Bergenin from Bergenia Species Produces a Protective Response against Myocardial Infarction in Rats †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Rat Housing Conditions
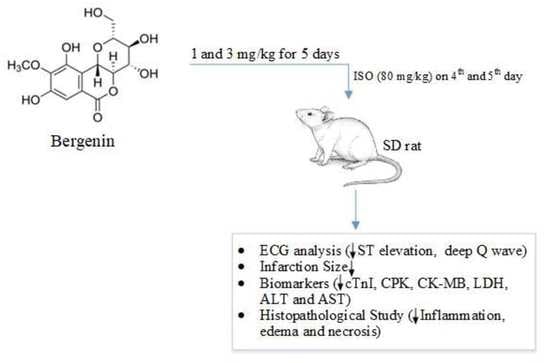
2.3. Cardioprotective Study
2.3.1. Response of Bergenin against the Isoproterenol-Induced MI in Rats
2.3.2. Analysis of Cardiac Biomarkers
2.3.3. Histopathological Study
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bergenin Response against Myocardial Injury Induced by Isoproterenol in Rats
3.1.1. Bergenin Prevented Changes in the ECG Pattern
3.1.2. Effect of Bergenin on Heart-To-Body-Weight Ratio, Structural Anatomy, and Infarct Size
3.1.3. Effect of Bergenin on Cardiac Biomarkers
3.1.4. Effect of Bergenin on Histopathological Variations Induced by ISO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kubler, W.; Haass, M. Cardioprotection: Definition, classification, and fundamental principles. Heart 1996, 75, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimokawa, H.; Yasuda, S. Myocardial ischemia: Current concepts and future perspectives. J. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egred, M.; Shaw, S.; Mohammad, B.; Waitt, P.; Rodrigues, E. Under-use of beta-blockers in patients with ischaemic heart disease and concomitant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2005, 98, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Gilani, A.-H. Studies on Blood Pressure Lowering, Vasodilator and Cardiac Suppressant Activities of Vitex Negundo: Involvement of K+ Channel Activation and Ca++ Channel Blockade. Available online: https://scialert.net/abstract/?doi=ijp.2015.137.142 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Shah, S.M.A.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Munir, N.; Rasool, G. Cardioprotective Potential of Plant-Derived Molecules: A Scientific and Medicinal Approach. Dose-Response 2019, 17, 1559325819852243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epure, A.; Pârvu, A.E.; Vlase, L.; Benedec, D.; Hanganu, D.; Gheldiu, A.-M.; Toma, V.A.; Oniga, I. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant, Cardioprotective and Nephroprotective Activity of Romanian Chicory Extract. Plants 2020, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Siddesha, J.M.; Urooj, A.; Vishwanath, B.S. Radical scavenging and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activities of standardized extracts of Ficus racemosa stem bark. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Rawat, A.K.S. A Comprehensive Review on Bergenin, a Potential Hepatoprotective and Antioxidative Phytocon-stituent. Herba Pol. 2008, 54, 66–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Makarova, M.N.; Makarov, V.G.; Wagner, H. Bergenia crassifolia (L.) Fritsch—Pharmacology and phytochemistry. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Pandey, N.; Agnihotri, V.; Singh, K.K.; Pandey, A. Antioxidant, antimicrobial activity and bioactive compounds of Bergenia ciliata Sternb.: A valuable medicinal herb of Sikkim Himalaya. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, K.; Sakai, K.; Uchida, M. Effects of bergenin on experimental ulcers—Prevention of stress induced ulcers in rats. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1980, 11, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Jang, D.S.; Jin, J.L.; Yun-Choi, H.S. Anti-Platelet Aggregating and Anti-Oxidative Activities of 11-O-(4′-O-Methylgalloyl)-bergenin, a New Compound Isolated from Crassulacv. ‘Himaturi’. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 776–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, U.; Barik, A.; Priyadarsini, K.I. Reactions of hydroxyl radical with bergenin, a natural poly phenol studied by pulse radiolysis. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6008–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.L.; De Oliveira, V.G.; Yano, T.; Nunomura, R.D.C.S. Antimicrobial activity of bergenin from Endopleura uchi (Huber) Cuatrec. Acta Amaz. 2009, 39, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Patel, D.K.; Prasad, S.K.; Laloo, D.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Hemalatha, S. Type 2 antidiabetic activity of bergenin from the roots of Caesalpinia digyna Rottler. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.-J.; Guo, M.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Wang, T.-C.; Cao, Y.-G.; Zhang, N.-S. Bergenin Plays an Anti-Inflammatory Role via the Modulation of MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in a Mouse Model of LPS-Induced Mastitis. Inflammation 2014, 38, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, G.A.; Araujo, A.K.; Pacheco, G.; Oliveira, A.P.; Carvalho, J.L.; Chaves, L.S.; Sousa, G.C.; Lopes, A.L.; Silva, P.C.; Leódido, A.C.M. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Bergenin in Mice. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 069–077. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xie, Y.-H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, S.-W.; Zhang, B.-L.; Wang, J.-B.; Cao, W.; Bi, L.-L.; Sun, J.-Y.; Miao, S.; et al. Cardioprotective Effect of Paeonol and Danshensu Combination on Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Injury in Rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahu, B.D.; Anubolu, H.; Koneru, M.; Kumar, J.M.; Kuncha, M.; Rachamalla, S.S.; Sistla, R. Cardioprotective effect of embelin on isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats: Possible involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2014, 107, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Lim, J.E.; Oh, A.B. Validation of Non-invasive Method for Electrocardiogram Recording in Mouse using Lead II. Biomed. Sci. Lett. 2015, 21, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Chini, N.; Fairchild, D.G.; Engle, S.K.; Reagan, W.J.; Summers, S.D.; Mirsalis, J.C. Evaluation of Cardiac Toxicity Biomarkers in Rats from Different Laboratories. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 44, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.-B.; Tian, S.; Yang, F.; Yang, H.-G.; Yang, X.-Y.; Du, G.-H. Cardioprotective effect of salvianolic acid A on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 615, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Gul, S.; Ze Jaafar, H.; Moga, M.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Dima, L. Anti-Platelet Effects of Nimesulide in Isopro-terenol-Induced Myocardial Ischaemia and Infarction in Rabbits. Acta Cardiol. 2015, 70, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Gao, M.; Kong, Y.; Shen, X.; Du, X.; Son, Y.-O.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Mo, X. Cardioprotective effect of total paeony glycosides against isoprenaline-induced myocardial ischemia in rats. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Li, X.; Cao, X. Cardioprotective Effects of Phenylethanoid Glycoside-rich Extract from Cistanche deserticola in Ischemia-Reperfusion–Induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 34, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Yan, L.; Iwatsubo, K.; Vatner, D.E.; Vatner, S.F. Modulation of β-adrenergic receptor signaling in heart failure and longevity: Targeting adenylyl cyclase type 5. Heart Fail. Rev. 2010, 15, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lucia, C.; Eguchi, A.; Koch, W.J. New Insights in Cardiac β-Adrenergic Signaling During Heart Failure and Aging. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wexler, B.C. Myocardial infarction in young vs old male rats: Pathophysiologic changes. Am. Heart J. 1978, 96, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhi, M.P.; White, F.N. The Electrocardiogram of the Normal and Hypertensive Rat. Circ. Res. 1960, 8, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajadurai, M.; Prince, P.S.M. Preventive effect of naringin on cardiac mitochondrial enzymes during isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats: A transmission electron microscopic study. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2007, 21, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antman, E.M.; Bassand, J.-P.; Klein, W.; Ohman, M.; Sendon, J.L.L.; Rydén, L.; Simoons, M.L.; Tendera, M. Myocardial infarction redefined—A consensus document of the joint european society of cardiology/american college of cardiology committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction: The Joint European Society of Cardiology/ American College of Cardiology Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suchalatha, S.; Devi, C.S.S. Protective effect of Terminalia chebula against experimental myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 42, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D.; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Circulation 2018, 138, e618–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.J.; Prince, P.S.M. Protective effects of sinapic acid on cardiac hypertrophy, dyslipidaemia and altered electrocardiogram in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 699, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Body, R.; McDowell, G.; Carley, S.; Wibberley, C.; Ferguson, J.; Mackway-Jones, K. A FABP-ulous ‘rule out’ strategy? Heart fatty acid binding protein and troponin for rapid exclusion of acute myocardial infarction. Resuscitation 2011, 82, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, A.; Hellgren, A.; Rafatnia, F.; Hammarsten, O.; Ljung, R.; Carlsson, A.C.; Holzmann, M.J. Investigations, findings, and follow-up in patients with chest pain and elevated high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T levels but no myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 232, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, R.; Stefanello, S.; Mauriz, J.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Soares, F. Creatine and the Liver: Metabolism and Possible Interactions. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, M.F.; Graham, S.M.; Baker, J.S.; Bickerstaff, G.F. Creatine-Kinase- and Exercise-Related Muscle Damage Implications for Muscle Performance and Recovery. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jnme/2012/960363/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Akila, P.; Vennila, L. Chlorogenic acid a dietary polyphenol attenuates isoproterenol induced myocardial oxidative stress in rat myocardium: An in vivo study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythili, S.; Malathi, N. Diagnostic markers of acute myocardial infarction. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wen, J.; Ming, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Correlation of Serum Alanine Aminotransferase and Aspartate Ami-notransferase with Coronary Heart Disease. Int J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 4399–4404. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore, N.; John, S.; Kale, M.; Bhatnagar, D. Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Enzymes in Isoproterenol In-duced Oxidative Stress in Rat Tissues. Pharmacol. Res. 1998, 38, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.L.; Stratman, F.W.; Lardy, H.A. Antioxidant enzyme systems in rat liver and skeletal muscle: Influences of Selenium Deficiency, Chronic Training, and Acute Exercise. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1988, 263, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hecker, J.G.; Chiamvimonvat, N. Antioxidant enzyme gene transfer for ischemic diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jani, S.; Shukla, V.J.; Harisha, C.R. Comparative pharmacognostical and phytochemical study on Bergenia ligulata Wall. and Ammania buccifera Linn. Ayu 2013, 34, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, S.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Verma, R.J. Antioxidative mechanism involved in the preventive efficacy of Bergenia ciliatarhizomes against experimental nephrolithiasis in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, D.; Kaushal, R.; Kaur, T.; Bijarnia, R.K.; Puri, S.; Singla, S.K. The most potent antilithiatic agent ameliorating renal dysfunction and oxidative stress from Bergenia ligulata rhizome. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendary, E.; Francis, R.R.; Ali, H.M.G.; Sarwat, M.I.; El Hady, S. Antioxidant and structure–activity relationships (SARs) of some phenolic and anilines compounds. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2013, 58, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padmanabhan, M.; Prince, P.S.M. Preventive effect of S-allylcysteine on lipid peroxides and antioxidants in normal and isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: A histopathological study. Toxicology 2006, 224, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Chen, K.; Xu, L.; Wang, T.; Guo, C. Bergenin Exerts Hepatoprotective Effects by Inhibiting the Release of Inflammatory Factors, Apoptosis and Autophagy via the PPAR-γ Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| S.NO. | Groups | Experiment Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Group I (Control group) |
|
| 2 | Group II (ISO group) |
|
| 3 | Group III (Atenolol + ISO) |
|
| 4 | Group IV, V (Bergenin + ISO) |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, T.; Haq, I.U.; Khan, T.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Alasmary, M.Y.; Almedhesh, S.A.; Shehri, H.A.; Alshahrani, M.A.; Shah, A.J. Bergenin from Bergenia Species Produces a Protective Response against Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Processes 2022, 10, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071403
Ahmad T, Haq IU, Khan T, Mahnashi MH, Alasmary MY, Almedhesh SA, Shehri HA, Alshahrani MA, Shah AJ. Bergenin from Bergenia Species Produces a Protective Response against Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Processes. 2022; 10(7):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071403
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Taseer, Imran Ul Haq, Taous Khan, Mater H. Mahnashi, Mohammed Y. Alasmary, Sultan A. Almedhesh, Hamdan Al Shehri, Mohammed A. Alshahrani, and Abdul Jabbar Shah. 2022. "Bergenin from Bergenia Species Produces a Protective Response against Myocardial Infarction in Rats" Processes 10, no. 7: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071403
APA StyleAhmad, T., Haq, I. U., Khan, T., Mahnashi, M. H., Alasmary, M. Y., Almedhesh, S. A., Shehri, H. A., Alshahrani, M. A., & Shah, A. J. (2022). Bergenin from Bergenia Species Produces a Protective Response against Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Processes, 10(7), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10071403