Selected Papers from IMETI
A project collection of Materials (ISSN 1996-1944).
Papers displayed on this page all arise from the same project. Editorial decisions were made independently of project staff and handled by the Editor-in-Chief or qualified Editorial Board members.
Viewed by 66953
Share This Project Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Yi-Chang Wu
Prof. Dr. Yi-Chang Wu
 Prof. Dr. Yi-Chang Wu
Prof. Dr. Yi-Chang Wu
E-Mail
Collection Editor
Department of Automation Engineering, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Yunlin, Taiwan
Interests: magnetic gear; finite-element analysis; magnetic materials; mechatronics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Project Overview
Dear Colleagues,
The International Multi-Conference on Engineering and Technology Innovation (IMETI) was launched in 2011, and has attracted many participants joined the events since then. It covers a wide range of fields in science and engineering innovation and aims to bring together engineering technology expertise. This conference enables interdisciplinary collaboration between science and engineering technologists in the academic and industrial fields as well as networking internationally. During the conference, there should be substantial time for presentation and discussion. Attendees will find various activities useful in bringing together a diverse group of engineers and technologists from across disciplines for the generation of new ideas, collaboration potential and business opportunities. The professional from the industry, academia and government to discourse on research and development, professional practice, business and management in the science and engineering fields are welcome to the conference. IMETI consists of the following sub-conferences:
- International Conference on Biomedical Engineering Innovation (ICBEI)
- International Conference on Environmental and Civil Engineering Innovation (ICECEI)
- International Conference on Advanced Technology Innovation (ICATI)
IMETI will follow up the success of the past conferences by bringing together researchers and application developers from different areas focusing on unifying themes. This Special Issue focuses on the recent development of various fields or cross-field of materials. The submissions from distinguished researchers and leading experts in the scientific community are much welcome.
Prof. Dr. Wen-Hsiang Hsieh
Prof. Dr. Yi-Chang Wu
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- IMETI, ICBEI, ICETI, ICECEI, ICATI
- Material engineering and Science
- Photovoltaic
- Construction Material
- Biomedical Material
- Polymer
- Composite
- Sensor
- Functional Materials
- Nanomaterial
- Electrochemistry
- Corrosion
Published Papers (20 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Expansion Control of Alkali-Activated Materials Using Waste Glass Cullet from Photovoltaic Panels as Fine Aggregates
by
Ryo Yamanouchi, Kentaro Yasui, Hiroshi Yamada, Takayuki Fukunaga and Hideki Harada
Viewed by 1074
Abstract
Glass cullet (GC) generated from the disposal of photovoltaic (PV) panels are typically landfilled, and effective GC utilization methods must be established for PV generation. In this study, alkali-activated material (AAM) mortars were prepared from the paste of fine blast-furnace slag powder, fly
[...] Read more.
Glass cullet (GC) generated from the disposal of photovoltaic (PV) panels are typically landfilled, and effective GC utilization methods must be established for PV generation. In this study, alkali-activated material (AAM) mortars were prepared from the paste of fine blast-furnace slag powder, fly ash, and sodium orthosilicate (SO) and mixed with crushed sand and GC to investigate the potential use of GC as a fine aggregate in AAM. The replacement of crushed sand with GC did not considerably affect the flowability of the mortar, whereas the compressive strength decreased with the increasing GC replacement rates. Although expansion due to the alkali–silica reaction (ASR) was observed in mortars wherein GC replaced crushed sand, the expansion can be controlled by reducing the amount of mixed SO, autoclaving the GC, performing preleaching to remove the Si that causes the ASR, and replacing the blast-furnace slag with fly ash. By enforcing measures against the expansion, the possibility of using GC as fine aggregate is enhanced considerably, thus increasing the feasibility of continuous PV production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of the Grapevine Biochar on the Properties of PLA Composites
by
Chien-Chung Huang, Chun-Wei Chang, Kousar Jahan, Tzong-Ming Wu and Yeng-Fong Shih
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2419
Abstract
This study found that biochar made from grapevines (GVC), an agricultural waste product, can be used as a nucleating agent to promote the crystallization of polylactic acid (PLA). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis of GVC/PLA composites showed that different particle sizes (200 and
[...] Read more.
This study found that biochar made from grapevines (GVC), an agricultural waste product, can be used as a nucleating agent to promote the crystallization of polylactic acid (PLA). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis of GVC/PLA composites showed that different particle sizes (200 and 100 mesh size) and amounts (1 wt%, 10 wt%) of biochar affect the re-crystallization of PLA, with 200 mesh GVC in the amount of 10 wt% being the most significant. In addition, it was found that there were two peaks related to imperfect and perfect crystals in the T
m part for GVC/PLA composites. TGA analysis showed that adding GVC tends to lower the maximum decomposition temperature of PLA, revealing that GVC may accelerate the degradation reaction of PLA. This research also studied the effects of GVC in various particle sizes and amounts on the mechanical properties and degradation of PLA. The results revealed that the tensile and impact strengths of GVC/PLA composite could reach 79.79 MPa and 22.67 J/m, respectively, and the increments were 41.4% and 32.1%, greater than those of pristine PLA. Moreover, the molecular weight of PLA decreased as the amount of GVC increased. Therefore, GVC particles can be used as reinforcing fillers for PLA to improve its mechanical properties and adjust its molecular weight. These agricultural-waste-reinforced biocomposites can reduce both greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and the cost of biodegradable polymers and achieve the goals of a circular economy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Large-Scale Fabrication of Graded Convex Structure for Superhydrophobic Coating Inspired by Nature
by
Yu Wang and Jin-Tian Huang
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2178
Abstract
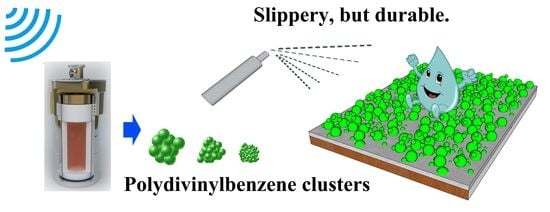
The addition of toxic substances and poor durability severely limit the market applications of superhydrophobic coatings in the oil–water-separation industry, anti-icing, and self-cleaning surfaces. In order to solve the above problems, a stable, strong, fluorine-free superhydrophobic coating was prepared according to natural inspiration.
[...] Read more.
The addition of toxic substances and poor durability severely limit the market applications of superhydrophobic coatings in the oil–water-separation industry, anti-icing, and self-cleaning surfaces. In order to solve the above problems, a stable, strong, fluorine-free superhydrophobic coating was prepared according to natural inspiration. In this study, polydivinylbenzene (PDVB) was produced by the hydrothermal method, and micro-nanoparticle clusters composed of PDVB particles of different sizes were prepared by controlling the ratio of raw materials, which was then attached to the substrate surface by a simple spraying technique. A rough coating with a lotus-leaf-like layered protruding structure was constructed by depositing particle clusters of different sizes. In the end, the prepared coating showed attractive superhydrophobicity, with a maximum contact angle (CA) that reached up to 160°. In addition, the coating had long-lasting superhydrophobic properties in various environments, such as common liquid and acidic and alkaline solutions. Moreover, in the oil–water-separation process, the superhydrophobic filter paper was still able to obtain a separation efficiency of more than 85% after being used 50 times, and it maintained a contact angle of >150°. At the same time, the coating had excellent dye resistance and self-cleaning performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Performance of Green Concrete and Inorganic Coating Materials
by
Sung-Ching Chen, Wei-Ting Lin, Ran Huang and Hui-Mi Hsu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2525
Abstract
Green concrete (GC) was developed for realizing sustainable development, recycling waste materials, and reducing environmental pollution. For the practical use of GC, various harmful materials must blocked from entering its cracks and pores; and its strength and durability must be improved. The use
[...] Read more.
Green concrete (GC) was developed for realizing sustainable development, recycling waste materials, and reducing environmental pollution. For the practical use of GC, various harmful materials must blocked from entering its cracks and pores; and its strength and durability must be improved. The use of an inorganic coating material (ICM) for GC effectively prevents the intrusion of harmful materials and repairs the concrete. ICMs can reduce the permeability and increase the durability of concrete. This study investigated GC, construction waste, and ICMs and used recycled sand and gravel as well as construction waste as substitutes for cement. The results indicate that the coarse aggregate substitution, water-binder ratio, and recycled fine aggregate substitution must be controlled suitably in GC. Furthermore, the coating layer, fine aggregate substitution, and aging of the ICM mut be controlled suitably. GC with an ICM showed poorer performance than conventional concrete, mainly because of the high porosity. Nonetheless, the ICM somewhate reduces the porosity and resists the penetration of chloride ions, thereby promoting concrete quality.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Wall Thickness on Stress–Strain Response and Buckling Behavior of Hollow-Cylinder Rubber Fenders
by
Ming-Yuan Shen, Yung-Chuan Chiou, Chung-Ming Tan, Chia-Chin Wu and Wei-Jen Chen
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3743
Abstract
In this study, the effect of wall thickness (15–25 mm) on the stress–strain response of hollow-cylinder rubber fenders were investigated by conducting monotonic compression tests. It was found that a progressive increase in lateral bending deformation was observed during monotonic compression. Simultaneously, the
[...] Read more.
In this study, the effect of wall thickness (15–25 mm) on the stress–strain response of hollow-cylinder rubber fenders were investigated by conducting monotonic compression tests. It was found that a progressive increase in lateral bending deformation was observed during monotonic compression. Simultaneously, the extent of the lateral deflection decreased notably with an increasing wall thickness. From the experimental results, the fact is accepted that buckling occurred in the tested fender due to the fact that the ratio of the height to the wall thickness was higher than four in all of the considered cases. Moreover, an s-shape profile appeared in the stress–strain curves, which became clearer as the wall thickness was reduced from 25 to 15 mm. To assess the performance of fenders objectively, an energy-effectiveness index,
, was introduced to quantify the energy absorption capacity of the fender. From the experimental observations, it was inferred that the contact area of the folded inner surface of the fender produced under compression generated an additional reaction force and affected the shape of the stress–strain curve since the measured load consisted of two reaction forces: one caused by the self-contact area, and the other resulted from the compression-bending deformation that occurred in the side wall of the fender. To examine this assertion, a finite element analysis (FEA) was conducted and confirmed the effect of the reaction force on the sensitivity of the s-shape characteristic of the stress–strain curve. Finally, a polynomial regression was conducted and the calculated results based on the fourth-degree stress polynomial function correlated very well with the measured stress–strain curves.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Glass Fiber Molding Process Design by Reverse Warping
by
Han-Jui Chang and Zhi-Ming Su
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2821
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to clarify the influence of changes in glass fiber properties on warpage prediction, and to demonstrate the importance of accurate material property data in the numerical simulation of injection molding. In addition, this study proposes an optimization
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study is to clarify the influence of changes in glass fiber properties on warpage prediction, and to demonstrate the importance of accurate material property data in the numerical simulation of injection molding. In addition, this study proposes an optimization method based on the reverse warping agent model, in which the thermal conductivity of the plastic material is reduced, and the solidified layer on the surface of the mold is reduced and transferred from the molding material to the mold wall. This means that by the end of the cooling phase, the shrinkage of the molten zone within the component will continue, resulting in warpage. Based on the optimal process parameters, the sensitivity of the warpage prediction to the relationship between the two most important material properties, the glass fiber and holding pressure time, was analyzed. The material property model constants used for numerical simulations can sometimes vary significantly due to inherent experimental measurement errors, the resolution of the test device, or the manner in which the curve fit is performed to determine the model constants. This model has been developed to intelligently determine the preferred processing parameters and to gradually correct the details of the molding conditions. Thus, the cavity is separated in the critical warpage region, and a new cavity geometry with a reverse warped profile is placed into the mold base slot. The results show that the hypothetical and reasonable variation of the glass fiber model constant and the holding pressure time relationship may significantly affect the magnitude of the warpage prediction of glass fiber products. The greatest differences were found as a result of the warping orientation of the glass fiber material.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
On the Directivity of Lamb Waves Generated by Wedge PZT Actuator in Thin CFRP Panel
by
Sergey Shevtsov, Valery Chebanenko, Maria Shevtsova, Shun-Hsyung Chang, Evgenia Kirillova and Evgeny Rozhkov
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2774
Abstract
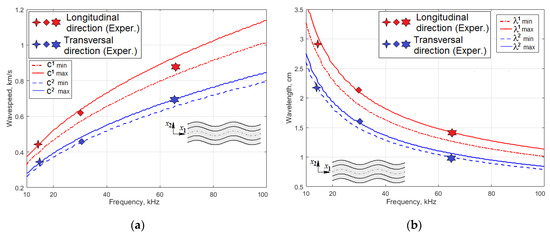
This paper addresses investigation of guided-wave excitation by angle-beam wedge piezoelectric (PZT) transducers in multilayered composite plate structure with orthotropic symmetry of the material. The aim of the present study is to determine the capability of such actuators to provide the controlled generation
[...] Read more.
This paper addresses investigation of guided-wave excitation by angle-beam wedge piezoelectric (PZT) transducers in multilayered composite plate structure with orthotropic symmetry of the material. The aim of the present study is to determine the capability of such actuators to provide the controlled generation of an acoustic wave of a desirable type with the necessary wavelength, propagation distance and directivity. The studied CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic) panel is considered to be homogenous, with effective elastic moduli and anisotropic structural damping, whose parameters were determined experimentally. According to the results of dispersion analysis and taking into account the data of wave attenuation in a highly damping CFRP composite, the two types of propagating waves A0 and S0 were considered theoretically and experimentally in the frequency range of 10–100 kHz. Using the results of a previous study, we reconstructed the structure of the wedge actuator, to develop its finite-element (FE) model, and a modal analysis was carried out that revealed the most intense natural vibration modes and their eigenfrequencies within the frequency range used. Both experimental and numerical studies of the generation, propagation, directivity and attenuation of waves in the orthotropic composite panel under study revealed the influence of the angular orientation of the actuator on the formation of wave patterns and allowed to determine the capabilities of the wave’s directivity control.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Mechanical Properties of Short Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymers Made by Casted and 3D Printing Methods: A Comparative Study
by
Kinga Korniejenko, Michał Łach, Shih-Yu Chou, Wei-Ting Lin, An Cheng, Maria Hebdowska-Krupa, Szymon Gądek and Janusz Mikuła
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 4279
Abstract
The main objective of this article is to develop ceramic-based materials for additive layer manufacturing (3D printing technology) that are suitable for civil engineering applications. This article is focused on fly ash-based fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites. It is based on experimental research, especially research
[...] Read more.
The main objective of this article is to develop ceramic-based materials for additive layer manufacturing (3D printing technology) that are suitable for civil engineering applications. This article is focused on fly ash-based fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites. It is based on experimental research, especially research comparing mechanical properties, such as compressive and flexural strength for designed compositions. The comparison includes various composites (short fiber-reinforced geopolymers and plain samples), different times of curing (investigation after 7 and 28 days), and two technologies of manufacturing (casted and injected samples—simulations of the 3D printing process). The geopolymer matrix is based on class F fly ash. The reinforcements were green tow flax and carbon fibers. The achieved results show that the mechanical properties of the new composites made by injection methods (simulations of 3D technology) are comparable with those of the traditional casting process. This article also discusses the influence of fiber on the mechanical properties of the composites. It shows that the addition of short fibers could have a similar influence on both of the technologies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Decreasing of Leaching and Improvement of Geopolymer Properties by Addition of Aluminum Calcium Cements and Titanium Oxide
by
Michał Łach, Kinga Korniejenko, Janusz Walter, Anna Stefańska and Janusz Mikuła
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3021
Abstract
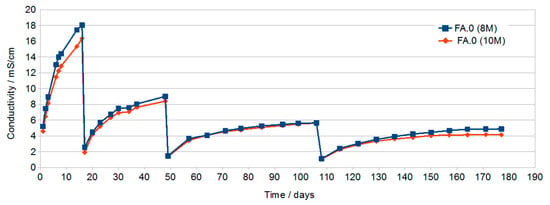
The article presents the latest results of the leaching of alkali from geopolymers depending on the introduced additions in the form of aluminum calcium cement and nanometric titanium oxide. Aluminum calcium cements were introduced in two variants: G40 (>40% Al
2O
3
[...] Read more.
The article presents the latest results of the leaching of alkali from geopolymers depending on the introduced additions in the form of aluminum calcium cement and nanometric titanium oxide. Aluminum calcium cements were introduced in two variants: G40 (>40% Al
2O
3) and G70 (>70% Al
2O
3) in amounts of 0%, 2%, and 4% by weight. Titanium oxide was also incorporated in amounts of 2% and 4% by weight. The results of conductivity tests of solutions in which geopolymers were immersed were carried out. On this basis, it was found that geopolymers cured in the aquatic environment have a lower risk of efflorescence in the later periods of their use due to leaching of compounds at the stage of aquatic curing. In addition, it was found that the addition of calcium aluminum cements decreases the leaching of substances from geopolymers. It was also found that geopolymers based on an 8 M NaOH solution have greater leaching than when using a 10 M solution. The results of the compressive strength tests for the tested samples were also presented.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Hardware-In-The-Loop Simulations of Hole/Crack Identification in a Composite Plate
by
Yen-Chu Liang and Yun-Ping Sun
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2380
Abstract
The technology of hardware-in-the-loop simulations (HILS) plays an important role in the design of complex systems, for example, the structural health monitoring (SHM) of aircrafts. Due to the high performance of personal computers, HILS can provide practical solutions to many problems in engineering
[...] Read more.
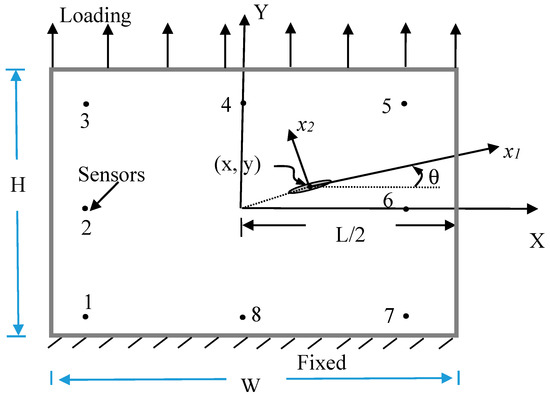
The technology of hardware-in-the-loop simulations (HILS) plays an important role in the design of complex systems, for example, the structural health monitoring (SHM) of aircrafts. Due to the high performance of personal computers, HILS can provide practical solutions to many problems in engineering and sciences, especially in the huge systems, giant dams for civil engineering, and aircraft system. This study addresses the HILS in hole/crack identification in composite laminates. The multiple loading modes method is used for hole/crack identification. The signals of strains measured from the data-acquisition (DAQ) devices are accomplished by the graphical software LabVIEW. The results represent the actual responses of multiple loading mode tests of real specimens. A personal computer is employed to execute the identification work according to the strain data from DAQ devices by using a nonlinear optimization approach. When all the criteria are satisfied, the final identification results will be obtained. HILS will achieve real time identification of hole/crack in the composite plate by using the actual response measured from the sensors. Not only the size, but also the location and orientation of the crack/hole in a composite plate are successfully identified herein.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Circulation Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash as Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregates in Roller Compacted Concrete
by
Wei-Ting Lin, Kae-Long Lin, Kailun Chen, Kinga Korniejenko, Marek Hebda and Michał Łach
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 2567
Abstract
Recently, many people around the world have been concerned with environmental protection and sustainability. The goal of various countries’ research has been focused on how to regenerate existing resources. Circulation fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) technology is one of the emerging combustion technologies for
[...] Read more.
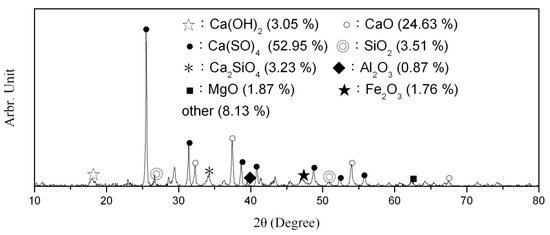
Recently, many people around the world have been concerned with environmental protection and sustainability. The goal of various countries’ research has been focused on how to regenerate existing resources. Circulation fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) technology is one of the emerging combustion technologies for electricity generation and produces more than 800,000 tons of CFBC fly ash (CFA) per year for combustion. CFA has been widely applied in cement additive, new building materials and cement-based materials. The goal of this study was to discuss the engineering properties of roller-compacted concrete containing CFA. Test subjects included compressive strength, flexural strength, absorption, setting time, unit weight, sulfate resistance, SEM microscopic observations and XRD ingredient analysis. Test results indicate the following: (1) using CFA as a substitute of fine aggregates up to 10 wt.% would improve the development of later flexural strength; (2) the increases in pre-pressure would increase the compressive strength and unit weight and decrease absorption; (3) using CFA would reduce the initial setting time by 30%–60% and reduce the final setting time by 16%–20%; (4) using CFA would reduce the absorption; (5) using CFA would reduce the unit weight by 0.5%–2.8%, and the increases in pre-pressure would increase the unit weight by about 0.9%–2.1%; (6) CaO in CFA helps to improve sulfate resistance; (7) scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation shows that the increases in pre-pressure would reduce the pores; and (8) X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis shows that the inclusion of CFA would increase the content of Ca(OH)
2 in concrete.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Stress-Strain Response of Cylindrical Rubber Fender under Monotonic and Cyclic Compression
by
Chia-Chin Wu and Yung-Chuan Chiou
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 4827
Abstract
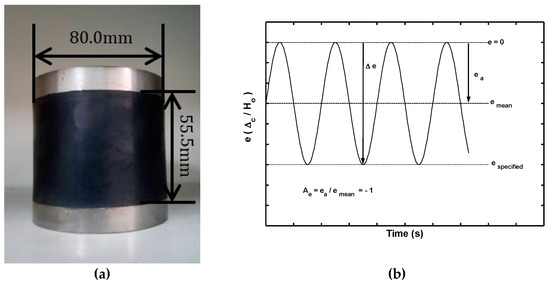
The study was devoted to the observation and modeling the mechanical behaviors of a hybrid SBR/NR (Styrene-Butadiene/Natural Rubber) hybrid vulcanized rubber fender under monotonic/cyclic compression. In experimental observations of the monotonic compression tests, it was found that lateral deformation occurred on the tested
[...] Read more.
The study was devoted to the observation and modeling the mechanical behaviors of a hybrid SBR/NR (Styrene-Butadiene/Natural Rubber) hybrid vulcanized rubber fender under monotonic/cyclic compression. In experimental observations of the monotonic compression tests, it was found that lateral deformation occurred on the tested fender and was more significant with increasing the extent of the compressive strain. The relationship between the transmission stress
and the compressive strain
was nonlinear and the absorbed strain-energy-density was increased monotonically with the increment of the compressive strain. Among all cyclic compression tests with strain controlled, the reductions in both the stress range and the absorbed strain-energy-density up to the ten-thousandth cycle were found and then both of the cyclic properties remain approximately constant in the following compression cycles. Two new properties, the softening factor and the energy reduction factor, were introduced to quantify the effect of the strain range on the extent of the reduction in stress range and that on the absorbed strain-energy-density, respectively. It was found that both of the calculated values of the new properties increase with the increment of strain range. In mathematical modeling of the relationship between the transmission stress and the compressive strain, a new approach based on energy-polynomial-function
was presented and was successfully used to simulate the monotonic curve and the stable hysteresis loop curves of the tested rubber fender in compression. Essentially, the energy-polynomial-function
was obtained by performing a polynomial regression on a large amount of (
data. Moreover, the least-square approach was applied to determine the corresponding regression coefficients in
. Clearly, the stress-polynomial-function in modeling the
curve could be obtained from the differentiation of the energy-polynomial-function with respect to the compressive strain. In addition, to provide an adequate estimation of the mechanical properties of the cylindrical rubber fender under compression, the named cyclic stress-strain curve and cyclic energy-strain curve were developed and also modeled in this study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Synergistic Effect on the Thermomechanical and Electrical Properties of Epoxy Composites with the Enhancement of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nano Platelets
by
Yi-Ming Jen and Jui-Cheng Huang
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 4015
Abstract
The synergetic effect of adding multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) on the thermomechanical properties and electric resistance of epoxy polymers were experimentally analyzed in this study. The total content of two employed carbon fillers were kept constant at 0.4 wt
[...] Read more.
The synergetic effect of adding multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) on the thermomechanical properties and electric resistance of epoxy polymers were experimentally analyzed in this study. The total content of two employed carbon fillers were kept constant at 0.4 wt %, and seven filler ratios between two fillers (MWCNTs:GNPs), i.e., 10:0, 1:9, 3:7, 5:5, 7:3, 9:1, and 0:10, were considered in the experimental program to investigate the influences of employed nano-filler ratios on the viscoelastic and electrical properties of the studied nanocomposites. The thermomechanical properties and the sheet resistance of the nanocomposites were analyzed using a dynamic mechanical analyzer and four-point probe, respectively. Moreover, the thermogravimetric analyzer was utilized to measure the pyrolysis temperature of the nanocomposites. Experimental results show that the synergistic effect of adding two nano-fillers were clear for the improvement of the storage moduli, glass transition temperatures, and electric conductivity. Oppositely, the employment of two fillers has a slight effect on the pyrolysis temperatures of the studied nanocomposites. The composites with the MWCNT:GNP ratio of 1:9 display the most apparent enhancement of the thermomechanical properties. The improvement results from the uniform distribution and the high aspect ratio of GNPs. The addition of a small amount of MWCNTs provides more linkage in the matrix. Moreover, the specimens with the MWCNT:GNP ratio of 1:9 shows remarkable electrical properties, which result from the large contact surface areas of GNPs with each other. The employment of few MWCNTs plays an important bridging role between the layered GNPs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
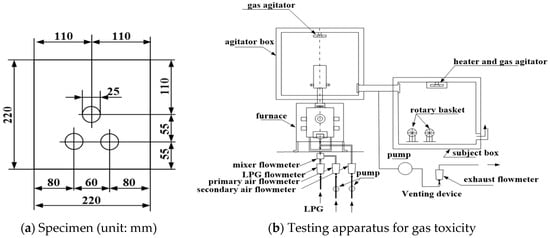
The Development of a Surface Finisher of Car Park Slab Using Waterborne Silicon Acrylic with Polyamide [Part I: Performance Evaluation]
by
Hoseong Jeong, Junho Gong, Wanseok Yoon and Dooyong Cho
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3022
Abstract
A waterborne coating system for car park slab has recently gained interest as an alternative for solvent-based finishing materials due to environmental concerns and prolongation of service life. However, water-based finishers, regardless of their eco-friendly properties, have relatively lower hardness compared to traditional
[...] Read more.
A waterborne coating system for car park slab has recently gained interest as an alternative for solvent-based finishing materials due to environmental concerns and prolongation of service life. However, water-based finishers, regardless of their eco-friendly properties, have relatively lower hardness compared to traditional finishing systems. In order to overcome this obstacle, a hybrid technology was used to develop a substitute surface finisher for car park slab and its performance was evaluated according to the KS (Korean Standard) F 4937. Initially, the proper mix ratio of polyamide was found by comparing adhesion via pull-off-test results and other performance evaluation tests. From the test results, it was found that mixing polyamide with silicon acrylic finisher caused an increase in adhesion strength. Silicon acrylic with a 30% mix ratio of polyamide resin (SA+PR30%) was selected to perform the rest of the tests and the results satisfied the acceptance criteria of KS F 4937 and were compared with a recent water-based polyurethane finisher with cementitious powder (WPC). Finally, it was verified that the developed finisher could be an alternative finisher of urethane and epoxy finishers as it has good mechanical properties and emit less volatile organic compounds (VOC).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Development of a Surface Finisher of Car Park Slab Using Waterborne Silicon Acrylic with Polyamide [Part II: Safety Tests]
by
Junho Gong, Hoseong Jeong and Dooyong Cho
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2805
Abstract
Due to the environmental concerns of solventborne coating systems, environmental directives have recently been promulgated in many countries. Additionally, integrated environmental policies have been pushed in many fields to minimise influences on the environment. Waterborne silicon acrylic finishers have gained much interest to
[...] Read more.
Due to the environmental concerns of solventborne coating systems, environmental directives have recently been promulgated in many countries. Additionally, integrated environmental policies have been pushed in many fields to minimise influences on the environment. Waterborne silicon acrylic finishers have gained much interest to replace the traditional finishing system. To satisfy the requirements, a waterborne finisher with polyamide was previously developed and its performance was determined. For further safety assessment, various tests were conducted, such as gas toxicity, heavy metals tests, chemical resistance test and chloride migration test, followed by equivalent standards. In the cases of gas toxicity and heavy metals evaluations, both results were acceptable considering their corresponding standards, e.g. KS F 2271, KS F 3888-2 and BS EN 71-3. Based on the evaluation, silicon acrylic with 30% mix ratio of polyamide resin (SA+PR30%) could be implemented as an environmentally friendly finisher for various applications. In the chemical resistance and chloride migration test results, the developed finisher showed a barrier effect in the chemical environment. Thus, the developed finisher could be an alternative finisher applicable for slabs in chemical industrial areas.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Feasibility and Characterization Mortar Blended with High-Amount Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag
by
Wei-Ting Lin, Chia-Jung Tsai, Jie Chen and Weidong Liu
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3836
Abstract
Basic oxygen furnace slag (BOFS) was ground to three levels of fineness as a replacement for cement at weight proportions of 10, 30, 50, and 70 wt.%. Fineness and weight proportion were shown to have significant effects on the flowability and setting time
[...] Read more.
Basic oxygen furnace slag (BOFS) was ground to three levels of fineness as a replacement for cement at weight proportions of 10, 30, 50, and 70 wt.%. Fineness and weight proportion were shown to have significant effects on the flowability and setting time of the mortars. The expansion of BOFS mortars increased with an increase in the proportion of cement replaced, thereby exacerbating the effects of cracking. Optimal mechanical properties were achieved when 10 wt.% of the cement was replaced using BOFS with fineness of 10,000 cm
2/g. The compressive strength of BOFS mortar is similar to that of ordinary Portland mortar, which makes BOFS suitable for the partial replacement of cement as a supplementary cementitious material. Scanning electron microscopy results revealed that the reaction of CaO with H
2O results in the formation of C–S–H colloids, whereas the reaction of SiO
2 with Al
2O
3 produces C–A–S–H colloids. The use of BOFS as a partial replacement for Portland cement could make a tremendous contribution to the steel industry and help to lower CO
2 emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
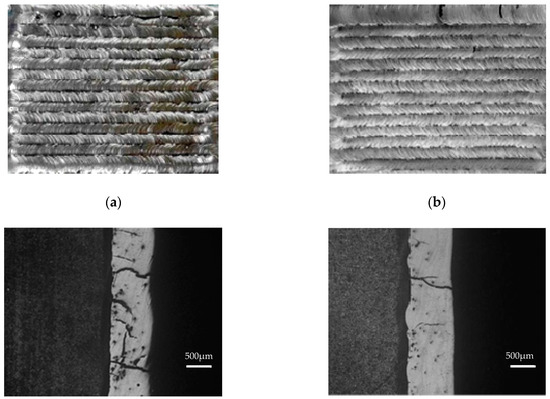
Crack Restraining Methods and their Effects on the Microstructures and Properties of Laser Cladded WC/Fe Coatings
by
Qiu-Lian Dai, Can-bin Luo and Fang-yi You
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 3834
Abstract
Laser cladded WC/Fe coatings have the advantages of low cost and high abrasion wear resistance. However, cracks always appear in WC/Fe coatings, which limits their industrial application. In this paper, the co-effects of the re-melting process, heat treatments, and amount of Co element
[...] Read more.
Laser cladded WC/Fe coatings have the advantages of low cost and high abrasion wear resistance. However, cracks always appear in WC/Fe coatings, which limits their industrial application. In this paper, the co-effects of the re-melting process, heat treatments, and amount of Co element on the cracking susceptibility, microstructures, and mechanical properties of WC/Fe laser cladding coatings were studied. Experimental results show that re-melting process is helpful to improve the surface quality of the coating and to reduce the cracking susceptibility. The hardness of the coating decreases slightly but distributes more uniformly. Cracks in the coating can be inhibited effectively by preheating the substrate to 250 °C and maintaining the temperature during the laser cladding process, as well as applying an annealing treatment at 300 °C for 1 h. Heat treatment also results in a slight decrease in the hardness. Crack initiation cannot be restrained completely by applying the above two methods when laser cladding a big area of coating. On the basis of the above two methods, addition of Co element to the coating can further improve its toughness and decrease the crack susceptibility. Crack-free WC/Fe coating can be manufactured when 8% Co is added, and its wear resistance is much better than that of the hardened medium steel, especially when the wear time is long.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
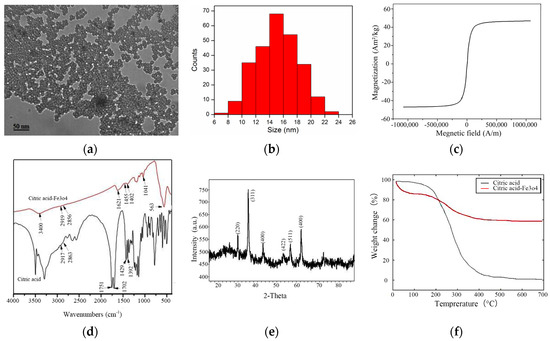
Thrombolysis Enhancing by Magnetic Manipulation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
by
Qian Li, Xiaojun Liu, Ming Chang and Zhen Lu
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 4679
Abstract
In this paper, an effective method of accelerating urokinase-administrated thrombolysis through a rotating magnetic field (RMF) of guided magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) in the presence of low-dose urokinase is proposed. The dispersed Fe
3O
4 NPs mixed with urokinase were injected into microfluidic
[...] Read more.
In this paper, an effective method of accelerating urokinase-administrated thrombolysis through a rotating magnetic field (RMF) of guided magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) in the presence of low-dose urokinase is proposed. The dispersed Fe
3O
4 NPs mixed with urokinase were injected into microfluidic channels occluded by thrombus prepared in vitro. These magnetic NPs aggregated into elongated clusters under a static magnetic field, and were then driven by the RMF. The rotation of Fe
3O
4 aggregates produced a vortex to enhance the diffusion of urokinase to the surface of the thrombus and accelerate its dissolution. A theoretical model based on convective diffusion was constructed to describe the thrombolysis mechanism. The thrombus lysis speed was determined according to the change of the thrombus dissolution length with time in the microfluidic channel. The experimental results showed that the thrombolysis speed with rotating magnetic NPs is significantly increased by nearly two times compared with using the same dose of pure urokinase. This means that the magnetically-controlled NPs approach provides a feasible way to achieve a high thrombolytic rate with low-dose urokinase in use.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
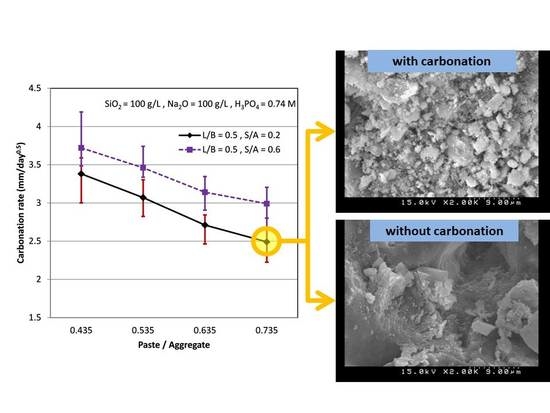
Effect of Mixture Variables on Durability for Alkali-Activated Slag Cementitious
by
Chi-Che Hung, Yuan-Chieh Wu, Wei-Ting Lin, Jiang-Jhy Chang and Wei-Chung Yeih
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2601
Abstract
In this study, the influence of three mixture variables named Sand/Aggregate ratio, Liquid/Binder ratio, and Paste/Aggregate ratio on the cementitious properties were studied. The durability of cementitious including absorption, absorption rate, resistivity, rapid chloride permeability index, and carbonation rate were examined. Results showed
[...] Read more.
In this study, the influence of three mixture variables named Sand/Aggregate ratio, Liquid/Binder ratio, and Paste/Aggregate ratio on the cementitious properties were studied. The durability of cementitious including absorption, absorption rate, resistivity, rapid chloride permeability index, and carbonation rate were examined. Results showed that the alkali-activated slag cementitious has superior durability. The trends of influences on the composites properties for these three mixture variables are similar to those for the ordinary Portland cement concrete. It means that the experiences for making the ordinary Portland cement concrete should be able to be used for the alkali-activated slag cementitious. This paper also provides a lot of data for the alkali-activated slag cementitious for future development of the mix design.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Temperature Modeling of AISI 1045 Steel during Surface Hardening Processes
by
Tsung-Pin Hung, Hao-En Shi and Jao-Hwa Kuang
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 5964
Abstract
A Coupled thermo-mechanical finite element model was employed to simulate the possible effects of varying laser scanning parameters on the surface hardening process for AISI 1045 and AISI 4140 steels. We took advantage of the high-power density of laser beams to heat the
[...] Read more.
A Coupled thermo-mechanical finite element model was employed to simulate the possible effects of varying laser scanning parameters on the surface hardening process for AISI 1045 and AISI 4140 steels. We took advantage of the high-power density of laser beams to heat the surface of workpieces quickly to achieve self-quenching effects. The finite element model, along with the temperature-dependent material properties, was applied to characterize the possible quenching and tempering effects during single-track laser surface heat treatment. We verified the accuracy of the proposed model through experiments. The effects of laser surface hardening parameters, such as power variation, scanning speed, and laser spot size, on the surface temperature distribution, hardening width, and hardening depth variations during the single-track surface laser treatment process, were investigated using the proposed model. The analysis results show that laser power and scanning speed are the key parameters that affect the hardening of the material. The numerical results reveal that the proposed finite element model is able to simulate the laser surface heat treatment process and tempering effect of steel.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures