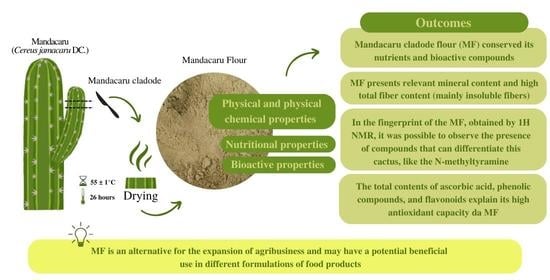
Physical, Nutritional, and Bioactive Properties of Mandacaru Cladode Flour (Cereus jamacaru DC.): An Unconventional Food Plant from the Semi-Arid Brazilian Northeast
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation of Mandacaru Cladode Flour (MF)
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. MF Quality Control
2.4. Physical–Chemical Characterization of MF
2.5. Acquisition of the 1H NMR Spectrum
2.6. Antioxidant Properties of MF
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MF Quality Control
3.2. Physicochemical and Technological Characterization of MF
3.3. Profile of MF Sugars and Organic Acids
3.4. Antioxidant Potential of MF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chance, E.; Ashton, W.; Pereira, J.; Mulrow, J.; Norberto, J.; Derrible, S.; Guilbert, S. The Plant—An experiment in urban food sustainability. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, L.D.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Cámara, M. An international regulatory review of food health-related claims in functional food products labeling. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinusha, K.S.; Deepika, K.; Johnson, T.S.; Agrawal, G.K.; Rakwal, R. Proteomic studies on lactic acid bacteria: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.V.; Guzzetti, L.; Panzeri, D.; De Giuseppe, R.; Coccetti, P.; Labra, M.; Cena, H. Bioactive compounds in legumes: Implications for sustainable nutrition and health in the elderly population. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 117, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamagasorn, M.; Pharino, C. An analysis of food waste from a flight catering business for sustainable food waste management: A case study of halal food production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.A.D.G.; Pacheco, M.T.B.; Queiroga, R.d.C.R.d.E.; Cavalcante, L.M.; Bezerril, F.F.; Ormenese, R.d.C.S.C.; Garcia, A.d.O.; Nabeshima, E.H.; Pintado, M.M.E.; de Oliveira, M.E.G. Nutritional, physicochemical and sensorial acceptance of functional cookies enriched with xiquexique (Pilosocereus gounellei) flour. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.L.G.; Mársico, E.T.; Soares Junior, M.S.; Magalhães, A.O.; Canto, A.C.V.C.S.; Costa-Lima, B.R.C.; Alvares, T.S.; Conte Junior, C.A. Nutritional profile and chemical stability of pasta fortified with Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) flour. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araújo, D.F.S.; Oliveira, M.E.G.; Carvalho, P.O.A.A.; Tavares, E.A.; Guerra, G.C.B.; Queiroga, R.C.R.E.; Langassner, S.M.Z.; Bezerril, F.F.; Silveira, A.C.S.; Medeiros, G.K.V.V.; et al. Food Plants in the Caatinga. In Local Food Plants of Brazil, Ethnobiology, 1st ed.; Jacob, M.C.M., Albuquerque, U.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Chapter 11; pp. 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerril, F.F.; Souza, M.D.F.V.D.; Lima, M.D.S.; Pacheco, M.T.B.; de Carvalho, P.O.A.A.; Sampaio, K.B.; de Sousa, Y.R.F.; Milani, R.F.; Goldbeck, R.; Borges, G.D.S.C. Physicochemical characteristics and bioactive compounds of the Xique-xique (Pilosocereus gounellei) cactus from Caatinga Brazilian: Are they nutritive and functional? J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 3284–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Hunt, D.R. Cactaceae. In Flowering Plants Dicotyledons: Magnoliid, Hamamelid and Caryophyllid Families, 1st ed.; Kubitzki, K., Rohwer, J.G., Bitttich, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Chapter 17; pp. 161–197. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, T.K.N.; De Lucena, C.M.; Lima, J.R.F.; Da Cruz, D.D.; De Lucena, R.F.P. Local botanical knowledge of cacti in the semi-arid region of Paraíba, northeastern Brazil. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2019, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.C.; Majure, L.C.; Cornejo-Romero, A.; Hernández-Hernández, T. Phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary trends in the cactus family. J. Hered. 2019, 110, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.; Guschal, M.; Kowarik, I.; de Almeida-Cortez, J.S.; Sampaio, E.V.D.S.B.; Cierjacks, A. Grazing reduces plant species diversity of caatinga dry forests in northeastern Brazil. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2019, 22, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.M.N.; Silva, G.M.; Buriti, F.C.A.; Alves, H.S. Cereus jamacaru D.C. (Mandacaru): A promising native Brazilian fruit as a source of nutrients and bioactives derived from its pulp and skin. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2021, 76, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destaw, F.; Fenta, M. Climate change adaptation strategies and their predictors amongst rural farmers in Ambassel district, Northern Ethiopia. J. Disaster Risk Stud. 2021, 13, a974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Cactus stems (Opuntia spp.): A review on their chemistry, technology, and uses. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazizi, S.; Montevecchi, G.; Antonelli, A.; Hamdi, M. Effects of prickly pear (Opuntia ficus-indica L.) peel flour as an innovative ingredient in biscuits formulation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 124, 109155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, M.; Limberger, C.; Thys, R.C.S.; Rios, A.d.O.; Flôres, S.H. Mucilage and cladode flour from cactus (Opuntia monacantha) as alternative ingredients in gluten-free crackers. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahdoura, H.; Chaouch, M.A.; Chouchéne, W.; Chahed, A.; Achour, S.; Adouni, K.; Mosbah, H.; Majdoub, H.; Flamini, G.; Achour, L. Incorporation of Opuntia macrorhiza Engelm. in cake-making: Physical and sensory characteristics. LWT 2018, 90, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, D.L.d.S.; Viera, V.B.; Soares, J.K.B.; dos Santos, K.M.O.; Egito, A.S.d.; Figueirêdo, R.M.F.; Lima, M.d.S.; Machado, N.A.F.; Souza, M.d.F.V.d.; da Conceição, M.L.; et al. Pilosocereus gounellei (xique-xique) flour: Improving the nutritional, bioactive, and technological properties of probiotic goat-milk yogurt. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 158, 113165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods, 5th ed.; Armer Public Health: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 995. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, T.B.N.; Pereira, A.P.A.; Pastore, G.M.; Moreira, R.F.A.; Ferreira, M.S.L.; Fai, A.E.C. Chemical composition and physicochemical characterization for cabbage and pineapple by-products flour valorization. LWT 2020, 124, 109028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 21st ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019; p. 3172. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. Available online: https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(18)64849-5/pdf (accessed on 23 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Prosky, L.; Asp, N.-G.; Schweizer, T.F.; Devries, J.W.; Furda, I. Determination of insoluble and soluble dietary fiber in foods and food products. J. AOAC Int. 1992, 75, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, D.T.; Romuald, M.M.; Ysidor, K.N.; Daouda, S.; Adama, C.; Marius, B.G.H. Nutritive contents of cakes enriched with almonds powder of Terminalia catappa of Côte d’Ivoire. Asian Res. J. Agric. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, E.M.; Padilha, C.V.d.S.; Miskinis, G.A.; de Sá, A.G.B.; Pereira, G.E.; de Azevêdo, L.C.; Lima, M.d.S. Simultaneous analysis of sugars and organic acids in wine and grape juices by HPLC: Method validation and characterization of products from northeast Brazil. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 66, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padilha, C.V.d.S.; Miskinis, G.A.; de Souza, M.E.A.O.; Pereira, G.E.; de Oliveira, D.; Bordignon-Luiz, M.T.; Lima, M.d.S. Rapid determination of flavonoids and phenolic acids in grape juices and wines by RP-HPLC/DAD: Method validation and characterization of commercial products of the new Brazilian varieties of grape. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batista, K.S.; Alves, A.F.; Lima, M.d.S.; da Silva, L.A.; Lins, P.P.; Gomes, J.A.d.S.; Silva, A.S.; Toscano, L.T.; Meireles, B.R.L.d.A.; Cordeiro, A.M.T.d.M.; et al. Beneficial effects of consumption of acerola, cashew or guava processing by-products on intestinal health and lipid metabolism in dyslipidaemic female Wistar rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.d.S.; Ferreira, S.R.S.; Vitali, L.; Block, J.M. May the superfruit red guava and its processing waste be a potential ingredient in functional foods? Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.Q.; Weber, C.; Lee, C.Y.; Brown, J.; Liu, R.H. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of raspberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2926–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, R.; Bravo, L.; Saura-Calixto, F. Antioxidant activity of dietary polyphenols as determined by a modified ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3396–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sariburun, E.; Şahin, S.; Demir, C.; Türkben, C.; Uylaşer, V. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of raspberry and blackberry cultivars. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C328–C335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil. Resolução RDC nº 331, de 23 de Dezembro de 2019. Brasília: Diário Oficial da República. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-vegetal/legislacao-1/biblioteca-de-normas-vinhos-e-bebidas/resolucao-rdc-no-331-de-23-de-dezembro-de-2019.pdf/view (accessed on 11 March 2021). (In Portuguese)
- Canalis, M.S.B.; León, A.E.; Ribotta, P.D. Incorporation of dietary fiber on the cookie dough. Effects on thermal properties and water availability. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressiani, J.; Oro, T.; Da Silva, P.; Montenegro, F.; Bertolin, T.; Gutkoski, L.; Gularte, M. Influence of milling whole wheat grains and particle size on thermo-mechanical properties of flour using Mixolab. Czech J. Food Sci. 2019, 37, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Effects of particle size on the quality attributes of wheat flour made by the milling process. Cereal Chem. 2000, 97, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Mohamed, A.S.; Ahmed, A.I.; Sitohy, M.Z. Impact of cucumber pomace fortification on the nutritional, sensorial and technological quality of soft wheat flour-based noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3255–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhare, S.D.; Inamdar, A.A.; Soumya, C.; Indrani, D.; Rao, G.V. Effect of flour particle size on microstructural, rheological and physico-sensory characteristics of bread and south Indian parotta. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 4108–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez, M.; Gutkoski, L.C.; Bravo-Núñez, Á. Understanding whole-wheat flour and its effect in breads: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3241–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Zhu, F. Effect of ultrasound on structural and physicochemical properties of sweetpotato and wheat flours. Ultrason. SonoChem. 2020, 66, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belorio, M.; Sahagún, M.; Gómez, M. Influence of flour particle size distribution on the quality of maize gluten-free cookies. Foods 2019, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.Z.I.; Elgadir, M.A.; Ferdosh, S.; Akanda, M.J.H.; Aditiawati, P.; Noda, T. Rheological behavior of starch-based biopolymer mixtures in selected processed foods. Starch-Stärke 2012, 65, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Raychaudhuri, U.; Chakraborty, R. An overview of encapsulation of active compounds used in food products by drying technology. Food Biosci. 2016, 13, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdoux, S.; Li, D.; Rajkovic, A.; Devlieghere, F.; Uyttendaele, M. Performance of drying technologies to ensure microbial safety of dried fruits and vegetables. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selani, M.M.; Brazaca, S.G.C.; Dias, C.T.S.; Ratnayake, W.S.; Flores, R.A.; Bianchini, A. Characterisation and potential application of pineapple pomace in an extruded product for fibre enhancement. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boukid, F.; Boukid, Z.; Mejri, M. Opuntia cladodes: Physicochemical parameters, functional properties and application in formulation of rolled cake of cladode flour fabric (Part 2). Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. 2015, 1, 30–34. Available online: www.mahendrapublications.com (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Brasília: Diário Oficial da União. Resolução N° 12 de Julho de 1978. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/anvisa/2001/anexos/anexos_res0012_02_01_2001.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2021). (In Portuguese)
- Nabil, B.; Ouaabou, R.; Ouhammou, M.; Essaadouni, L.; Mahrouz, M. Functional properties, antioxidant activity, and organoleptic quality of novel biscuit produced by moroccan cladode flour “Opuntia ficus-indica”. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 3542398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, T.; Shen, J.; Wang, M. Differences in physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility between tartary buckwheat flour and starch modified by heat-moisture treatment. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 86, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, G.; Sezer, B.; Eseller, K.E.; Berberoglu, H.; Koksel, H.; Boyaci, I.H. Ash analysis of flour sample by using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2016, 124, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.R. Ash Analysis. In Food Analysis; Nielsen, S.N., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; Chapter 7; pp. 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, N.T.; Petrova, I.; Ivanov, I.; Mihov, R.; Hadjikinova, R.; Ognyanov, M.; Nikolova, V. Nutritional and antioxidant potential of carob (Ceratonia siliqua) flour and evaluation of functional properties of its polysaccharide fraction. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 2189–2195. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/38822787/Nutritional_and_antioxidant_potential_of_carob_Ceratonia_siliqua_flour_and_evaluation_of_functional_properties_of_its_polysaccharide_fraction?msclkid=0f04c848aac911ecbf62b9877b3f3d46 (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Argel, N.S.; Ranalli, N.; Califano, A.N.; Andrés, S.C. Influence of partial pork meat replacement by pulse flour on physicochemical and sensory characteristics of low-fat burgers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3932–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, R.; Giallanza, A.; Russo, G.; La Scalia, G. Selection of a sustainable functional pasta enriched with Opuntia using ELECTRE III methodology. Sustainability 2017, 9, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, A.G.d.O.; de Alencar, S.M.; Bastos, D.H.M.; Regitano d’Arce, M.A.B.; Skibsted, L.H. Effect of water activity on lipid oxidation and nonenzymatic browning in Brazil nut flour. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafati, L.; Restuccia, C.; Palmeri, R.; Fallico, B.; Arena, E. Characterization of prickly pear peel flour as a bioactive and functional ingredient in bread preparation. Foods 2020, 9, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and modification of high dietary fiber flour: A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E.C.; Duar, R.M.; Armet, A.M.; Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Jin, M.; Walter, J. Modulation of the gastrointestinal microbiome with nondigestible fermentable carbohydrates to improve human health. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, G.A. Dietary fiber, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Vela, J.; Totosaus, A.; Pérez-Chabela, M.L. Integration of agroindustrial co-products as functional food ingredients: Cactus pear (Opuntia ficus indica) flour and pineapple (Ananas comosus) peel flour as fiber source in cooked sausages inoculated with lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, B.N.P.; Vasiljevic, T.; McKechnie, S.; Donkor, O.N. Physicochemical, textural and rheological properties of probiotic yogurt fortified with fibre-rich pineapple peel powder during refrigerated storage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, M.M.; Al Juhaimi, F.Y. Nutritive value and chemical composition of prickly pear seeds (Opuntia ficus indica L.) growing in Turkey. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Munir, N.; Daniyal, M.; Egbuna, C.; Găman, M.A.; Onyekere, P.F.; Olatunde, A. Vitamins and Minerals: Types, Sources and Their Functions. In Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals; Egbuna, C., Tupas, G.D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Chapter 9; pp. 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawiak, B.; Bednarczyk, P.; Szewczyk, A. Multidimensional regulation of cardiac mitochondrial potassium channels. Cells 2021, 10, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Mao, Y. Magnesium and liver disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Avula, B.; Khan, I.A. Detection and quantification of phenethylamines in sports dietary supplements by NMR approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 151, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhn, J.G.; Lindgren, J.E. Cactaceae alkaloids. XXIII. Alkaloids of Pachycereus pecten-aboriginum and Cereus jamacaru. Lloydia 1976, 39, 175–177. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/948243/ (accessed on 23 March 2022). [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tapia, M.; Aguilar-López, M.; Pérez-Cruz, C.; Pichardo-Ontiveros, E.; Wang, M.; Donovan, S.M.; Tovar, A.R.; Torres, N. Nopal (Opuntia ficus indica) protects from metabolic endotoxemia by modifying gut microbiota in obese rats fed high fat/sucrose diet. Scientific Reports 2017, 1, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Al-Ghazzewi, F.H.; Tester, R.F. Dietary fiber, gastric emptying, and carbohydrate digestion: A mini-review. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1700346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Pérez, M.G.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Paredes-López, O.; Mondragón-Jacobo, C.; Reynoso-Camacho, R. Phytochemical composition and in vitro analysis of nopal (O. ficus-indica) cladodes at different stages of maturity. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 21, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Torres, L.; Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Torrestiana-Sanchez, B.; Katthain, R. Rheological properties of the mucilage gum (Opuntia ficus indica). Food Hydrocoll. 2000, 14, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, R.; Aladdin, A.; Othman, N.Z.; Abd Malek, R.; Leng, O.M.; Aziz, R.A.; El Enshasy, H. Lactic acid applications in pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 729–735. Available online: https://www.jocpr.com/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Castro-Muñoz, R. Pervaporation: The emerging technique for extracting aroma compounds from food systems. J. Food Eng. 2019, 253, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.; Abbas, W.; Huang, J.; He, Q.; Zhen, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of blending encapsulated essential oils and organic acids as an antibiotic growth promoter alternative on growth performance and intestinal health in broilers with necrotic enteritis. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Schieber, A.; Carle, R. Phytochemical and nutritional significance of cactus pear. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 212, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chbani, M.; Matthäus, B.; Charrouf, Z.; El Monfalouti, H.; Kartah, B.; Gharby, S.; Willenberg, I. Characterization of phenolic compounds extracted from cold pressed cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica L.) seed oil and the effect of roasting on their composition. Foods 2020, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.; Ortigoza, Á.; Moore, P. Magnesium and malic acid supplement for fibromyalgia. Medwave 2019, 19, e7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, O.; Ikhu-Omoregbe, D.I.O.; Jideani, V. Effect of citric acid on physical stability of sunflower oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by gelatinized bambara groundnut flour. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 10, 2260–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. In vivo antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds: Facts and gaps. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabulici, C.M.; Sârbu, I.; Vamanu, E. The bioactive potential of functional products and bioavailability of phenolic compounds. Foods 2020, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Frez, F.C.; Sehaber-Sierakowski, C.C.; Perles, J.V.C.M.; Bossolani, G.D.P.; Verri Jr, W.A.; do Nascimento, R.C.; Guarnier, F.A.; Bordini, H.P.; Blegniski, F.P.; Martins, H.A.; et al. Anti-and pro-oxidant effects of quercetin stabilized by microencapsulation on interstitial cells of Cajal, nitrergic neurons and M2-like macrophages in the jejunum of diabetic rats. Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Anwar, H.; Iqbal, S.; Ismail, H.; Ashraf, A.; Mustafa, S.; Samad, A. Protective effect of myricetin on nonylphenol-induced testicular toxicity: Biochemical, steroidogenic, hormonal, spermatogenic, and histological-based evidences. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22742–22757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Villarreal, D.; Camacho, A.; Castro, H.; Ortiz-Lopez, R.; de la Garza, A.L. Anti-obesity effects of kaempferol by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, D.D.S.; Pacheco, M.T.; Frozza, R.L.; Bernardi, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol: Mechanistic insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos-Díaz, M.d.S.; Camarena-Rangel, N.G. Cacti for production of metabolites: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8657–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelena, C.H.; Giorgio, R.; Justyna, G.; Neda, M.-D.; Natasa, S.; Artur, B.; Giuseppe, G. Beneficial Effects of Polyphenols on Chronic Diseases and Ageing. In Polyphenols: Properties, Recovery and Applications, 1st ed.; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 3; pp. 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomová, K.; Hudecova, L.; Lauro, P.; Simunkova, M.; Alwasel, S.H.; Alhazza, I.M.; Valko, M. A switch between antioxidant and prooxidant properties of the phenolic compounds myricetin, morin, 3′, 4′-dihydroxyflavone, taxifolin and 4-hydroxy-coumarin in the presence of copper (II) ions: A spectroscopic, absorption titration and DNA damage study. Molecules 2019, 24, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luna-Guevara, M.L.; Luna-Guevara, J.J.; Hernández-Carranza, P.; Ruíz-Espinosa, H.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E. Phenolic Compounds: A Good Choice Against Chronic Degenerative Diseases. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, 1st ed.; Rahman, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 3; pp. 79–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, A.; De Wit, M.; Osthoff, G.; Hugo, A. Antioxidant properties of fresh and processed cactus pear cladodes from selected Opuntia ficus-indica and O. robusta cultivars. South Afr. J. Bot. 2018, 118, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, K.; Wojciechowska, N.; Alipour, S.; Kalemba, E.M. Ascorbic acid—The little-known antioxidant in woody plants. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Njus, D.; Kelley, P.M.; Tu, Y.-J.; Schlegel, H.B. Ascorbic acid: The chemistry underlying its antioxidant properties. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 159, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, T.H.; Atsbha, M.K. Nutritional composition, antinutritional factors, antioxidant activities, functional properties, and sensory evaluation of cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) seeds grown in tigray region, Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Sci. 2019, 2019, 5697052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huyut, Z.; Beydemir, Ş.; Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant and antiradical properties of selected flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Biochem. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7616791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Parameters | MF |
|---|---|
| aw 1 | 0.937 ± 0.000 |
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 13.20 ± 0.69 |
| FMR (g/100 g) 2 | 2.66 ± 0.16 |
| Proteins (g/100 g) | 0.88 ± 0.09 |
| Fat (g/100 g) | 0.23 ± 0.09 |
| Total carbohydrates (g/100 g) | 86.24 ± 0.17 |
| Dietary fiber (g/100 g) | |
| Insoluble dietary fiber | 4.57 ± 0.60 |
| Soluble dietary fiber | 2.67 ± 0.61 |
| Total dietary fiber | 7.24 ± 1.20 |
| Antioxidant potential | |
| Ascorbic acid (mg/100 g) | 18.15 ± 0.10 |
| Total Phenolics (mg GAE/100 g) 3 | 21.32 ± 0.52 |
| Total Flavonoids (mg CE/100 g) 4 | 25.10 ± 0.20 |
| FRAP (µmol Trolox TEAC/100 g) 5 | 0.89 ± 0.08 |
| ABTS (µmol Trolox TEAC/g) 6 | 2.64 ± 0.30 |
| Parameters | MF |
|---|---|
| aw 1 | 0.423 ± 0.003 |
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 8.24 ± 0.21 |
| FMR (g/100 g) 2 | 2.82 ± 0.02 |
| Proteins (g/100 g) | 5.18 ± 0.10 |
| Fat (g/100 g) | 1.88 ± 0.14 |
| Total Carbohydrates (g/100 g) | 74.48 ± 0.20 |
| Dietary fiber (g/100 g) | |
| Insoluble dietary fiber | 48.08 ± 7.55 |
| Soluble dietary fiber | 0.38 ± 0.06 |
| Total dietary fiber | 48.46 ± 7.61 |
| Macro and microelements (%) | |
| Na | 0.95 ± 0.34 |
| Mg | 15.21 ± 0.29 |
| K | 5.94 ± 0.18 |
| Ca | 76.33 ± 0.69 |
| Mn | 0.54 ± 0.29 |
| Fe | 0.05 ± 0.29 |
| Cu | 0.59 ± 0.40 |
| Zn | 0.39 ± 0.47 |
| Parameters | MF |
|---|---|
| Simple Sugars (g/100 g) | |
| Glycose | 1.33 ± 0.02 |
| Fructose | <LOD |
| Maltose | <LOD |
| Rhamnose | <LOD |
| Organics Acids (g/100 g) | |
| Citric | 3.96 ± 0.36 |
| Latic | 0.52 ± 0.02 |
| Malic | 9.41 ± 0.22 |
| Succinic | 1.53 ± 0.02 |
| Formic | 1.04 ± 0.07 |
| Acetic | <LOD |
| Butyric | <LOD |
| Propionic | <LOD |
| Variables | MF |
|---|---|
| Phenolic Compound Profiles (mg/100 g) | |
| Syringic acid | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| Hesperidin | 0.62 ± 0.05 |
| Resveratrol | 17.84 ± 1.58 |
| Naringenin | 0.21 ± 0.02 |
| Procyanidin B1 | 0.79 ± 0.05 |
| Catechin | 0.45 ± 0.26 |
| Procyanidin B2 | 0.13 ± 0.05 |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 0.50 ± 0.03 |
| Epicatequin | 0.04 ± 0.05 |
| Epicatechin gallate | 2.84 ± 0.22 |
| Procyanidin A2 | 0.52 ± 0.26 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.23 ± 0.02 |
| Caffeic acid | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| Trans-resveratrol | 0.44 ± 0.03 |
| Miricetin | 72.30 ± 5.91 |
| Quercitin | 1.74 ± 0.34 |
| Rutine | 0.03 ± 0.02 |
| Kaempferol | 99.40 ± 8.89 |
| Ascorbic acid (mg/100 g) | 35.22 ± 0.50 |
| Total phenolics (mg GAE/100 g) 1 | 1285.47 ± 0.10 |
| Total flavonoids (mg CE/100 g) 2 | 15.19 ± 0.50 |
| FRAP (µmol Trolox TEAC/100 g) 3 | 249.45 ± 0.20 |
| ABTS (µmol Trolox TEAC/g) 4 | 0.39 ± 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, A.C.S.; Medeiros, G.K.V.d.V.; Silva, J.Y.P.d.; Viera, V.B.; Barros, P.d.S.; Lima, M.d.S.; Silva, M.S.d.; Tavares, J.F.; Nascimento, Y.M.d.; Silva, E.F.d.; et al. Physical, Nutritional, and Bioactive Properties of Mandacaru Cladode Flour (Cereus jamacaru DC.): An Unconventional Food Plant from the Semi-Arid Brazilian Northeast. Foods 2022, 11, 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233814
Martins ACS, Medeiros GKVdV, Silva JYPd, Viera VB, Barros PdS, Lima MdS, Silva MSd, Tavares JF, Nascimento YMd, Silva EFd, et al. Physical, Nutritional, and Bioactive Properties of Mandacaru Cladode Flour (Cereus jamacaru DC.): An Unconventional Food Plant from the Semi-Arid Brazilian Northeast. Foods. 2022; 11(23):3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233814
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Ana Cristina S., Gracy Kelly V. de V. Medeiros, Jaielison Yandro P. da Silva, Vanessa B. Viera, Paternak de S. Barros, Marcos dos S. Lima, Marcelo S. da Silva, Josean F. Tavares, Yuri M. do Nascimento, Evandro F. da Silva, and et al. 2022. "Physical, Nutritional, and Bioactive Properties of Mandacaru Cladode Flour (Cereus jamacaru DC.): An Unconventional Food Plant from the Semi-Arid Brazilian Northeast" Foods 11, no. 23: 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233814
APA StyleMartins, A. C. S., Medeiros, G. K. V. d. V., Silva, J. Y. P. d., Viera, V. B., Barros, P. d. S., Lima, M. d. S., Silva, M. S. d., Tavares, J. F., Nascimento, Y. M. d., Silva, E. F. d., Soares, J. K. B., Souza, E. L. d., & Oliveira, M. E. G. d. (2022). Physical, Nutritional, and Bioactive Properties of Mandacaru Cladode Flour (Cereus jamacaru DC.): An Unconventional Food Plant from the Semi-Arid Brazilian Northeast. Foods, 11(23), 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233814