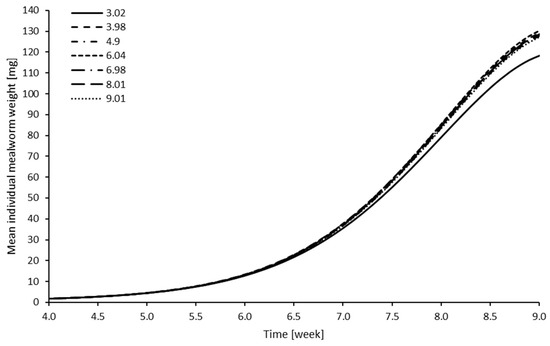
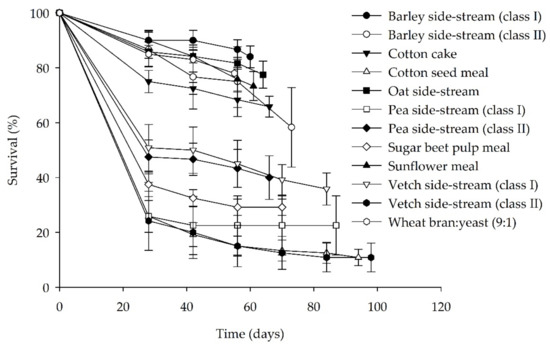
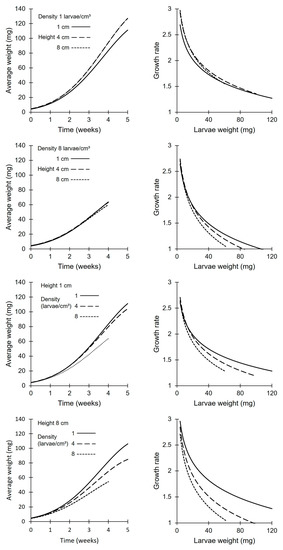
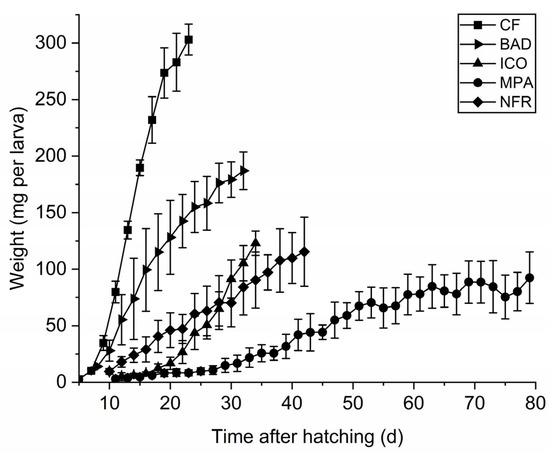
Sustainable Insect Farming: Feed the Future
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Agriculture".
Viewed by 61315Editors
Interests: stored-product insects; post-harvest entomology; integrated plant protection; edible insects; insect farming; insects as food and feed
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: food science; edible insects; sustainable farming systems; insects as food and feed
Interests: pheromones and semiochemicals; insect parasitoids; population ecology; sampling and trapping; invasive biology; integrated pest management; microbial control; chemical control; non-chemical control; stored-product protection
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
During the last decade, we all have witnessed tremendous scientific interest in the exploitation of insects as food and feed, which has been aligned with a concomitant impressive commercial growth of the insect sector. To highlight the milestones in this ongoing process, in 2017, the EU approved the inclusion of insect protein in aquafeeds, and at the beginning of this year, EFSA released its affirmative opinion on the safety of dried yellow mealworms for human consumption. Moreover, the green light for the expansion of the use of insects to the poultry and swine industry at the EU level is expected to be given soon. Similar advances regarding the utilization of insects as a protein source are occurring worldwide.
One of the main advantages of insect farming that pours water over the mill of insect exploitation is its sustainability profile. In contrast to other agricultural systems that rely on intensification and external inputs, insect farming avoids the overexploitation of natural resources (e.g., land, water, etc.), and the use of organic side-streams as insect feed contributes to the sustainable management of biowastes.
In this context, the focus of this Topical Collection is on recent advances in sustainable insect production related to (but not limited to):
- Insect-rearing technologies and methods (diet formulations, rearing protocols, etc.);
- The inclusion of insects in animal diets and aquafeeds (feeding trials, etc.);
- Environmental footprints;
- Insect-based food and feed products (insect processing, nutritional value, etc.);
- Economic and business aspects (marketing, etc.);
- Waste management through insect bioconversion;
- Insect–plant synergies for complete protein design in food and feed;
- Novel uses of insects and their products/byproducts (fertilizers, etc.);
- Public perception and consumers’ acceptance of the use of insects for food and feed;
- Lifecycle assessment (LCA), social LCA (SLCA), and technoeconomic assessment (TEA).
Therefore, we kindly invite you to submit papers to this Topical Collection that will further illuminate and unfold the potential of insect exploitation.
Dr. Christos I. Rumbos
Mr. János-István Petrusán
Prof. Dr. Christos G. Athanassiou
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- insects as food and feed
- sustainability
- insect farming
- circular economy
- alternative nutrient source
- waste management
- new protein sources
- entomophagy