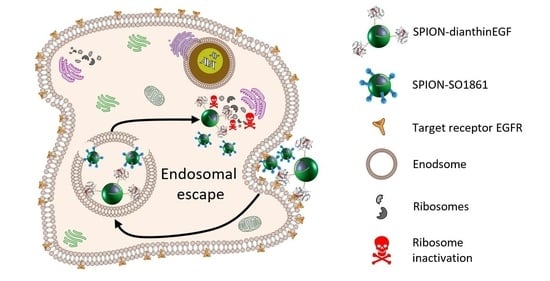
Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Dianthin Targeting for Controlled Drug Release Using the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. SPION Synthesis and APTES Modification
2.3. BCN Modification
2.4. Expression and Purification of Dia and DiaEGF
2.5. Modification of Dia and DiaEGF
2.6. Determination of Enzymatic Activity
2.7. RIP Conjugation to SPIONs (SPION-Dia, SPION-DiaEGF)
2.8. SO1861 Isolation
2.9. Synthesis of SPION-SO1861
2.10. Cell Culture
2.11. Characterization of SPIONs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Expression, Purification and Modification of Dia and DiaEGF
3.2. Characterization of Synthesized and RIP-Functionalized SPIONs
3.3. Synthesis of SPION-SO1861
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
3.5. Relaxivity Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastan, I.; Hassan, R.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Kreitman, R.J. Immunotoxin therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, O.M.; Rubinstein, I.; Onyuksel, H. Role of nanotechnology in targeted drug delivery and imaging: A concise review. Nanomedicine 2005, 1, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, C.L. Epidermal growth factor receptor dependence in human tumors: More than just expression? Oncologist 2002, 7 (Suppl. 4), 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, D.S.; Brandt, R.; Ciardiello, F.; Normanno, N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1995, 19, 183–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Soares, H.P.; Raez, L.E.; Singal, R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 2007, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, N.; FitzGerald, D. Immunotoxin Therapies for the Treatment of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent Cancers. Toxins 2016, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wykosky, J.; Fenton, T.; Furnari, F.; Cavenee, W.K. Therapeutic targeting of epidermal growth factor receptor in human cancer: Successes and limitations. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canton, I.; Battaglia, G. Endocytosis at the nanoscale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2718–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M.; Kaur, I.; Perugini, M.A.; Gupta, R.C. Ribosome-inactivating proteins: Current status and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Selby, L.I.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Such, G.K. The Endosomal Escape of Nanoparticles: Toward More Efficient Cellular Delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, C.; Dürkop, H.; Zhao, X.; Weng, A.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H. Targeted dianthin is a powerful toxin to treat pancreatic carcinoma when applied in combination with the glycosylated triterpene SO1861. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1527–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, H.; Niesler, N.; Trautner, A.; Sama, S.; Jerz, G.; Panjideh, H.; Weng, A. Glycosylated Triterpenoids as Endosomal Escape Enhancers in Targeted Tumor Therapies. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baluna, R.; Vitetta, E.S. Vascular leak syndrome: A side effect of immunotherapy. Immunopharmacology 1997, 37, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuus-Reichel, K.; Grauer, L.S.; Karavodin, L.M.; Knott, C.; Krusemeier, M.; Kay, N.E. Will immunogenicity limit the use, efficacy, and future development of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies? Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 1994, 1, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selbo, P.K.; Bostad, M.; Olsen, C.E.; Edwards, V.T.; Høgset, A.; Weyergang, A.; Berg, K. Photochemical internalisation, a minimally invasive strategy for light-controlled endosomal escape of cancer stem cell-targeting therapeutics. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 1433–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, D. Cell-penetrating peptides as noninvasive transmembrane vectors for the development of novel multifunctional drug-delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2016, 229, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, H.; Bachran, C.; Flavell, D. Diving through Membranes: Molecular Cunning to Enforce the Endosomal Escape of Antibody-Targeted Anti-Tumor Toxins. Antibodies 2013, 2, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ag Seleci, D.; Seleci, M.; Stahl, F.; Scheper, T. Tumor homing and penetrating peptide-conjugated niosomes as multi-drug carriers for tumor-targeted drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33378–33384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachran, C.; Bachran, S.; Sutherland, M.; Bachran, D.; Fuchs, H. Preclinical Studies of Saponins for Tumor Therapy. In Recent Advances in Medicinal Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, Choudhary, M.I., Perry, G., Eds.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2014; pp. 272–302. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, H.; Bachran, D.; Panjideh, H.; Schellmann, N.; Weng, A.; Melzig, M.F.; Sutherland, M.; Bachran, C. Saponins as tool for improved targeted tumor therapies. Curr. Drug Targets 2009, 10, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachran, C.; Bachran, S.; Sutherland, M.; Bachran, D.; Fuchs, H. Saponins in tumor therapy. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Mergel, K.; Thakur, M.; Mallinckrodt, B.; von Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H.; Weng, A. Real-time analysis of membrane permeabilizing effects of oleanane saponins. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2013, 21, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinckrodt, B.; von Thakur, M.; Weng, A.; Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Dürkop, H.; Brenner, W.; Lukas, M.; Beindorff, N.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H. Dianthin-EGF is an effective tumor targeted toxin in combination with saponins in a xenograft model for colon carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, A.; Thakur, M.; Beceren-Braun, F.; Bachran, D.; Bachran, C.; Riese, S.B.; Jenett-Siems, K.; Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H. The toxin component of targeted anti-tumor toxins determines their efficacy increase by saponins. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachran, C.; Weng, A.; Bachran, D.; Riese, S.B.; Schellmann, N.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H. The distribution of saponins in vivo affects their synergy with chimeric toxins against tumours expressing human epidermal growth factor receptors in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Liu, F.; Nasr, K.; Misra, P.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Design considerations for tumour-targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, D.; Hyeon, T. Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small 2013, 9, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrinet, P.; Bengele, H.H.; Bonnemain, B.; Dencausse, A.; Idee, J.-M.; Jacobs, P.M.; Lewis, J.M. Preclinical safety and pharmacokinetic profile of ferumoxtran-10, an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide magnetic resonance contrast agent. Investig. Radiol. 2006, 41, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsula, V.; Moskvin, M.; Dutz, S.; Horák, D. Size-dependent magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 88, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D. Enhancing endosomal escape for nanoparticle mediated siRNA delivery. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6415–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, V.; Frank, C.; Porsiel, J.C.; Zellmer, S.; Garnweitner, G.; Stosch, R. Step-by-step monitoring of a magnetic and SERS-active immunosensor assembly for purification and detection of tau protein. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e201960090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadian-Birjand, M.; Biglione, C.; Bergueiro, J.; Cappelletti, A.; Rahane, C.; Chate, G.; Khandare, J.; Klemke, B.; Strumia, M.C.; Calderón, M. Transferrin Decorated Thermoresponsive Nanogels as Magnetic Trap Devices for Circulating Tumor Cells. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Thakur, M.; Weise, C.; Dernedde, J.; Mallinckrodt, B.; von Fuchs, H.; Weng, A. Small structural differences of targeted anti-tumor toxins result in strong variation of protein expression. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 91, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Weng, A.; Trautner, A.; Weise, C.; Schmid, D.; Bhargava, C.; Niesler, N.; Wookey, P.J.; Fuchs, H.; Thakur, M. Combinatorial approach to increase efficacy of Cetuximab, Panitumumab and Trastuzumab by dianthin conjugation and co-application of SO1861. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Thakur, M.; Haussmann, K.; Niesler, N.; Bhargava, C.; Görick, C.; Fuchs, H.; Weng, A. Saponins from Saponaria officinalis L. Augment the Efficacy of a Rituximab-Immunotoxin. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balin-Gauthier, D.; Delord, J.-P.; Rochaix, P.; Mallard, V.; Thomas, F.; Hennebelle, I.; Bugat, R.; Canal, P.; Allal, C. In vivo and in vitro antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in combination with cetuximab in human colorectal tumor cell lines expressing different level of EGFR. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anido, J.; Matar, P.; Albanell, J.; Guzmán, M.; Rojo, F.; Arribas, J.; Averbuch, S.; Baselga, J. ZD1839, a specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces the formation of inactive EGFR/HER2 and EGFR/HER3 heterodimers and prevents heregulin signaling in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zarinwall, A.; Waniek, T.; Saadat, R.; Braun, U.; Sturm, H.; Garnweitner, G. Comprehensive Characterization of APTES Surface Modifications of Hydrous Boehmite Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2020. [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H. Dianthin and Its Potential in Targeted Tumor Therapies. Toxins 2019, 11, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, A. A novel adenine-releasing assay for ribosome-inactivating proteins. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1072, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masthoff, I.-C.; Kraken, M.; Mauch, D.; Menzel, D.; Munevar, J.A.; Baggio Saitovitch, E.; Litterst, F.J.; Garnweitner, G. Study of the growth process of magnetic nanoparticles obtained via the non-aqueous sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4705–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Vo, C.L.-N.; Kang, T.; Oh, E.; Lee, B.-J. New method and characterization of self-assembled gelatin-oleic nanoparticles using a desolvation method via carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC/NHS) reaction. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, S.; Gatalica, Z.; Wang, Z.-Y. Update on the molecular profile of the MDA-MB-453 cell line as a model for apocrine breast carcinoma studies. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachran, D.; Schneider, S.; Bachran, C.; Urban, R.; Weng, A.; Melzig, M.F.; Hoffmann, C.; Kaufmann, A.M.; Fuchs, H. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression affects the efficacy of the combined application of saponin and a targeted toxin on human cervical carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayne, A.S.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Kreitman, R.J.; Pastan, I. Immunotoxins for leukemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2470–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, J.E.; Chan, L.; Shieh, D.-B.; Gu, F.X. Iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer imaging and diagnostics. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhong, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Mao, H. Improving the magnetic resonance imaging contrast and detection methods with engineered magnetic nanoparticles. Theranostics 2012, 2, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohrer, M.; Bauer, H.; Mintorovitch, J.; Requardt, M.; Weinmann, H.-J. Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions at different magnetic field strengths. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| w/o SO1861/M | +SO1861/M | EF | +SPION-SO1861/M | EF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPION@APTES | >2 × 10−3 | 4.5 × 10−5 | – | 2.2 × 10−5 | – |
| SPION-BCN | >2 × 10−3 | – | – | – | – |
| SPION-Dia | 5.5 × 10−4 | 2.6 × 10−8 | 21,000 | 2.0 × 10−6 | 270 |
| SPION-DiaEGF | 1.3 × 10−5 | 4.0 × 10−10 | 33,000 | 7.5 × 10−9 | 1800 |
| Targeting Effect | 42 | 65 | – | 267 | – |
| Gain in Specificity | – | – | 1.6 | – | 6.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarinwall, A.; Asadian-Birjand, M.; Seleci, D.A.; Maurer, V.; Trautner, A.; Garnweitner, G.; Fuchs, H. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Dianthin Targeting for Controlled Drug Release Using the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041057
Zarinwall A, Asadian-Birjand M, Seleci DA, Maurer V, Trautner A, Garnweitner G, Fuchs H. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Dianthin Targeting for Controlled Drug Release Using the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041057
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarinwall, Ajmal, Mazdak Asadian-Birjand, Didem Ag Seleci, Viktor Maurer, Alexandra Trautner, Georg Garnweitner, and Hendrik Fuchs. 2021. "Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Dianthin Targeting for Controlled Drug Release Using the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041057
APA StyleZarinwall, A., Asadian-Birjand, M., Seleci, D. A., Maurer, V., Trautner, A., Garnweitner, G., & Fuchs, H. (2021). Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Dianthin Targeting for Controlled Drug Release Using the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041057