Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription in Italy—A Crosstalk between Citizen Science and DNA Barcoding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Survey
2.2. DNA Barcoding Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sampling
3.2. DNA Barcoding
3.3. Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription
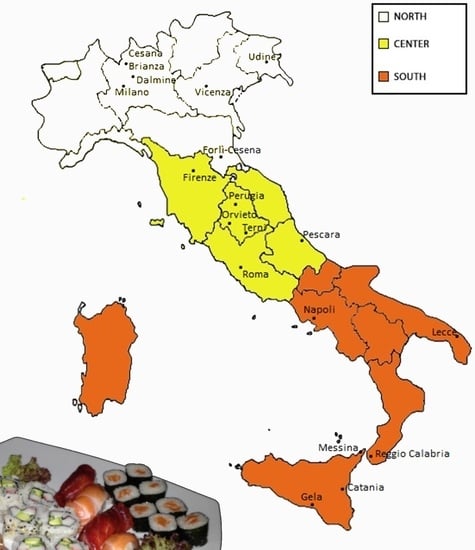
3.3.1. Northern Italy
3.3.2. Central Italy
3.3.3. Southern Italy
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, N.H.; Yun, A.-R.; Rhee, M.S. Prevalence and classification of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus isolated from refrigerated ready-to-eat foods (sushi, kimbab and California rolls) in Korea. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscolino, D.; Giarratana, F.; Beninati, C.; Tornambene, A.; Panebianco, A.; Ziino, G. Hygienic-sanitary evaluation of sushi and sashimi sold in Messina and Catania, Italy. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2014, 3, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.-L.; Pan, Y.-L.; Cheng, H.-L.; Li, T.-C.; Yu, P.H.-F.; Chan, S.-W. The microbiological quality of take-away raw salmon finger sushi sold in Hong Kong. Food Control 2016, 69, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, P.; Dordevic, D.; Gambus, F.; Szczurowska, K.; Zajac, M. Heavy metal contamination, microbiological spoilage and biogenic amine content in sushi available on the Polish market. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardone, L.; Armani, A.; Nucera, D.; Costanzo, F.; Mattiucci, S.; Bruschi, F. Human anisakiasis in Italy: A retrospective epidemiological study over two decades. Parasite 2018, 25, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramires, T.; Iglesias, M.A.; Vitola, H.S.; Nuncio, A.S.P.; Kroning, I.S.; Kleinubing, N.R.; Fiorentini, A.M.; da Silva, W.P. First report of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 in ready-to-eat sushi. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 128, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehel, J.; Yaucat-Guendi, R.; Darnay, L.; Palotas, P.; Laczay, P. Possible food safety hazards of ready-to-eat raw fish containing product (sushi, sashimi). Crit Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoel, S.; Mehli, L.; Bruheim, T.; Vadstein, O.; Jakobsen, A.N. Assessment of Microbiological Quality of Retail Fresh Sushi from Selected Sources in Norway. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, J.H.; Burger, J.; Jeitner, C.W.; Amato, G.; Kolokotronis, S.-O.; Gochfeld, M. DNA barcodes reveal species-specific mercury levels in tuna sushi that pose a health risk to consumers. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M.; Jeitner, C.; Donio, M.; Pittfield, T. Sushi consumption rates and mercury levels in sushi: Ethnic and demographic differences in exposure. J. Risk Res. 2014, 17, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, S.G.; Griffiths, A.M.; Taylor, S.-A.; Di Muri, C.; Hankard, E.A.; Towne, J.A.; Watson, M.; Mariani, S. Sushi barcoding in the UK: Another kettle of fish. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- House, J. Sushi in the United States, 1945–1970. Food Foodways 2018, 26, 40–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Scientific and technical assistance on the evaluation of the temperature to be applied to pre-packed fishery products at retail level. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Protecting the Food Supply from Intentional Adulteration, Such as Acts of Terrorism. 2017. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/FSMA/ucm587803.htm (accessed on 24 January 2018).
- Benard-Capelle, J.; Guillonneau, V.; Nouvian, C.; Fournier, N.; Le Loët, K.; Dettai, A. Fish mislabeling in France: Substitution rates and retail types. PeerJ 2015, 2, e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christiansen, H.; Dettai, A.; Heindler, F.M.; Collins, M.A.; Duhamel, G.; Hautecoeur, M.; Steinke, D.; Volckaert, A.M.; Van de Putte, A.P. Diversity of Mesopelagic fishes in the Southern Ocean—A phylogeographic perspective using DNA barcoding. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, T.D.; Choi, T.J.; Kim, J.; An, H.E.; Park, Y.J.; Karagozlu, M.Z.; Kim, C.B. Assessment of marine fish mislabelling in South Korea’s markets by DNA barcoding. Food Control 2019, 100, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Perez, J.; Martinez, J.L.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Lopez, B.; Karaiskou, N.; Triantafyllidis, A. High level of mislabelling in Spanish and Greek hake markets suggests the fraudulent introduction of African species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, L.; Ferrito, V.; Costagliola, D.; Marsilio, A.; Pappalardo, A.M.; Stingo, V.; Tigano, C. Genetic divergence among and within four Italian populations of Aphanius fasciatus (Teleostei, Cyprinodontiformes). Ital. J. Zool. 2007, 74, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V.; Messina, A.; Patarnello, T.; De Pinto, V.; Guarino, F.; Tigano, C. Genetic structure of the killifish Aphanius fasciatus Nardo 1827 (Teleostei, Cyprinodontidae), results of mitochondrial DNA analysis. J. Fish. Biol. 2008, 72, 1154–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrito, V.; Pappalardo, A.M.; Canapa, A.; Barucca, M.; Doadrio, I.; Olmo, E.; Tigano, C. Mitochondrial phylogeography of the killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Teleostei, Cyprinodontidae) reveals highly divergent Mediterranean populations. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 3193–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttitta, A.; Patti, B.; Maggio, T.; Quinci, E.M.; Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V.; De Pinto, V.; Torri, M.; Falco, F.; Nicosia, A.; et al. Larval population structure of Engraulis encrasicolus in the Strait of Sicily as revealed by morphometric and genetic analyses. Fish. Ocean 2015, 24, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Federico, C.; Sabella, G.; Saccone, S.; Ferrito, V. A COI nonsynonymous mutation as diagnostic tool for intraspecific discrimination in the European Anchovy Engraulis encrasicolus (Linnaeus). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa-Gerasmio, I.R.; Agmata, A.B.; Santos, M.D. Genetic diversity, population genetic structure, and demographic history of Auxis thazard (Perciformes), Selar crumenophthalmus (Perciformes), Rastrelliger kanagurta (Perciformes) and Sardinella lemuru (Clupeiformes) in Sulu-Celebes Sea inferred by mitochondrial DNA sequences. Fish. Res. 2015, 162, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, T.; Uy, S.; Chheng, P.; So, N.; Thi Tran, T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Pomeroy, R.; Egna, H. Genetic diversity and structure of striped snakehead (Channa striata) in the Lower Mekong Basin: Implications for aquaculture and fisheries management. Fish. Res. 2019, 218, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, S.; Al Amouri, M.; Gonzalez, E.G.; Alcaraz, L.; Yahyaoui, A.; Doadrio, I. Influence of historical and human factors on genetic structure and diversity patterns in peripheral populations: Implications for the conservation of Moroccan trout. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinteiro, J.; Vidal, R.; Izquierdo, M.; Sotelo, C.G.; Chapela, M.J.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Rehbein, H.; Hold, G.L.; Russell, V.J.; Pryde, S.E.; et al. Identification of hake species (Merluccius genus) using sequencing and PCR-RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA control region sequences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5108–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Kocour, M.; Kunal, S.P. Mitochondrial DNA variation and phylogenetic relationships among five tune species based on sequencing of D-loop region. Mitoch. DNA Part A 2016, 27, 1976–1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ceruso, M.; Mascolo, C.; De Luca, P.; Venuti, I.; Smaldone, G.; Biffali, E.; Anastasio, A.; Pepe, T.; Sordino, P. A rapid method for the identification of fresh and processed Pagellus erythrinus species against frauds. Foods 2020, 9, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; de Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergence, among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paquin, R.; Hedin, M. The power and perils of ‘molecular taxonomy’: A case study of eyeless and endangered Cicurina (Araneae: Dictynidae) from Texas caves. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 3239–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebure, T.; Douady, C.J.; Gouy, M.; Gibert, J. Relationship between morphological taxonomy and molecular divergence within Crustacea: Proposal of a molecular threshold to help species delimitation. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 2006, 40, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, D.G.M.; Viscuso, R.; D’Urso, V.; Gibilras, S.; Sardella, A.; Marletta, A.; Pappalardo, A.M. Morphostructural analysis of the male reproductive system and DNA barcoding in Balclutha brevis Lindberg 1954 (Homoptera, Cicadellidae). Micron 2015, 79, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, E.; Mulder, C.; Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V.; Costa, G. How soil granulometry, temperature and water predict genetic differentiation in namibian Ariadna spiders and explain their behaviour. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4382–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutarelli, A.; Amoroso, M.G.; De Roma, A.; Girardi, S.; Galiero, G.; Guarino, A.; Corrado, F. Italian market fish species identification and commercial frauds revealing by DNA sequencing. Food Control 2014, 37, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V. DNA barcoding species identification unveils mislabeling of processed flatfish products in southern Italy markets. Fish. Res. 2015, 164, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Cuttitta, A.; Sardella, A.; Musco, M.; Maggio, T.; Patti, B.; Mazzola, S.; Ferrito, V. DNA barcoding and COI sequence variation in Mediterranean lanternfishes larvae. Hydrobiologia 2015, 745, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Copat, C.; Ferrito, V.; Grasso, A.; Ferrante, M. Heavy metal content and molecular species identification in canned tuna: Insights into human food safety. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3430–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Copat, C.; Raffa, A.; Rossitto, L.; Grasso, A.; Fiore, M.; Ferrante, M.; Ferrito, V. Fish-based baby food concern—From species authentication to exposure risk assessment. Molecules 2020, 25, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acutis, P.L.; Cambiotti, V.; Riina, M.V.; Meistro, S.; Maurella, C.; Massaro, M.; Stacchini, P.; Gili, S.; Malandra, R.; Pezzolato, M.; et al. Detection of fish species substitution frauds in Italy: A targeted national Monitoring plan. Food Control 2019, 101, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V. A COIBar-RFLP strategy for the rapid detection of Engraulis encrasicolus in processed anchovy products. Food Control 2015, 57, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrito, V.; Bertolino, V.; Pappalardo, A.M. White fish authentication by COIBar-RFLP: Toward a common strategy for the rapid identification of species in convenience seafood. Food Control 2016, 70, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Ferrito, V. Differential flatfish species detection by COIBar-RFLP in processed seafood products. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Petraccioli, A.; Capriglione, T.; Ferrito, V. From fish eggs to fish name: Caviar species discrimination by COIBar-RFLP, an efficient molecular approach to detect fraud in the caviar trade. Molecules 2019, 24, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrito, V.; Raffa, A.; Rossitto, L.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Pappalardo, A.M. Swordfish or shark slice? A rapid response by COIBar–RFLP. Foods 2019, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, L.; Lu, J.; Qu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhai, Y. Methodology and application of PCR-RFLP for species identification in tuna sashimi. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3138–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Yuan, F.; Huang, M.; Lu, L.; Xiong, X.; Wen, J. DNA Barcoding revealed mislabeling and potential health concerns with roasted fish products sold across China. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Huang, M.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, M.; Xiong, X. Using real time fluorescence loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid species authentication of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 95, 103659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, J.H.; Amato, G.; Kolokotronis, S.O. The real maccoyii: Identifying tuna sushi with DNA barcodes—Contrasting characteristic attributes and genetic distances. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin Chin, T.; Adibah, A.B.; Danial Hariz, Z.A.; Siti Azizah, M.N. Detection of mislabelled seafood products in Malaysia by DNA barcoding: Improving transparency in food market. Food Control 2016, 64, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibah, A.B.; Syazwan, S.; Haniza Hanim, M.Z.; Badrul Munir, M.Z.; Intan Faraha, A.G.; Siti Azizah, M.N. Evaluation of DNA barcoding to facilitate the authentication of processed fish products in the seafood industry. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Hanner, R.; Levin, J.; Lu, X. Study of fish products in Metro Vancouver using DNA barcoding methods reveals fraudulent labeling. Food Control 2018, 94, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armani, A.; Tinacci, L.; Lorenzetti, R.; Benvenuti, A.; Susini, F.; Gasperetti, L.; Ricci, E.; Guarducci, M.; Guidi, A. Is raw better? A multiple DNA barcoding approach (full and mini) based on mitochondrial and nuclear markers reveals low rates of misdescription in sushi products sold on the Italian market. Food Control 2017, 79, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonney, R.; Shirk, J.L.; Phillips, T.B.; Wiggins, A.; Ballard, H.L.; Miller-Rushing, A.J.; Parrish, J.K. Next Steps for Citizen Science. Science 2014, 343, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmala, M.; Wiggins, A.; Swanson, A.; Simmons, B. Assessing Data Quality in Citizen Science. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D.N. Universal primer cocktails for fish DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.X.; Hewitt, G.M. Nuclear integrations: Challenges for mitochondrial DNA markers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oceana Europe 2015. Too Cheap to Be True, Seafood Fraud in Brussel. Available online: https://eu.oceana.org/sites/default/files/421/oceana_factsheet_seafood_fraud_brussels_eng.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- But, G.W.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Shaw, P.-C. Identification of fish species of sushi products in Hong Kong. Food Control 2019, 98, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatés, A.; Martín, P.; Raya, V. Changes in life-history traits in relation to climate change: Bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix) in the north-western Mediterranean. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 69, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azzurro, E.; Cerri, J. The bluefish Pomatomus saltatrix (Pisces: Pomatomidae) in the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian Seas, can we call it climate invader? OSF Prepr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, G.E.; Bledsoe, C.D.; Rasco, B. Caviars and fish roe products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 317–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokina, A.V.; Syromyatnikov, M.Y.; Savinkova, O.V.; Popov, V.N. The Use of DNA Barcoding and Metabarcoding for Food and Environment Quality Control. In Green Technologies and Infrastructure to Enhance Urban Ecosystem Services; Vasenev, V., Dovletyarova, E., Cheng, Z., Valentini, R., Calfapietra, C., Eds.; SSC 2018; Springer Geography Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallstrom, M.A.; Morris, K.A.; Carlson, L.V.; Marko, P.B. Seafood mislabeling in Honolulu, Hawai’i. Forensic Sci. Int. Rep. 2020, 2, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.A.; Jimenez, E.; Viðarsson, J.R.; Olafsson, K.; Olafsdottir, G.; Daníelsdottir, A.K.; Perez-Villareal, B. DNA barcoding revealing mislabeling of seafood in European mass caterings. Food Control 2018, 92, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Code * | Retail Point | Menu/Label Description | Scientific Nameof Declared Species | Identified Species by DNA Barcoding and BLAST Search | GenBank Acc. Number of Obtained Sequences | Matched GenBank Accession from BLAST ° | Matched BOLD ID | % Identity with 100% Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714726 | KP330301 | GBMIN94166-17 | 99.69 |
| MIL1T [3] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714727 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 99.54 |
| MIL2B [1] | Takeaway | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714728 | KY176457 | GBMIN121550-17 | 99.37 |
| MIL2T [3] | Takeaway | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714729 | MH638777 | ANGBF54806-19 | 98.47 |
| MIL3B [3] | Takeaway | sea bream | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714730 | KP330301 | GBMIN94165-17 | 98.74 |
| MIL4B [3] | Takeaway | common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Sparus aurata | MW714731 | MF438138 | ANGBF45411-19 | 99.54 |
| CES1B [3] | Takeaway | common bass | Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714732 | KP330300 | GBMIN94165-17 | 99.06 |
| DAL1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714733 | JQ623999 | DNATR096-12 | 99.24 |
| DAL1T [3] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714734 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 99.24 |
| DAL1E [3] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys oxycephalus | MW714735 | KX769042 | GBMIN125981-17 | 99.02 |
| VI1T [3] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus thynnus | MW714736 | KP975912 | FCSF387-14 | 98.92 |
| VI1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714737 | KC501553 | DNATR1582-13 | 98.78 |
| VI1E [3] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys affinis | MW714738 | JQ842898 | TOBA086-09 | 99.52 |
| FC1B [3] | Takeaway | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Seriola lalandi | MW714739 | MH211123 | GBMNA18700-19 | 99.39 |
| FC1T [3] | Takeaway | maguro Yaki (red tuna) | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus thynnus | MW714740 | KC501694 | DNATR1720-13 | 99.39 |
| FC2B [1] | Takeaway | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714741 | MF438138 | ANGBF45411-19 | 99.69 |
| UD1B [3] | Restaurant | kajiki roll (swordfish) | Xiphias gladius | Xiphias gladius | MW714742 | MK295657 | ANGBF51916-19 | 99.38 |
| UD1T [2] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus obesus | MW714743 | GU451774 | GBGCA1353-13 | 99.08 |
| UD1E [3] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Mallotus villosus | MW714744 | HM421773 | DSFAL635-09 | 99.39 |
| Code * | Retail Point | Menu/Label Description | Scientific Name of Declared Species | Identified Species by DNA Barcoding and BLAST Search | GenBank Acc. Number of Obtained Sequences | Matched GenBank Accession from BLAST ° | Matched BOLD ID | % Identity with 100% Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIR1B [3] | Takeaway | common bass | Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714657 | KP330300 | GBMIN94165-17 | 99.21 |
| FIR1T [3] | Takeaway | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714658 | MH638777 | ANGBF54806-19 | 99.85 |
| FIR1E [3] | Takeaway | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys affinis | MW714659 | JQ842898 | TOBA9086 | 99.52 |
| PER1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Sparus aurata | MW714660 | MF438138 | ANGBF45411-19 | 99.54 |
| PER1T [3] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714661 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 99.39 |
| PER1E [1] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys affinis | MW714662 | JQ842898 | TOBA9086 | 99.35 |
| PER2B [3] | Takeaway | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714663 | KP330301 | GBMIN94166-17 | 99.21 |
| ORV1B [3] | Takeaway | common bass | Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714664 | KP330301 | GBMIN94166-17 | 98.58 |
| ORV1T [2] | Takeaway | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714665 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 98.17 |
| ORV1E [3] | Takeaway | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys affinis | MW714666 | JQ842898 | TOBA086-09 | 99.52 |
| ORV2B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714667 | KC501553 | DNATR1582-13 | 98.47 |
| TER1B [3] | Takeaway | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714668 | KC501557 | DNATR1596-13 | 99.39 |
| TER1T [3] | Takeaway | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus orientalis | MW714669 | JN097817 | GBGCA1390-13 | 99.70 |
| TER1E [3] | Takeaway | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys affinis | MW714670 | JQ842898 | TOBA9086 | 99.52 |
| PE1B [3] | Restaurant | common bass | Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714671 | KP330301 | GBMIN94166-17 | 98.58 |
| PE1T [3] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714672 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 98.92 |
| PE1E [1] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys coromandelensis | MW714673 | KX379460 | ANGBF32076-19 | 98.73 |
| RO1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Seriola lalandi | MW714674 | MF069453 | ANGBF17684-19 | 99.24 |
| RO1T [3] | Restaurant | tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714675 | HM007768 | ANGBF7098-12 | 99.39 |
| RO1E [1] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Mallotus villosus | MW714676 | FJ205579 | GBGC7486-09 | 99.23 |
| Code * | Retail Point | Menu/Label Description | Scientific Name of Declared Species | Identified Species by DNA Barcoding and BLAST Search | GenBank Acc. Number of Obtained Sequences | Matched GenBank Accession from BLAST ° | Matched BOLD ID | % Identity with 100% Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAT1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714949 | KC501553 | DNATR1582-13 | 99.08 |
| CAT1T [3] | Restaurant | Tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714950 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 99.54 |
| CAT1E [3] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Mallotus villosus | MW714951 | FJ205579 | GBGC7486-09 | 99.39 |
| CAT3B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata | Xiphias gladius | MW714952 | JN049558 | ANGBF7251-12 | 99.54 |
| GE1B [3] | Restaurant | common bass | Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714953 | KP330301 | GBMIN94166-17 | 99.53 |
| GE1T [3] | Restaurant | Tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714954 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 99.08 |
| GE1E [3] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Hirundichthys affinis | MW714955 | JQ842898 | TOBA086-09 | 99.52 |
| GE2B [3] | Restaurant | common bass | Dicentrarchus labrax | Dicentrarchus labrax | MW714956 | KP330301 | GBMIN94166-17 | 99.53 |
| ME1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714957 | MF438138 | ANGBF45411-19 | 99.85 |
| ME1T [3] | Restaurant | Tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714958 | MH638762 | ANGBF54791-19 | 98.93 |
| ME1E [3] | Restaurant | lumpfish roe | Cyclopterus lumpus | Cyclopterus lumpus | MW714959 | MG421634 | TZAIC166-05 | 99.54 |
| ME2B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714960 | MF438138 | ANGBF45411-19 | 99.39 |
| ME2E [2] | Restaurant | Ikura | salmon eggs | Oncorhynchus keta | MW714961 | LC094477 | ANGBF41103-19 | 98.93 |
| RC1B [3] | Takeaway | Anago | Anguilla sp | Anguilla rostrata | MW714962 | KX459333 | SERCA165-12 | 98.31 |
| RC1T [3] | Takeaway | Tuna | Thunnus thynnus | Thunnus albacares | MW714963 | MH638785 | ANGBF54814-19 | 99.39 |
| RC1E [2] | Takeaway | Ikura | salmon eggs | Oncorhynchus keta | MW714964 | LC094477 | ANGBF41103-19 | 99.54 |
| RC2E [2] | Takeaway | lumpfish roe | Cyclopterus lumpus | Cyclopterus lumpus | MW714965 | MG421634 | TZAIC166-05 | 99.07 |
| LE1B [3] | Restaurant | sea bream | Sparus aurata | Sparus aurata | MW714966 | MF438138 | ANGBF45411-19 | 98.93 |
| LE1E [1] | Restaurant | tobiko/flying fish egg | Hirundichthys affinis ° | Mallotus villosus | MW714967 | FJ205579 | GBGC7486-09 | 99.39 |
| NA1B [3] | Takeaway | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Sparus aurata | MW714968 | KC501554 | DNATR1599-13 | 99.24 |
| NA2B [3] | Takeaway | sea bream or common bass | Sparus aurata/Dicentrarchus labrax | Pomatomus saltatrix | MW714969 | KC501113 | DNATR1143-13 | 99.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pappalardo, A.M.; Raffa, A.; Calogero, G.S.; Ferrito, V. Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription in Italy—A Crosstalk between Citizen Science and DNA Barcoding. Foods 2021, 10, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040756
Pappalardo AM, Raffa A, Calogero GS, Ferrito V. Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription in Italy—A Crosstalk between Citizen Science and DNA Barcoding. Foods. 2021; 10(4):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040756
Chicago/Turabian StylePappalardo, Anna Maria, Alessandra Raffa, Giada Santa Calogero, and Venera Ferrito. 2021. "Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription in Italy—A Crosstalk between Citizen Science and DNA Barcoding" Foods 10, no. 4: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040756
APA StylePappalardo, A. M., Raffa, A., Calogero, G. S., & Ferrito, V. (2021). Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription in Italy—A Crosstalk between Citizen Science and DNA Barcoding. Foods, 10(4), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040756