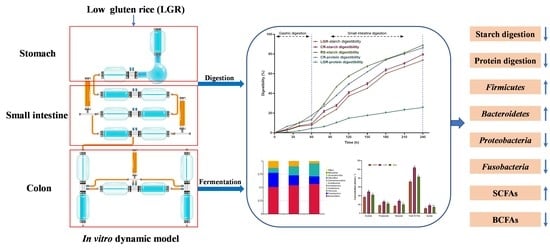
In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Low-Gluten Rice and Its Effect on the Gut Microbiota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. In Vitro Gastric and Small Intestine Digestion
2.3. Culture of Gut Microbiota in the Colon In Vitro
2.4. SCFAs, BCFAs, and Lactic Acid
2.5. Determination of the Ammonia Content
2.6. S rDNA Amplicon Sequencing Method
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Starch Digestibility
3.2. A. muciniphila Growth and Metabolism
3.3. Gut Microbiota Growth and Metabolism
3.4. Gut Microbiota Structure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watanabe, S.; Ohtsubo, K.I. Low-Protein Diet: History and Use of Processed Low-Protein Rice for the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease. Foods 2021, 10, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.B.S.; Roager, H.M.; Søndertoft, N.B.; Gøbel, R.J.; Kristensen, M.; Vallès-Colomer, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Hansen, T.; Lauritzen, L.; Gupta, R.; et al. A low-gluten diet induces changes in the intestinal microbiome of healthy Danish adults. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Rufaye, T.A.H.; Al-Sheikh, W.M.S.; Ghaleb, I.K. Detection of Lgc1 Gene Low Glutelin Content in Rice Cultivars Iraq using Indel Markers. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2018, 10, 19–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ji-Yoon, L.; Jong-Hee, L.; Jun-Hyun, C.; Sang-Yeol, K.; Choon-Song, K.; Young-Bo, S.; Un-Sang, Y.; Choon-Woo, L.; Min-Hee, N. Analysis of Eating Quality in Recombinant Inbred Lines and Selection of Elite Line with Low Glutelin Content in Rice. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2012, 44, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Ling, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Qiu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B. Evaluation of the Quality of a High-Resistant Starch and Low-Glutelin Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Generated through CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9733–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-h.; Chen, Y.-l.; Ding, Y.-f.; Geng, C.-m.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.-h.; Wang, S.-h.; Tang, S. Charactering protein fraction concentrations as influenced by nitrogen application in low-glutelin rice cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, S.J.; Ji, S.L.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, C.M.; Jiang, L.; Wan, J.M. Fine mapping and marker-assisted selection (MAS) of a low glutelin content gene in rice. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, C.-X.; Min, L.; Zhu, L.-Y. Good or bad: Gut bacteria in human health and diseases. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, P.P.; Koh, A.Y. The gut microbiota in transplant patients. Blood Rev. 2020, 39, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Xu, X.; Miwa, H. Role of Gut Microbiota-Gut Hormone Axis in the Pathophysiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Bäckhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barczynska, R.; Litwin, M.; Slizewska, K.; Szalecki, M.; Berdowska, A.; Bandurska, K.; Libudzisz, Z. Bacterial Microbiota and Fatty Acids in the Faeces of Overweight and Obese Children. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 560–569. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Buch, H.; Zhang, F. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeckx, K.; Cotter, P.; López-Expósito, I.; Kleiveland, C.; Lea, T.; Mackie, A.; Requena, T.; Swiatecka, D.; Wichers, H. The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Minekus, M. The TNO Gastro-Intestinal Model (TIM). In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Verhoeckx, K., Cotter, P., Lopez-Exposito, I., Kleiveland, C., Lea, T., Mackie, A., Requena, T., Swiatecka, D., Wichers, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.-t.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.-l.; Zhan, X.-b.; Gao, M.-j. New dynamic digestion model reactor that mimics gastrointestinal function. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 154, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Wang, J.W.; Hu, X.H.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, M.J.; Zhan, X.B. The effects of high-fat foods on gut microbiota and small molecule intestinal gases: Release kinetics and distribution in vitro colon model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.T.; Hu, G.A.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Z.C.; Yun, J.; Gao, M.J.; Zhan, X.B. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation of highly resistant starch rice and its effect on the gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemejane, C.; Denis, S.; Marsset-Baglieri, A.; Alric, M.; Aymard, P.; Michon, C. In vitro digestion of short-dough biscuits enriched in proteins and/or fibres using a multi-compartmental and dynamic system (2): Protein and starch hydrolyses. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, Q.; Yin, B.; Fang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium adolescentis Exerts Strain-Specific Effects on Constipation Induced by Loperamide in BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Ma, R.; Zhan, J.; Wang, F.; Tian, Y. The role of protein and its hydrolysates in regulating the digestive properties of starch: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 125, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, A.; Waters, D.L.E.; Liu, L. The impact of rice protein on in vitro rice starch digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; Liu, R.H. In Vitro fermentation of mulberry fruit polysaccharides by human fecal inocula and impact on microbiota. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4637–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenen, M.E.; Cruz Rubio, J.M.; Mueller, M.; Venema, K. The effect of agave fructan products on the activity and composition of the microbiota determined in a dynamic in vitro model of the human proximal large intestine. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P. Beneficial modulation of the gut microbiota. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 45, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, T.-P.-T.; Tidjani Alou, M.; Bachar, D.; Levasseur, A.; Brah, S.; Alhousseini, D.; Sokhna, C.; Diallo, A.; Wieringa, F.; Million, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Alteration is Characterized by a Proteobacteria and Fusobacteria Bloom in Kwashiorkor and a Bacteroidetes Paucity in Marasmus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peck, S.C.; Denger, K.; Burrichter, A.; Irwin, S.M.; Balskus, E.P.; Schleheck, D. A glycyl radical enzyme enables hydrogen sulfide production by the human intestinal bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3171–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, S.M.M.; Rodloff, A.C.; Stingu, C.-S. Diversity of antimicrobial resistance genes in Bacteroides and Parabacteroides strains isolated in Germany. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 24, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Tarentino, A.L.; Grimwood, B.G.; Plummer, T.H.; Cui, T.; Guan, C.; Van Roey, P. Crystal structure of glycosylasparaginase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 1998, 7, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardini, A.; Cuesta, T.; Tomás, A.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Martínez, J.L.; Sánchez, M.B. The intrinsic resistome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, I.; Khanra, K.; Maity, P.; Patra, A.; Maity, G.N.; Pati, B.R.; Nag, A.; Mondal, S.; Bhattacharyya, N. Structure and biological properties of exopolysaccharide isolated from Citrobacter freundii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidaurrazaga, M.M.; McKinley, G.F.; Camins, B.C. Postpartum Fusobacterium gonidiaformans bacteremia. Anaerobe 2020, 62, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonder, M.J.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Cai, X.; Trynka, G.; Cenit, M.C.; Hrdlickova, B.; Zhong, H.; Vatanen, T.; Gevers, D.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The influence of a short-term gluten-free diet on the human gut microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leylabadlo, H.E.; Ghotaslou, R.; Feizabadi, M.M.; Farajnia, S.; Moaddab, S.Y.; Ganbarov, K.; Khodadadi, E.; Tanomand, A.; Sheykhsaran, E.; Yousefi, B.; et al. The critical role of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in human health: An overview. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, J.J.; Nielsen, D.W.; Looft, T. Complete Genome Sequence and Annotation for Romboutsia sp. Strain CE17. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00382-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Beamer, M.A.; Fiedler, T.L.; Austin, M.N.; Sizova, M.V.; Strenk, S.M.; Agnew, K.J.; Nagana-Gowda, G.A.; Rabe, L.K.; Raftery, D.; et al. Characterization of novel megasphaera species from the female reproductive tract. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 219, 648–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.-T.; Han, S.-X.; Pu, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, M.-J.; Zhan, X.-B.; Xu, S. In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Low-Gluten Rice and Its Effect on the Gut Microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040855
Li Z-T, Han S-X, Pu J-Y, Wang Y-Y, Jiang Y, Gao M-J, Zhan X-B, Xu S. In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Low-Gluten Rice and Its Effect on the Gut Microbiota. Foods. 2023; 12(4):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040855
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhi-Tao, Shuang-Xin Han, Jia-Yang Pu, Yu-Ying Wang, Yun Jiang, Min-Jie Gao, Xiao-Bei Zhan, and Song Xu. 2023. "In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Low-Gluten Rice and Its Effect on the Gut Microbiota" Foods 12, no. 4: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040855
APA StyleLi, Z. -T., Han, S. -X., Pu, J. -Y., Wang, Y. -Y., Jiang, Y., Gao, M. -J., Zhan, X. -B., & Xu, S. (2023). In Vitro Digestion and Fecal Fermentation of Low-Gluten Rice and Its Effect on the Gut Microbiota. Foods, 12(4), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040855