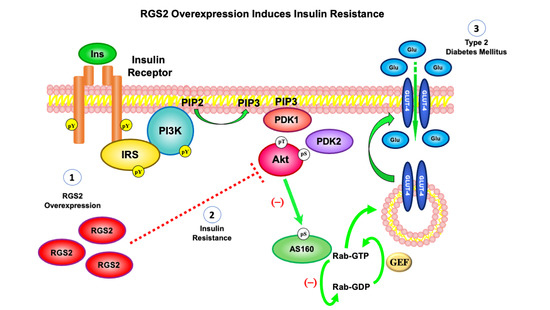
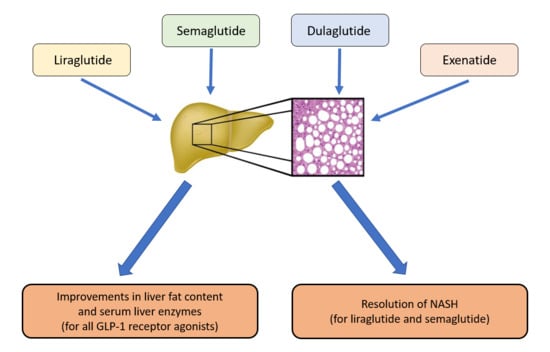
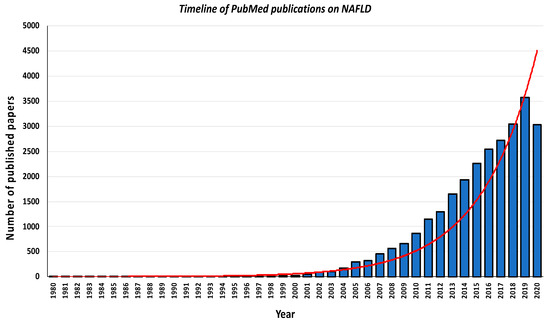
Insulin Resistance in the 2020's
A topical collection in Metabolites (ISSN 2218-1989). This collection belongs to the section "Endocrinology and Clinical Metabolic Research".
Viewed by 27421Editor
2. Formerly Professor of Internal Medicine, School of Specialization of Allergology and Clinical Immunology, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, 41121 Modena, Italy
Interests: NAFLD-MAFLD; cirrhosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; metabolic syndrome; insulin resistance; sex differences
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Insulin resistance (IR) is defined as the impaired intracellular signaling of endogenous and exogenous insulin. IR is a major key player in those metabolic derangements that characterize physiological states (e.g., puberty and pregnancy) and pathological conditions (e.g., diabesity and metabolic syndrome). In particular, IR is a key determinant of a wide-ranging spectrum of diseases spanning cardio-nephro-metabolic disorders to the end-stage failure of such vital organs as the heart, the kidney and the liver, and also certain types of cancer such as, for example, gastrointestinal and breast cancers.
The obesogenic world in which a large part of the human population resides is a recognized facilitator of IR development and progression. However, genetic traits may predispose to the specific array of complications and manifestations that typically characterize patients. Therefore, owing to its epidemiological and clinical burden, IR is an attractive topic both in basic and clinical research. Interest in molecular mechanisms, translational approaches and strong interdisciplinarity characterize IR research, which brings together investigator-driven studies as well as industry-sponsored investigations.
The aim of this Topic Collection is to publish high-quality review and research papers in IR. We make a call for well-written review articles and original papers spanning the areas of glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, obesity, cardiovascular and fatty liver disease. The scope of this Topic Collection includes, but is not limited to: homeostatic model assessment, insulin sensitivity, Type 2 diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, oxidative stress, inflammation, beta cell function and hepatic steatosis.
Dr. Amedeo Lonardo
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Metabolites is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- abdominal obesity
- adipokines
- adipose tissue
- adiposopathy
- aldosteronism
- Alzheimer’s disease
- android obesity
- apolipoprotein
- androgens
- arterial hypertension
- atherogenic dyslipidemia
- atherosclerosis
- beta cell function
- beta cell secretion
- bile acids
- biomarkers
- body mass index
- cancer
- cardiovascular disease
- cell biology
- childhood obesity
- chronic kidney disease
- cardiovascular risk
- coronary artery disease
- COVID-19
- diabetes
- diabetic foot
- diagnosis
- dyslipidemia
- drug management
- endoplasmic reticulum stress
- estrogens
- extracellular vesicles
- fertility
- genetics
- geriatric medicine
- gestational diabetes
- glp-1 receptor agonists
- glucose (in)tolerance
- glucose homeostasis
- glucose metabolism
- glucose transport
- gut microbiota
- growth hormone
- hepatic steatosis
- hepatokines
- high-fat diet
- histology
- HIV
- homeostatic model assessment (HOMA)
- hyperadrenalism
- hypercortisolism
- hyperinsulinemia
- imaging techniques
- insulin-like growth factor
- insulin resistance
- insulin receptor
- insulin sensitivity
- insulin signaling
- insulin secretion
- insulin sensitizers
- lifestyle
- lipid metabolism
- lipotoxicity
- metabolic syndrome
- metformin
- molecular biology
- natural history
- nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- oxidative stress
- pediatric medicine
- peripheral artery disease
- personalized medicine
- polycystic ovary syndrome
- prediabetes
- randomized clinical trial
- SARS-CoV-2
- type 2 diabetes
- peroxisome proliferator
- protein kinase
- sex differences
- skeletal muscle
- thiazolidinediones
- thyroid
- viral hepatitis