Effect of Diatomaceous Biosilica and Talc on the Properties of Dielectric Elastomer Based Composites
Abstract
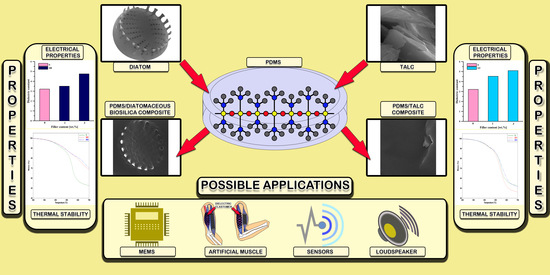
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Formation of Composites
2.3. Characterization Methods of Obtained Composites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Obtained Composites Using SEM and AFM
3.2. Determining Thermal Properties by Means of Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Dielectric Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bar-Cohen, Y.; Zhang, Q. Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Sensors. MRS Bull. 2016, 33, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamal, E.M.A.; Joy, P.A.; Kurian, P.; Anantharaman, M.R. On the magnetic and dielectric properties of nickel-neoprene nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.I.; Brown, R.N.C.; Kempel, L.C.; Kofinas, P. Controlled synthesis of core-shell iron-silica nanoparticles and their magneto-dielectric properties in polymer composites. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kofod, G.; Risse, S.; Stoyanov, H.; McCarthy, D.N.; Sokolov, S.; Kraehnert, R. Broad-spectrum enhancement of polymer composite dielectric constant at ultralow volume fractions of silica-supported copper nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiubianu, G.; Bele, A.; Cazacu, M.; Racles, C.; Vlad, S.; Ignat, M. Dielectric silicone elastomers with mixed ceramic nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 71, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpi, F.; De Rossi, D. Improvement of electromechanical actuating performances of a silicone dielectric elastomer by dispersion of titanium dioxide powder. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romasanta, L.J.; Leret, P.; Casaban, L.; Hernández, M.; De La Rubia, M.A.; Fernández, J.F.; Kenny, J.M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. Towards materials with enhanced electro-mechanical response: CaCu 3Ti4O12-polydimethylsiloxane composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24705–24712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.Z.; Ohlan, P.; Saini, S.K. Study on the Thermal and Dielectric Properties of SrTiO3/Epoxy Nanocomposites. Energies 2017, 10, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewicki, J.P.; Liggat, J.J.; Hayward, D.; Pethrick, R.A.; Patel, M. Degradative thermal analysis and dielectric spectroscopy studies of aging in polysiloxane nanocomposites. ACS Symp. Ser. 2009, 1004, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Lu, H.; Song, L. Morphology, thermal, and mechanical properties of flame-retardant silicone rubber/montmorillonite nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 3275–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hag, A.H.; Simon, L.C.; Jayaram, S.H.; Cherney, E.A. Physicochemical properties of silica filled silicone rubber nanocomposites. Annu. Rep. Conf. Electr. Insul. Dielectr. Phenomena CEIDP 2004, 1, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Drum, R.W. The Chemical Basis of Diatom Morphogenesis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1994, 150, 243–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Seibert, M. Prospects for commercial production of diatoms. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popovich, C.A.; Pistonesi, M.; Hegel, P.; Constenla, D.; Bielsa, G.B.; Martín, L.A.; Damiani, M.C.; Leonardi, P.I. Unconventional alternative biofuels: Quality assessment of biodiesel and its blends from marine diatom Navicula cincta. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Nelson, D.R.; Mystikou, A.; Daakour, S.; Salehi-Ashtiani, K. Advances in microalgal research and engineering development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 59, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Pomastowski, P.; Hornowska, M.; Król, A.; Rafińska, K.; Buszewski, B. Naturally organic functionalized 3D biosilica from diatom microalgae. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Somasundaran, P. Adsorption and conformation of carboxymethyl cellulose at solid-liquid interfaces using spectroscopic, AFM and allied techniques. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 291, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, W. Flotation Behavior of Malachite Using Hydrophobic Talc Nanoparticles as Collectors. Minerals 2020, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirak, A.; Yilmaz, H.; Güler, S.; Güler, Ç. Dielectric properties and electric conductivity of talc and doped talc. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöne, J.; Kotter, I.; Grellmann, W. Properties of Polypropylene Talc Compounds with different talc particle size and loading. J. Plast. Technol. 2012, 8, 231–251. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, E.A.; Edlund, M.B.; Spaulding, S.A. Description and ultrastructure of araphid diatom species (Bacillariophyceae) morphologically similar to Pseudostaurosira elliptica (Schumann) Edlund et al. Phycol. Res. 2010, 58, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.P.; Sprynskyy, M.; Brzozowska, W.; Lisowska-Oleksiak, A. Electrochemical behavior of a composite material containing 3D-structured diatom biosilica. Algal Res. 2019, 41, 101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnay, C.; Lagerge, S.; Partyka, S. Assessment of the surface heterogeneity of talc materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 233, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kee, D. De Mass Transport Through PDMS/Clay Nanocomposite Membranes. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 85, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segad, M.; Jönsson, B.; Cabane, B. Tactoid formation in montmorillonite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25425–25433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.S. PDMS-silica composite membranes with silane coupling for propylene separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 344, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewnik, E.; Garman, K.; Piechota, G.; Czerwiński, W. Thermal properties of nanocomposites based on polyethylene and n-heptaquinolinum modified montmorillonite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 110, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.T.; Biefeld, R.M.; Sayre, J.A. High-temperature electrical conductivity and thermal decomposition of Sylgard® 184 and mixtures containing hollow microspherical fillers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1984, 24, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulym, I.; Klonos, P.; Borysenko, M.; Pissis, P.; Gun’ko, V.M. Dielectric and thermal studies of segmental dynamics in silica/PDMS and silica/titania/PDMS nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, n/a-n/a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Zhou, N.L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Shen, J. Synthesis and antifungal activities of polymer/montmorillonite-terbinafine hydrochloride nanocomposite films. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuram, E. Hybridization effect of talc/glass fiber as a filler in polycarbonate/acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 173, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bele, A.; Cazacu, M.; Stiubianu, G.; Vlad, S.; Ignat, M. Polydimethylsiloxane-barium titanate composites: Preparation and evaluation of the morphology, moisture, thermal, mechanical and dielectric behavior. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, N.; Zhou, N.L. Synthesis and properties of PDMS/montmorillonite-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-heparin films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Shim, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Joo, J.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Influence of clay modification on the reinforcement of vinyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane networks. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.L.Q.A.; Romero, R.B.; do Gonçalves, M.C.; Yoshida, I.V.P. High molar mass silicone rubber reinforced with montmorillonite clay masterbatches: Morphology and mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, T. Crystallization behavior of poly(ε-caprolactone)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.L.G.; Aziz, A.W. Dielectric behaviour and ultrasonic absorption of aged butyl rubber loaded with white fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1993, 41, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romasanta, L.J.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. Increasing the performance of dielectric elastomer actuators: A review from the materials perspective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 188–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, G.; Yu, B.; Zhang, X. The Research of Conductivity and Dielectric Properties of ZnO/LDPE Composites with Different Particles Size. Materials 2020, 13, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.J. Interfaces are the dominant feature of dielectrics at the nanometric level. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2004, 11, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Lv, S.; Guo, Z. Fabrication of PDA@SiO2@rGO/PDMS dielectric elastomer composites with good electromechanical properties. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 154, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkarat, M.; Lanagan, M.; Ghosh, D.; Lottes, A.; Budd, K.; Rajagopalan, R. High field dielectric properties of clay filled silicone rubber composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | Rq (nm) | Ra (nm) | Rmax (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 1.15 | 1.43 | 11.3 |
| SB1 | 1.29 | 1.62 | 12.3 |
| SB3 | 1.41 | 1.68 | 12.2 |
| ST1 | 1.31 | 1.68 | 12.3 |
| ST3 | 2.23 | 2.70 | 19.7 |
| Sample | Temperature (°C) at Mass Loss | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 30% | 50% | |
| S | 457.3 | 551.9 | - |
| SB1 | 479.7 | 683.1 | - |
| SB3 | 477.2 | 700.1 | - |
| ST1 | 459.2 | 542.0 | 616.9 |
| ST3 | 464.6 | 563.9 | - |
| Sample | Frequency (Hz) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 | |||||
| φ | φ | φ | φ | |||||
| S | 3.2771 | 0.0052 | 3.214 | 0.0170 | 3.120 | 0.0170 | 3.056 | 0.0100 |
| ST1 | 4.5292 | 0.0061 | 4.529 | 0.0001 | 4.514 | 0.0001 | 4.501 | 0.0010 |
| ST3 | 5.0962 | 0.0031 | 5.096 | 0.0001 | 5.065 | 0.0001 | 5.038 | 0.0001 |
| SB1 | 3.5453 | 0.0082 | 3.508 | 0.0080 | 3.481 | 0.0011 | 3.466 | 0.0001 |
| SB3 | 4.6314 | 0.0012 | 4.752 | 0.0010 | 4.746 | 0.0010 | 4.734 | 0.0010 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Brzozowska, W.; Adamczyk, A.; Gierszewska, M.; Wojtczak, I.; Sprynskyy, M. Effect of Diatomaceous Biosilica and Talc on the Properties of Dielectric Elastomer Based Composites. Energies 2020, 13, 5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215828
Olewnik-Kruszkowska E, Brzozowska W, Adamczyk A, Gierszewska M, Wojtczak I, Sprynskyy M. Effect of Diatomaceous Biosilica and Talc on the Properties of Dielectric Elastomer Based Composites. Energies. 2020; 13(21):5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215828
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlewnik-Kruszkowska, Ewa, Weronika Brzozowska, Arkadiusz Adamczyk, Magdalena Gierszewska, Izabela Wojtczak, and Myroslav Sprynskyy. 2020. "Effect of Diatomaceous Biosilica and Talc on the Properties of Dielectric Elastomer Based Composites" Energies 13, no. 21: 5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215828
APA StyleOlewnik-Kruszkowska, E., Brzozowska, W., Adamczyk, A., Gierszewska, M., Wojtczak, I., & Sprynskyy, M. (2020). Effect of Diatomaceous Biosilica and Talc on the Properties of Dielectric Elastomer Based Composites. Energies, 13(21), 5828. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215828