Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Source and Process
2.2. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.3. Ballistic Tests
2.4. Fracture Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
3.2. Ballistic Tests
3.3. Cost Comparison
4. Summary and Conclusions
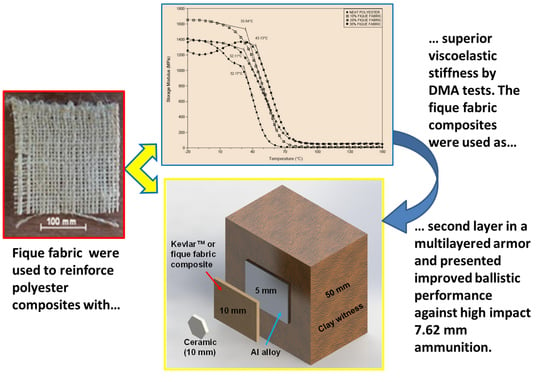
- The introduction of fique fabric raises the viscoelastic stiffness level and tends to shift the curves of the storage modulus (E′) to higher temperatures. This leads to a delay in the onset of the thermal softening of the composite. The peak α of the loss modulus (E″) is also shifted to higher glass transition temperatures (Tg), indicating less mobility in the polyester resin chains of the matrix by interaction with the fique fabric. The maximum in tan δ curves, associated with end of Tg, suffers not only a reduction in its amplitude but also a shift towards higher temperatures with the introduction of fique fabric. Hence, a high attenuation of internal vibration and increase in Tg occur with an increasing amount of fique fabric in the polyester matrix.
- A multilayered armor system (MAS), in which conventional Kevlar™ was replaced by a polyester matrix composite reinforced with 10 or 20 vol % of fique fabric as second layers, attended the NIJ trauma limit after ballistic tests with 7.62 mm ammunition. The depth of penetration into 20 vol % fique fabric composite, 15 mm, demonstrated this composite to be more efficient than conventional Kevlar™ with 23 mm as a second MAS layer.
- More than ballistic performance, the significantly lower cost in association with the environmental and societal benefits of using a natural material favor the substitution of fique fabric composite as an MAS second layer. As an economical advantage, armor vests with fique fabric composites would be 13 times cheaper than similar ones made with Kevlar™.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Sustainable Bio-Composites from Renewable Resources: Opportunities and Challenges in the Green Materials World. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netravali, A.N.; Chabba, S. Composites get greener. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, J. Natural materials innovative natural composites. Mater. Technol. 2008, 2–3, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Lopes, F.P.D.; Ferreira, A.S.; Nascimento, D.C.O. Natural-fiber polymer-matrix composites: Cheaper, tougher, and environmentally friendly. JOM 2009, 61, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, K.G.; Arizaga, G.G.; Wypych, F. Biodegradable composites based on lignocellulosic fibers—An overview. Prog. Polym Sci. 2009, 34, 982–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Lopes, F.P.D.; Barbosa, A.P.; Bevitori, A.B.; Silva, I.L.A.; Costa, L.L. Natural lignocellulosic fibers as engineering materials—An overview. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2963–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1555–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K.; Gupta, R.K. Review: Raw natural fiber-based polymer composites. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2014, 19, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, A.; Patil, V.; Mahindrakar, A.; Haque, R.; Thakur, V.K. Advances in industrial prospective of cellulosic macromolecules enriched banana biofibre resources: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.K.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Pappu, A. Synthesis and applications of biodegradable soy based graft copolymers: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, O.; Monteiro, S.N.; Moura, E.A.B.; Drelich, J.W. Re-emerging field of lignocellulosic fiber-polymer composites and ionizing radiation technology in their formulation. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 702–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, A.; Saxena, M.; Thakur, V.K.; Sahrma, A.; Haque, R. Facile extraction, processing and characterization of biorenewable sisal fibers for multifunctional applications. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2016, 53, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, K.L.; Efendy, M.G.A.; Le, T.M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappu, A.; Thakur, V.K. Towards sustainable micro and nano composites from fly ash and natural fibers for multifunctional applications. Vacuum 2017, 146, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, I.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibers: Can they replace glass in fiber reinforced plastics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Milanezi, T.L.; Louro, L.H.L.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Braga, F.O.; Gomes, A.V.; Drelich, J.W. Novel ballistic ramie fabric composite competing with Kevlar-fabric in multilayered armor. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbery, J.; Houston, D. Natural-fiber-reinforced polymer composites in automotive applications. JOM 2006, 58, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zah, R.; Hischier, R.; Leão, A.L.; Braun, I. Curauá fibers in the automobile industry—A sustainability assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Paul, S.A.; Pothan, L.A.; Deepa, B. Natural Fibers: Structure, Properties and Applications. In Cellulose Fibers: Bio- and Nano-Polymer Composites, 1st ed.; Kalia, S., Kaith, B.S., Kaur, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca, E.; Prifti, J.; Betheney, W.; Chou, S.C. Ballistic impact damage of S2-glass-reinforced plastic structural armor. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 58, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.M.; Paciornik, S.; d’Almeida, J.R.M. Evaluation of the damaged area of glass-fiber-reinforced epoxy-matrix composite materials submitted to ballistic impacts. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosur, M.V.; Vaidya, U.K.; Ulven, C.; Jeelani, S. Performance of stitched/unstitched woven carbon/epoxy composites under high velocity impact loading. Compos. Struct. 2004, 64, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Wetzel, E.D.; Wagner, N.J. The ballistic impact characteristic of Kevlar® woven fabrics impregnated with a colloidal shear thickening fluid. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.J.N.; Van Dingenen, J.L.J. Ballistic protection mechanisms in personal armor. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.L.; Song, J.W.; Ward, J.E. Failure of Spectra® polyethylene fiber-reinforced composites under ballistic impact loading. Compos. Mater. 1994, 28, 1202–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morye, S.S.; Hine, P.J.; Duckett, R.A.; Carr, D.J.; Ward, I.M. Modeling of the energy absorption by polymer composites upon ballistic impact. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 2631–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohen, L.A.; Margem, F.M.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Araujo, B.M.; Lima, E.S. Ballistic efficiency of an individual epoxy composite reinforced with sisal fibers in multilayered armor. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Louro, L.H.L.; Trindade, W.; Elias, C.N.; Ferreira, C.L.; Lima, E.S.; Weber, R.P.; Suarez, J.M.; Figueiredo, A.B.S.; Pinheiro, W.A.; et al. Natural curaua fiber-reinforced composites in multilayered ballistic armor. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 4567–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.B.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Monteiro, S.N.; Louro, L.H.L. Giant bamboo fiber reinforced epoxy composite in multilayered ballistic armor. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Luz, F.S.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N. Ballistic test of multilayered armor with intermediate epoxy composite reinforced with jute fabric. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Braga, F.O.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Louro, L.H.L.; Drelich, J.W. Promising curaua fiber-reinforced polyester composite for high-impact ballistic multilayered armor. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 57, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Holanda, L.I.F.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Gomes, A.V.; Lima, E.P., Jr. Natural Mallow Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composite for Ballistic Armor Against Class III-A Ammunition. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 4425–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gañan, P.; Mondragon, I. Surface modification of fique fibers. Effect on their physico-mechanical properties. Polym. Compos. 2002, 23, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gañan, P.; Mondragon, I.J. Thermal and degradation behaviour of fique fiber reinforced thermoplastic matrix composites. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 73, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altoe, G.R.; Netto, P.A.; Barcelos, M.; Gomes, A.; Margem, F.M.; Monteiro, S.N. Bending mechanical behavior of polyester matrix reinforced with fique fiber. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals and Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Altoe, G.R.; Netto, P.A.; Teles, M.C.A.; Daniel, G.; Margem, F.M.; Monteiro, S.N. Tensile strength of polyester composites reinforced with fique fibers. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals and Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Altoe, G.R.; Netto, P.A.; Teles, M.C.A.; Borges, L.G.X.; Margem, F.M.; Monteiro, S.N. Tensile strength of epoxy composites reinforced with fique fibers. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals and Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, P.A.; Altoe, G.R.; Margem, F.M.; Braga, F.O.; Monteiro, S.N.; Margem, I.M. Correlation between the Density and the Diameter of Fique Fibers. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 869, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Calado, V.; Rodriguez, R.J.S.; Margem, F.M.J. Thermogravimetric stability of polymer composites reinforced with less common lignocellulosic fibers—An overview. Mater. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrate, S. Ballistic Impact on Composite Structures, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdemirci, A.; Tunusoglu, G.; Guden, M. The effect of the interlayer on the ballistic performance of ceramic/composite armors: Experimental and numerical study. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalusuraman, G.; Siva, I.; Winowlin Jappes, J.T.; Gao, X.-Z.; Amico, S.C. Fibre loading effects on dynamic mechanical properties of compression moulded luffa fibre polyester composites. Int. J. Comput. Aided Eng. Technol. 2018, 10, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Verma, S.K.; Nayak, S.K. Dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of MAPE treated jute/HDPE composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.S.; Junior, E.P.L.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N. Ballistic Test of Multilayered Armor with Intermediate Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Jute Fabric. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedovski, E. Ballistic performance of armor ceramics: Influence of design and structure. Part 2. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Louro, L.H.L.; Silva, L.C.; Drelich, J.W. Unlocking function of aramid fibers in multilayered ballistic armor. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D., Jr.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 9th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 911–915. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, O.F.; Torres, L.M.; Roja, J.C. Definition of a Prospective Agenda for Investigation in the Productive Agroindustrial Chain of Fique from Technological Intelligence Systems (in Spanish), 2009. Available online: http://www.bdigital.unal.edu.co/2078/1/2009__Agenda_Fique.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento (CONAB-2017). 2017. Available online: http://sisdep.conab.gov.br/precosiagroweb/ (accessed on 6 December 2017). (In Portuguese)







| Intermediate Layer Material | Depth of Penetration (mm) |
|---|---|
| 10 vol % fique fabric | 17 ± 3 |
| 20 vol % fique fabric | 15 ± 3 |
| Kevlar™ | 23 ± 3 [45] |
| Composite Material | Cost (US$/Kg) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 64.8 vol % aramid laminate/epoxy | 49.59 | [48] |
| 72 vol % glass fiber/epoxy | 18.06 | [48] |
| 30 vol % sisal fiber/polyester | 3.23 | [49] |
| 30 vol % jute fiber/polyester | 3.24 | [50] |
| 30 vol % curaua fiber/polyester | 3.19 | [50] |
| 30 vol % piassava fiber/polyester | 3.21 | [50] |
| 20 vol % fique fabric/polyester | 3.61 | Present Work |
| 30 vol % fique fabric/polyester | 3.26 | Present Work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves Monteiro, S.; Salgado de Assis, F.; Ferreira, C.L.; Tonini Simonassi, N.; Pondé Weber, R.; Souza Oliveira, M.; Colorado, H.A.; Camposo Pereira, A. Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030246
Neves Monteiro S, Salgado de Assis F, Ferreira CL, Tonini Simonassi N, Pondé Weber R, Souza Oliveira M, Colorado HA, Camposo Pereira A. Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030246
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves Monteiro, Sergio, Foluke Salgado de Assis, Carlos Luiz Ferreira, Noan Tonini Simonassi, Ricardo Pondé Weber, Michelle Souza Oliveira, Henry A. Colorado, and Artur Camposo Pereira. 2018. "Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites" Polymers 10, no. 3: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030246
APA StyleNeves Monteiro, S., Salgado de Assis, F., Ferreira, C. L., Tonini Simonassi, N., Pondé Weber, R., Souza Oliveira, M., Colorado, H. A., & Camposo Pereira, A. (2018). Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites. Polymers, 10(3), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030246