Regulation of Cell Function by AMPK and Sirtuins: From Basic Research to Disease and Aging
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cellular Aging".
Viewed by 27661Editors
Interests: cAMP; AMPK; mitochondria; autophagy; heart failure; aging
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: cAMP; AMPK; mitochondria; vascular permeability; Rho GTPases; purinergic receptors; endothelial function; ROS
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: cardiac aging; inflammaging; cardiac inflammation; mitochondrial function; cellular senescence; immunosenescence; immunometabolism
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
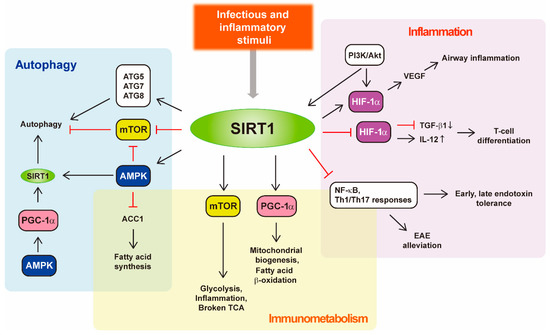
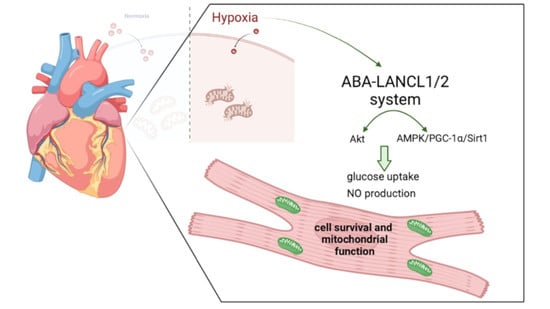
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase, or AMPK, is a multidimensional kinase that acts as an energy sensor, in addition to regulating numerous cellular processes involved in cell survival, health and lifespan. The close partners of AMPK are the sirtuins, a family of evolutionarily conserved NAD+-dependent protein deacetylases that are also widely considered to be metabolic sensors. Remarkably, there is an interaction between AMPK and sirtuins. In particular, Sirt1 mediates AMPK activity via deacetylation and the activation of the upstream AMPK kinase LKB1. In turn, the activation of AMPK can lead to either the overexpression of some sirtuins or to the stimulation of their activity through increasing the cellular NAD+ level. AMPK and sirtuins are activated by energy-depleting/expending conditions, such as caloric restriction or exercise, and have similar effects on such diverse processes as cellular metabolism, inflammation and mitochondrial function.
Both AMPK activity and SIRT1 abundance/activity are reduced with aging, overnutrition or physical inactivity, which may lead to numerous pathologies and diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, inflammation and cardiovascular as well as neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms regulating the activity and expression of AMPK and sirtuins may provide a basis with which to fight diseases and aging-associated malfunctions.
Authors are invited to submit manuscripts in all areas of current AMPK or sirtuins research, with an emphasis on basic as well as translational aspects. Studies addressing age-related changes in AMPK and sirtuin signaling are explicitly encouraged. This Topical Collection welcomes up-to-date hypotheses, reviews, research articles and short communications. Clinical studies, if relevant, as well as computational modeling are also welcome.
Dr. Yury Ladilov
Dr. Muhammad Aslam
Dr. Maria Luisa Barcena
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- AMPK
- sirtuins
- inflammation
- aging
- longevity
- autophagy
- mitophagy
- cell signaling
- mitochondrial function
- exercise
- fasting