Inflammation and Autophagy: A Convergent Point between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)-Related Genetic and Environmental Factors: Focus on Aluminum Adjuvants
Abstract
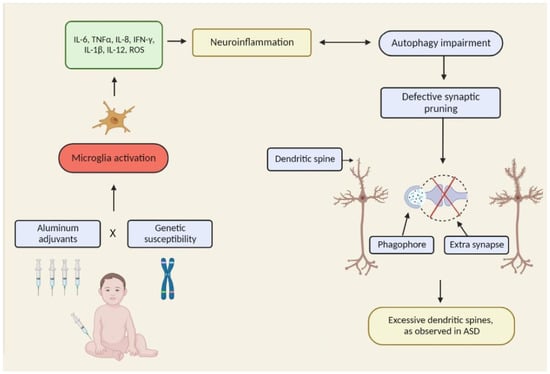
:1. Introduction
2. Autism Spectrum Disorder
2.1. Definition and Prevalence
2.2. Genetics
2.3. Immune Dysfunction
2.4. Immune System and Environment: A Convergent Point
3. Autophagy
3.1. Neuronal and Microglial Autophagy
3.2. Autophagy Disruption and ASD
3.3. Autophagy and Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB)
3.4. Autophagy and Microbiota
4. Al Adjuvants as Potential Environmental Stressors
4.1. Vaccinal Policy, Safety, and Al-Based Adjuvants
4.2. ABAs in Vaccines
4.3. Biological Effects of ABAs on the Immune System
4.4. Autophagy Modulation by Al Particles
4.5. Al, Autophagy, and BBB
4.6. ABAs and ASD: What Are the Facts?
- Epidemiological studies comparing different vaccination schedules and ABA exposure in children;
- Genetic studies of populations at risk, potentially targeting candidate genes in immune and autophagy pathways;
- Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Al adjuvants during both pre- and postnatal periods, in animal models;
- Fundamental immunological data in order to better understand the mechanisms of immune action of ABAs, in addition to their possible capacity of inducing neuroinflammation and alterations of immune-neural interactions during early postnatal life, e.g., using autophagy-deficient mouse models.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABAs | aluminum-based adjuvants |
| Al | aluminum |
| ASD | autism spectrum disorder |
| ASIA | autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BD | bipolar disorder |
| CDC | U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CNV | copy number variant |
| GxE | gene × environment |
| HBV | hepatitis b virus |
| IL | interleukin |
| ME/CFS | myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome |
| MIA | maternal immune activation |
| MMF | macrophagic myofasciitis |
| MMR | measles, mumps, rubella |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NNDs | neurodevelopmental disorders |
| PBMCs | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| SZ | schizophrenia |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Lander, E.S.; Schork, N.J. Genetic Dissection of Complex Traits. Science 1994, 265, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Santpere, G.; Kawasawa, Y.I.; Evgrafov, O.V.; Gulden, F.O.; Pochareddy, S.; Sunkin, S.M.; Li, Z.; Shin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Integrative Functional Genomic Analysis of Human Brain Development and Neuropsychiatric Risks. Science 2018, 362, eaat7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzotto, S.; Walsh, C.A. Genetic Mosaicism in the Human Brain: From Lineage Tracing to Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, I.; Rabaneda, L.G.; Schoen, H.; Novarino, G. Neurodevelopmental Disorders: From Genetics to Functional Pathways. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichard, J.; Zimmer-Bensch, G. The Epigenome in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 776809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Genomic Relationships, Novel Loci, and Pleiotropic Mechanisms across Eight Psychiatric Disorders. Cell 2019, 179, 1469–1482.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandal, M.J.; Zhang, P.; Hadjimichael, E.; Walker, R.L.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Won, H.; van Bakel, H.; Varghese, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Isoform-Level Dysregulation in ASD, Schizophrenia, and Bipolar Disorder. Science 2018, 362, eaat8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.M.; Lorusso, J.M.; Potter, H.G.; Neill, J.C.; Glazier, J.D.; Hager, R. Maternal Immune Activation in Rodent Models: A Systematic Review of Neurodevelopmental Changes in Gene Expression and Epigenetic Modulation in the Offspring Brain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 129, 389–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Dale, R.C. Maternal Immune Activation and Neuroinflammation in Human Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfried, C.; Bambini-Junior, V.; Francis, F.; Riesgo, R.; Savino, W. The Impact of Neuroimmune Alterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magdalon, J.; Mansur, F.; Silva, A.L.T.E.; de Goes, V.A.; Reiner, O.; Sertié, A.L. Complement System in Brain Architecture and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westacott, L.J.; Wilkinson, L.S. Complement Dependent Synaptic Reorganisation During Critical Periods of Brain Development and Risk for Psychiatric Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 840266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.G.; Ciesla, A.A. Maternal Immune Activation Hypotheses for Human Neurodevelopment: Some Outstanding Questions. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2022, 7, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Sonawane, B.; Mattison, D.; McCally, M.; Garg, A. Chemical Contaminants in Breast Milk and Their Impacts on Children’s Health: An Overview. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, A313–A315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sly, P.D.; Flack, F. Susceptibility of Children to Environmental Pollutants. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1140, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Research on Developmental Disabilities Collaborators. Developmental Disabilities among Children Younger than 5 Years in 195 Countries and Territories, 1990-2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1100–e1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.; Lambertini, L.; Birnbaum, L. A Research Strategy to Discover the Environmental Causes of Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disabilities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, a258–a260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grova, N.; Schroeder, H.; Olivier, J.-L.; Turner, J.D. Epigenetic and Neurological Impairments Associated with Early Life Exposure to Persistent Organic Pollutants. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019, 2085496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbo, S.D.; Block, C.L.; Bolton, J.L.; Hanamsagar, R.; Tran, P.K. Beyond Infection—Maternal Immune Activation by Environmental Factors, Microglial Development, and Relevance for Autism Spectrum Disorders. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, V.H.; Cunningham, C.; Boche, D. Atypical Inflammation in the Central Nervous System in Prion Disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2002, 15, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, R.K.; Coquet, M.; Cherin, P.; Belec, L.; Moretto, P.; Dreyfus, P.A.; Pellissier, J.F.; Chariot, P.; Authier, F.J. Macrophagic Myofasciitis Lesions Assess Long-Term Persistence of Vaccine-Derived Aluminium Hydroxide in Muscle. Brain 2001, 124, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Agmon-Levin, N. “ASIA”—Autoimmune/Inflammatory Syndrome Induced by Adjuvants. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 36, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomljenovic, L.; Shaw, C.A. Aluminum Vaccine Adjuvants: Are They Safe? Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Académie Nationale de Pharmacie. Rapport. Les Adjuvants Aluminiques: Le Point en 2016. 2016. Available online: http://www.acadpharm.org/dos_public/Rapport_Adjuvants_aluminiques_VF_CORR_5.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Madsen, K.M.; Hviid, A.; Vestergaard, M.; Schendel, D.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Thorsen, P.; Olsen, J.; Melbye, M. A Population-Based Study of Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Vaccination and Autism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hviid, A.; Hansen, J.V.; Frisch, M.; Melbye, M. Measles, Mumps, Rubella Vaccination and Autism: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombonne, E.; Zakarian, R.; Bennett, A.; Meng, L.; McLean-Heywood, D. Pervasive Developmental Disorders in Montreal, Quebec, Canada: Prevalence and Links with Immunizations. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e139–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willsey, H.R.; Willsey, A.J.; Wang, B.; State, M.W. Genomics, Convergent Neuroscience and Progress in Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DSM-5—Manuel Diagnostique et Statistique des Troubles Mentaux|Livre|9782294739293. Available online: https://www.elsevier-masson.fr/dsm-5-manuel-diagnostique-et-statistique-des-troubles-mentaux-9782294739293.html (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Constantino, J.N.; Charman, T. Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder: Reconciling the Syndrome, Its Diverse Origins, and Variation in Expression. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, A.J.; Brugha, T.S.; Erskine, H.E.; Scheurer, R.W.; Vos, T.; Scott, J.G. The Epidemiology and Global Burden of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.; Ferreira, H.; Martins, J.; Gonçalves, J.; Castelo-Branco, M. Male Sex Bias in Early and Late Onset Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Shared Aspects and Differences in Autism Spectrum Disorder, Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, and Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 135, 104577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenner, M.J.; Shaw, K.A.; Baio, J.; Washington, A.; Patrick, M.; DiRienzo, M.; Christensen, D.L.; Wiggins, L.D.; Pettygrove, S.; Andrews, J.G.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2020, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Leventhal, B.L.; Koh, Y.-J.; Fombonne, E.; Laska, E.; Lim, E.-C.; Cheon, K.-A.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, H.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorders in a Total Population Sample. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, S.J.; Bramlett, M.D.; Kogan, M.D.; Schieve, L.A.; Jones, J.R.; Lu, M.C. Changes in Prevalence of Parent-Reported Autism Spectrum Disorder in School-Aged U.S. Children: 2007 to 2011–2012. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. 2013, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Maenner, M.J.; Shaw, K.A.; Bakian, A.V.; Bilder, D.A.; Durkin, M.S.; Esler, A.; Furnier, S.M.; Hallas, L.; Hall-Lande, J.; Hudson, A.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2018. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2021, 70, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panesar, H.K.; Kennedy, C.L.; Keil Stietz, K.P.; Lein, P.J. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Risk Factors for Autism Spectrum Disorder? Toxics 2020, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Cui, H.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 284, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, M.; Boykin, A.A. Analysis of the 2000 to 2018 Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network Surveillance Reports: Implications for Primary Care Clinicians. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2022, 65, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, E.; Loi, E.; Vega-Benedetti, A.F.; Carta, M.; Doneddu, G.; Fadda, R.; Zavattari, P. An Overview of the Main Genetic, Epigenetic and Environmental Factors Involved in Autism Spectrum Disorder Focusing on Synaptic Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Chow, J.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Patterson, P.H. Modeling an Autism Risk Factor in Mice Leads to Permanent Immune Dysregulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12776–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abib, R.T.; Gaman, A.; Dargél, A.A.; Tamouza, R.; Kapczinski, F.; Gottfried, C.; Leboyer, M. Intracellular Pathogen Infections and Immune Response in Autism. Neuroimmunomodulation 2018, 25, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlezon, W.A.; Kim, W.; Missig, G.; Finger, B.C.; Landino, S.M.; Alexander, A.J.; Mokler, E.L.; Robbins, J.O.; Li, Y.; Bolshakov, V.Y.; et al. Maternal and Early Postnatal Immune Activation Produce Sex-Specific Effects on Autism-like Behaviors and Neuroimmune Function in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lammert, C.R.; Frost, E.L.; Bolte, A.C.; Paysour, M.J.; Shaw, M.E.; Bellinger, C.E.; Weigel, T.K.; Zunder, E.R.; Lukens, J.R. Cutting Edge: Critical Roles for Microbiota-Mediated Regulation of the Immune System in a Prenatal Immune Activation Model of Autism. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, D.L.; Nascimbene, C.; Krishnan, C.; Zimmerman, A.W.; Pardo, C.A. Neuroglial Activation and Neuroinflammation in the Brain of Patients with Autism. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Alberts, I.; Li, X. Brain IL-6 and Autism. Neuroscience 2013, 252, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintunde, M.E.; Rose, M.; Krakowiak, P.; Heuer, L.; Ashwood, P.; Hansen, R.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Van de Water, J. Increased Production of IL-17 in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Co-Morbid Asthma. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 286, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Mostafa, G.A. Elevated Serum Levels of Interleukin-17A in Children with Autism. J. Neuro Inflamm. 2012, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, K.; Kameno, Y.; Shimmura, C.; Kawai, S.; Yoshihara, Y.; Wakuda, T.; Takebayashi, K.; Takagai, S.; et al. Plasma Cytokine Profiles in Subjects with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennabi, M.; Tarantino, N.; Gaman, A.; Scheid, I.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Debré, P.; Bouleau, A.; Caralp, M.; Gueguen, S.; Le-Moal, M.L.; et al. Persistence of Dysfunctional Natural Killer Cells in Adults with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders: Stigma/Consequence of Unresolved Early Infectious Events? Mol. Autism 2019, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saresella, M.; Piancone, F.; Marventano, I.; Zoppis, M.; Hernis, A.; Zanette, M.; Trabattoni, D.; Chiappedi, M.; Ghezzo, A.; Canevini, M.P.; et al. Multiple Inflammasome Complexes Are Activated in Autistic Spectrum Disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 57, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guma, E.; Plitman, E.; Chakravarty, M.M. The Role of Maternal Immune Activation in Altering the Neurodevelopmental Trajectories of Offspring: A Translational Review of Neuroimaging Studies with Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorder and Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 104, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmiston, E.; Ashwood, P.; Van de Water, J. Autoimmunity, Autoantibodies, and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meltzer, A.; Van de Water, J. The Role of the Immune System in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottahedin, A.; Ardalan, M.; Chumak, T.; Riebe, I.; Ek, J.; Mallard, C. Effect of Neuroinflammation on Synaptic Organization and Function in the Developing Brain: Implications for Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, R.S.; Deth, R.C.; Mittal, R.; Aranke, M.; Kay, S.-I.S.; Moshiree, B.; Eshraghi, A.A. Early Disruption of the Microbiome Leading to Decreased Antioxidant Capacity and Epigenetic Changes: Implications for the Rise in Autism. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchezan, J.; Santos, E.G.A.W.D.; Deckmann, I.; Riesgo, R.D.S. Immunological Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Potential Target for Therapy. Neuroimmunomodulation 2018, 25, 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.B.; Yim, Y.S.; Wong, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.V.; Hoeffer, C.A.; Littman, D.R.; Huh, J.R. The Maternal Interleukin-17a Pathway in Mice Promotes Autism-like Phenotypes in Offspring. Science 2016, 351, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.P.; Li, J.; Garbett, K.; Mirnics, K.; Patterson, P.H. Maternal Immune Activation Alters Fetal Brain Development through Interleukin-6. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10695–10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chadman, K.K.; McCloskey, D.P.; Sheikh, A.M.; Malik, M.; Brown, W.T.; Li, X. Brain IL-6 Elevation Causes Neuronal Circuitry Imbalances and Mediates Autism-like Behaviors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druart, M.; Le Magueresse, C. Emerging Roles of Complement in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, K.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Zipp, F. Immunoneuropsychiatry—Novel Perspectives on Brain Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, M.L.; McAllister, A.K. Immune Mediators in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spencer, S.J.; Meyer, U. Perinatal Programming by Inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, B.; Kroemer, G. Biological Functions of Autophagy Genes: A Disease Perspective. Cell 2019, 176, 11–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Mizushima, N.; Virgin, H.W. Autophagy in Immunity and Inflammation. Nature 2011, 469, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamargo-Gómez, I.; Fernández, Á.F.; Mariño, G. Pathogenic Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Autophagy-Related Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Autophagy and Inflammation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.-G.; Zhou, X.-G.; Qiao, G.; Yu, L.; Tang, Y.; Yan, L.; Qiu, W.-Q.; Pan, R.; Yu, C.-L.; Law, B.Y.-K.; et al. Targeting Microglial Autophagic Degradation in NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neurodegenerative Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, F.; Cao, Z.; Aschner, M.; Luo, W. The Role of Autophagy in Modulation of Neuroinflammation in Microglia. Neuroscience 2016, 319, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, M.; Adlimoghaddam, A.; Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Sharifzad, F.; Yasavoli-Sharahi, H.; Lorzadeh, S.; Albensi, B.C.; Ghavami, S. Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis: Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy Focusing in Microglia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Gao, Y.; Chu, S.; Chen, N. Review of the Effects and Mechanisms of Microglial Autophagy in Ischemic Stroke. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoletopoulou, V.; Tavernarakis, N. Regulation and Roles of Autophagy at Synapses. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoda, T.; Yang, K.; Sawa, A. Neuronal Autophagy in Synaptic Functions and Psychiatric Disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-M.; Hwang, S.-K.; Lee, J.-A. Neuronal Autophagy and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Gudsnuk, K.; Kuo, S.-H.; Cotrina, M.L.; Rosoklija, G.; Sosunov, A.; Sonders, M.S.; Kanter, E.; Castagna, C.; Yamamoto, A.; et al. Loss of MTOR-Dependent Macroautophagy Causes Autistic-like Synaptic Pruning Deficits. Neuron 2014, 83, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Yan, J.; Zukin, R.S. Autophagy and Synaptic Plasticity: Epigenetic Regulation. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 59, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, J.-H.; Yue, Z. Autophagy Deficiency in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jülg, J.; Strohm, L.; Behrends, C. Canonical and Non-Canonical Autophagy Pathways in Microglia. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 41, e00389-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubova, S.G.; Suvorova, I.I.; Karpenko, M.N. Macrophage and Microglia Polarization: Focus on Autophagy-Dependent Reprogramming. Front. Biosci. Sch. Educ. 2022, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendeln, A.-C.; Degenhardt, K.; Kaurani, L.; Gertig, M.; Ulas, T.; Jain, G.; Wagner, J.; Häsler, L.M.; Wild, K.; Skodras, A.; et al. Innate Immune Memory in the Brain Shapes Neurological Disease Hallmarks. Nature 2018, 556, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiot, A.; Zaïdi, S.; Iltis, C.; Ribon, M.; Berriat, F.; Schiaffino, L.; Jolly, A.; de la Grange, P.; Mallat, M.; Bohl, D.; et al. Modifying Macrophages at the Periphery Has the Capacity to Change Microglial Reactivity and to Extend ALS Survival. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Delfino, D.V.; Fierabracci, A. Recent Insights on the Putative Role of Autophagy in Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.; Ammitzboell, M.; Nys, K.; Seidelin, J.B.; Nielsen, O.H. ATG16L1: A Multifunctional Susceptibility Factor in Crohn Disease. Autophagy 2015, 11, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markram, H.; Rinaldi, T.; Markram, K. The Intense World Syndrome--an Alternative Hypothesis for Autism. Front. Neurosci. 2007, 1, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Cho, M.-H.; Shim, W.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeon, E.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Yoon, S.-Y. Deficient Autophagy in Microglia Impairs Synaptic Pruning and Causes Social Behavioral Defects. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotajima-Murakami, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Kashii, H.; Sato, A.; Hagino, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Nishito, Y.; Takamatsu, Y.; Uchino, S.; Ikeda, K. Effects of Rapamycin on Social Interaction Deficits and Gene Expression in Mice Exposed to Valproic Acid in Utero. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-A.; Shin, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Shin, Y.-J.; Rajanikant, G.K.; Majid, A.; Baek, S.-H.; Bae, O.-N. Role of Autophagy in Endothelial Damage and Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-A.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Shin, Y.-J.; Kim, E.-S.; Akram, M.; Kim, E.-H.; Majid, A.; Baek, S.-H.; Bae, O.-N. Autophagy-Mediated Occludin Degradation Contributes to Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption during Ischemia in BEnd.3 Brain Endothelial Cells and Rat Ischemic Stroke Models. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthari, R.K.; Tikka, C.; Ommati, M.M.; Niu, R.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Arsenic Induces Autophagy in Developmental Mouse Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus by Inhibiting PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway: Involvement of Blood-Brain Barrier’s Tight Junction Proteins. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 3255–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Niu, F.; Hu, G.; Guo, M.-L.; Sil, S.; Buch, S. HIV Tat-Mediated Induction of Autophagy Regulates the Disruption of ZO-1 in Brain Endothelial Cells. Tissue Barriers 2020, 8, 1748983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gao, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Gu, Z.; Shi, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; et al. Mdivi-1 Alleviates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Cell Death in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury by Mitigating Autophagy Dysfunction and Mitophagy Activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 94, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qu, C.; Qu, C.; Shen, J.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J. Improvement of Autophagy Dysfunction as a Potential Mechanism for Environmental Enrichment to Protect Blood-Brain Barrier in Rats with Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 739, 135437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Autophagy Protects the Blood-Brain Barrier Through Regulating the Dynamic of Claudin-5 in Short-Term Starvation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadley, G.; Beard, D.J.; Couch, Y.; Neuhaus, A.A.; Adriaanse, B.A.; DeLuca, G.C.; Sutherland, B.A.; Buchan, A.M. Rapamycin in Ischemic Stroke: Old Drug, New Tricks? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, A.S.; Del Rosario, Y.; Mu, R.; Rodriguez, A.; Till, A.; Subramani, S.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Doran, K.S. The Role of Autophagy during Group B Streptococcus Infection of Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35711–35723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rihani, S.B.; Darakjian, L.I.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal-Rich Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Restores the Blood-Brain Barrier Function through NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition Simultaneously with Autophagy Induction in TgSwDI Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3543–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Li, J.; Niu, S.; Xue, Y.; Tang, M. Neurotoxicity of Metal-Containing Nanoparticles and Implications in Glial Cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, E.G.; Mukherjee, T.; Cabral-Fernandes, L.; Rocha, J.D.B.; Girardin, S.E.; Philpott, D.J. How Autophagy Controls the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Autophagy 2022, 18, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, M.A.; Flores, G.D.; Kilroy, E.; Labus, J.S.; Mayer, E.A.; Aziz-Zadeh, L. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome System: Pathways and Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, L.; Nemeş, S.-A.; Szabo, K.; Teleky, B.-E.; Vodnar, D.-C. Guts Imbalance Imbalances the Brain: A Review of Gut Microbiota Association with Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 813204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.K.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Bediwy, A.S.; El-Sawaf, Y.; Toema, O. Gut Microbiota in Various Childhood Disorders: Implication and Indications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1875–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, B. The Contribution of Vaccination to Global Health: Past, Present and Future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaccins et Vaccinations⋅Inserm, la Science Pour la Santé. Available online: https://www.inserm.fr/dossier/vaccins-et-vaccinations/ (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- Pittman, M.; Cox, C.B. Pertussis vaccine testing for freedom-from-toxicity. Appl. Microbiol. 1965, 13, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, R.K.; Crépeaux, G.; Authier, F.-J. Myalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Following Immunization: Macrophagic Myofasciitis and Animal Studies Support Linkage to Aluminum Adjuvant Persistency and Diffusion in the Immune System. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.A.; Li, D.; Tomljenovic, L. Are There Negative CNS Impacts of Aluminum Adjuvants Used in Vaccines and Immunotherapy? Immunotherapy 2014, 6, 1055–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.A.; Tomljenovic, L. Aluminum in the Central Nervous System (CNS): Toxicity in Humans and Animals, Vaccine Adjuvants, and Autoimmunity. Immunol. Res. 2013, 56, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pasquale, A.; Preiss, S.; Silva, F.T.D.; Garçon, N. Vaccine Adjuvants: From 1920 to 2015 and Beyond. Vaccines 2015, 3, 320–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrand, L.; Elnar, A.A.; Authier, F.-J.; Gherardi, R.K.; Crépeaux, G. Aluminium adjuvant exposure through vaccines in France in 2018. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2020, 78, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mold, M.; Shardlow, E.; Exley, C. Insight into the Cellular Fate and Toxicity of Aluminium Adjuvants Used in Clinically Approved Human Vaccinations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, G.; Angrand, L.; Masson, J.-D.; Crépeaux, G.; David, M.-O. Physico-Chemical Properties of Aluminum Adjuvants in Vaccines: Implications for Toxicological Evaluation. Vaccine 2022, 40, 4881–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shardlow, E.; Mold, M.; Exley, C. From Stock Bottle to Vaccine: Elucidating the Particle Size Distributions of Aluminum Adjuvants Using Dynamic Light Scattering. Front. Chem. 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, I.; Hidalgo, K.; Bondy, S.C.; Campbell, A. Distinctive Cellular Response to Aluminum Based Adjuvants. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 78, 103404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdohazi, M.; Newman, R.L. Aluminium Hydroxide Granuloma. Br. Med. J. 1971, 3, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrak, R.E. Muscle Granulomas Following Intramuscular Injection. Muscle Nerve 1982, 5, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Relyveld, E.H.; Lindblad, E.B.; Bizzini, B.; Ben-Efraim, S.; Gupta, C.K. Adjuvants--a Balance between Toxicity and Adjuvanticity. Vaccine 1993, 11, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, B.; Goldstein, J.; Levine, P. The Clinical and Scientific Basis of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome; Nightingale Research Foundation: Ottowa, ON, Canada, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, B. Is CFS Linked to Vaccinations? CFS Res. Rev. 2001, 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, L. Prevalence and Patterns of Gulf War Illness in Kansas Veterans: Association of Symptoms with Characteristics of Person, Place, and Time of Military Service. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotopf, M.; David, A.; Hull, L.; Ismail, K.; Unwin, C.; Wessely, S. Role of Vaccinations as Risk Factors for Ill Health in Veterans of the Gulf War: Cross Sectional Study. BMJ 2000, 320, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, R.K.; Coquet, M.; Chérin, P.; Authier, F.J.; Laforêt, P.; Bélec, L.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Mussini, J.M.; Pellissier, J.F.; Fardeau, M. Macrophagic Myofasciitis: An Emerging Entity. Groupe d’Etudes et Recherche Sur Les Maladies Musculaires Acquises et Dysimmunitaires (GERMMAD) de l’Association Française Contre Les Myopathies (AFM). Lancet 1998, 352, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, R.K.; Eidi, H.; Crépeaux, G.; Authier, F.J.; Cadusseau, J. Biopersistence and Brain Translocation of Aluminum Adjuvants of Vaccines. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, Y.; Kutai, M.; Jossiphov, J.; Livne, A.; Neeman, Z.; Arad, T.; Popovitz-Biro, R.; Atsmon, J.; Shapira, Y.; Soffer, D. Childhood Macrophagic Myofasciitis-Consanguinity and Clinicopathological Features. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, E.; Gómez-Arnáiz, M.; Ricoy, J.R.; Mateos, F.; Simón, R.; García-Peñas, J.J.; Garcia-Silva, M.T.; Martín, E.; Vázquez, M.; Ferreiro, A.; et al. Macrophagic Myofasciitis in Childhood: A Controversial Entity. Pediatr. Neurol. 2005, 33, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, B.; Cupler, E.J. Macrophagic Myofasciitis in Children Is a Localized Reaction to Vaccination. J. Child Neurol. 2008, 23, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, A.; Rajeshwari, M.; Nalwa, A.; Suri, V.; Sarkar, C.; Chakrabarty, B.; Gulati, S.; Sharma, M.C. Childhood Macrophagic Myofasciitis: A Series from the Indian Subcontinent. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Aluminum in Vaccines: Does It Create a Safety Problem? Vaccine 2018, 36, 5825–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lim, K.Y.; Kang, J.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.-H. Macrophagic Myofasciitis and Subcutaneous Pseudolymphoma Caused by Aluminium Adjuvants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, L.E.; Baker, B.; Perricone, C.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vaccines, Adjuvants and Autoimmunity. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 100, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Gómez, M.; Colomina, M.T. Risks of Aluminium Exposure during Pregnancy. Contrib. Sci. 2000, 1, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Affourtit, F.; Bakker, M.; Pronk, M. Human Health Risk Assessment of Aluminium; RIVM: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2020.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Aluminum; Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008.
- Exley, C. Human Exposure to Aluminium. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2013, 15, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, N.J.; Morley, R.; Day, J.P.; Lucas, A. Aluminum Neurotoxicity in Preterm Infants Receiving Intravenous-Feeding Solutions. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, J.M.; Newcomer, S.R.; Daley, M.F.; McClure, D.L.; Baxter, R.P.; Jackson, M.L.; Naleway, A.L.; Lugg, M.M.; DeStefano, F. Cumulative and Episodic Vaccine Aluminum Exposure in a Population-Based Cohort of Young Children. Vaccine 2015, 33, 6736–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekly Epidemiological Record, Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/global-advisory-committee-on-vaccine-safety/topics/adjuvants (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Exley, C.; Burgess, E.; Day, J.P.; Jeffery, E.H.; Melethil, S.; Yokel, R.A. Aluminum Toxicokinetics. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Yokel, R.A.; Nieboer, E.; Borchelt, D.; Cohen, J.; Harry, J.; Kacew, S.; Lindsay, J.; Mahfouz, A.M.; Rondeau, V. Human Health Risk Assessment for Aluminium, Aluminium Oxide, and Aluminium Hydroxide. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2007, 10 (Suppl. 1), 1–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, K.; Stübler, S.; Matheis, W.; Huisinga, W. Towards Toxicokinetic Modelling of Aluminium Exposure from Adjuvants in Medicinal Products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 88, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokel, R.A.; McNamara, P.J. Aluminium Toxicokinetics: An Updated Minireview. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 88, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flarend, R.E.; Hem, S.L.; White, J.L.; Elmore, D.; Suckow, M.A.; Rudy, A.C.; Dandashli, E.A. In Vivo Absorption of Aluminium-Containing Vaccine Adjuvants Using 26Al. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, J.-D.; Crépeaux, G.; Authier, F.-J.; Exley, C.; Gherardi, R.K. Critical Analysis of Reference Studies on the Toxicokinetics of Aluminum-Based Adjuvants. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 181, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crépeaux, G.; Eidi, H.; David, M.-O.; Tzavara, E.; Giros, B.; Exley, C.; Curmi, P.A.; Shaw, C.A.; Gherardi, R.K.; Cadusseau, J. Highly Delayed Systemic Translocation of Aluminum-Based Adjuvant in CD1 Mice Following Intramuscular Injections. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 152, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Combadière, C.; Authier, F.-J.; Itier, V.; Lux, F.; Exley, C.; Mahrouf-Yorgov, M.; Decrouy, X.; Moretto, P.; Tillement, O.; et al. Slow CCL2-Dependent Translocation of Biopersistent Particles from Muscle to Brain. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidi, H.; David, M.-O.; Crépeaux, G.; Henry, L.; Joshi, V.; Berger, M.-H.; Sennour, M.; Cadusseau, J.; Gherardi, R.K.; Curmi, P.A. Fluorescent Nanodiamonds as a Relevant Tag for the Assessment of Alum Adjuvant Particle Biodisposition. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.-D.; Angrand, L.; Badran de Miguel, R.; Crépeaux, G. Clearance, Biodistribution and Neuromodulatory effects of Aluminum-Based Adjuvants. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: What Do We Learn from Animal Studies? Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylor, N.W.; Egan, W.; Richman, P. Aluminum Salts in Vaccines--US Perspective. Vaccine 2002, 20 (Suppl. 3), S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons-Weiler, J.; Ricketson, R. Reconsideration of the Immunotherapeutic Pediatric Safe Dose Levels of Aluminum. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 48, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, C. An Aluminium Adjuvant in a Vaccine Is an Acute Exposure to Aluminium. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 57, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, G.; La Joie, E.; Thomas, P.; Lyons-Weiler, J. Acute Exposure and Chronic Retention of Aluminum in Three Vaccine Schedules and Effects of Genetic and Environmental Variation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 58, 126444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccines Shortly after Birth. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/parents/by-age/newborn-birth.html (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Miller, N.Z. Aluminum in Childhood Vaccines Is Unsafe. J. Am. Physicians Surg. 2016, 21, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Shardlow, E.; Linhart, C.; Connor, S.; Softely, E.; Exley, C. The Measurement and Full Statistical Analysis Including Bayesian Methods of the Aluminium Content of Infant Vaccines. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redhead, K.; Quinlan, G.J.; Das, R.G.; Gutteridge, J.M. Aluminium-Adjuvanted Vaccines Transiently Increase Aluminium Levels in Murine Brain Tissue. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1992, 70, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Arango, M.-T.; Kivity, S.; Katzav, A.; Gilburd, B.; Blank, M.; Tomer, N.; Volkov, A.; Barshack, I.; Chapman, J.; et al. Immunization with Hepatitis B Vaccine Accelerates SLE-like Disease in a Murine Model. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 54, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisser, K.; Göen, T.; Oduro, J.D.; Wangorsch, G.; Hanschmann, K.-M.O.; Keller-Stanislawski, B. Aluminium Toxicokinetics after Intramuscular, Subcutaneous, and Intravenous Injection of Al Citrate Solution in Rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miguel, R.; Asín, J.; Rodríguez-Largo, A.; Echeverría, I.; Lacasta, D.; Pinczowski, P.; Gimeno, M.; Molín, J.; Fernández, A.; de Blas, I.; et al. Growth Performance and Clinicopathological Analyses in Lambs Repetitively Inoculated with Aluminum-Hydroxide Containing Vaccines or Aluminum-Hydroxide Only. Animals 2021, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrik, M.S.; Wong, M.C.; Tabata, R.C.; Garry, R.F.; Shaw, C.A. Aluminum Adjuvant Linked to Gulf War Illness Induces Motor Neuron Death in Mice. Neuromolecular Med. 2007, 9, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.A.; Petrik, M.S. Aluminum Hydroxide Injections Lead to Motor Deficits and Motor Neuron Degeneration. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján, L.; Pérez, M.; Salazar, E.; Álvarez, N.; Gimeno, M.; Pinczowski, P.; Irusta, S.; Santamaría, J.; Insausti, N.; Cortés, Y.; et al. Autoimmune/Autoinflammatory Syndrome Induced by Adjuvants (ASIA Syndrome) in Commercial Sheep. Immunol. Res. 2013, 56, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.A.; Li, Y.; Tomljenovic, L. Administration of Aluminium to Neonatal Mice in Vaccine-Relevant Amounts Is Associated with Adverse Long Term Neurological Outcomes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 128, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crépeaux, G.; Eidi, H.; David, M.-O.; Baba-Amer, Y.; Tzavara, E.; Giros, B.; Authier, F.-J.; Exley, C.; Shaw, C.A.; Cadusseau, J.; et al. Non-Linear Dose-Response of Aluminium Hydroxide Adjuvant Particles: Selective Low Dose Neurotoxicity. Toxicology 2017, 375, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbar, R.; Weiss, R.; Tomljenovic, L.; Arango, M.-T.; Deri, Y.; Shaw, C.A.; Chapman, J.; Blank, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Behavioral Abnormalities in Female Mice Following Administration of Aluminum Adjuvants and the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Gardasil. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivity, S.; Arango, M.-T.; Molano-González, N.; Blank, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Phospholipid Supplementation Can Attenuate Vaccine-Induced Depressive-like Behavior in Mice. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.K.S.; Li, Y.; Shaw, C.A. Is Exposure to Aluminium Adjuvants Associated with Social Impairments in Mice? A Pilot Study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 181, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asín, J.; Pascual-Alonso, M.; Pinczowski, P.; Gimeno, M.; Pérez, M.; Muniesa, A.; de Pablo-Maiso, L.; de Blas, I.; Lacasta, D.; Fernández, A.; et al. Cognition and Behavior in Sheep Repetitively Inoculated with Aluminum Adjuvant-Containing Vaccines or Aluminum Adjuvant Only. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 203, 110934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidi, H.; Yoo, J.; Bairwa, S.C.; Kuo, M.; Sayre, E.C.; Tomljenovic, L.; Shaw, C.A. Early Postnatal Injections of Whole Vaccines Compared to Placebo Controls: Differential Behavioural Outcomes in Mice. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 212, 111200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlyne, G.M.; Yagil, R.; Ari, J.B.; Weinberger, G.; Knopf, E.; Danovitch, G.M. Aluminium Toxicity in Rats. Lancet 1972, 1, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, N.; Akama, K. Histopathological Studies of Reactions in Mice Injected with Aluminum-Adsorbed Tetanus Toxoid. Microbiol. Immunol. 1982, 26, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtulini, S.; Macchi, C.; Ballanti, P.; Cherel, Y.; Laval, A.; Theaker, J.M.; Bak, M.; Ferretti, E.; Morvan, H. Aluminium Hydroxide-Induced Granulomas in Pigs. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, F.; Burnett, R.; Michelet-Habchi, C.; Moretto, P.; Fievet-Groyne, F.; Sauzeat, E. Aluminium Assay and Evaluation of the Local Reaction at Several Time Points after Intramuscular Administration of Aluminium Containing Vaccines in the Cynomolgus Monkey. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Authier, F.-J.; Sauvat, S.; Christov, C.; Chariot, P.; Raisbeck, G.; Poron, M.-F.; Yiou, F.; Gherardi, R. Al(OH)3-Adjuvanted Vaccine-Induced Macrophagic Myofasciitis in Rats Is Influenced by the Genetic Background. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2006, 16, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, S.A.; Heath, M.D.; Kramer, M.F.; Skinner, M.A. Analysis of Aluminium in Rat Following Administration of Allergen Immunotherapy Using Either Aluminium or Microcrystalline-Tyrosine-Based Adjuvants. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HogenEsch, H.; Dunham, A.; Burlet, E.; Lu, F.; Mosley, Y.-Y.C.; Morefield, G. Preclinical Safety Study of a Recombinant Streptococcus Pyogenes Vaccine Formulated with Aluminum Adjuvant. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asín, J.; Molín, J.; Pérez, M.; Pinczowski, P.; Gimeno, M.; Navascués, N.; Muniesa, A.; de Blas, I.; Lacasta, D.; Fernández, A.; et al. Granulomas Following Subcutaneous Injection with Aluminum Adjuvant-Containing Products in Sheep. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, K.; Göen, T.; Oduro, J.D.; Wangorsch, G.; Hanschmann, K.-M.O.; Keller-Stanislawski, B. Aluminium from Adjuvanted Subcutaneous Allergen Immunotherapeutics in Rats Is Mainly Detected in Bone. Allergy 2020, 75, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miguel, R.; Asín, J.; Rodríguez-Largo, A.; Molín, J.; Echeverría, I.; de Andrés, D.; Pérez, M.; de Blas, I.; Mold, M.; Reina, R.; et al. Detection of Aluminum in Lumbar Spinal Cord of Sheep Subcutaneously Inoculated with Aluminum-Hydroxide Containing Products. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 204, 110871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Martínez, E.; Bilbao-Arribas, M.; Abendaño, N.; Asín, J.; Pérez, M.; de Andrés, D.; Luján, L.; Jugo, B.M. Whole Transcriptome Approach to Evaluate the Effect of Aluminium Hydroxide in Ovine Encephalon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, L.D.; Wolf, J.J.; Kaplanski, C.V.; Pauley, C.J.; Ledwith, B.J. Lack of Effects on Fertility and Developmental Toxicity of a Quadrivalent HPV Vaccine in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 83, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Wilby, O.K.; Willoughby, C.R.; Veenstra, S.; Deschamps, M. Evaluation of the Intramuscular Administration of CervarixTM Vaccine on Fertility, Pre- and Post-Natal Development in Rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, M.; Streifel, K.M.; Boosalis, C.A.; Heuer, L.; González, E.A.; Li, S.; Harvey, D.J.; Lein, P.J.; Van de Water, J. Acute Peripheral Immune Activation Alters Cytokine Expression and Glial Activation in the Early Postnatal Rat Brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Exley, C.; Siesjö, P.; Eriksson, H. The Immunobiology of Aluminium Adjuvants: How Do They Really Work? Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shardlow, E.; Mold, M.; Exley, C. Unraveling the Enigma: Elucidating the Relationship between the Physicochemical Properties of Aluminium-Based Adjuvants and Their Immunological Mechanisms of Action. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijman, S.; Brummelman, J.; van Els, C.A.C.M.; Marino, F.; Heck, A.J.R.; Mommen, G.P.M.; Metz, B.; Kersten, G.F.A.; Pennings, J.L.A.; Meiring, H.D. Novel Identified Aluminum Hydroxide-Induced Pathways Prove Monocyte Activation and pro-Inflammatory Preparedness. J. Proteom. 2018, 175, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulanova, M.; Tarkowski, A.; Hahn-Zoric, M.; Hanson, L.A. The Common Vaccine Adjuvant Aluminum Hydroxide Up-Regulates Accessory Properties of Human Monocytes via an Interleukin-4-Dependent Mechanism. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morefield, G.L.; Sokolovska, A.; Jiang, D.; HogenEsch, H.; Robinson, J.P.; Hem, S.L. Role of Aluminum-Containing Adjuvants in Antigen Internalization by Dendritic Cells in Vitro. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; Soullié, T.; van Nimwegen, M.; Willart, M.A.M.; Muskens, F.; Jung, S.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. Alum Adjuvant Boosts Adaptive Immunity by Inducing Uric Acid and Activating Inflammatory Dendritic Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Willingham, S.B.; Ting, J.P.-Y.; Re, F. Cutting Edge: Inflammasome Activation by Alum and Alum’s Adjuvant Effect Are Mediated by NLRP3. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszycka, E.; Lavelle, E.C. Immunomodulatory Properties of the Vaccine Adjuvant Alum. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viezeliene, D.; Beekhof, P.; Gremmer, E.; Rodovicius, H.; Sadauskiene, I.; Jansen, E.; Ivanov, L. Selective Induction of IL-6 by Aluminum-Induced Oxidative Stress Can Be Prevented by Selenium. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2013, 27, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Qi, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Gu, H.; Zou, J.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, Z. Neonatal Vaccination with Bacillus Calmette–Guérin and Hepatitis B Vaccines Modulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Rats. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 288, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawdi, S.H.; El-Denshary, E.S.; Safar, M.M.; Eidi, H.; David, M.-O.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Neuroprotective Effect of Nanodiamond in Alzheimer’s Disease Rat Model: A Pivotal Role for Modulating NF-ΚB and STAT3 Signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 1906–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Xu, F.; Zhuang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Aluminum Chloride Induces Neuroinflammation, Loss of Neuronal Dendritic Spine and Cognition Impairment in Developing Rat. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dera, H.S. Protective Effect of Resveratrol against Aluminum Chloride Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Saudi Med. J. 2016, 37, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borai, I.H.; Ezz, M.K.; Rizk, M.Z.; Aly, H.F.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Matloub, A.A.; Fouad, G.I. Therapeutic Impact of Grape Leaves Polyphenols on Certain Biochemical and Neurological Markers in AlCl3-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafaga, A.F. Exogenous Phosphatidylcholine Supplementation Retrieve Aluminum-Induced Toxicity in Male Albino Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 15589–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, C. A Biogeochemical Cycle for Aluminium? J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, A.M.; Al-Abbassi, R.; Al-Binni, M. Academic Stress-Induced Changes in Th1- and Th2-Cytokine Response. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, N.; Tsuchida, T.; Tamaki, K. Estrogen Enhancement of Anti-Double-Stranded DNA Antibody and Immunoglobulin G Production in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1999, 42, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Edwards, J.E. Type 1/Type 2 Immunity in Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 76–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seubert, A.; Monaci, E.; Pizza, M.; O’Hagan, D.T.; Wack, A. The Adjuvants Aluminum Hydroxide and MF59 Induce Monocyte and Granulocyte Chemoattractants and Enhance Monocyte Differentiation toward Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5402–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Tseng, S.; Horner, R.M.; Tam, C.; Loda, M.; Rollins, B.J. Control of TH2 Polarization by the Chemokine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1. Nature 2000, 404, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, V.; Bauernfeind, F.; Halle, A.; Samstad, E.O.; Kono, H.; Rock, K.L.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E. Silica Crystals and Aluminum Salts Activate the NALP3 Inflammasome through Phagosomal Destabilization. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotta, G. Vaccines and Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Public Health Safe 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Qi, F.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zou, J.; Guo, K.; Yao, Z. Neonatal Hepatitis B Vaccination Impaired the Behavior and Neurogenesis of Mice Transiently in Early Adulthood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 73, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Y.; Qi, F.; Zuo, Z.; Xu, J.; Yao, Z. IL-4 Mediates the Delayed Neurobehavioral Impairments Induced by Neonatal Hepatitis B Vaccination That Involves the down-Regulation of the IL-4 Receptor in the Hippocampus. Cytokine 2018, 110, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.M.K.; Ryter, S.W.; Levine, B. Autophagy in Human Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Chen, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Q. Neurodevelopmental Toxicity of Alumina Nanoparticles to Zebrafish Larvae: Toxic Effects of Particle Sizes and Ions. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Chang, L.; Shang, N.; Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Niu, Q.; et al. Involvement of Mitophagy in Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticle-Induced Impairment of Learning and Memory in Mice. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohignac, V.; Landry, M.J.; Boczkowski, J.; Lanone, S. Autophagy as a Possible Underlying Mechanism of Nanomaterial Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 548–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sarkar, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Toxic Metals and Autophagy. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, H.; Jacobson, L.S.; Goldberg, M.F.; Chandran, K.; Diaz-Griffero, F.; Lisanti, M.P.; Brojatsch, J. Role of Lysosome Rupture in Controlling Nlrp3 Signaling and Necrotic Cell Death. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1868–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivane, A.; Hilton, D.A.; Moate, R.M.; Bond, P.R.; Endean, A. Macrophagic Myofasciitis: A Report of Second Case from UK. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2012, 38, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N. Methods for Monitoring Autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.-D.; Authier, F.-J.; Gherardi, R.K.; Crépeaux, G. Cellular response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to immune challenge in a paradigm of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: An exploratory study (in preparation).
- Kumar, V.; Gill, K.D. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Aluminium Neurotoxicity and Its Amelioration: A Review. Neurotoxicology 2014, 41, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Puri, B.K.; Frye, R.E. The Putative Role of Environmental Aluminium in the Development of Chronic Neuropathology in Adults and Children. How Strong Is the Evidence and What Could Be the Mechanisms Involved? Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1335–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, C.E.; Mostardeiro, V.B.; Weis, G.C.C.; Reichert, K.P.; de Oliveira Alves, A.; Miron, V.V.; Bagatini, M.D.; Palma, T.V.; de Andrade, C.M.; Pillat, M.M.; et al. Aluminum-Induced Alterations in Purinergic System Parameters of BV-2 Brain Microglial Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 2695490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Toborek, M. Autophagy Is Involved in Nanoalumina-Induced Cerebrovascular Toxicity. Nanomedicine 2013, 9, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneff, S.; Davidson, R.M.; Liu, J. Empirical Data Confirm Autism Symptoms Related to Aluminum and Acetaminophen Exposure. Entropy 2012, 14, 2227–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomljenovic, L.; Shaw, C.A. Mechanisms of Aluminum Adjuvant Toxicity and Autoimmunity in Pediatric Populations. Lupus 2012, 21, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mold, M.; Umar, D.; King, A.; Exley, C. Aluminium in Brain Tissue in Autism. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 46, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovski, I.; Fletcher, M.W.; Ivanovski, A.; Nikolić, D.; Ivanovski, P. Do the Vaccines Harm? J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 55, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A. Reviewing the Association between Aluminum Adjuvants in the Vaccines and Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 126764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomljenovic, L.; Shaw, C.A. Do Aluminum Vaccine Adjuvants Contribute to the Rising Prevalence of Autism? J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, C.M.; Goodman, M.S. Hepatitis B Vaccination of Male Neonates and Autism Diagnosis, NHIS 1997–2002. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2010, 73, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A. Testing New Hypotheses of Neurological and Immunological Outcomes with Aluminum-Containing Vaccines Is Warranted. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 51, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gateff, C.; Relyveld, E.H.; Le Gonidec, G.; Vincent, J.; Labusquière, R.; McBean, M.; Monchicourt, D.; Chambon, L. Study of a new pentavalent vaccine combination. Ann. Microbiol. 1973, 124, 387–409. [Google Scholar]
- Masson, J.-D.; Thibaudon, M.; Bélec, L.; Crépeaux, G. Calcium Phosphate: A Substitute for Aluminum Adjuvants? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC 2012: Updated Recommendations for Use of Tetanus Toxoid, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid, and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine (Tdap) in Pregnant Women—Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). 2012. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6207a4.htm (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Get the Whooping Cough Vaccine during Each Pregnancy. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/pregnant/mom/get-vaccinated.html (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Recommandation Vaccinale Contre la Coqueluche Chez la Femme Enceinte. Available online: https://www.has-sante.fr/jcms/p_3084228/fr/recommandation-vaccinale-contre-la-coqueluche-chez-la-femme-enceinte (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Liste des Vaccins Anti-Coqueluche (mes vaccins.net). Available online: https://www.mesvaccins.net/web/vaccines?utf8=%E2%9C%93&name_or_disease=disease&search-by-name=&search-by-disease=3&commit=Chercher&search-by-age=&age_unit=ans (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Anane, R.; Bonini, M.; Creppy, E.E. Transplacental Passage of Aluminum from Pregnant Mice to Fetus Organs after Maternal Transcutaneous Exposure. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1997, 16, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, P.C.; Schell, L.M.; Stark, A.D.; Parsons, P.J. A Study of the Distribution of Aluminium in Human Placental Tissues Based on Alkaline Solubilization with Determination by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Metallomics 2010, 2, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumoto, S.; Nagai, H.; Kakimi, S.; Matsuzaki, H. 26Al Incorporation into the Brain of Rat Fetuses through the Placental Barrier and Subsequent Metabolism in Postnatal Development. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2010, 268, 1328–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen-Correa, S.; Martin, C.F.; Kirk, A.B. Evaluation of Fetal Exposures to Metals and Metalloids through Meconium Analyses: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crépeaux, G.; Authier, F.-J.; Exley, C.; Luján, L.; Gherardi, R.K. The Role of Aluminum Adjuvants in Vaccines Raises Issues That Deserve Independent, Rigorous and Honest Science. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Casillas, A.; Redwan, E.M.; Uversky, V.N. Aluminum Adjuvant in Vaccines: A New Research Avenue is Demanded. Asia Pac. J. Med. Toxicol. 2022, 11, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, U.; Feldon, J.; Dammann, O. Schizophrenia and Autism: Both Shared and Disorder-Specific Pathogenesis via Perinatal Inflammation? Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 26R–33R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craddock, N.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Owen, M.J. Psychosis Genetics: Modeling the Relationship between Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Mixed (or “Schizoaffective”) Psychoses. Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Vawter, M.P. Shared Gene Expression Alterations in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angrand, L.; Masson, J.-D.; Rubio-Casillas, A.; Nosten-Bertrand, M.; Crépeaux, G. Inflammation and Autophagy: A Convergent Point between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)-Related Genetic and Environmental Factors: Focus on Aluminum Adjuvants. Toxics 2022, 10, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090518
Angrand L, Masson J-D, Rubio-Casillas A, Nosten-Bertrand M, Crépeaux G. Inflammation and Autophagy: A Convergent Point between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)-Related Genetic and Environmental Factors: Focus on Aluminum Adjuvants. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngrand, Loïc, Jean-Daniel Masson, Alberto Rubio-Casillas, Marika Nosten-Bertrand, and Guillemette Crépeaux. 2022. "Inflammation and Autophagy: A Convergent Point between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)-Related Genetic and Environmental Factors: Focus on Aluminum Adjuvants" Toxics 10, no. 9: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090518
APA StyleAngrand, L., Masson, J. -D., Rubio-Casillas, A., Nosten-Bertrand, M., & Crépeaux, G. (2022). Inflammation and Autophagy: A Convergent Point between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)-Related Genetic and Environmental Factors: Focus on Aluminum Adjuvants. Toxics, 10(9), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090518