Physical Stability of Chestnut Lily Beverages (CLB): Effects of Shear Homogenization on Beverage Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Sensory Properties
Abstract
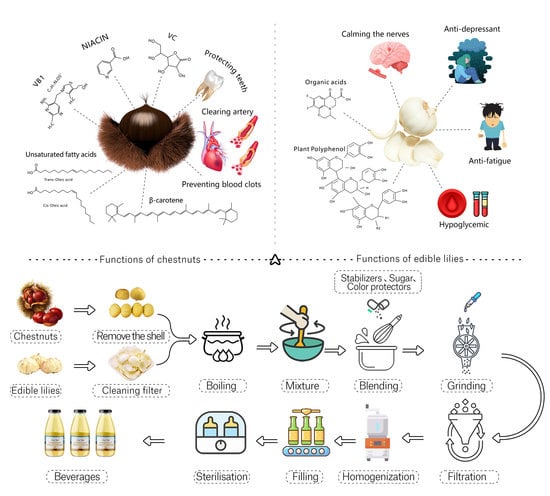
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Product Development
2.3. HSH Treatment of CLB
2.4. Rheological Properties of CLB
2.5. Microstructure Observation
2.6. The Sedimentation Test and Sedimentation Index
2.7. Turbidity Measurement
2.8. Color Parameters
2.9. pH and TSS
2.10. Ascorbic Acid
2.11. Organoleptic Evaluation
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flow Behavior and Shear Viscosity of Beverages
3.1.1. Steady-State Rheological Properties
3.1.2. Dynamic Frequency Scan
3.2. Particle Size Analysis
3.3. The Sedimentation Test and Settlement Index
3.4. Turbidity
3.5. Color Value
3.6. pH and TSS
3.7. Ascorbic Acid
3.8. Sensory Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anoma, C.; Fereidoon, S. Herbal beverages: Bioactive compounds and their role in disease risk reduction—A review. J. Tradit. Complementary Med. 2018, 8, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Massantini, R.; Moscetti, R.; Frangipane, M.T. Evaluating progress of chestnut quality: A review of recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, E.; Giordani, E.; Marinelli, C.; Perucca, B. Funghini: Marrone del mugello PGI chestnut nutritional and organoleptic quality. Acta Horticulturae. Acta Hortic 2005, 693, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of nutrition components in Lanzhou lily bulb by confocal Raman microscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 244, 118837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Y. Diverse genotypic variations of photosynthetic capacity, transpiration and antioxidant enzymes of lily hybrids to increasing salinity stress. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 280, 109939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saricaoglu, F.T.; Atalar, I.; Yilmaz, V.A.; Odabas, H.L.; Gul, O. Application of multi pass high pressure homogenization to improve stability, physical and bioactive properties of rosehip (Rosa canina L.) nectar. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahdouh, L.; Delalonde, M.; Ricci, J.; Ruiz, E.; Wisnewski, C. Influence of high shear rate on particles size, rheological behavior and fouling propensity of fruit juices during crossflow microfiltration: Case of orange juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 48, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Cao, F.; Ding, Y.; Peng, J. Effects of high pressure homogenization on physical stability and carotenoid degradation kinetics of carrot beverage during storage. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrin, M.; Ding, L.; Akoum, O.; Brou, A. A hydrodynamic comparison between rotating disk and vibratory dynamic filtration systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T. Other types of homogenizer (high-speed mixing, ultrasonics, microfluidizers, membrane emulsification. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2011, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, R. Effects of high-speed homogenization and high-pressure homogenization on structure of tomato residue fibers. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, A.; Baker, M.; Pacek, A.W. The effect of stator geometry on the flow pattern and energy dissipation rate in a rotor–stator mixer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H.; Engel, R. Product and Formulation Engineering of Emulsions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2004, 82, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Fischer, N.; Suppiger, D.; Windhab, E.J. Impact of static pressure and volumetric energy input on the microstructure of food foam whipped in a rotor–stator device. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, L.M.; Cortés-Rodríguez, M.; Galeano, F.J.C.; Arango, J.C. Physicochemical stability of pineapple suspensions: The integrated effects of enzymatic processes and homogenization by shear. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turabi, E.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Rheological properties and quality of rice cakes formulated with different gums and an emulsifier blend. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guan, Y.; Bi, J.; Liu, X.; Yi, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhou, M. Change of the rheological properties of mango juice by high pressure homogenization. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Araya-Farias, R.; Doyen, R.; Trudel, R.; Tetu, R. Effect of process unit operations and long-term storage on catechin contents in EGCG-enriched tea drink. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-Z.; Li, Y.-Z.; Nan, J. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on rheology and microstructure of pineapple juice. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2009, 30, 142–144. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, B.; Decker, E.; Panya, A. The influence of flaxseed gum on the microrheological properties and physicochemical stability of whey protein stabilized β-carotene emulsions. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, M.; Stuparić, M.; Neidhart, S.; Carle, R. The role of process technology in carrot juice cloud stability. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pan, S.; Chen, J.; Pang, X.; Guo, X.; Gao, L.; Liao, X.; Wu, J.J.F. Comparing the Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure and Ultrahigh Temperature on Quality and Shelf Life of Cloudy Ginger Juice. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, W.F.; Tiwari, B.K.; Rodriguez, O.; Brito, E.D.; Narciso Fernandes, F.A.; Rodrigues, S. Effect of ultrasound followed by high pressure processing on prebiotic cranberry juice. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, L.I.; Qian, L.I.; Jin-Long, X.U.; Liu, C.M.; Wang, Z.Y. Effects of Dynamic High-pressure Microfluidization Treatment on Vitamin C, the Total Polyphenol Content and the Antioxidant Activity of Pineapple Juice. Chin. J. High Press. Phys. 2013, 27, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Vasudha, N.; Murthy, K. Rheology of mustard paste: A controlled stress measurement. J. Food Eng. 1999, 41, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, G.V.; Silva, E.K.; Costa, A.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Cavalcanti, R.N.; Esmerino, E.A.; Guimar?Es, J.T.; Freitas, M.Q.; Sant’Ana, A.; Cunha, R.L. Whey-grape juice drink processed by supercritical carbon dioxide technology: Physical properties and sensory acceptance. LWT- Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Hemar, Y.; Balaban, M.O.; Liao, X. The effect of ultrasound on particle size, color, viscosity and polyphenol oxidase activity of diluted avocado puree. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 27, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.C.; Shangguan, X.; Wang, H.; Bansal, N. Rheological behavior, emulsifying properties and structural characterization of phosphorylated fish gelatin. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, M.; Rafe, A.; Yeganehzad, S. Effect of different bulk sweeteners on the dynamic oscillatory and shear rheology of chocolate. Appl. Rheol. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangary, Y.S.; Barigou, M.; Seville, J. Simulation of Yoghurt Flow and Prediction of Its End-of-Process Properties Using Rheological Measurements. Food Bioprod. Processing 1999, 77, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieserling, K.; Meyer, L.; Drusch, S.; Schalow, S. Influence of mechanical and thermal treatment on particle structure, leaching of alcohol insoluble substances and water binding properties of pectin-rich orange fibre. Eur. Food Res. 2019, 245, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moelants, K.R.N.; Jolie, R.P.; Palmers, S.K.J.; Cardinaels, R.; Christiaens, S.; Van Buggenhout, S.; Van Loey, A.M.; Moldenaers, P.; Hendrickx, M.E. The Effects of Process-Induced Pectin Changes on the Viscosity of Carrot and Tomato Sera. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 2870–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, G.; Huang, Z. Effect of high speed shear on the non-linear rheological properties of SPI/&&IT-carrageenan hybrid dispersion and fractal analysis. J. Food Eng. 2018, 218, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, D.B.; Lozano, J.E.; Rao, M.A. The rheology of colloidal and noncolloidal food dispersions. J. Food Sci. 2010, 72, R11–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, S.; Van Buggenhout, S.; Chaula, D.; Moelants, K.; David, C. In situ pectin engineering as a tool to tailor the consistency and syneresis of carrot puree. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, J. Effects of the size and content of protein aggregates on the rheological and structural properties of soy protein isolate emulsion gels induced by CaSO4. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszek, A.; Berski, W.; Ptaszek, P.; Witczak, T.; Repelewicz, U.; Grzesik, M. Viscoelastic properties of waxy maize starch and selected non-starch hydrocolloids gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, P.; Svelander, C.; Bialek, L.; Schumm, S.; Langton, M. Rheology and Microstructure of Carrot and Tomato Emulsions as a Result of High-Pressure Homogenization Conditions. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, E130–E140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Kerr, W.L. Rheological properties and microstructure of tomato puree subject to continuous high pressure homogenization. J. Food Eng. 2015, 166, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.; Ibarz, A.; Cristianini, M. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on the rheological properties of tomato juice: Viscoelastic properties and the Cox–Merz rule. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, Z.; Zhao, M.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, Q. Effects of sterilization conditions and milk protein composition on the rheological and whipping properties of whipping cream—ScienceDirect. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Guo, X.; Liao, X. Comparison of Microbial Inactivation and Rheological Characteristics of Mango Pulp after High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatment and High Temperature Short Time Treatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.H.; Zhu, Y.D.; Li, L.T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hua, Z.; Zhu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.D.; Huang, Z.G. Rheological Properties and Microstructure of Soy Protein Isolate / κ -Carrageenan Gels under High-Speed Shear Treatment. J. Food Eng. 2018, 236, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Boulenguer, P.; Kravtchenko, T.P. Effect of the Addition of High Methoxy Pectin on the Rheology and Colloidal Stability of Acid Milk Drinks. In Food Hydrocoll.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. Effects of high-speed shear homogenization on the emulsifying and structural properties of myofibrillar protein under low-fat conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6500–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, A.K.; Anthon, G.E.; Dungan, S.R.; Barrett, D.M. Effect of Pectin Methylesterase on Carrot (Daucus carota) Juice Cloud Stability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.K.; Muthukumarappan, K.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Cullen, P.J. Inactivation kinetics of pectin methylesterase and cloud retention in sonicated orange juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollov, P.; Mihalev, K.; Buleva, M.; Petkanchin, I. Cloud stability of apple juices in relation to their particle charge properties studied by electro-optics. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Jing, L.; Zhang, H.; Ping, C.; Zhou, J. The stabilization mechanism of acidified milk drinks induced by carboxymethylcellulose. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2007, 87, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Bi, X.; Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Liao, X. Changes of quality of high hydrostatic pressure processed cloudy and clear strawberry juices during storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiani, K.; Yi, J.; Kebede, B.; Grauwet, T.; Hendrickx, M. Minimizing quality changes of cloudy apple juice: The use of kiwifruit puree and high pressure homogenization. Food Chem. 2017, 249, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.W.; Streaker, C.B.; Zhang, Q.H.; Min, D.B. Effects of pulsed electric fields on the quality of orange juice and comparison with heat pasteurization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Song, H. Combined effect of high pressure carbon dioxide and mild heat treatment on overall quality parameters of watermelon juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 13, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Kranthi, V.S.; Vijaya, R. Influence of high-intensity ultrasound on bioactive compounds of strawberry juice: Profiles of ascorbic acid, phenolics, antioxidant activity and microstructure. Food Control 2018, 96, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Liao, X.; Zhang, R. Application of nisin-assisted thermosonication processing for preservation and quality retention of fresh apple juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Colloids in Food: Ingredients, Structure, and Stability. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 2015, 6, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Jacobo, A.; Saldo, J.; Ruefer, C.E.; Guamis, B.; Roig-Sagues, A.X.; Gervilla, R. Aseptically packaged UHPH-treated apple juice: Safety and quality parameters during storage. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Augusto, P.; Cristianini, M. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on the physical stability of tomato juice. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tromp, R.H.; de Kruif, C.G.; van Eijk, M.; Rolin, C. On the mechanism of stabilisation of acidified milk drinks by pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Shivhare, U.S.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Rheological characteristics and kinetics of colour degradation of green chilli puree. J. Food Eng. 2000, 44, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.L. High-Shear Mixing: Applications in the Food Industry. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; p. B978008100596503095X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.D.; Paula, M.D.; Costa, G.; Barão, C.; Silva, A.; Raices, R.; Gomes, R.G.; Pimentel, T.C. Orange juice added with L. casei: Is there an impact of the probiotic addition methodology on the quality parameters? LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 106, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-C.; Yin, Y.-X.; Ao, H.-P.; Yin, H.; Ren, D.-F.; Lu, J. The shelf-life of chestnut rose beverage packaged in PEN/PET bottles under long term storage: A comparison to packaging in ordinary PET bottles. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Rpm | 0 | 4000 | 8000 | 12,000 | 16,000 | 20,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 81.0 ± 0.5 a | 81.2 ± 0.1 a | 80.5 ± 0.1 a | 80.9 ± 0.2 a | 80.7 ± 0.4 a | 74.3 ± 0.2 b |
| a | −3.3 ± 0.3 a | −3.3 ± 0.1 a | −3.3 ± 0.1 a | −3.3 ± 0.1 a | −3.3 ± 0.1 a | −2.8 ± 0.1 a |
| b | 6.8 ± 0.1 a | 7.0 ± 0.1 a | 6.6 ± 0.1 b | 6.7 ± 0.1 a | 6.7 ± 0.1 a | 6.7 ± 0.0 a |
| ΔE | 0 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.68 |
| pH | 4.5 ± 0.2 a | 4.57 ± 0.14 a | 4.4 ± 0.1 a | 4.3 ± 0.1 a | 4.22 ± 0.1 a | 3.81 ± 0.1 b |
| TSS | 12.4 ± 0.2 b | 12.9 ± 0.2 b | 13.5 ± 0.1 b | 13.7 ± 0.1 b | 14.1 ± 0.1 a | 14.4 ± 0.2 a |
| Ascorbic acid | 10.5 ± 0.1 a | 9.64 ± 0.2 a | 7.8 ± 0.1 b | 7.85 ± 0.2 b | 7.4 ± 0.1 b | 6.0 ± 0.1 c |
| Appearance | 5.2 ± 1.0 b | 5.7 ± 0.8 ab | 5.9 ± 1.3 a | 6.6 ± 0.9 a | 5.6 ± 1.1 ab | 6.1 ± 1.2 a |
| Aroma | 6.2 ± 1.0 a | 6.2 ± 0.8 a | 5.2 ± 0.5 b | 6.2 ± 0.7 a | 4.7 ± 1.6 b | 4.5 ± 0.9 b |
| Mouthfeel | 5.2 ± 1.1 b | 6.3 ± 1.4 a | 6.1 ± 1.2 ab | 6.8 ± 0.8 a | 7.1 ± 0.6 a | 5.1 ± 0.9 a |
| Taste | 5.4 ± 1.8 b | 6.0 ± 1.9 a | 6.7 ± 1.3 a | 6.5 ± 1.1 a | 6.2 ± 1.2 a | 5.2 ± 1.2 b |
| Overall acceptability | 5.9 ± 1.0 a | 6.1 ± 1.4 a | 6.5 ± 1.2 a | 6.3 ± 1.2 a | 7.1 ± 0.7 a | 5.5 ± 1.2 b |
| Temperature | 4.1 ± 0.7 °C | 18.1 ± 0.5 °C | 26.6 ± 1.1 °C | 30.5 ± 1.2 °C | 35.3 ± 0.4 °C | 41.0 ± 1.2 °C |
| Relative turbidity | 56.2 ± 2.2 c | 70.2 ± 1.3 b | 72.1 ± 1.2 b | 80.3 ± 0.9 a | 76.4 ± 2.1 ab | 72.1 ± 2.6 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; Li, P.; Luo, D.; Guo, J. Physical Stability of Chestnut Lily Beverages (CLB): Effects of Shear Homogenization on Beverage Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Sensory Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11203188
Cui Y, Liu J, Han S, Li P, Luo D, Guo J. Physical Stability of Chestnut Lily Beverages (CLB): Effects of Shear Homogenization on Beverage Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Sensory Properties. Foods. 2022; 11(20):3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11203188
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yao, Jianxue Liu, Sihai Han, Peiyan Li, Denglin Luo, and Jinying Guo. 2022. "Physical Stability of Chestnut Lily Beverages (CLB): Effects of Shear Homogenization on Beverage Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Sensory Properties" Foods 11, no. 20: 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11203188
APA StyleCui, Y., Liu, J., Han, S., Li, P., Luo, D., & Guo, J. (2022). Physical Stability of Chestnut Lily Beverages (CLB): Effects of Shear Homogenization on Beverage Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Sensory Properties. Foods, 11(20), 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11203188