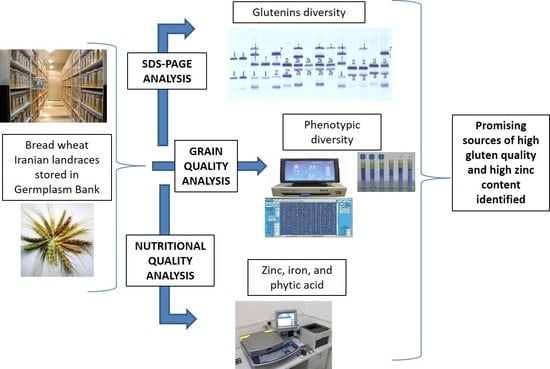
Variability for Glutenins, Gluten Quality, Iron, Zinc and Phytic Acid in a Set of One Hundred and Fifty-Eight Common Wheat Landraces from Iran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Grain Quality Parameters
2.3. Glutenins Composition (SDS-PAGE)
2.4. Nutritional Quality Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Grain Quality Parameters Variation
3.2. HMWGs and LMWGs Variability
3.3. Effects of Glutenin Alleles on Gluten Quality
3.4. Micronutrients and Phytic Acid Content
3.5. Pearson Correlation among Quality Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peña-Bautista, R.J.; Hernandez-Espinosa, N.; Jones, J.M.; Guzmán, C.; Braun, H.J. CIMMYT Series on Carbohydrates, Wheat, Grains, and Health: Wheat-Based Foods: Their Global and Regional Importance in the Food Supply, Nutrition, and Health. Cereal Foods World 2017, 62, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R. Wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1537–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrigley, C.; Batey, I.; Skylas, D.; Sharp, P. (Eds.) Gliadin and Glutenin: The Unique Balance of Wheat Quality; AACCI Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jurowski, K.; Szewczyk, B.; Nowak, G.; Piekoszewski, W. Biological consequences of zinc deficiency in the pathomechanisms of selected diseases. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eagling, T.; Wawer, A.A.; Shewry, P.R.; Zhao, F.; Fairweather-tait, S.J. Iron bioavailability in two commercial cultivars of wheat: Comparison between wholegrain and white flour and the effects of nicotianamine and 2′-deoxymugineic acid on iron uptake into Caco-2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10320–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.; Velu, G. Zinc-biofortified wheat: Harnessing genetic diversity for improved nutritional quality. Sci. Br. Biofortification 2017, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The Second Report on the State of the World’s Animal Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture; Scherf, B.D., Pilling, D., Eds.; FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture Assessments: Rome, Italy, 2015; ISBN 9789251065341. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, J.B.; Guzmán, C. Interspecific and intergeneric hybridization as a source of variation for wheat grain quality improvement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed.; AACC: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pena, R.J.; Amaya, A.; Rajaram, S.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A. Variation in quality characteristics associated with some spring 1B/1R translocation wheats. J. Cereal Sci. 1990, 12, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Espinosa, N.; Payne, T.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Cervantes, F.; Gonzalez-Santoyo, H.; Ammar, K.; Guzmán, C. Preliminary characterization for grain quality traits and high and low molecular weight glutenins subunits composition of durum wheat landraces from Iran and Mexico. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 88, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.A.; Morel, M.H.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Branlard, G.; Metakovsky, E.V.; Redaelli, R. Proposal for combining the classification systems of alleles of Gli-1 and Glu-3 loci in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Genet. Breed. 1996, 50, 321–336. [Google Scholar]
- Branlard, G.; Dardevet, M.; Amiour, N.; Igrejas, G. Allelic diversity of HMW and LMW glutenin subunits and omega-gliadins in French bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2003, 50, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallanes-López, A.M.; Hernandez-Espinosa, N.; Velu, G.; Posadas-Romano, G.; Ordoñez-Villegas, V.M.G.; Crossa, J.; Ammar, K.; Guzmán, C. Variability in iron, zinc and phytic acid content in a worldwide collection of commercial durum wheat cultivars and the effect of reduced irrigation on these traits. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Li, Q.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Hsam, S.L.K.; Zeller, F.J. Genetic diversity of European spelt wheat (Triticum aestivum ssp. spelta L. em. Thell.) revealed by glutenin subunit variations at the Glu-1 and Glu-3 loci. Euphytica 2005, 146, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.B.; Guzmán, C. Recovery of wheat heritage for traditional food: Genetic variation for high molecular weight glutenin subunits in neglected/underutilized wheat. Agronomy 2019, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chegdali, Y.; Ouabbou, H.; Essamadi, A.; Cervantes, F.; Ibba, M.I.; Guzmán, C. Assessment of the Glutenin Subunits Diversity in a Durum Wheat (T. turgidum ssp. durum) Collection from Morocco. Agronomy 2020, 10, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdouh, A.; Khelifi, D.; Carrillo, J.M.; Nieto-Taladriz, M.T. The high and low molecular weight glutenin subunit polymorphism of Algerian durum wheat landraces and old cultivars. Plant. Breed. 2005, 124, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.S.; Khan, K.; Klindworth, D.L.; Nygard, G. Evaluation and characterization of high-molecular weight 1D glutenin subunits from Aegilops tauschii in synthetic hexaploid wheats. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrells, M.E.; Barbosa, J.; Nachit, M.M.; Ketata, H.; Autrique, E. Relationships among 81 Durum Genotypes Based RFLPs, Gliadins, Parentage, and Quality Traits; Options Méditerranéennes: Zaragoza, Spain, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, P.; Franco, J.; Burgueño-Ferreira, J.; Li, H.; Sehgal, D.; Saint Pierre, C.; Ortiz, C.; Sneller, C.; Tattaris, M.; Guzman, C.; et al. Unlocking the genetic diversity of Creole wheats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, H.; Bihamta, M.R.; Mohammadi, V.; Peyghambari, S.A.; Bai, G.; Zhang, G. Genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) revealed molecular genetic diversity of Iranian wheat landraces and cultivars. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Espinosa, N.; Mondal, S.; Autrique, E.; Gonzalez-Santoyo, H.; Crossa, J.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Singh, R.P.; Guzmán, C. Milling, processing and end-use quality traits of CIMMYT spring bread wheat germplasm under drought and heat stress. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 215, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallanes-López, A.M.; Ammar, K.; Morales-Dorantes, A.; González-Santoyo, H.; Crossa, J.; Guzmán, C. Grain quality traits of commercial durum wheat varieties and their relationships with drought stress and glutenins composition. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; Mondal, S.; Govindan, V.; Autrique, J.E.; Posadas-Romano, G.; Cervantes, F.; Crossa, J.; Vargas, M.; Singh, R.P.; Peña, R.J. Use of rapid tests to predict quality traits of CIMMYT bread wheat genotypes grown under different environments. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; Autrique, J.E.; Mondal, S.; Singh, R.P.; Govindan, V.; Morales-Dorantes, A.; Posadas-Romano, G.; Crossa, J.; Ammar, K.; Peña, R.J. Response to drought and heat stress on wheat quality, with special emphasis on bread-making quality, in durum wheat. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 186, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahraei, S.; Saidi, A.; Alizadeh, D. High molecular weight glutenin subunits of current bread wheats grown in Iran. Euphytica 2004, 137, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparzadeh, N.; Sofalian, O.; Javanmard, A.; Hejazi, M.S.; Zarandi, L. Study of glutenin subunits in some wheat landraces from northwest of Iran by SDS-PAGE technique. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2008, 10, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Velu, G.; Guzman, C.; Mondal, S.; Autrique, J.E.; Huerta, J.; Singh, R.P. Effect of drought and elevated temperature on grain zinc and iron concentrations in CIMMYT spring wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokten, K.; Akcura, M. Mineral concentrations of grain of bread wheat landraces originated from eastern Anatolia of Turkey. Prog. Nutr. 2018, 20, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, B.; Padash, S.; Dadkhodaie, A. Variations in micronutrients, bread quality and agronomic traits of wheat landrace varieties and commercial cultivars. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2016, 10, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.F.; Chacón, E.A.; Carrillo, J.M.; Benavente, E. Grain mineral density of bread and durum wheat landraces from geochemically diverse native soils. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2018, 69, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, C.; Medina-Larque, A.S.; Velu, G.; Gonzalez-Santoyo, H.; Singh, R.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Pena, R.J. Use of wheat genetic resources to develop biofortified wheat with enhanced grain zinc and iron concentrations and desirable processing quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Gangoliya, S.S.; Singh, N.K. Screening and characterization of wheat germplasms for phytic acid and iron content. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Maqsood, M.; Miller, L. Bioavailable zinc in grains of bread wheat varieties of Pakistan. Cereal Res. Commun. 2012, 40, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IZiNCG. Assessment of the Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Populations and Options for Its Control; United Nations University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; ISSN 0379-5721. [Google Scholar]
- Hurrell, R.; Egli, I. Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1461S–1467S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Iranian Landraces | Local Check (cv. Sokoll) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | Values | |
| Test weight (kg/hL) | 76.1 | 67.1–81.5 | 76.4 |
| Thousand kernel weight (g) | 44.7 | 32.4–58.3 | 49.4 |
| Grain protein (%) | 15.7 | 13.4–18.9 | 13.5 |
| SDS Sedimentation (mL) | 17.9 | 9.5–23.5 | 14.5 |
| SDS Sedimentation index | 1.14 | 0.61–1.60 | 1.07 |
| Grain zinc (mg/kg) | 43.6 | 27.9–65.0 | 37.9 |
| Grain iron (mg/kg) | 38.6 | 30.2–52.1 | 33.9 |
| Grain phytic acid (g/100 g) | 0.808 | 0.491–1.342 | 0.766 |
| Phytic acid:zinc molar ratio | 18.4 | 10.4–27.1 | 20.0 |
| Phytic acid:iron molar ratio | 17.8 | 9.8–29.8 | 19.1 |
| Glutenin | Locus | Allele | N. of Accessions | % of Accessions | GPRO (%) | SDSS (mL) | SDSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMWGs | Glu-A1 | 1 (a) | 4 | 2.5 | 15.0 | 20.4 | 1.37 |
| 2* (b) | 65 | 41.1 | 16.0 | 18.6 | 1.17 | ||
| null (c) | 88 | 55.7 | 15.6 | 17.3 | 1.11 | ||
| 2.1+ (bb) | 1 | 0.6 | 16.9 | 19.5 | 1.15 | ||
| Glu-B1 | 7 + 8 (b) | 135 | 85.4 | 15.8 | 17.5 | 1.11 | |
| 7 + 9 (c) | 6 | 3.7 | 15.8 | 18.7 | 1.18 | ||
| 6 + 8 (d) | 2 | 1.2 | 17.8 | 23.0 | 1.29 | ||
| 20 + 20 (e) | 1 | 0.6 | 14.5 | 14.5 | 1.00 | ||
| 17 + 18(i) | 7 | 4.4 | 14.9 | 20.5 | 1.38 | ||
| 14* + 15* (bj) | 1 | 0.6 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 0.94 | ||
| 7 + 22 (ch) | 2 | 1.2 | 15.3 | 22.5 | 1.48 | ||
| 14* (cp) | 3 | 1.8 | 14.5 | 22.7 | 1.57 | ||
| 7 + 33 (cq) | 1 | 0.6 | 16.6 | 21.0 | 1.27 | ||
| Glu-D1 | 2 + 12 (a) | 129 | 81.6 | 15.7 | 17.6 | 1.12 | |
| 3 + 12 (b) | 10 | 6.3 | 16.7 | 20.5 | 1.23 | ||
| 5 + 10 (d) | 3 | 1.8 | 15.6 | 19.7 | 1.27 | ||
| 12 (l) | 1 | 0.6 | 15.4 | 11.0 | 0.71 | ||
| 2.1 + 10.1 (v) | 8 | 5.0 | 14.7 | 19.3 | 1.31 | ||
| 2+ + 12 (bx) | 1 | 0.6 | 15.6 | 18.0 | 1.15 | ||
| 2+ + 12+ (by) | 1 | 0.6 | 17.3 | 15.5 | 0.90 | ||
| LMWGs | Glu-A3 | a | 1 | 0.6 | 14.4 | 23.0 | 1.60 |
| b | 6 | 3.8 | 15.7 | 21.8 | 1.40 | ||
| c | 95 | 60.1 | 15.7 | 18.2 | 1.16 | ||
| d | 1 | 0.6 | 16.3 | 21.0 | 1.29 | ||
| e | 42 | 26.5 | 16.2 | 17.2 | 1.06 | ||
| f | 8 | 5.0 | 14.9 | 13.9 | 0.93 | ||
| g | 5 | 3.1 | 14.4 | 19.6 | 1.36 | ||
| Glu-B3 | b | 21 | 13.2 | 15.8 | 16.9 | 1.07 | |
| b’ | 8 | 5.0 | 15.8 | 18.4 | 1.16 | ||
| c | 52 | 32.9 | 15.8 | 17.7 | 1.13 | ||
| d | 16 | 10.1 | 15.2 | 18.2 | 1.21 | ||
| g | 43 | 27.2 | 15.9 | 18.6 | 1.17 | ||
| i | 14 | 8.8 | 15.6 | 18.5 | 1.19 | ||
| j | 4 | 2.5 | 16.3 | 15.9 | 0.98 | ||
| Glu-D3 | a | 98 | 62.0 | 15.7 | 17.6 | 1.13 | |
| b | 44 | 27.8 | 16.1 | 19.8 | 1.23 | ||
| c | 16 | 10.1 | 15.3 | 15.0 | 0.98 | ||
| Total average | 15.7 | 17.9 | 1.14 | ||||
| TW | TKW | GPC | SDSS | SDSI | ZnC | FeC | PhyC | Phy:Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TKW | −0.10 | ||||||||
| GPC | −0.39 | −0.21 | |||||||
| SDSS | 0.28 | −0.33 | 0.10 | ||||||
| SDSI | 0.38 | −0.27 | −0.20 | 0.95 | |||||
| ZnC | −0.17 | 0.07 | 0.45 | −0.08 | −0.22 | ||||
| FeC | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.37 | |||
| PhyC | −0.19 | 0.09 | 0.46 | −0.13 | −0.27 | 0.57 | 0.13 | ||
| Phy:Zn | −0.08 | 0.05 | 0.11 | −0.10 | −0.13 | −0.25 | −0.19 | 0.64 | |
| Phy:Fe | −0.28 | 0.07 | 0.35 | −0.22 | −0.31 | 0.39 | −0.31 | 0.90 | 0.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maryami, Z.; Huertas-García, A.B.; Azimi, M.R.; Hernández-Espinosa, N.; Payne, T.; Cervantes, F.; Govindan, V.; Ibba, M.I.; Guzman, C. Variability for Glutenins, Gluten Quality, Iron, Zinc and Phytic Acid in a Set of One Hundred and Fifty-Eight Common Wheat Landraces from Iran. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111797
Maryami Z, Huertas-García AB, Azimi MR, Hernández-Espinosa N, Payne T, Cervantes F, Govindan V, Ibba MI, Guzman C. Variability for Glutenins, Gluten Quality, Iron, Zinc and Phytic Acid in a Set of One Hundred and Fifty-Eight Common Wheat Landraces from Iran. Agronomy. 2020; 10(11):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111797
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaryami, Zahra, Ana Belén Huertas-García, Mohammad Reza Azimi, Nayelli Hernández-Espinosa, Thomas Payne, Fausto Cervantes, Velu Govindan, Maria Itria Ibba, and Carlos Guzman. 2020. "Variability for Glutenins, Gluten Quality, Iron, Zinc and Phytic Acid in a Set of One Hundred and Fifty-Eight Common Wheat Landraces from Iran" Agronomy 10, no. 11: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111797
APA StyleMaryami, Z., Huertas-García, A. B., Azimi, M. R., Hernández-Espinosa, N., Payne, T., Cervantes, F., Govindan, V., Ibba, M. I., & Guzman, C. (2020). Variability for Glutenins, Gluten Quality, Iron, Zinc and Phytic Acid in a Set of One Hundred and Fifty-Eight Common Wheat Landraces from Iran. Agronomy, 10(11), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111797