Feeding Cattle for Health Improvement
A topical collection in Animals (ISSN 2076-2615). This collection belongs to the section "Cattle".
Viewed by 137595
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Marta I. Miranda Castañón
Prof. Dr. Marta I. Miranda Castañón
 Prof. Dr. Marta I. Miranda Castañón
Prof. Dr. Marta I. Miranda Castañón
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Departamento de Anatomía, Producción Animal y Ciencias Clínicas Veterinarias, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Facultad de Veterinaria, Campus Terra, Lugo, Spain
Interests: cattle; toxic and trace elements; organic farming; conventional farming; cattle medicine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Marta López Alonso
Prof. Dr. Marta López Alonso
 Prof. Dr. Marta López Alonso
Prof. Dr. Marta López Alonso
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Departamento de Patoloxía Animal, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Facultad de Veterinaria, Campus Terra, Lugo, Spain
Interests: cattle; toxic and trace elements; organic farming; conventional farming; cattle medicine
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Adequate provision of suitable feed is one of the primary objectives of farmers to ensure the health and performance of their livestock. Nutrition can be modulated to improve growing, production, reproduction, and in general “to improve health”. Adequate nutrition requires knowledge of the nutritional requirements of all components of the diet for the different periods of growing and production. In recent years, many innovations in cattle nutrition have been proposed, and the aim of this Special Issue is to publish original research papers or reviews concerning cattle nutrition (both dairy and beef) and the interrelations between nutrition, health and the environment.
Areas of interest: Nutrient requirements for cattle. The effect of feeding on animal health (growing, reproduction, immunity, udder health, etc.) and quality of their products (meat and milk). Nutrition in different farming systems. Additives and novel ingredients. The effects of feeding on environment.
We invite you to share your recent findings through this Special Issue.
Prof. Marta I. Miranda Castañón
Prof. Marta López Alonso
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Animals is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Cattle
- Nutrition
- Heath
- Milk
- Meat
- Feed additives
- Novel ingredients
- Environment
Published Papers (29 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Replacing Corn Grain and Soybean Meal with Field Peas at Different Levels on Feed Intake, Milk Production, and Metabolism in Dairy Cows under a Restrictive Grazing
by
Ruben G. Pulido, Ignacio E. Beltran, Jorge A. Aleixo, Álvaro G. Morales, Marcelo Gutierrez, Matias Ponce and Pedro Melendez
Viewed by 692
Abstract
This study assessed the effects of replacing soybean meal (SBM) and corn grain with field peas in the concentrate of grazing dairy cows on milk production, intake, ruminal fermentation, and blood indicators. Twelve multiparous lactating Holstein-Friesian cows were utilized in a replicated 3
[...] Read more.
This study assessed the effects of replacing soybean meal (SBM) and corn grain with field peas in the concentrate of grazing dairy cows on milk production, intake, ruminal fermentation, and blood indicators. Twelve multiparous lactating Holstein-Friesian cows were utilized in a replicated 3 × 3 Latin square design, comprising three periods and three treatments: (1) Pea-0 (Control diet): 6 kg dry matter (DM) of fresh pasture, 7.2 kg DM of grass silage, and 7 kg DM of a concentrate containing 0% pea; (2) Pea-30: Control diet with the concentrate composed of 30% pea; (3) Pea-60: Control diet with the concentrate composed of 60% pea. The effect of treatments on productive and metabolic parameters was evaluated using linear-mixed models. Pasture and total DM intake, milk production, and composition were unaffected by treatments. Despite the concentrates being isonitrogenous and isoenergetic, crude protein (CP) intake was slightly higher in Pea-30 and significantly higher in Pea-60 due to higher pasture CP content in the pasture grazed by these groups, leading to higher milk urea content, though within recommended ranges. Blood parameters showed no significant changes, except for plasma β-hydroxybutyrate, which was lowest in the Pea-60 treatment; however, all values were within ranges not indicative of subclinical ketosis. Ruminal fermentation parameters were similar across treatments. These findings support the use of field peas as a viable alternative to replace SBM and corn grain in concentrates, enabling similar milk production and composition in grazing dairy cows.
Full article
Open AccessReview
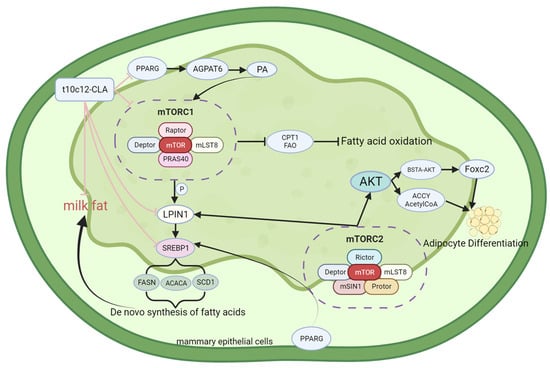
Research Progress on the Mechanism of Milk Fat Synthesis in Cows and the Effect of Conjugated Linoleic Acid on Milk Fat Metabolism and Its Underlying Mechanism: A Review
by
Yuanyin Guo, Ziang Wei, Yi Zhang and Jie Cao
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3126
Abstract
Milk fat synthesis in cows mainly includes the synthesis of short- and medium-chain fatty acids, the uptake, transport, and activation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs), the synthesis of triglycerides, and the synthesis of the genes, transcription factors, and signaling pathways involved. Although the
[...] Read more.
Milk fat synthesis in cows mainly includes the synthesis of short- and medium-chain fatty acids, the uptake, transport, and activation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs), the synthesis of triglycerides, and the synthesis of the genes, transcription factors, and signaling pathways involved. Although the various stages of milk fat synthesis have been outlined in previous research, only partial processes have been revealed. CLA consists of an aggregation of positional and geometric isomers of linoleic fatty acid, and the accumulated evidence suggests that the two isomers of the active forms of CLA (cis-9, trans-11 conjugated linoleic acid and trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid, abbreviated as c9, t11-CLA and t10, c12-CLA) can reduce the fat content in milk by regulating lipogenesis, fatty acid (FA) uptake, oxidation, and fat synthesis. However, the mechanism through which CLA inhibits milk fat synthesis is unique, with most studies focusing only on the effects of CLA on one of the genes, transcription factors, or signaling pathways involved. In this study, we summarized the structure and function of classic genes and pathways (mTOR, SREBP, AMPK, and PPARG) and new genes or pathways (THRSP, METTL3, ELOVL, and LPIN1) involved in each stage of milk fat synthesis and demonstrated the interactions between genes and pathways. We also examined the effects of other substances (melanin, nicotinic acid, SA, etc.). Furthermore, we evaluated the influence of β-sitosterol, sodium butyrate, Met arginine, and
Camellia oleifera Abel on milk fat synthesis to improve the mechanism of milk fat synthesis in cows and provide a mechanistic reference for the use of CLA in inhibiting milk fat biosynthesis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
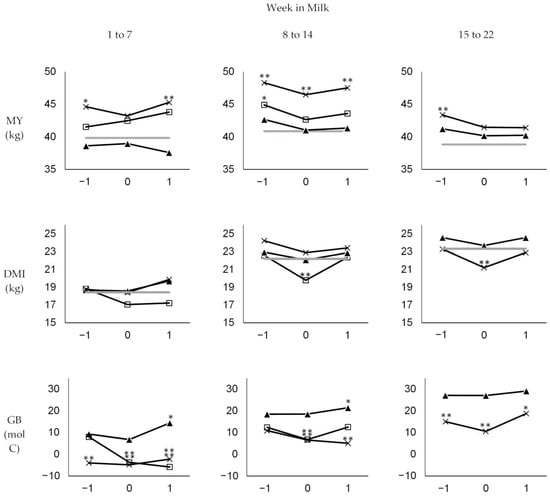
Dairy Cows Are Limited in Their Ability to Increase Glucose Availability for Immune Function during Disease
by
Jonas Habel and Albert Sundrum
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1769
Abstract
Shortages of energy and glucose have been hypothesized to play a key role in the development of and responses to production diseases in dairy cows during early lactation. Given the importance of glucose for immune functions, we used a recently established method for
[...] Read more.
Shortages of energy and glucose have been hypothesized to play a key role in the development of and responses to production diseases in dairy cows during early lactation. Given the importance of glucose for immune functions, we used a recently established method for the estimation of glucose balance (GB) to evaluate glucose availability during disease phases. A dataset comprising ration analyses as well as individual daily milk yields (MY), dry matter intake (DMI), body weights, and health records of 417 lactations (298 cows) was used to calculate individual daily GB and energy balance (EB). The magnitude and dynamics of MY, DMI, GB, and EB were evaluated in the weeks before, at, and after diagnoses of inflammatory diseases in different stages of early lactation from week in milk 1 to 15. Diagnoses were categorized as mastitis, claw and leg diseases, and other inflammatory diseases. Mixed linear models with a random intercept and slope term for each lactation were used to evaluate the effect of diagnosis on MY, DMI, GB, and EB while accounting for the background effects of week in milk, parity, season, and year. When unaffected by disease, in general, the GB of cows was close to zero in the first weeks of lactation and increased as lactation progressed. Weekly means of EB were negative throughout all lactation stages investigated. Disease decreased both the input of glucose precursors due to a reduced DMI as well as the output of glucose via milk due to a reduced MY. On average, the decrease in DMI was −1.5 (−1.9 to −1.1) kg and was proportionally higher than the decrease in MY, which averaged −1.0 (−1.4 to −0.6) kg. Mastitis reduced yield less than claw and leg disease or other diseases. On average, GB and EB were reduced by −3.8 (−5.6 to −2.1) mol C and −7.5 (−10.2 to −4.9) MJ in the week of diagnosis. This indicates the need to investigate strategies to increase the availability of glucogenic carbon for immune function during disease in dairy cows.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
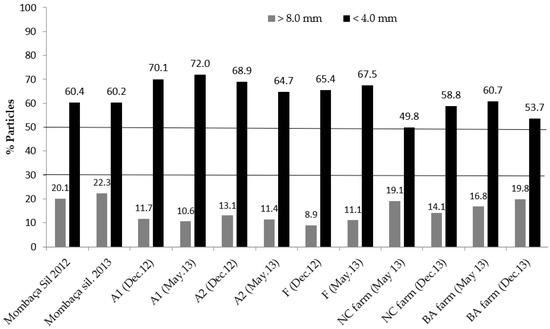
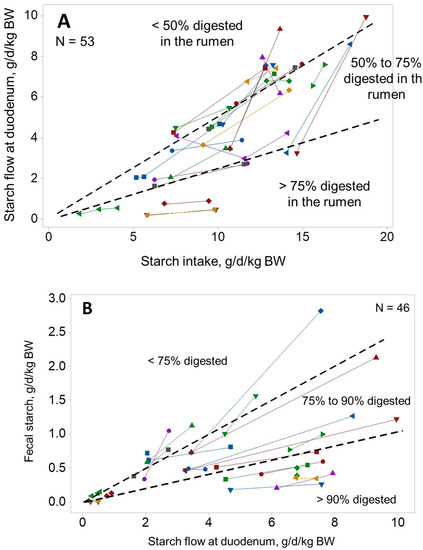
Physicochemical Evaluations of Diets, Rumen Fluid, Blood and Faeces of Beef Cattle under Two Different Feedlot Systems
by
Pedro Malafaia, Vinícius Carneiro de Souza and Diogo Fleury Azevedo Costa
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1995
Abstract
The physicochemical characteristics of diets and faeces were evaluated in combination with data of rumen fluid and blood lactate collected from two distinct feedlot systems in Brazil to understand the causes and correlations to digestive disorders in these production systems. The data were
[...] Read more.
The physicochemical characteristics of diets and faeces were evaluated in combination with data of rumen fluid and blood lactate collected from two distinct feedlot systems in Brazil to understand the causes and correlations to digestive disorders in these production systems. The data were collected during two visits to a finishing system which fed about 80,000 head per year, and four visits to two properties that fed 150 to 180 straight bred Nellore bulls per year to be sold as stud cattle. The findings suggest that ruminal acidosis occurred when there was high intake of starch-rich concentrate, and that subacute rumen acidosis (SARA) most likely occurred in situations where more than 4% of faecal dry matter was excreted as particles larger than 4 mm. The latter were associated with diets having less than 15% of particles smaller than 8 mm and faecal pH under 6.30. It is concluded that ancillary tests, such as ruminal and faecal pH, and particle size distribution in the faeces, can potentially be used in combination with information on diet nutritional composition and a series of best practice management protocols to increase not only animal productivity but to reduce the risks of SARA and ensure the welfare of animals.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
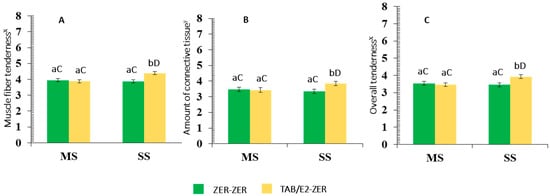
The Effects of Castration, Implant Protocol, and Supplementation of Bos indicus-Influenced Beef Cattle under Tropical Savanna Conditions on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, and Meat Quality
by
Nelson Huerta-Leidenz, Nancy Jerez-Timaure, Argenis Rodas-González, Jhones Onorino Sarturi, Mindy M. Brashears, Markus F. Miller and Michel Todd Brashears
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2523
Abstract
The effects of castration, supplementation, and implant protocol (IP) on growth, carcass characteristics, and meat quality of grass-fed cattle were evaluated. Two experiments followed a two-way ANOVA and a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement. Experiment-I, 99 bulls were evaluated for: (a) supplementation (mineral
[...] Read more.
The effects of castration, supplementation, and implant protocol (IP) on growth, carcass characteristics, and meat quality of grass-fed cattle were evaluated. Two experiments followed a two-way ANOVA and a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement. Experiment-I, 99 bulls were evaluated for: (a) supplementation (mineral (MS) or strategic protein-energy supplementation (SS), and (b) IP (repeated (day-0 and day-90) Zeranol-72 mg implantation (Zeranol–Zeranol) or Trenbolone Acetate-140 mg/Estradiol-20 mg (day-0) followed by Zeranol-72 mg (day-90) (TBA/E2–Zeranol). Experiment II, 50 animals were evaluated for: (a) IP (like Experiment-I), and (b) male class (steers vs. bulls). In Experiment-I, SS bulls had greater growth rate, carcass yield, and yield of high-valued boneless lean cuts than MS bulls, while decreasing (
p < 0.05) time to harvest. Steaks from SS-bulls on TBA/E2–Zeranol IP were more (
p = 0.05) tender than SS/Zeranol–Zeranol counterparts. Experiment-II bulls had greater growth than steers, but decreased (
p < 0.05) carcass quality aspects. Zeranol–Zeranol increased (
p < 0.01) meat tenderness of steers. Interactions (
p < 0.05) affected cutability (Experiment-II) and meat sensory traits (Experiment-I/II). The SS improved growth, carcass yield, and shortened days until harvest of bulls, while TBA/E2–Zeranol IP positively affected tenderness in bull meat only. Castration improved carcass quality while the implant effects on cutability and tenderness were male-class dependent.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
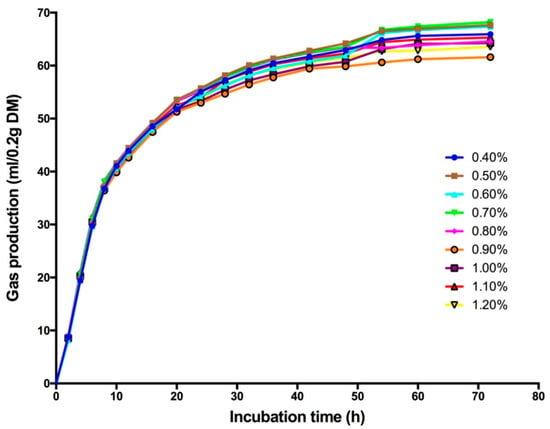
Effect of High Sulfur Diet on Rumen Fermentation, Microflora, and Epithelial Barrier Function in Steers
by
Hao Wu, Yan Li, Qingxiang Meng and Zhenming Zhou
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3415
Abstract
These experiments were conducted to evaluate the effect of excessive sulfur on rumen fermentation, microflora, and epithelial barrier function in steers through in vitro gas production and animal feeding experiments. Nine and four levels of sulfur addition were evaluated in in vitro ruminal
[...] Read more.
These experiments were conducted to evaluate the effect of excessive sulfur on rumen fermentation, microflora, and epithelial barrier function in steers through in vitro gas production and animal feeding experiments. Nine and four levels of sulfur addition were evaluated in in vitro ruminal fermentation and animal feeding experiment, respectively. The results showed that increasing the level of sulfur in substrates decreased the total gas and methane production linearly, while increasing the production of hydrogen sulfide gas (
p < 0.01). Volatile fatty acid concentrations, especially that of butyric acid, were increased by extra sulfur (
p < 0.01). Sulfur content in the diet had no significant effect (
p > 0.05) on most of the rumen microbes, except for
Desulfovibrio, one of the major sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in the rumen, whose population increased by adding extra sulfur (
p < 0.001). The changes in the morphology of rumen epithelium and thickening of the total epithelial layer were mainly attributed to the increase in the acanthosis cell layer and stratum basale (
p < 0.05). Further, the relative expressions of two tight junction protein regulating genes, CLDN-1 and TJP1, were reduced (
p < 0.05). Excessive sulfur in the diet can change the type of rumen fermentation, sulfate metabolism and SRB population, and the rumen epithelial barrier function. The results of this study demonstrated that sulfur can be used as a methane inhibitor with the mechanism that SRB competitively used protons to produce hydrogen sulfide. However, a higher level of sulfur in the diet could increase the inflammatory reaction of the rumen epithelium which may affect nutrient absorption.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Supplement Based on Fermented Milk Permeate for Feeding Newborn Calves: Influence on Blood, Growth Performance, and Faecal Parameters, including Microbiota, Volatile Compounds, and Fatty and Organic Acid Profiles
by
Laurynas Vadopalas, Egle Zokaityte, Paulina Zavistanaviciute, Romas Gruzauskas, Vytaute Starkute, Ernestas Mockus, Jolita Klementaviciute, Modestas Ruzauskas, Vita Lele, Darius Cernauskas, Dovile Klupsaite, Agila Dauksiene, Antanas Sederevicius, Sarunas Badaras and Elena Bartkiene
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3609
Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of a feed supplement, namely milk permeate (MP) fermented with
Lactobacillus uvarum LUHS245, on the newborn calves’ growth performance and blood and faecal parameters, including microbiota and volatile compound and fatty acid profiles.
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of a feed supplement, namely milk permeate (MP) fermented with
Lactobacillus uvarum LUHS245, on the newborn calves’ growth performance and blood and faecal parameters, including microbiota and volatile compound and fatty acid profiles. Ten female Holstein calves in the control group (CON group) were fed with a standard milk replacer diet and colostrum only, from day 2 to 14 of life, while 10 calves of the treated group (MP group) were fed with the same diet supplemented with 50 mL of the fermented MP. After 14 days, there were no significant differences between the groups in blood parameters, growth performance, or faecal pH. There was a significantly higher percentage of live lactic acid bacteria (by 17.02%), a lower percentage of enterobacteria (by 10.38%), a higher overall number of probiotic bacteria, a 1.7-fold higher species variety, and a higher content of dry matter in the faeces of the MP group (
p < 0.05). The fatty acid and volatile compound profiles differed significantly between the groups. The results suggest that supplementing calves’ feed with fermented milk permeate has a positive effect on certain health parameters but not on blood parameters or growth performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
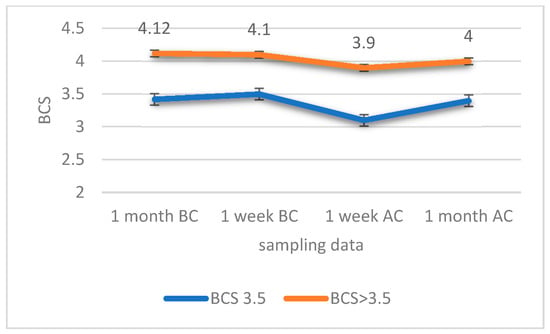
Effects of Calving Body Condition Score on Blood Acid–Base Balance of Primiparous Holstein-Friesian Dairy Cows in a Commercial Dairy Farm: A Case Study
by
Rodrigo Muiño, Joaquín Hernández, José L. Benedito and Cristina Castillo
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3898
Abstract
The study was carried out on 27 healthy primiparous Holstein heifers (620 ± 50 kg) kept in a commercial dairy herd. The animals were divided into two groups taking into account the body condition score (BCS) index: BCS < 3.5,
n = 12;
[...] Read more.
The study was carried out on 27 healthy primiparous Holstein heifers (620 ± 50 kg) kept in a commercial dairy herd. The animals were divided into two groups taking into account the body condition score (BCS) index: BCS < 3.5,
n = 12; BCS > 3.5
n = 15. The study period started one month before calving (BC), and ran until one month after calving (AC). Venous blood samples were collected 1 month and 1 week BC, and 1 week and 1 month AC. This study had two objectives: (i) to assess whether a higher or lower BCS affected total milk production and its quality; (ii) to assess changes in the internal fluid (venous pH; partial pressure of CO
2, ppCO
2; bicarbonate; total CO
2, TCO
2; base excess, BE; electrolytes Na
+, K
+, Cl
−; and anion gap, AG) that occur during this phase depending on the BCS. We can conclude that the BCS at calving does not affect the productive status during lactation, both in terms of the quantity and quality of milk produced. The excess of crude protein (CP) added through the ration in the lactation phase can trigger a tendency to an alkalotic state, in this case compensated by respiratory buffering mechanisms, as reflected by the TCO
2. The changes in electrolytes are a reflection of the movement of free water for milk production, where a balance between measurable anions and cations is observed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Strategies for Feeding Unweaned Dairy Beef Cattle to Improve Their Health
by
Maria Devant and Sonia Marti
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 4747
Abstract
In order to answer the question of whether nutritional interventions may help to reduce the incidence of respiratory disease in dairy beef calves at arrival, the present review is divided in three sections. In the first section, the nutrition of calves previous to
[...] Read more.
In order to answer the question of whether nutritional interventions may help to reduce the incidence of respiratory disease in dairy beef calves at arrival, the present review is divided in three sections. In the first section, the nutrition of calves previous to the arrival from the origin farm to the final rearing farm is reviewed. In the second section, the possible consequences of this previous nutrition on gut health and immune status upon arrival to the rearing farm are described. The main consequences of previous nutrition and management that these unweaned calves suffer at arrival are the negative energy balance, the increased intestinal permeability, the oxidative stress, the anemia, and the recovery feed consumption. Finally, in the third section, some considerations to advance in future nutritional strategies are suggested, which are focused on the prevention of the negative consequences of previous nutrition and the recovery of the gut and immune status. Moreover, additional suggestions are formulated that will be also helpful to reduce the incidence of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) that are not directly linked to nutrition like having a control golden standard in the studies or designing risk categories in order to classify calves as suitable or not to be transported.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
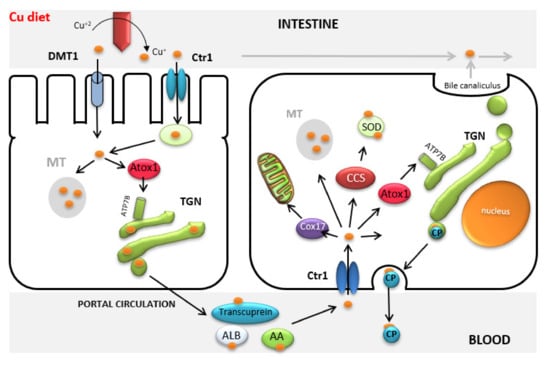
Copper Supplementation, A Challenge in Cattle
by
Marta López-Alonso and Marta Miranda
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 6766
Abstract
Ensuring adequate copper supplementation in ruminants is a challenging task due to the complexity of copper metabolism in these animals. The three-way interaction between copper, molybdenum and sulphur (Cu-Mo-S) in the rumen makes ruminants, particularly cattle, very susceptible to suffering from secondary copper
[...] Read more.
Ensuring adequate copper supplementation in ruminants is a challenging task due to the complexity of copper metabolism in these animals. The three-way interaction between copper, molybdenum and sulphur (Cu-Mo-S) in the rumen makes ruminants, particularly cattle, very susceptible to suffering from secondary copper deficiency. Paradoxically, excessive copper storage in the liver to prevent deficiency becomes a hazard when ruminants are fed copper-supplemented diets even slightly above requirements. While cattle were traditionally thought to be relatively tolerant of copper accumulation, and reports of copper poisoning were until recently somewhat rare, in recent years an increased number of episodes/outbreaks of copper toxicity in cattle, particularly in dairy cattle, have been reported worldwide. The growing number of lethal cases reported seems to indicate that copper intoxication is spreading silently in dairy herds, urging the development of strategies to monitor herd copper status and improve farmers’ awareness of copper toxicity. In fact, monitoring studies carried out on numerous samples collected from culled animals in slaughterhouses and/or diagnostic laboratories have demonstrated that large numbers of animals have hepatic copper concentrations well above adequate levels in many different countries. These trends are undoubtedly due to copper supplementation aimed at preventing copper deficiency, as dietary copper intake from pasture alone is unlikely to cause such high levels of accumulation in liver tissue. The reasons behind the copper overfeeding in cattle are related both to a poor understanding of copper metabolism and the theory of “if adding a little produces a response, then adding a lot will produce a better response”. Contrary to most trace elements, copper in ruminants has narrow margins of safety, which must also be formulated considering the concentrations of copper antagonists in the diet. This review paper aims to provide nutritionists/veterinary practitioners with the key points about copper metabolism in cattle to guarantee an adequate copper supply while preventing excessive hepatic copper loading, which requires à la carte copper supplementation for each herd.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
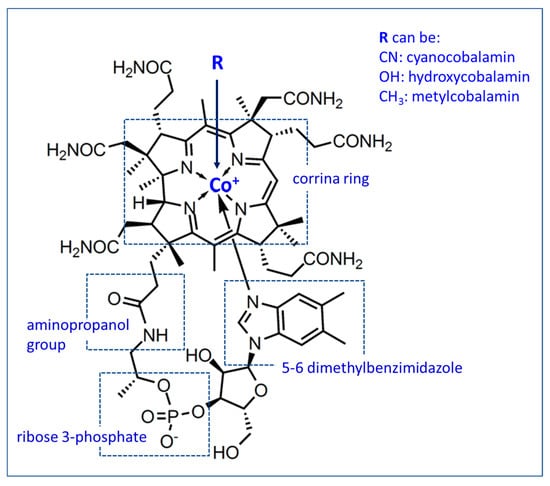
Relationship between Vitamin B12 and Cobalt Metabolism in Domestic Ruminant: An Update
by
Jose-Ramiro González-Montaña, Francisco Escalera-Valente, Angel J. Alonso, Juan M. Lomillos, Roberto Robles and Marta E. Alonso
Cited by 83 | Viewed by 13222
Abstract
Cobalt, as a trace element, is essential for rumen microorganisms for the formation of vitamin B12. In the metabolism of mammals, vitamin B12 is an essential part of two enzymatic systems involved in multiple metabolic reactions, such as in the metabolism of carbohydrates,
[...] Read more.
Cobalt, as a trace element, is essential for rumen microorganisms for the formation of vitamin B12. In the metabolism of mammals, vitamin B12 is an essential part of two enzymatic systems involved in multiple metabolic reactions, such as in the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, some amino acids and DNA. Adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin are coenzymes of methylmalonyl coenzyme A (CoA) mutase and methionine synthetase and are essential for obtaining energy through ruminal metabolism. Signs of cobalt deficiency range from hyporexia, reduced growth and weight loss to liver steatosis, anemia, impaired immune function, impaired reproductive function and even death. Cobalt status in ruminant animals can be assessed by direct measurement of blood or tissue concentrations of cobalt or vitamin B12, as well as the level of methylmalonic acid, homocysteine or transcobalamin in blood; methylmalonic acid in urine; some variables hematological; food consumption or growth of animals. In general, it is assumed that the requirement for cobalt (Co) is expressed around 0.11 ppm (mg/kg) in the dry matter (DM) diet; current recommendations seem to advise increasing Co supplementation and placing it around 0.20 mg Co/kg DM. Although there is no unanimous criterion about milk production, fattening or reproductive rates in response to increased supplementation with Co, in some investigations, when the total Co of the diet was approximately 1 to 1.3 ppm (mg/kg), maximum responses were observed in the milk production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Impact of Nutrients on the Hoof Health in Cattle
by
Lucie Langova, Ivana Novotna, Petra Nemcova, Miroslav Machacek, Zdenek Havlicek, Monika Zemanova and Vladimir Chrast
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 9700
Abstract
Lameness is currently one of the most important and economically demanding diseases in cattle. It is manifested in a change in locomotion that is associated with lesions, especially the pelvic limbs. The disease of the hoof is painful, affecting the welfare of dairy
[...] Read more.
Lameness is currently one of the most important and economically demanding diseases in cattle. It is manifested in a change in locomotion that is associated with lesions, especially the pelvic limbs. The disease of the hoof is painful, affecting the welfare of dairy cows. Important factors that influence the health of the limbs include nutrition, animal hygiene, stable technology, and genetic and breeding predispositions. Nutrition is one of the basic preventive factors affecting the quality and growth of the hoof horn, and the associated prevalence of hoof disease. The strength and structure of the hoof horn are affected by the composition of the feed ration (amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and toxic substances contaminating the feed ration, or arising in the feed ration as metabolites of fungi).
Full article
Open AccessReview
Targeting the Hindgut to Improve Health and Performance in Cattle
by
M. Victoria Sanz-Fernandez, Jean-Baptiste Daniel, Dave J. Seymour, Sara K. Kvidera, Zeno Bester, John Doelman and Javier Martín-Tereso
Cited by 37 | Viewed by 5714
Abstract
An adequate gastrointestinal barrier function is essential to preserve animal health and well-being. Suboptimal gut health results in the translocation of contents from the gastrointestinal lumen across the epithelium, inducing local and systemic inflammatory responses. Inflammation is characterized by high energetic and nutrient
[...] Read more.
An adequate gastrointestinal barrier function is essential to preserve animal health and well-being. Suboptimal gut health results in the translocation of contents from the gastrointestinal lumen across the epithelium, inducing local and systemic inflammatory responses. Inflammation is characterized by high energetic and nutrient requirements, which diverts resources away from production. Further, barrier function defects and inflammation have been both associated with several metabolic diseases in dairy cattle and liver abscesses in feedlots. The gastrointestinal tract is sensitive to several factors intrinsic to the productive cycles of dairy and beef cattle. Among them, high grain diets, commonly fed to support lactation and growth, are potentially detrimental for rumen health due to their increased fermentability, representing the main risk factor for the development of acidosis. Furthermore, the increase in dietary starch associated with such rations frequently results in an increase in the bypass fraction reaching distal sections of the intestine. The effects of high grain diets in the hindgut are comparable to those in the rumen and, thus, hindgut acidosis likely plays a role in grain overload syndrome. However, the relative contribution of the hindgut to this syndrome remains unknown. Nutritional strategies designed to support hindgut health might represent an opportunity to sustain health and performance in bovines.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
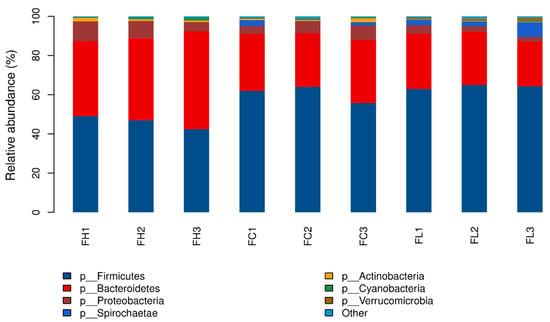
The Effects of Different Concentrate-to-Forage Ratio Diets on Rumen Bacterial Microbiota and the Structures of Holstein Cows during the Feeding Cycle
by
Lijun Wang, Yang Li, Yonggen Zhang and Lihua Wang
Cited by 37 | Viewed by 3718
Abstract
The objectives of this study were to investigate the ruminal bacterial changes during the feeding cycle. Six ruminally cannulated Holstein cows were used in this experiment. The high-forage (HF) and high-concentrate (HC) diets contained 70% and 30% dietary forage, respectively. Dairy cows were
[...] Read more.
The objectives of this study were to investigate the ruminal bacterial changes during the feeding cycle. Six ruminally cannulated Holstein cows were used in this experiment. The high-forage (HF) and high-concentrate (HC) diets contained 70% and 30% dietary forage, respectively. Dairy cows were fed their respective diets for at least 28 days, then samples were collected at 0, 2, 4, 9, 12, 16 and 20 h post-feeding. The results showed that pH, the concentration of (total volatile fatty acids) TVFAs and the percentages of acetate, propionate and butyrate were significantly affected by diet and time interactions. The diversity of rumen microbiota in HF dietary treatments was significantly higher than that in the HC dietary treatments. ACE (Abundance-based Coverage Estimator) and Chao 1 indices peak at 12 h post-feeding and then decline over the next 8 h. The rumen microbiota was mainly composed of the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria without considering the diet and time. The Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) functional profile prediction indicated that the carbohydrate metabolism was different at 9, 12 and 20 h post-feeding time, which revealed that the soluble carbohydrates were enough for microbial fermentation shortly after feeding. This research gave a further explanation of the interactions among rumen microorganisms, which could further help manipulate the rumen metabolism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
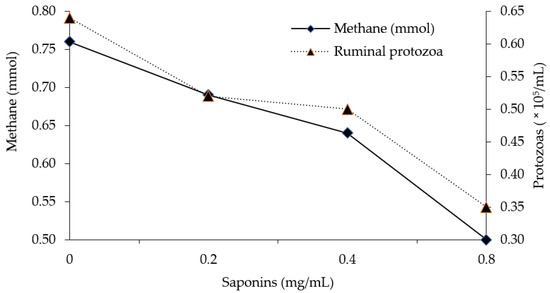
Mitigation of Rumen Methane Emissions with Foliage and Pods of Tropical Trees
by
Jorge Canul-Solis, María Campos-Navarrete, Angel Piñeiro-Vázquez, Fernando Casanova-Lugo, Marcos Barros-Rodríguez, Alfonso Chay-Canul, José Cárdenas-Medina and Luis Castillo-Sánchez
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 4980
Abstract
Methane produced by enteric fermentation contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere. Methane is one of the GHG resulting from anthropogenic activities with the greater global warming contribution. Ruminant production systems contribute between 18% and 33% of methane emissions.
[...] Read more.
Methane produced by enteric fermentation contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere. Methane is one of the GHG resulting from anthropogenic activities with the greater global warming contribution. Ruminant production systems contribute between 18% and 33% of methane emissions. Due to this, there has been growing interest in finding feed alternatives which may help to mitigate methane production in the rumen. The presence of a vast range of secondary metabolites in tropical trees (coumarins, phenols, tannins, and saponins, among others) may be a valuable alternative to manipulate rumen fermentation and partially defaunate the rumen, and thus reduce enteric methane production. Recent reports suggest that it is possible to decrease methane emissions in sheep by up to 27% by feeding them saponins from the tea leaves of
Camellia sinensis; partial defaunation (54%) of the rumen has been achieved using saponins from
Sapindus saponaria. The aim of this review was to collect, analyze, and interpret scientific information on the potential of tropical trees and their secondary metabolites to mitigate methane emissions from ruminants.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
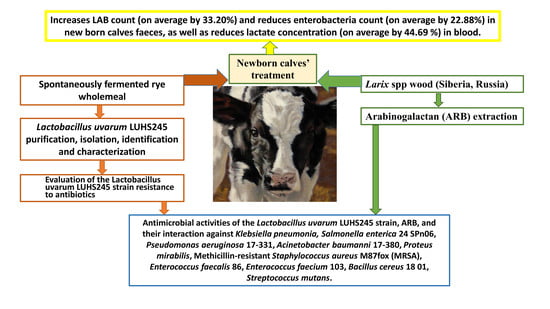
Separate and Synergic Effects of Lactobacillus uvarum LUHSS245 and Arabinogalactan on the In Vitro Antimicrobial Properties as Well as on the Fecal and Metabolic Profile of Newborn Calves
by
Paulina Zavistanaviciute, Vita Lele, Ramūnas Antanaitis, Mindaugas Televičius, Modestas Ruzauskas, Qendrim Zebeli and Elena Bartkiene
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 4050
Abstract
In this study, arabinogalactan (ARB) and
Lactobacillus uvarum LUHS245 antimicrobial properties against pathogenic bacteria (
Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 17-331,
Acinetobacter baumanni 17-380,
Proteus mirabilis, MRSA M87fox,
Enterococcus faecalis 86,
Enterococcus faecium 103,
Bacillus cereus 18 01, and
Streptococcus mutans) and
[...] Read more.
In this study, arabinogalactan (ARB) and
Lactobacillus uvarum LUHS245 antimicrobial properties against pathogenic bacteria (
Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 17-331,
Acinetobacter baumanni 17-380,
Proteus mirabilis, MRSA M87fox,
Enterococcus faecalis 86,
Enterococcus faecium 103,
Bacillus cereus 18 01, and
Streptococcus mutans) and resistance to antibiotics were evaluated and the role of their supplementation on the main metabolic and fecal variables of newborn calves was established. The animal trial involved 48 Holstein female calves randomly allocated in four homogeneous groups of 12 animals each, on the basis of body weight in the second day of life. Calves were fed with a standard milk replacer diet from the second day of life until 14th day, either unsupplemented or supplemented with 50 mL of LUHS245 (≥7.5 log
10 CFU mL
−1), 30 g of ARB, or with both (50 mL of LUHS245 and 30 g ARB). In vitro data showed that the LUHS245 inhibited the growth of
Salmonella enterica and
Bacillus cereus (inhibition zones 13.0 and 21.3 mm, respectively). Supplementation of LUHS245 and ARB either alone or together, lowered total bacterial count in the feces and reduced lactate and serum alanine aminotransferase concentrations in blood. This study showed that LUHS245 supplementation alone or together with ARB seemed to have some positive influence on certain health parameters in newborn calves. Further research with larger cohorts of animals is warranted to validate the beneficial effects of the tested supplements.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Extruded Linseed and Soybean Dietary Supplementation on Lactation Performance, First-Service Conception Rate, and Mastitis Incidence in Holstein Dairy Cows
by
Ahmed Dawod, Hamada Ahmed, Reham Abou-Elkhair, Hamed T. Elbaz, Ayman E. Taha, Ayman A. Swelum, Ibrahim A. Alhidary, Islam M. Saadeldin, Muath Q. Al-Ghadi, Hani A. Ba-Awadh, Elsayed O. S. Hussein and Adham A. Al-Sagheer
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3681
Abstract
This study quantifies the effects of extruded linseed and soybean (ELS) dietary supplementation on milk yield, composition, and fatty acid profiles, as well as first-service conception rate in Holstein dairy cows. Seventy-eight open Holstein dairy cows were divided into two groups: (1) a
[...] Read more.
This study quantifies the effects of extruded linseed and soybean (ELS) dietary supplementation on milk yield, composition, and fatty acid profiles, as well as first-service conception rate in Holstein dairy cows. Seventy-eight open Holstein dairy cows were divided into two groups: (1) a control, which received a basal diet; and (2) a test group, which received a basal diet supplemented with the ELS (650 g/kg of extruded linseed and 150 g/kg of extruded soybean) at a rate of 100 g/kg. In the ELS group, milk yield per day and solid not fat (SNF) yield increased by 3.26% and 0.88%, respectively, in relation to the control. Percentage milk fat decreased significantly by 1.4% in the ELS group when compared with the control. The ELS supplement resulted in a decrease in saturated fatty acids (SFAs) and an increase in monounsaturated (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in milk. In conclusion, the supplementation of dairy cow feed with 100 g/kg of ELS increases milk yield and milk unsaturated fatty acids (especially MUFAs and PUFAs). ELS supplementation also causes a decrease in percentage fat and SFA levels but does not affect the first-service conception rate or the incidence rate of mastitis.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
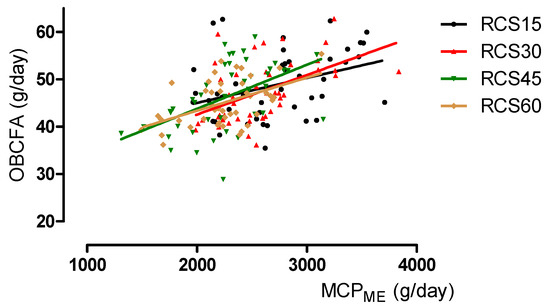
Relationship of Milk Odd- and Branched-Chain Fatty Acids with Urine Parameters and Ruminal Microbial Protein Synthesis in Dairy Cows Fed Different Proportions of Maize Silage and Red Clover Silage
by
Edwin Westreicher-Kristen, Joaquín Castro-Montoya, Mario Hasler and Andreas Susenbeth
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3958
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship of milk odd- and branched-chain fatty acids (OBCFA) with urinary purine derivates and estimated ruminal microbial crude protein (MCP) synthesis. Forty-four lactating Holstein cows were used in a 4 × 4 Latin square
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship of milk odd- and branched-chain fatty acids (OBCFA) with urinary purine derivates and estimated ruminal microbial crude protein (MCP) synthesis. Forty-four lactating Holstein cows were used in a 4 × 4 Latin square design with 21-day periods comprised of a 13-day adaptation phase to diet followed by an 8-day sampling phase. Differences in estimated MCP yield and milk OBCFA composition were found by feeding total mixed rations containing forage (maize silage, MS; red clover silage, RCS) and concentrates (0.75:0.25) with targeted proportions of RCS to MS of 0.15:0.60, 0.30:0.45, 0.45:0.30, and 0.60:0.15 on a dry matter basis. The MCP was estimated from the total urinary purine derivate (PD) excretion (MCPPD) and intakes of metabolizable energy (MCPME) or digestible organic matter (MCPdOM). The Pearson correlations of individual OBCFA with urinary parameters (uric acid, allantoin, PD and nitrogen) were generally weak (
r = −0.37 to 0.55). Yields of individual OBCFA correlated positively with MCPME and MCPdOM (
r = 0.21 to 0.55). The prediction of urinary PD concentration was moderate (R
2 = 0.64) when including the proportion of iso-C17:0. The prediction of total PD excretion was low (R
2 = 0.21) with yields of iso-C15:0, anteiso-C17:0, and iso-C16:0. The prediction of MCPPD was high (R
2 = 0.99) when including the iso-C16:0 and cis-9 C17:1 concentrations, while those of MCPME and MCPdOM were low (R
2 = 0.37 and 0.36, respectively) when including yields of iso-C15:0, cis-9 C17:1, and iso-C18:0. The correlations and regression analyses demonstrate that the estimated MCP synthesis and urinary PD excretion can be only moderately predicted by yields and concentrations of individual or total OBCFA in cow’s milk. However, milk OBCFA can still be seen as a promising, non-invasive method for predicting rumen function and microbial protein supply in dairy cows because MCP flow was not directly measured in this study but instead indirectly estimated probably comprising considerable deviations of the assumed values from the true ones.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
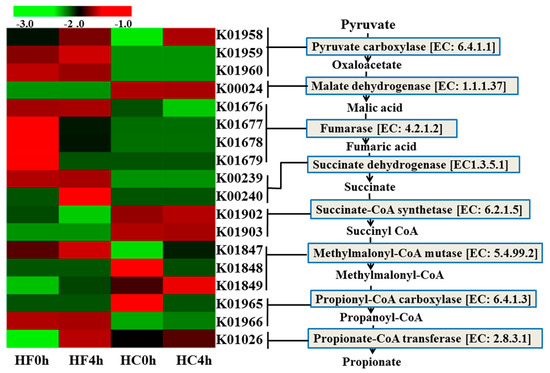
Effects of High Forage/Concentrate Diet on Volatile Fatty Acid Production and the Microorganisms Involved in VFA Production in Cow Rumen
by
Lijun Wang, Guangning Zhang, Yang Li and Yonggen Zhang
Cited by 118 | Viewed by 8947
Abstract
The objectives of this study were to investigate the difference in the mechanism of VFAs production combined with macrogenome technology under different forage-to-concentrate ratios and sampling times. Six ruminally cannulated Holstein cows were used in a randomized complete block design. The high forage
[...] Read more.
The objectives of this study were to investigate the difference in the mechanism of VFAs production combined with macrogenome technology under different forage-to-concentrate ratios and sampling times. Six ruminally cannulated Holstein cows were used in a randomized complete block design. The high forage (HF) and high concentrate (HC) diets contained 70 and 35% dietary forage, respectively. The results showed that pH was affected by sampling time, at 4 h after feeding had lower value. Excepted for acetate, the VFAs was increased with forage decreased. Propionate formation via the succinic pathway, in which succinate CoA synthetase (EC 6.2.1.5) and propionyl CoA carboxylase (EC 2.8.3.1) were key enzymes, and significantly higher in HC treatment than in HF treatment,
Selenomonas,
Ruminobacter,
Prevotella, and
Clostridium were the main microorganism that encodes these key enzymes. Butyrate formation via the succinic pathway, in which phosphate butyryltransferase (EC 2.3.1.19), butyrate kinase (EC 2.7.2.7) and pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.7.1) are the important enzymes,
Prevotella and
Bacteroides played important role in encodes these key enzymes. This research gave a further explanation on the metabolic pathways of VFAs, and microorganisms involved in VFAs production under different F:C ration, which could further reveal integrative information of rumen function.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Adding Various Silage Additives to Whole Corn Crops at Ensiling on Performance, Rumen Fermentation, and Serum Physiological Characteristics of Growing-Finishing Cattle
by
Yawei Zhang, Xiangwei Zhao, Wanbao Chen, Zhenming Zhou, Qingxiang Meng and Hao Wu
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4073
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effect of applying various silage additives to whole corn crops at ensiling on growth performance, rumen fermentation, and blood physiology in growing–finishing bulls. Sixty Simmental × Yellow Cattle crossbred bulls were blocked by initial body weight (BW;
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to investigate the effect of applying various silage additives to whole corn crops at ensiling on growth performance, rumen fermentation, and blood physiology in growing–finishing bulls. Sixty Simmental × Yellow Cattle crossbred bulls were blocked by initial body weight (BW; 324.0 ± 5.4 kg) into 15 blocks. Animals in each block were randomly assigned to one of four diets formulated based on the following corn silage: control (CON), inoculated with complex lactic acid bacteria (CLB), ensilaged with mixed organic acid salts (MS), and ensilaged with CLB and MS (CLBMS). The feeding experiment lasted over 155 days, with an additional 7 days for adaptation. The results showed that bulls fed CLB-inoculated silage had greater (
p < 0.05) daily dry matter intake than the other groups. The experimental treatment had no significant effect on average daily gain (
p = 0.33) and feed-to-gain ratio (
p = 0.13), although bulls fed CLB-inoculated silage had a larger numeric average daily gain. All additive-treated silage increased ruminal NH
3–N content (
p < 0.05) and reduced the acetate-to-propionate ratio (
p < 0.05) of bulls compared with the control group. Bulls fed CLB-inoculated silage had a lower ruminal pH value (
p < 0.05) than that of the other groups. Compared with the control group, bulls fed CLB-inoculated silage had greater blood cholesterol, albumin, and urea nitrogen (
p < 0.05). Blood physiological responses were similar in bulls fed MS-treated and control silage, whereas those in cattle fed CLBMS-treated silage were between bulls fed CLB- and MS-treated silages and more similar to the former. Taking animal performance and cost effectiveness into consideration, the application of CLB alone to whole corn crops at ensiling appears to be a better choice compared with the application of either MS alone or both of them together.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Variations in Fecal Bacterial Community and Fermentation Profile of Holstein Steers in Response to Three Stepwise Density Diets
by
Qinghua Qiu, Yangxiang Zhu, Xinjun Qiu, Chaoyu Gao, Jingjing Wang, Haibo Wang, Yang He, Muhammad Aziz ur Rahman, Binghai Cao and Huawei Su
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 4126
Abstract
The objective of this study was to track the dynamic variations in fecal bacterial composition and fermentation profile of finishing steers in response to three stepwise diets varied in energy and protein density. A total of 18 Holstein steers were divided into three
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to track the dynamic variations in fecal bacterial composition and fermentation profile of finishing steers in response to three stepwise diets varied in energy and protein density. A total of 18 Holstein steers were divided into three groups in such a way that each group contained six animals and received one of three stepwise dietary treatments. Dietary treatments were C = standard energy and protein diet, H = high energy and protein diet, and L = low energy and protein diet. Animals were fattened for 11 months with a three-phase fattening strategy. Fecal samples were collected to evaluate the dynamics of fecal fermentation and bacterial composition in response to dietary treatments and fattening phases using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Fecal acetate, propionate, and butyrate increased with increasing density of diet and as the fattening phase continued. The relative abundances of
Firmicutes and
Bacteroidetes dominated and showed 56.19% and 33.58%, respectively. Higher dietary density decreased the fecal bacterial diversity,
Firmicutes to
Bacteroidetes ratio, and the relative abundances of
Ruminococcaceae_UCG-005,
Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, and
Bacteroides, whereas higher dietary density increased the abundance of
Prevotella_9. Our results indicated that both fecal fermentation profile and bacterial composition share a time-dependent variation in response to different dietary densities. This knowledge highlights that both diet and fattening phase impact fecal fermentation profile and bacterial composition, and may provide insight into strategies to reduce fecal contamination from the origin by optimizing diet and fattening time.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Dietary Alkyl Polyglycoside Supplementation on Lactation Performance, Blood Parameters and Nutrient Digestibility in Dairy Cows
by
Xiaoli Zhang, Chunyu Jiang, Qinghua Gao, Duanqin Wu, Shaoxun Tang, Zhiliang Tan and Xuefeng Han
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2936
Abstract
This study evaluated the effects of alkyl polyglycoside (APG), which is a non-ionic surfactant, on lactation performance, nutrient digestibility and blood metabolites in dairy cows. Twenty dairy cows were randomly divided into four groups and fed a basal diet that included pelleted concentrate,
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the effects of alkyl polyglycoside (APG), which is a non-ionic surfactant, on lactation performance, nutrient digestibility and blood metabolites in dairy cows. Twenty dairy cows were randomly divided into four groups and fed a basal diet that included pelleted concentrate, distillers grains, and fresh limpograss. The four treatments included 0, 5.5, 11 and 22 mL APG per kg of pelleted concentrate on a dry matter basis; treatments were defined as APG0, APG5.5, APG11, and APG22, respectively. Dry matter intake was not affected by APG supplementation. There was an increase in milk yield (from 13.96 to 16.71 kg/day) and increases in milk fat (quadratic,
p = 0.04), protein (quadratic,
p = 0.10), and lactose concentrations (linear,
p = 0.07) with increasing APG supplementation. In addition, APG supplementation increased (
p ≤ 0.03) the milk fat, protein, solid non-fat, and total solid yields, while the lactose yield increased (linear,
p = 0.01) as the APG level increased. Dietary APG supplementation had no effect on nutrient digestibility and blood metabolites. It was concluded that the addition of APG at doses up to 22 mL/kg of pelleted concentrate had positive effects on the milk composition in dairy cows.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Determination of Essential and Toxic Elements in Cattle Blood: Serum vs Plasma
by
Diego Luna, Marta López-Alonso, Yolanda Cedeño, Lucas Rigueira, Víctor Pereira and Marta Miranda
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4433
Abstract
This study was designed to evaluate the influence of type of blood sample (serum or plasma) on essential and toxic element analysis in cattle. Paired plasma and serum samples (
n = 20) were acid digested, and the concentrations of As, B, Ba,
[...] Read more.
This study was designed to evaluate the influence of type of blood sample (serum or plasma) on essential and toxic element analysis in cattle. Paired plasma and serum samples (
n = 20) were acid digested, and the concentrations of As, B, Ba, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Li, Mg, Mn. Mo, Ni, P, Pb, Sb, Se, Sr and Zn were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The study findings indicate that plasma and serum samples appear suitable and interchangeable for the determination of most of the essential and toxic elements in blood in cattle. The only exceptions are Cu and Se, the concentrations of which were significantly lower (40.9 and 29.9% respectively) in serum than in plasma. Some of the Cu in blood samples from bovine ruminants is known to be sequestered during clotting. However, further research on Se in ruminants and other animal species is warranted. Finally, the significantly higher Mn (9.9%) concentrations in serum than in plasma may have been caused by haemolysis of some samples. Special attention should be paid to preventing haemolysis of samples during collection and processing, in order to prevent overestimation of elements present at high concentrations inside erythrocytes (i.e., Fe, Mn and Zn).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
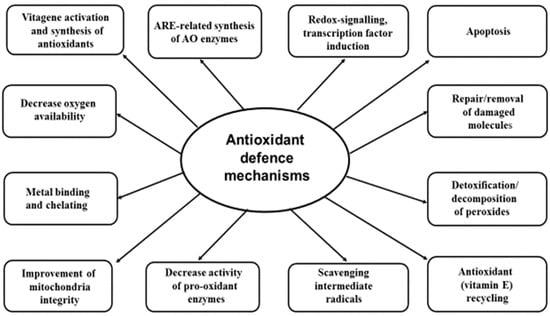
Revisiting Oxidative Stress and the Use of Organic Selenium in Dairy Cow Nutrition
by
Peter F. Surai, Ivan I. Kochish, Vladimir I. Fisinin and Darren T. Juniper
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 9351
Abstract
In commercial animals production, productive stress can negatively impact health status and subsequent productive and reproductive performance. A great body of evidence has demonstrated that as a consequence of productive stress, an overproduction of free radicals, disturbance of redox balance/signaling, and oxidative stress
[...] Read more.
In commercial animals production, productive stress can negatively impact health status and subsequent productive and reproductive performance. A great body of evidence has demonstrated that as a consequence of productive stress, an overproduction of free radicals, disturbance of redox balance/signaling, and oxidative stress were observed. There is a range of antioxidants that can be supplied with animal feed to help build and maintain the antioxidant defense system of the body responsible for prevention of the damaging effects of free radicals and the toxic products of their metabolism. Among feed-derived antioxidants, selenium (Se) was shown to have a special place as an essential part of 25 selenoproteins identified in animals. There is a comprehensive body of research in monogastric species that clearly shows that Se bioavailability within the diet is very much dependent on the form of the element used. Organic Se, in the form of selenomethionine (SeMet), has been reported to be a much more effective Se source when compared with mineral forms such as sodium selenite or selenate. It has been proposed that one of the main advantages of organic Se in pig and poultry nutrition is the non-specific incorporation of SeMet into general body proteins, thus forming an endogenous Se reserve that can be utilized during periods of stress for additional synthesis of selenoproteins. Responses in ruminant species to supplementary Se tend to be much more variable than those reported in monogastric species, and much of this variability may be a consequence of the different fates of Se forms in the rumen following ingestion. It is likely that the reducing conditions found in the rumen are responsible for the markedly lower assimilation of inorganic forms of Se, thus predisposing selenite-fed animals to potential Se inadequacy that may in turn compromise animal health and production. A growing body of evidence demonstrates that organic Se has a number of benefits, particularly in dairy and beef animals; these include improved Se and antioxidant status and better Se transfer via the placenta, colostrum, and milk to the newborn. However, there is a paucity in the data concerning molecular mechanisms of SeMet assimilation, metabolism and selenoprotein synthesis regulation in ruminant animals, and as such, further investigation is required.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Grazing on the Behaviour, Oxidative and Immune Status, and Production of Organic Dairy Cows
by
Antonino Di Grigoli, Adriana Di Trana, Marco Alabiso, Giuseppe Maniaci, Daniela Giorgio and Adriana Bonanno
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 3872
Abstract
This study compared the effects of a short daily grazing time with those of permanent free-stall housing on the behaviour, oxidative status, immune response, and milk production of organically reared cows. During a 63-day period, two homogeneous groups of eight lactating Brown cows
[...] Read more.
This study compared the effects of a short daily grazing time with those of permanent free-stall housing on the behaviour, oxidative status, immune response, and milk production of organically reared cows. During a 63-day period, two homogeneous groups of eight lactating Brown cows were allocated to either housing (H) in a free-stall building for 24 h/day. Feeding was based on a total mixed ration or grazing (G) on barley grass for 5 h/day, and housing in a free-stall structure with feeding was based on the same total mixed ration offered to the H group. With regard to behaviour, H cows spent more time idling, walking, drinking, and self-grooming, whereas G cows showed a greater intent to eat and interact socially. Moreover, G cows exhibited slightly higher reactive oxygen metabolites and similar biological antioxidant potential concentrations than the H group, which indicates that short grazing resulted in an almost negligible increase in oxidative stress and an unchanged antioxidant capacity. Skin tests, performed by injecting phytohemoagglutinin intradermally, indicated that G cows had thicker skin than H cows at the end of the trial, an index of a better cell-mediated immune response. Grazing did not affect milk yield but improved milk quality in terms of an increase in fat and a reduction in urea content, somatic cell count, and total microbial count. Milk from G cows was richer in saturated fatty acids, likely because of the contribution of palmitic acid present in the grazed barley grass, and also showed higher contents of some healthy fatty acids, such as rumenic acid and α-linolenic acid, and a lower omega-6/omega-3 ratio. These results show that including a short grazing time in the diets of organic dairy cows does not have negative consequences for milk production and contributes to improved milk quality as well as to a more efficient immune response in the cows.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Feeding Glycerin on Ruminal Environment and In Situ Degradability of Feedstuffs in Young Bulls
by
Josefa Madrid, Silvia Martínez, Carmen Villodre, Miguel J. López, Juan Alcázar, Juan Orengo, Guillermo Ramis and Fuensanta Hernández
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3785
Abstract
This work studied the effect of feeding glycerin in bulls that were fed high levels of concentrate on the ruminal environment and in situ degradability of feedstuffs. Four ruminally cannulated young bulls were assigned to a 4 × 4 Latin square arrangement of
[...] Read more.
This work studied the effect of feeding glycerin in bulls that were fed high levels of concentrate on the ruminal environment and in situ degradability of feedstuffs. Four ruminally cannulated young bulls were assigned to a 4 × 4 Latin square arrangement of treatments. The diets consisted of 15% barley straw and 85% concentrate in dry matter (DM). There were four different concentrates: without glycerin, and with 20, 40 or 80 g of glycerin per kg of DM. Each diet was offered for 24 days, the ruminal fluid was sampled to evaluate the ruminal metabolism and to determine the ruminal bacterial population by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis, and the in situ degradability of six different feedstuffs was measured. The treatment with the highest level of glycerin provided the lower pH (
p < 0.001), and the acetic/propionic molar ratio decreased (
p < 0.001) as glycerin increased. The incorporation of glycerin in the diet did not affect the DNA copies/µL of the total bacteria,
Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens and
Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus (
p > 0.05) in the DNA extract of rumen fluid, but at high levels increased
Selenomonas ruminantium (
p < 0.01). Very few effects of glycerin incorporation were found for the in situ degradability. In young bulls that were fed high levels of concentrate, glycerin at 20 or 40 g/kg of feed could be included without affecting the ruminal pH and raising the propionic acid, but at 80 g/kg the ruminal pH dropped, despite the increase of
Selenomonas ruminantium.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
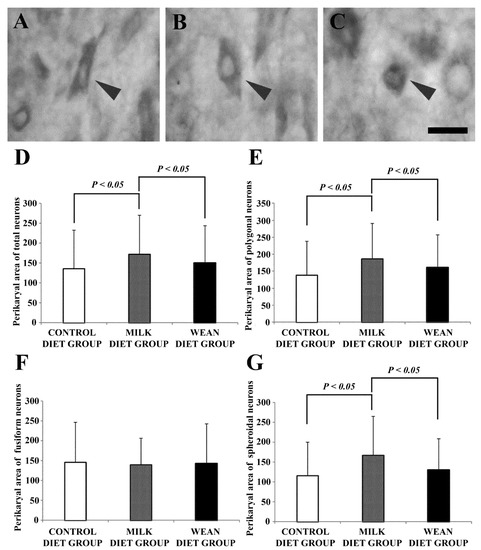
Environment and Behavior: Neurochemical Effects of Different Diets in the Calf Brain
by
Angelo Peli, Annamaria Grandis, Marco Tassinari, Paolo Famigli Bergamini, Claudio Tagliavia, Mariana Roccaro and Cristiano Bombardi
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2749
Abstract
Calves reared for the production of white veal are subjected to stressful events due to the type of liquid diet they receive. Stress responses are mediated by three main stress-responsive cerebral regions: the prefrontal cortex, the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, and the
[...] Read more.
Calves reared for the production of white veal are subjected to stressful events due to the type of liquid diet they receive. Stress responses are mediated by three main stress-responsive cerebral regions: the prefrontal cortex, the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, and the nucleus of the solitary tract of the brainstem. In the present study, we have investigated the effects of different diets on these brain regions of ruminants using immunohistochemical methods. In this study, 15 calves were used and kept in group housing systems of five calves each. They were fed with three different diets: a control diet, a milk diet, and a weaned diet. Brain sections were immunostained to evaluate the distribution of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein immunoreactivity in the prefrontal cortex; the expression of oxytocin in the paraventricular nucleus; and the presence of c-Fos in the A2 group of the nucleus of the solitary tract. The main results obtained indicate that in weaned diet group the oxytocin activity is lower than in control diet and milk diet groups. In addition, weaning appears to stimulate myelination in the prefrontal cortex. In summary, this study supports the importance of maintaining a nutritional lifestyle similar to that occurring in natural conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
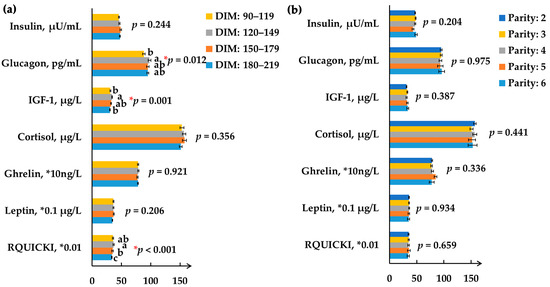
Open AccessBrief Report
Days-in-Milk and Parity Affected Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormone Profiles in Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows
by
Xuehui Wu, Hui-Zeng Sun, Mingyuan Xue, Diming Wang, Leluo Guan and Jianxin Liu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3621
Abstract
It is well known that serum biochemical parameters and hormones contribute greatly to the physiological and metabolic status of dairy cows. However, few studies have focused on the variation of these serum parameters in multiparous mid-lactation cows without the interference of diet and
[...] Read more.
It is well known that serum biochemical parameters and hormones contribute greatly to the physiological and metabolic status of dairy cows. However, few studies have focused on the variation of these serum parameters in multiparous mid-lactation cows without the interference of diet and management. A total of 287 Holstein dairy cows fed the same diet and maintained under the same management regime were selected from a commercial dairy farm to evaluate the effects of days-in-milk (DIM) and parity on serum biochemical parameters and hormone profiles. Milk yield and milk protein content were affected by DIM and parity (
p < 0.05). Milk protein yield showed a numerically decreasing trend with parity, and it was relatively constant in cows with parities between 2 and 4 but lower in cows with parity 6 (
p = 0.020). Ten and five serum biochemical parameters related to protein status, energy metabolism, liver and kidney function, and oxidative stress were affected by DIM and parity, respectively (
p < 0.05). Glucagon, insulin-like growth factor 1 concentration, and the revised quantitative insulin sensitivity check index were significantly different (
p < 0.05) among cows with different DIM. Parity had no effect on hormone concentrations. An interaction between DIM and parity effect was only detected for glucagon concentration (
p = 0.015), which showed a significantly increasing trend with DIM and overall decreasing trend with parity. In summary, DIM and parity played an important role in affecting the serum biochemical parameters and/or hormones of dairy cows, with serum parameters affected more by DIM than parity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
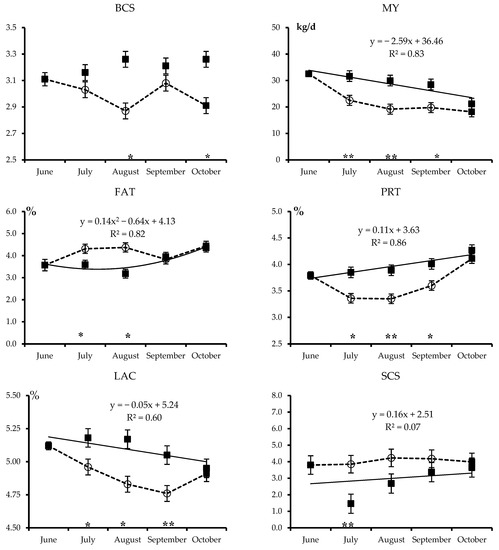
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Summer Transhumance of Dairy Cows to Alpine Pastures on Body Condition, Milk Yield and Composition, and Cheese Making Efficiency
by
Sudeb Saha, Nicolò Amalfitano, Enrico Sturaro, Stefano Schiavon, Franco Tagliapietra, Giovanni Bittante, Ilaria Carafa, Elena Franciosi and Luigi Gallo
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3905
Abstract
Summer transhumance to alpine pastures (ALP) is widespread in dairy systems of alpine regions. This study aimed to investigate the effects of transhumance of Brown Swiss cows to ALP on the yield, composition, and coagulation properties of milk (MCP), and on cheese yield
[...] Read more.
Summer transhumance to alpine pastures (ALP) is widespread in dairy systems of alpine regions. This study aimed to investigate the effects of transhumance of Brown Swiss cows to ALP on the yield, composition, and coagulation properties of milk (MCP), and on cheese yield (CY). The study involved 12 multiparous cows kept at a mountain lowland permanent farm (PF), which were divided into two equal groups: One remained at the PF, the other was moved to the ALP (1860 m above sea level) from July to September. Every month (June to October), daily milk yield (MY) and body condition score (BCS) were recorded, and individual milk samples (
n = 60, 2000 mL each) were collected to assess milk composition, MCP, and CY. Compared with PF, ALP cows had a reduced MY and BCS, which was maintained on return to the PF, greater fat and lower protein contents of milk. Neither MCP nor CY were affected by summer transhumance. In conclusion, summer transhumance did not affect the cheese making efficiency of milk but depressed MY and consequently daily cheese yield, which was nearly 2 kg/d lower for the ALP than the PF cows and was only partially recovered after returning to the PF in autumn.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures