Imaging Biomarker in Oncology
A topical collection in Cancers (ISSN 2072-6694). This collection belongs to the section "Cancer Biomarkers".
Viewed by 68758Editor
Interests: imaging; oncology; CT; MRI; artificial intelligence; radiomics; response to therapy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
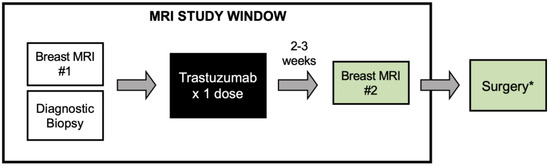
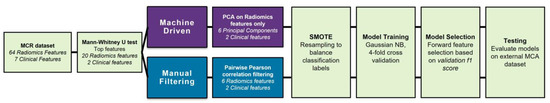
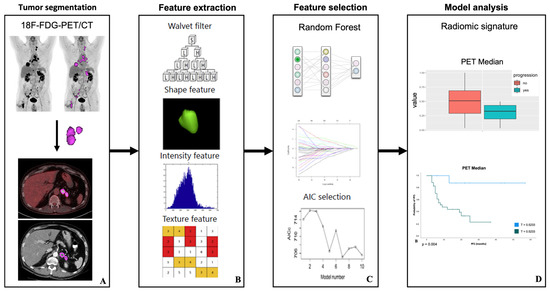
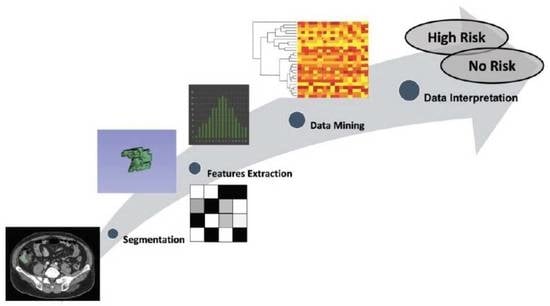
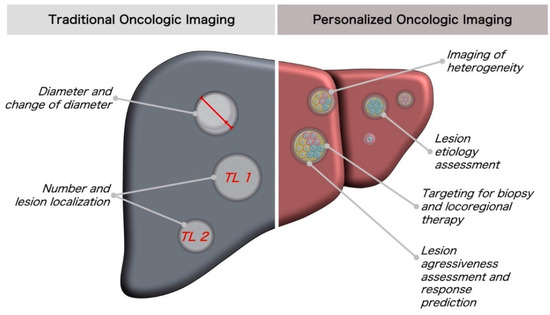
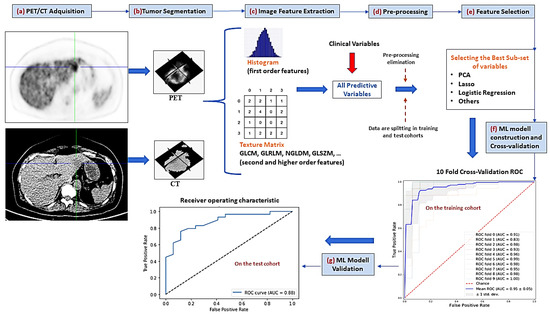
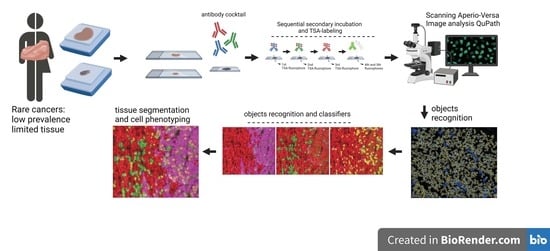
Cancers affect a large percentage of chronic and fragile patients, and their workup and therapeutic options depend on timing of diagnosis, staging, and tumor aggressiveness. In such a scenario, imaging has been acquiring a pivotal role in oncology by providing some relevant non-invasive biomarkers extracted from medical images. Conventional radiological evaluation, based on qualitative and subjective assessment of images, is the recognized imaging approach to study cancer patients. However, the main drawbacks of subjective images assessment are represented by their subjective nature and the difficulty to reproduce the measures. Today, imaging is shifting from a qualitative to a quantitative approach, especially in tumor diagnosis, prognosis prediction, and assessment of response to therapy. In such a scenario, radiomics has been overcoming conventional imaging using dedicated software having the ability to extract high dimensional data having the expectancy to provide objective and quantitative non-invasive imaging biomarkers in cancer patients. Medical images could narrow some quantitative data reflecting microenvironmental tumor heterogeneity, neoplasm phenotypes and heterogeneity, usually correlated with tumor aggressiveness and patient prognosis. Then, radiomic data could be extracted, analyzed, and integrated with clinical data using the strengths of Artificial Intelligence, helpful to overcome the main limitations of traditional tumor management, starting from conventional lesion biopsy, often affected by bias in tumor sampling, lack of repeatability, and possible procedure complications.
In the new era of target therapy, imaging is expected to become a supporting tool for clinicians by providing non-invasive biomarkers. In this manner, imaging could have the ability to outline the profile of tumors based on several features extracted from medical images, assessed with both qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Dr. Damiano Caruso
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cancers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- imaging
- tumor diagnosis
- prognosis prediction
- oncology
- radiomics
- biomarker