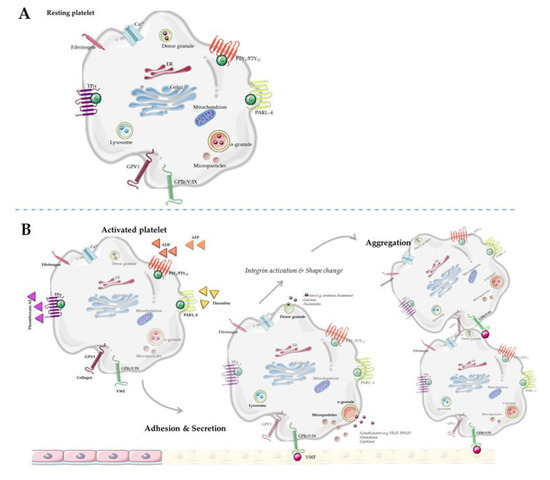
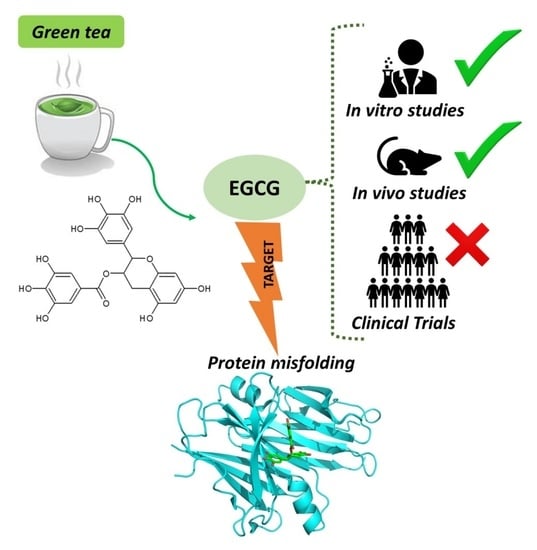
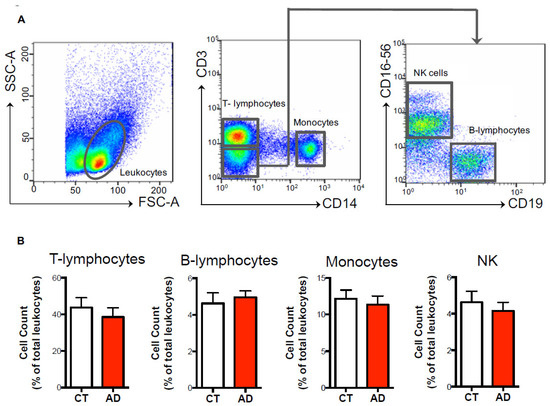
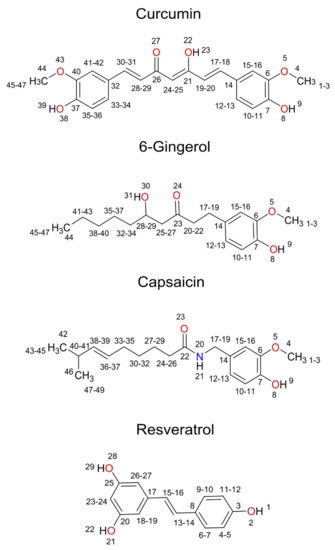
Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Neurodegenerative Disorders (Closed)
A topical collection in Biomolecules (ISSN 2218-273X). This collection belongs to the section "Molecular Medicine".
Viewed by 104774Editors
Interests: biomaterials; bone regeneration, stem cells; oxidative stress; apoptosis; neuroprotection; antitumoral drugs; cell culture; in vitro systems; flow cytometry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: membrane trafficking; Golgi apparatus; cell morphology; electron microscopy; Hailey-Hailey disease
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The nervous system is susceptible to many diseases and disorders, such as stroke, trauma, ischemia, schizophrenia, mood disorders, autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.
The cellular mechanisms that regulate the occurrence of most of these conditions include calcium influx/calcium overload, excitatory amino acid release, oxidative stress, inflammation, and glial dysfunction. However, the underlying mechanism of neuronal death is still not fully understood, and there are no effective therapies for most of these neurological disorders. Mostly, the research is focused on seeking new compounds able to slow down disease progression and/or to restore nervous system homeostasis.
Natural compounds, covering both endogenous and exogenous molecules, have emerged as new pharmaceuticals in the management of many neurological conditions, including cancer and aging, presenting heterogeneous chemical structure and varied pharmacological activity, useful in the treatment of high-complexity diseases. They also serve as inspiration for the synthesis of novel compounds with neuroprotective potential.
The purpose of this Special Issue, “Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Neurodegenerative Disorders”, is to explore the potential therapeutic role of many compounds in the management of pathological conditions in the nervous system and discuss the role of both natural and synthetic molecules in the development of psychiatric disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and trauma. We invite authors to submit original research and review articles related to any of these aspects.
Dr. Viviana di Giacomo
Dr. Massimo Micaroni
Dr. Sergio Oddi
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Biomolecules is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- neurogenesis
- neuroprotection
- neurodegenerative disease(s)
- natural compound(s)
- synthetic compound(s)
- oxidative stress
- (neuro)inflammation
- glia
- neuron(s)
- nervous system
- disorder(s)
- therapeutic potential
- endogenous compounds
- pro-homeostatic mechanism(s)