Advanced Technology of Internal Combustion Engines in China
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Feiyang Zhao
Prof. Dr. Feiyang Zhao
 Prof. Dr. Feiyang Zhao
Prof. Dr. Feiyang Zhao
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, China
Interests: advanced combustion of low-carbon fuel; advanced power system of green energy; digital twin and machine learning in traffic industry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Chinese scientists have made great contributions to the basic science and engineering of internal combustion engines. It is their unremitting efforts that have revolutionized China’s internal combustion engine technology in recent decades. More recently, the number of papers published annually in China has become the second largest in the world. With the joint efforts of Chinese researchers, in addition to traditional gasoline engines and diesel engines, great achievements have been made in many new engine technologies, such as HCCI, RCCI, and LTC. Therefore, this issue on “Advanced Technology of Internal Combustion Engines in China” aims to provide a platform to demonstrate the innovation of Chinese scientific and technological workers in basic research and engineering research on advanced internal combustion engine technology, which will represent the latest research results in China.
Prof. Dr. Wenbin Yu
Prof. Dr. Feiyang Zhao
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- In-cylinder flow
- Mixture distribution
- Ignition and combustion
- Exhaust emissions
- Combustion and emissions
- Engine performance
- Fuel injection systems
- Fuel spray technology
- Fuels and lubricants
- Alternative fuels
- Gas exchange processes
- After-treatment technology
- Electronic engine control
- Simulations of relevant thermophysical processes
- Engines and auxiliary power units for hybrid vehicles
- Stationary power generation
Published Papers (2 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Combustion Performance and Emission Characteristics of Marine Engine Burning with Different Biodiesel
by
Ning Yang, Xiaowen Deng, Bin Liu, Liwei Li, Yuan Li, Peng Li, Miao Tang and Lin Wu
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 3064
Abstract
Ship emissions are one of the main sources of air pollution in port cities. The prosperous maritime trade has brought great harm to the air quality of port cities while promoting the development of the world economy. During the berthing process, ship auxiliary
[...] Read more.
Ship emissions are one of the main sources of air pollution in port cities. The prosperous maritime trade has brought great harm to the air quality of port cities while promoting the development of the world economy. During the berthing process, ship auxiliary machines emit a large amount of air pollutants, which have a great impact on air quality and public health. Alternative marine fuels are being studied and used frequently to reduce ship emissions. This research was carried out to investigate the gaseous and particles emission characteristics of a marine diesel engine during the application of experimental biodiesel fuels. To study the influence of mixed fuels on engine performance, measurements were made at different engine loads and speeds. Different diesel fuels were tested using various ratios between biodiesel and BD0 (ultra-low sulfur diesel) of 0%, 10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, 90%, and 100%. The results indicated the use of biodiesel has little influence on the combustion performance but has a certain impact on exhaust emissions. The octane number and laminar flame speed of biodiesel are higher than those of BD0, so the combustion time of the test diesel engine is shortened under the mixed mode of biodiesel. In addition, a high ratio of biodiesel leads to a decrease of the instantaneous peak heat release rate, causing the crank angle to advance. As the biodiesel blending ratio increased, most of the gaseous pollutants decreased, especially for CO, but it led to an increase of particle numbers. The particle size distribution exhibits a unimodal distribution under various conditions, with the peak value appearing at 30–75 nm. The use of biodiesel has no effect on this phenomenon. The peak positions strongly depend on fuel types and engine conditions. The particulate matter (PM) emitted from the test engine included large amounts of organic carbon (OC), which accounted for between 30% and 40% of PM. Whereas the elemental carbon (EC) accounted for between 10% and 20%, the water-soluble ions components accounted for 6–15%. Elemental components, which accounted for 3–8% of PM emissions, mainly consisted of Si, Fe, Sn, Ba, Al, Zn, V, and Ni. Generally, biodiesel could be a reliable alternative fuel to reduce ship auxiliary engine emissions at berth and improve port air quality.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Study on the Relationship between Combustion Parameters and Cylinder Head Vibration Signal in Time Domain
by
Shaobo Ji, Yang Li, Guohong Tian, Rongze Ma, Minglei Shu, Shiqiang Zhang, Wenbin Yu, Xin Lan and Yong Cheng
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2383
Abstract
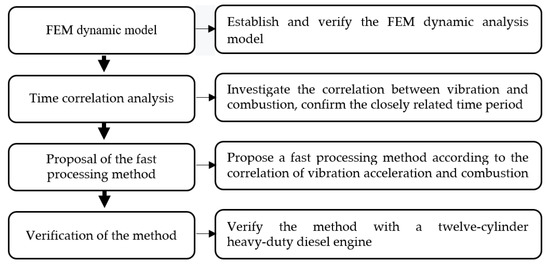
Combustion-related characteristic parameters, such as the start of combustion (SoC) and the timing of the peak pressure increase rate (PIR), can be used as the feedback signals for the closed-loop control of combustion. A dynamic Finite Element Method (FEM) model was firstly developed
[...] Read more.
Combustion-related characteristic parameters, such as the start of combustion (SoC) and the timing of the peak pressure increase rate (PIR), can be used as the feedback signals for the closed-loop control of combustion. A dynamic Finite Element Method (FEM) model was firstly developed to confirm the closely related time period between combustion pressure and vibration. On this basis, a fast processing method was developed to estimate the timings of SoC and the peak PIR in the closely related time period. This method was verified on a twelve-cylinder heavy-duty diesel engine at various engine speed and load. Results showed that the maximum deviation of the two parameters were within 2 °CA and 1.5 °CA, respectively, which suggested that the proposed method had an adequate accuracy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures