids by glassy carbon in acetonitrile: Implications for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 8350–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.D.; Tyler, S.F.; McGuire, C.M.; Zeller, M.; Fanwick, P.E.; Evans, D.H.; Peters, D.G.; Ren, T. Nickel complexes of C-substituted cyclams and their activity for CO2 and H+ reduction. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3966–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.Y.; Nedd, D.G.; Evans, R.; Bocarsly, A.B. Mechanistic insights into CO2 conversion to CO using cyano manganese complexes. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 7524–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, E.S.; Felton, G.A.N. Electrochemical analysis of cyclopentadienylmetal carbonyl dimer complexes: Insight into the design of hydrogen-producing electrocatalysts. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 711, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Siewert, I. Manganese and rhenium tricarbonyl complexes equipped with proton relays in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, e202000738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of ShelX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 339–341. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with ShelXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C27, 3–8. [Google Scholar]







| Complex | Epc1 (V) a | Epa1 (V) a | ṽCO (cm−1) b | Mean ṽCO (cm−1) | MLCT (nm) c | ϵ M−1 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-1 | −2.30 | 0.60 | 2028, 1931, 1890 | 1950 | 359 | 1580 |
| Mn-2 | −2.35 | 0.62 | 2030, 1932, 1888 | 1950 | 355 | 1930 |
| Re-1 | −2.75 | 0.89 | 2025, 1915, 1861 | 1934 | 261, 543 | 4700, 88 |
| Q (C) | µmol CO | FE b CO (%) | µmol H2 | FE b H2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-1 | 35 ± 1.4 | 157 ± 5 | 86 ± 3 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.8 |
| Mn-2 | 33 ± 2 | 148 ± 6 | 85 ± 4 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.7 |
| Re-1 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 27 ± 5 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 21 ± 4 |
| Catalyst-free | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 7 ± 4 | 5.4 ± 0.8 | 65 ± 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhakal, B.; Corbin, B.A.; Sosa Parada, A.; Sakai, J.G.; Felton, E.A.; McDonald, L.T.; Gross, A.J.; Nichol, G.S.; Felton, G.A.N. Manganese(I) Diamine Electrocatalysts: Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction to Carbon Monoxide. Inorganics 2023, 11, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090374
Dhakal B, Corbin BA, Sosa Parada A, Sakai JG, Felton EA, McDonald LT, Gross AJ, Nichol GS, Felton GAN. Manganese(I) Diamine Electrocatalysts: Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction to Carbon Monoxide. Inorganics. 2023; 11(9):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090374
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhakal, Badrinath, Brooke A. Corbin, Alberto Sosa Parada, Jonathan G. Sakai, Emily A. Felton, Lauren T. McDonald, Anthony J. Gross, Gary S. Nichol, and Greg A. N. Felton. 2023. "Manganese(I) Diamine Electrocatalysts: Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction to Carbon Monoxide" Inorganics 11, no. 9: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090374
APA StyleDhakal, B., Corbin, B. A., Sosa Parada, A., Sakai, J. G., Felton, E. A., McDonald, L. T., Gross, A. J., Nichol, G. S., & Felton, G. A. N. (2023). Manganese(I) Diamine Electrocatalysts: Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction to Carbon Monoxide. Inorganics, 11(9), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090374