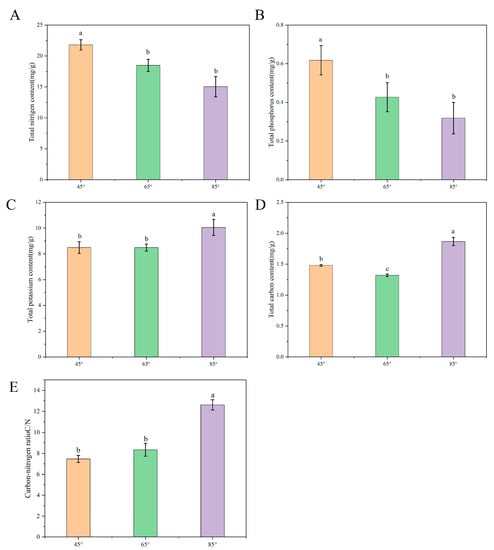
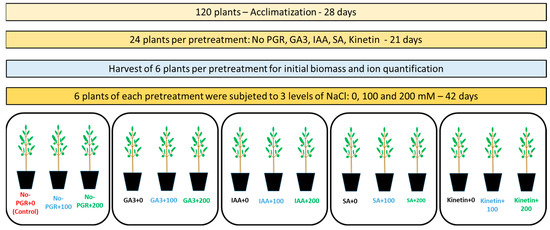
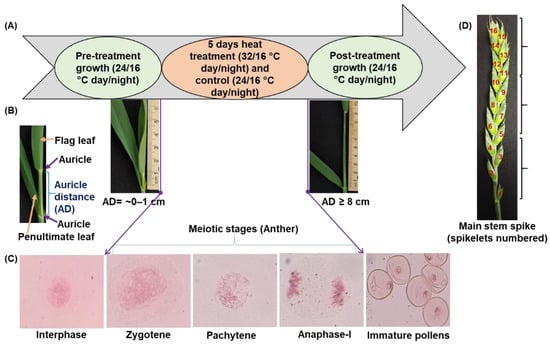
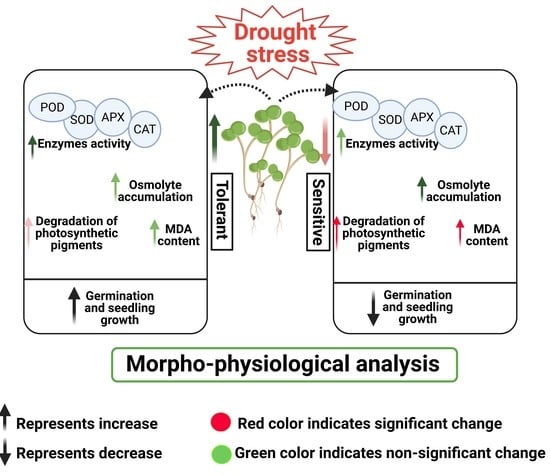
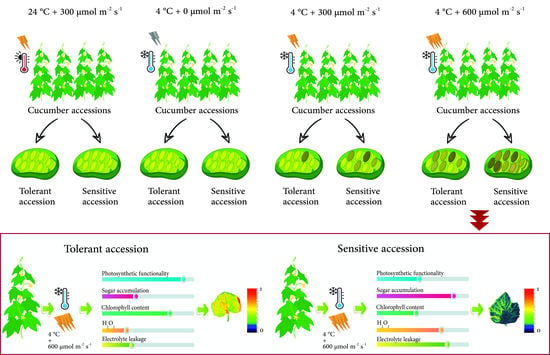
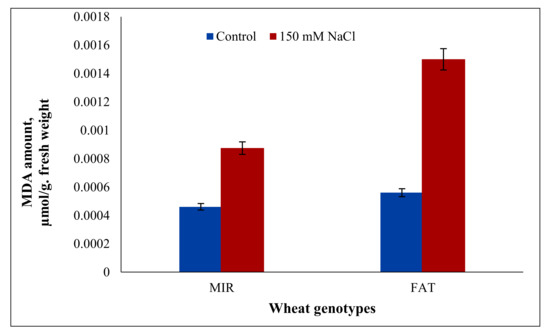
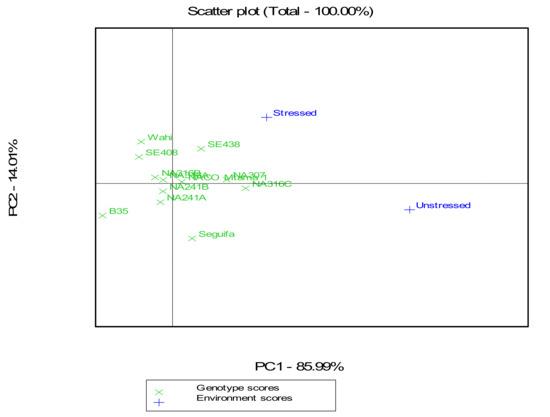
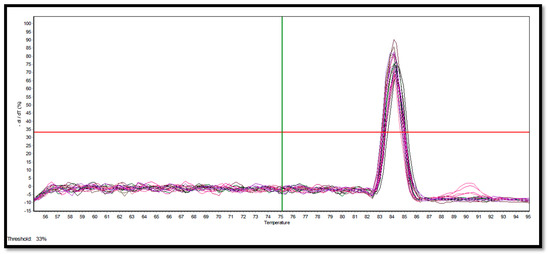
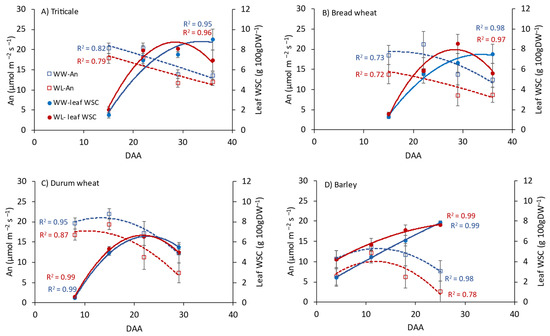
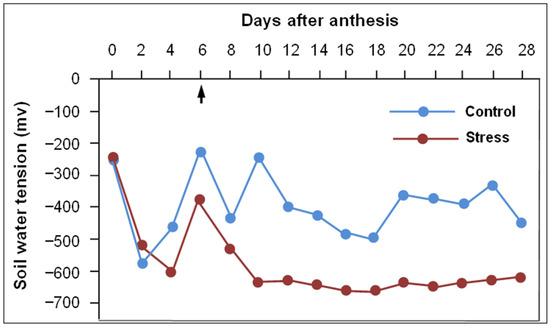
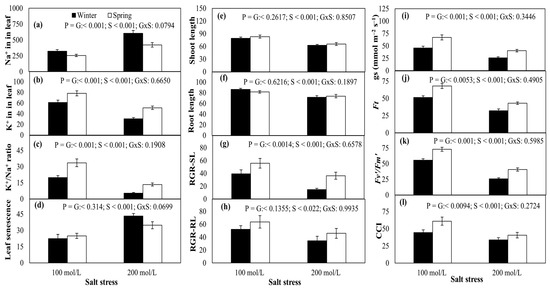
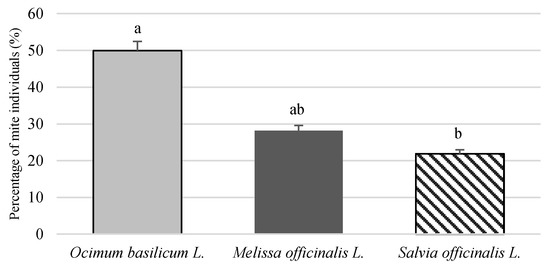
Crop Physiology and Stress
A topical collection in Agronomy (ISSN 2073-4395). This collection belongs to the section "Plant-Crop Biology and Biochemistry".
Viewed by 89542Editor
Interests: salt stress; ecophysiology of halophytes; salt tolerance; ecophysiology of olives; plant osmoregulation; polyamines in plants under saline stress; halophyte utilities; biotic stress
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Agriculture faces challenges such as environmental change and an increasing world population. The increase in the quantity and quality of agricultural products is of great interest. This requires adequate growth and development of the plant and proper crop management. There are several lines of research aimed at studying the physiology of plants and crops. This Collection aims to include the main lines of study that are being developed considering the optimal and stress scenarios that are affecting crops.
This Topical Collection will focus on “Crop Physiology”. We welcome novel research and reviews covering all topics related, but not limited, to environment–plant interaction, stress physiology, plant–microbe interaction, adaptation of plants to the environment, plants’ response to stress, and production and stress.
Prof. Dr. María del Pilar Cordovilla
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Agronomy is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- plant ecophysiology
- carbon utilization
- photosynthesis
- water relations
- plant water potential
- plant mineral nutrition
- plant growth regulators
- crop production
- plant-microbe interactions
- genetic resources
- differences between cultivars
- soil-plant interaction
- environment-plant interaction
- environmental stress physiology
- abiotic stress
- climate change
- adaptation of plants to the environment