Graphene Oxide–Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
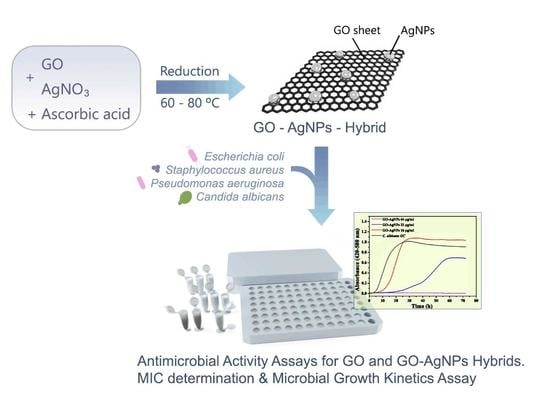
2.2. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide (GO) and Graphene Oxide–Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids (GO–AgNPs)
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. FTIR Analysis
2.3.2. UV–vis Analysis
2.3.3. XPS Analysis
2.3.4. Raman Analysis
2.3.5. XRD Analysis
2.3.6. TEM Analysis
2.3.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.4. Microbial Strains and Culture
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity Assays for GO and GO–AgNP Nanohybrids. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
2.6. Microbial Growth Kinetics Assay in the Presence of GO–AgNP Nanohybrids
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. Structure and Morphology
FTIR Analysis
UV-Vis Analysis
XPS Analysis
Raman Analysis
XRD Analysis
TEM
3.1.2. Thermal Stability
3.1.3. Antimicrobial Activity Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faramarzi, M.A.; Sadighi, A. Insights into biogenic and chemical production of inorganic nanomaterials and nanostructures. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2013, 189−190, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.; Tripathy, S.K.; Poinern, G.E.J. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials 2015, 8, 7278–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Dias, H.V.R.; Kharisov, B.I.; Perez, B.O.; Pérez, V.M.J. The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, A.; Piperno, A.; Hada, A.; Astilean, S.; Vulpoi, A.; Ginestra, G.; Marino, A.; Nostro, A.; Zammuto, V.; Gugliandolo, C. Marine bacterial exopolymers-mediated green synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Núñez, Y.A.R.; Castro, R.I.; Arenas, F.A.; Lopez-Cabaña, Z.E.; Carreño, G.; Carrasco-Sanchez, V.; Marican, A.; Villaseñor, J.; Vargas, E.; Santos, L.S.; et al. Preparation of hydrogel/silver nanohybrids mediated by tunable-size silver nanoparticles for potential antibacterial applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C.W. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramirez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, P. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 360, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.R.; Sarma, R.K.; Saikia, R.; Kale, V.S.; Shelke, M.V.; Sengupta, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension of graphene oxide sheets and its antimicrobial activity. Colloid Surf. B 2011, 83, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.R.; Sarma, R.K.; Borah, S.; Kumari, R.; Saikia, R.; Deshmukh, A.B.; Shelke, M.V.; Sengupta, P.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. The synthesis of citrate-modified silver nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension of graphene oxide nanosheets and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 105, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Shi, M.; Li, N.; Yan, B.; Ma, H.; Hu, Y.; Ye, M. Facile synthesis and application of Ag-chemically converted graphene nanocomposite. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chook, S.W.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Ayob, M.K.; Chee, K.L.; Huang, N.M.; Neoh, H.M.; Lim, H.N.; Jamal, R.; Rahman, R.M.F.R.A. Antibacterial performance of Ag nanoparticles and AgGO nanocomposites prepared via rapid microwave-assisted synthesis method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Yong, Y.; Zhao, X.S. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial properties of silver-modified graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Cheng, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Peng, R. Graphene oxide−silver nanocomposite as a highly effective antibacterial agent with species-specific mechanisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 3867–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca de Faria, A.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Meira, S.M.M.; Mazarin de Moraes, A.C.; Brandelli, A.; Souza Filho, A.G.; Alves, O.L. Anti-adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 113, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, L. Green synthesis of graphene/Ag nanocomposites. App. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lin, M.; Tan, S.; Mai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X. The use of polyethyleneimine-modified reduced graphene oxide as a substrate for silver nanoparticles to produce a material with lower cytotoxicity and long-term antibacterial activity. Carbon 2012, 50, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, R.; Gupta, S.; Srivastava, A.K. A facile and novel synthesis of Ag–graphene-based nanocomposites. Small 2009, 5, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.S.; Hui, K.N.; Dinh, D.A.; Tsang, C.H.; Cho, Y.R.; Zhou, W.; Hong, X.; Chun, H.H. Green synthesis of dimension-controlled silver nanoparticle-graphene oxide with in situ ultrasonication. Acta Mater. 2014, 64, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shi, M.; Yan, B.; Ma, H.; Li, N.; Ye, M. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of Ag-reduced graphene oxide composite with ionic liquid. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7795–7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.A.; Chen, Y.J.; Tai, N.H. Fast Process to decorate silver nanoparticles on carbon nanomaterials for preparing high-performance flexible transparent conductive films. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8433–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayán-Varela, M.; Fernández-Merino, M.J.; Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Guardia, L.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Highly efficient silver-assisted reduction of graphene oxide dispersions at room temperature: Mechanism, and catalytic and electrochemical performance of the resulting hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7295–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Metal nanoparticles supported on two-dimensional graphenes as heterogeneous catalysts. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2016, 312, 99–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kuang, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles–graphene oxidenanocomposite and its application in electrochemical sensing of tryptophan. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Xu, D.; Zhan, C.; Liang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, H.; Ma, X. Surfactant-free synthesis of graphene oxide coated silver nanoparticles for SERS biosensing and intracellular drug delivery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2748–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vi, T.T.T.; Kumar, S.R.; Rout, B.; Liu, C.; Wong, C.; Chang, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. The preparation of graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites: The effect of silver loads on Gram-positive and Gram-negative antibacterial activities. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matharu, R.K.; Ciric, L.; Edirisinghe, M. Nanocomposites: Suitable alternatives as antimicrobial agents. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 282001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alenezi, H.; Cam, M.; Edirisinghe, M. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the fluid behavior during polymeric fiber formation with and without pressure. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 041401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, R.K.; Porwal, H.; Ciric, L.; Edirisinghe, M. The effect of graphene-poly(methyl methacrylate) fibres on microbial growth. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20170058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burdusel, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoanta, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: An up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobos, M.; González, B.; Fernández, M.J.; Fernández, M.D. Chitosan–graphene oxide nanocomposites: Effect of graphene oxide nanosheets and glycerol plasticizer on thermal and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanoff, D.D., Jr.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C. Ag/graphene heterostructures: Synthesis, characterization and optical properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 8, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Särkkä, H.; Sillanpää, M. Bioprospective of Sorbus aucuparia leaf extract in development of silver and gold nanocolloids. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 80, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W. Study on synthesis and antibacterial properties of AgNPs/GO nanocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2016, 5685967. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Environmentally friendly, one-pot synthesis of ag nanoparticle decorated reduced graphene oxide composites and their application to photocurrent generation. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 4742–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.C.; Chen, W.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Xiong, S.X.; Yu, A.B. Role of temperature in the growth of silver nanoparticles through a synergetic reduction approach. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, J. Effect of temperature on the size of biosynthesized silver nanoparticle: Deep insight into microscopic kinetics analysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 23, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Bakar, M.A. Health care-associated infections—An overview. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quindós, G.; Marcos-Arias, C.; San Millán, R.; Mateo, E.; Eraso, E. The continuous changes in the aetiology and epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: From the familiar Candida albicans to multiresistant Candida Auris. Int. Microbiol. 2018, 21, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Schwebke, I.; Kampf, G. How long do nosocomial pathogens persist on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review. BMC. Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laupland, K.B.; Lyytikainen, O.; Sogaard, M.; Kennedy, K.J.; Knudsen, J.D.; Ostergaard, C.; Galbraith, J.C.; Valiquette, L.; Jacobsson, G.; Collignon, P.; et al. The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection: A multinational population-based surveillance study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spadafino, J.T.; Cohen, B.; Liu, J.; Larson, E. Temporal trends and risk factors for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in adults with catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2014, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazeli, H.; Akbari, R.; Moghim, S.; Narimani, T.; Arabestani, M.R.; Ghoddousi, A.R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in patients, hospital means, and personnel’s specimens. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2012, 17, 332–337. [Google Scholar]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Bischoff, T.; Tallent, S.M.; Seifert, H.; Wenzel, R.P.; Edmond, M.B. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, O.N.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Wang, B.; Brown, N.A.; Luo, P.G.; McNamara, N.D.; Vangsness, M.; Sun, Y.P.; Bunker, C.E. Graphene oxide: A nonspecific enhancer of cellular growth. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8100–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, B.; Zhao, R.; Guan, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Chai, Z.; Feng, W. Graphene oxide as an anaerobic membrane scaffold for the enhancement of B. adolescentis proliferation and antagonistic effects against pathogens E. coli and S. aureus. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 165101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Peng, C.; Luo, W.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. Graphene-based antibacterial paper. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, F.; Fonseca de Faria, A.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial properties of graphene oxide nanosheets: Why size matters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7226–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, M.; Zeng, T.H.; Wu, R.; Jiang, R.; Wei, J.; Wang, L.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Lateral dimension-dependent antibacterial activity of graphene oxide sheets. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12364–12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.D.; Lin, M.; Mustapha, A. Toxicity of graphene oxide on intestinal bacteria and caco-2 cells. J. Food Protect. 2015, 78, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhi, X.; Wang, K.; Cui, D. The antifungal activity of graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thani, R.F.; Patan, N.K.; Al-Maadeed, M.A. Graphene oxide as antimicrobial against two Gram-positive and two Gram-negative bacteria in addition to one fungus. OnLine J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 14, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of the antimicrobial activities of graphene materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Esfandiar, A. Wrapping bacteria by graphene nanosheets for isolation from environment, reactivation by sonication, and inactivation by near-infrared irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 6279–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.-H. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hui, L.; Piao, J.-G.; Auletta, J.; Hu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Meyer, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, L. Availability of the basal planes of graphene oxide determines whether it is antibacterial. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13183–13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusev, A.; Zakharova, O.; Muratov, D.S.; Vorobeva, N.S.; Sarker, M.; Rybkin, I.; Bratashov, D.; Kolesnikov, E.; Lapanje, A.; Kuznetsov, D.V.; et al. Medium-dependent antibacterial properties and bacterial filtration ability of reduced graphene oxide. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theophel, K.; Schacht, V.J.; Schlüter, M.; Schnell, S.; Stingu, C.S.; Schaumann, R.; Bunge, M. The importance of growth kinetic analysis in determining bacterial susceptibility against antibiotics and silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Lei, B.; Chen, W. Facile fabrication of graphene oxide loaded with silver nanoparticles as antifungal materials. Mater. Res. Express 2014, 1, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jung, A.; Gielerak, G.; Biernat, J.; Jaremek, H.; Łojkowski, W.; Woźniak, B.; Wojnarowicz, J.; et al. Graphene oxide-based nanocomposites decorated with silver nanoparticles as an antibacterial agent. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, W.; Liu, X.; Min, H.; Dong, G.; Feng, Q.; Zuo, S. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanocomposite. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 6966–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnejad, J.; Yazdian, F.; Omidi, M.; Rostami, A.D.; Rasekh, B.; Fathinia, A. Graphene oxide/silver nanohybrid: Optimization, antibacterial activity and its impregnation on bacterial cellulose as a potential wound dressing based on GO–Ag nanocomposite-coated BC. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Rong, K.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Size-dependent antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles against oral anaerobic pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Dai, G.; Wu, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panacek, A.; Kvıtek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolar, M.; Vecerova, R.; Pizurova, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevecna, T.; Zboril, R. Silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Niño-Martínez, N.; Martínez-Gutierrez, F.; Martínez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Su, M.; Ma, L.; Ma, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z. Preparation of graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle nanohybrids with highly antibacterial capability. Talanta 2013, 117, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Merino, M.J.; Guardia, L.; Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Developing green photochemical approaches towards the synthesis of carbon nanofiber-and graphene-supported silver nanoparticles and their use in the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 18323–18331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lok, C.N.; Ho, C.M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.Y.; Yu, W.Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.; Chiu, J.F.; Che, C.M. Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samberg, M.E.; Orndorff, P.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles of different sizes, surface conditions and synthesis methods. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5−100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, C.; Pradhan, A.; Pakstis, L.; Pochan, D.J.; Shah, S.I. Synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles. , J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Jee, S.-C.; Shinde, S.K.; Mistry, B.M.; Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Sung, J.-S.; Kadam, A.A. Green-synthesis of anisotropic peptone-silver nanoparticles and its potential application as anti-bacterial agent. Polymers 2019, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De-la-Pinta, I.; Cobos, M.; Ibarretxe, J.; Montoya, E.; Eraso, E.; Guraya, T.; Quindós, G. Effect of biomaterials hydrophobicity and roughness on biofilm development. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.; De-La-Pinta, I.; Quindós, G.; Fernández, M.J.; Fernández, M.D. One-step eco-friendly synthesized silver-graphene oxide/poly(vinylalcohol) antibacterial nanocomposites. Carbon 2019, 150, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.; Ullah, A.K.; Hossain, K.F.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visani de Luna, L.; Mazarin de Moraes, A.; Consonni, S. Comparative in vitro toxicity of a graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite and the pristine counterparts toward macrophages. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.W.; Gurunathan, S.; Jeong, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kwon, D.N.; Park, J.K.; Kim, J.H. Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Gong, F.; Huang, Y.; Tang, M. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by silver nanoparticles in human liver HepG2 cells in different dispersion media. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 36, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, M.; Park, H.S.; Shin, U.S.; Gong, M.S.; Kim, H.W. Size-dependent cellular toxicity of silver nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.C.; Seligy, V.L.; Massarsky, A.; Moon, T.W.; Rippstein, P.; Tan, J.; Tayabali, A.F. Comparison of toxicity of uncoated and coated silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 429, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, S.J.; Hosseinian, F.; Willmore, W.G. A Current Overview of the Biological and Cellular Effects of Nanosilver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 12, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, M.V.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; de la Fonteyne, L.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matteis, V.; Cascione, M.; Toma, C.C.; Leporatti, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthetic Routes, In vitro toxicity and theranostic applications for cancer disease. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.-H. Nanoparticle-Mediated Combination Therapy: Two-in-One Approach for Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavinkumar, T.; Varunkumar, K.; Ravikumar, V.; Manivannan, S. Anticancer activity of graphene oxide- reduced graphene oxide- silver nanoparticle composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Gurunathan, S.; Kim, J.H. Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite enhances cytotoxic and apoptotic potential of salinomycin in human ovarian cancer stem cells (OvCSCs): A novel approach for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Sample | Experimental Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Concentration of AgNO3 (mM) | |
| GO–AgNP-A | 60 | 1.50 |
| GO–AgNP-B | 60 | 2.00 |
| GO–AgNP-C | 80 | 1.50 |
| GO–AgNP-D | 80 | 2.00 |
| Material | D | G | 2D | D+G | 2G | ID/IG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm−1) | (cm−1) | (cm−1) | (cm−1) | (cm−1) | ||
| GO | 1353 | 1598 | 2741 | 2944 | 3181 | 0.83±0.02 |
| GO–AgNPs-A | 1345 | 1594 | 2712 | 2934 | 3176 | 1.03±0.01 |
| MIC (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Microorganism | GO | GO–AgNP-A |
| Escherichia coli | >128 | 64 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >128 | 64 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | >128 | 32 |
| Candida albicans | >128 | 32 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cobos, M.; De-La-Pinta, I.; Quindós, G.; Fernández, M.J.; Fernández, M.D. Graphene Oxide–Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020376
Cobos M, De-La-Pinta I, Quindós G, Fernández MJ, Fernández MD. Graphene Oxide–Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020376
Chicago/Turabian StyleCobos, Mónica, Iker De-La-Pinta, Guillermo Quindós, M. Jesús Fernández, and M. Dolores Fernández. 2020. "Graphene Oxide–Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020376
APA StyleCobos, M., De-La-Pinta, I., Quindós, G., Fernández, M. J., & Fernández, M. D. (2020). Graphene Oxide–Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020376