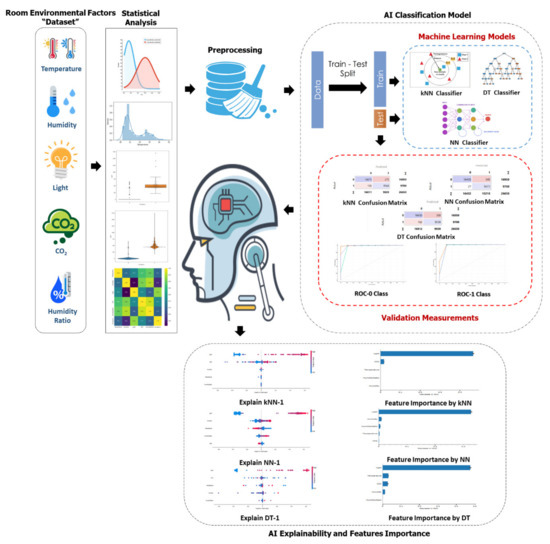
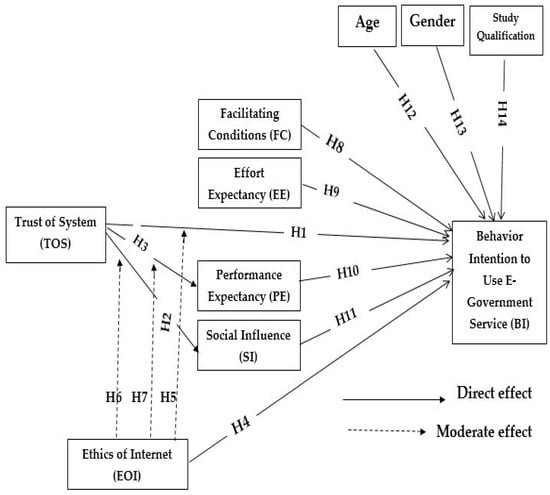
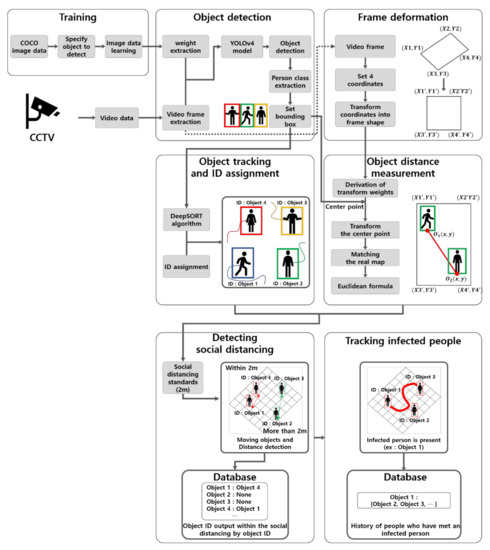
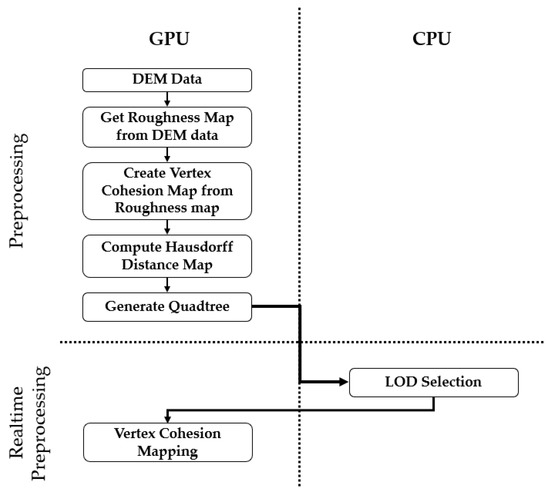
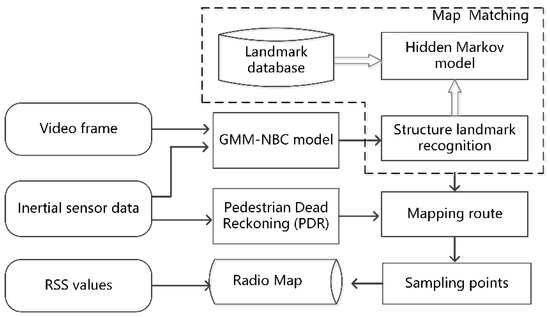
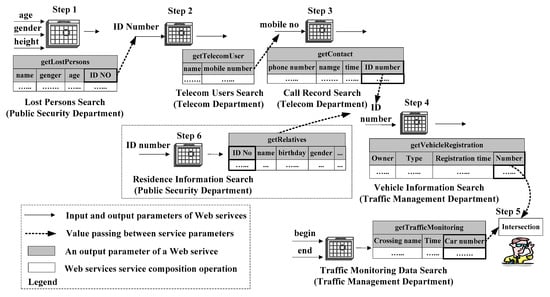
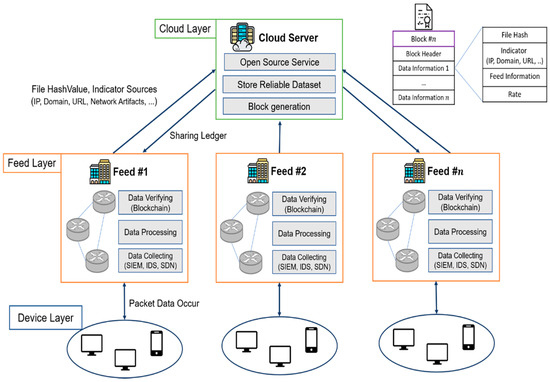
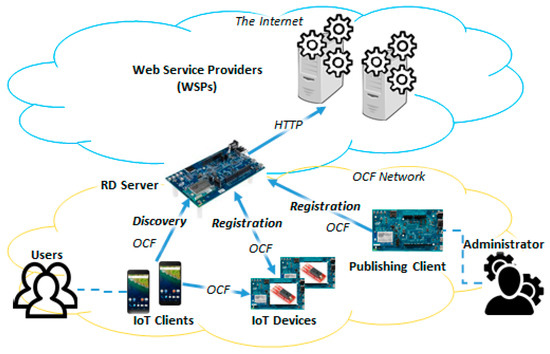
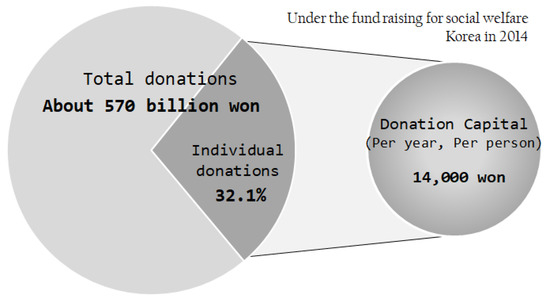
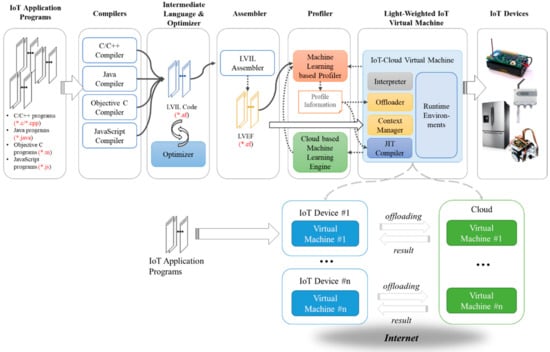
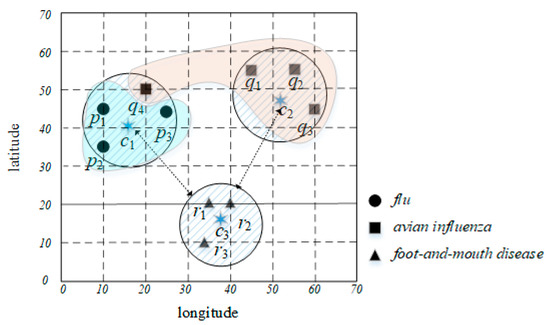
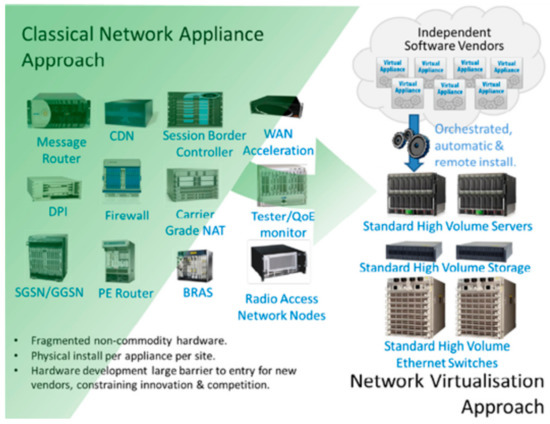
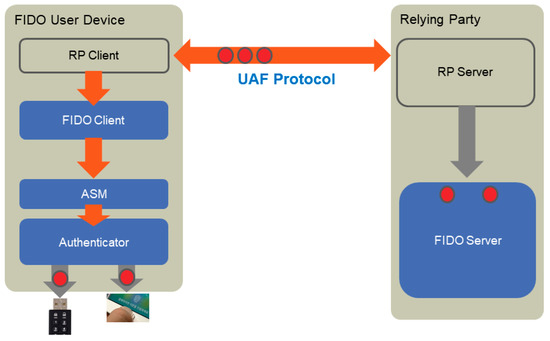
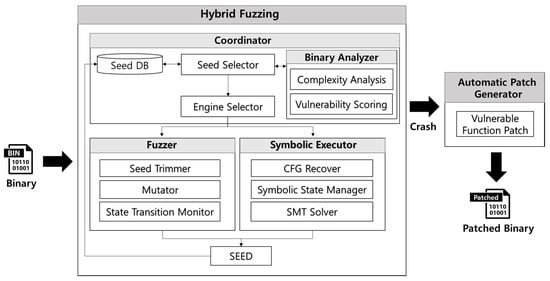
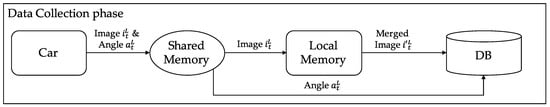
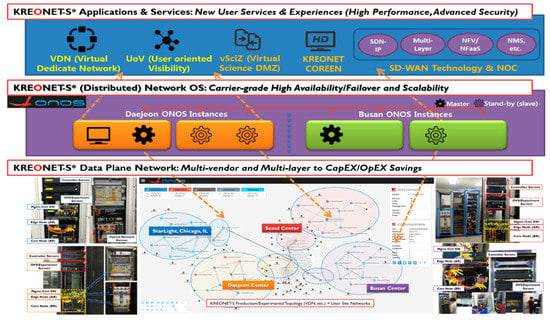
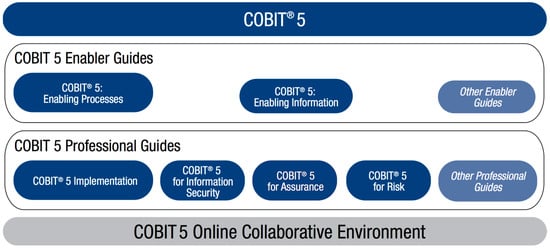
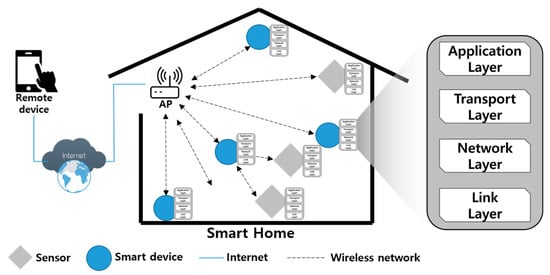
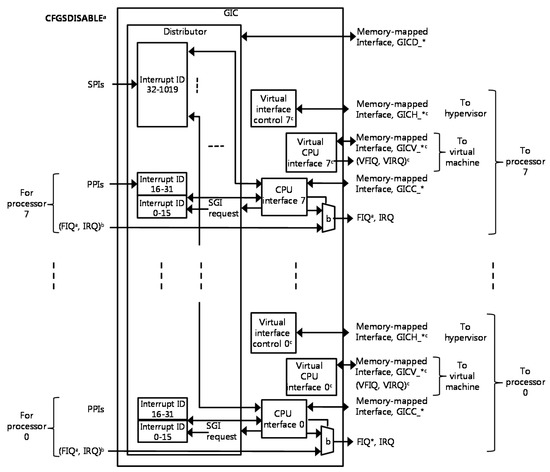
Advanced IT based Future Sustainable Computing
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050).
Viewed by 175663Editor
Interests: IoT; human-centric ubiquitous computing; information security; digital forensics; vehicular cloud computing; multimedia computing
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Future Sustainability Computing (FSC) is a principle that embraces a range of policies, procedures, programs, and attitudes that run the length and breadth of any uses of information technologies for abundant life. It must address sustainability problems in different computing and information processing environments and technologies. Solutions for these problems, information processing, integration, utilization, aggregation, and generation, can call upon a wide range of algorithmic and computational frameworks within cloud, cluster and mobile computing, such as optimization, machine learning, dynamical systems, prediction and control, decision support systems, and meta-heuristics, security and safety, and so on.
This Topical Collection covers pure research and applications within the novel scopes related to sustainability computing, such as smart devices, cloud storage organization, data transfer in new communication environment, software and information processing, and efficient algorithmic information distribution/processing. In addition, it is dealing with hardware/software technologies, new frameworks and architectures, efficient modeling-simulation, specific mathematical models, and designs on theories for the future sustainability computing are recommended.
All submitted papers will be peer-reviewed and selected on the basis of both their quality and their relevance to the theme of this topical collection. This Topical Collection solicits innovative ideas and solutions in all aspects around the future sustainable computing for advanced information technology. Topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Theoretical and algorithms aspect of energy in FSC
- New paradigm software, middleware and systems in FSC
- Energy-efficient communication protocols in FSC
- Optimization, machine learning, prediction and control, decision support systems for FSC
- Smart networking and real-time systems in FSC
- Management in memory, disk, storage and other peripheral devices with cloud computing
- Monitoring and visualization methodologies and tools in FSC
- Ecosystem for FSC
- Security and safety for FSC
- Wearable computing in FSC
- Sustainable information technologies for governance
- Other sustainable systems and applications for FSC
Prof. Dr. James Park
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- energy-efficient
- optimization and control
- green cloud
- ecosystem
- smart networking
- security and safety
- monitoring