Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Protective Strategies
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cells of the Cardiovascular System".
Viewed by 54054Editors
2. CIBER de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CIBERCV), 28029 Madrid, Spain
Interests: ischemia-reperfusion injury; myocardial infarction; gap junctions; connexin 43; mitochondrial; succinate dehydrogenase; heart failure
2. CIBER de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CIBERCV), 28029 Madrid, Spain
Interests: mitochondria; calcium; AGEs; aging; ischemia/reperfusion injury; heart failure
2. CIBER de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CIBERCV), 28029 Madrid, Spain
Interests: myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; heart failure; calpains; fibrosis; hypertrophy; nitric oxide; guanylate cyclase
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
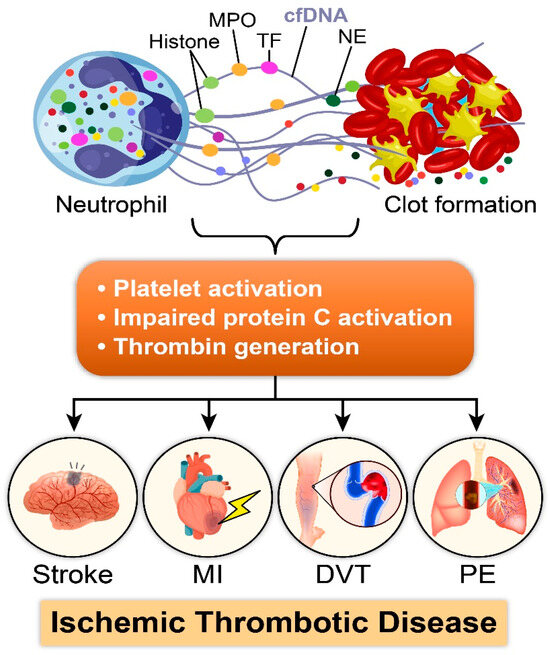
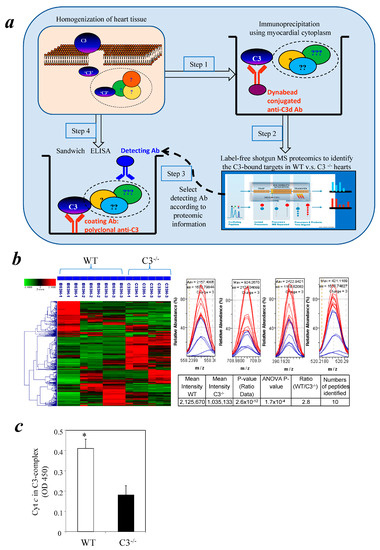
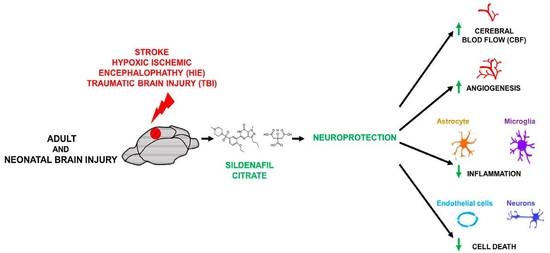
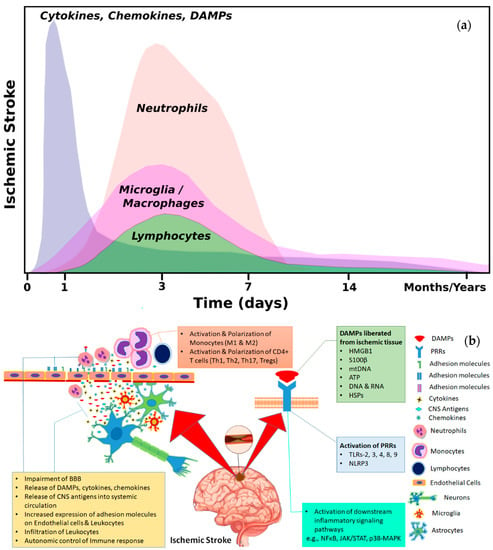
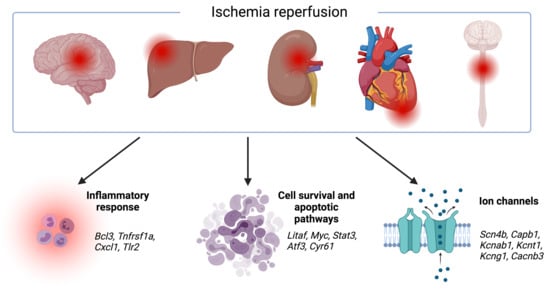
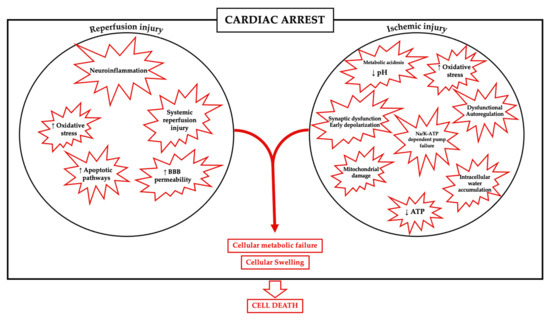
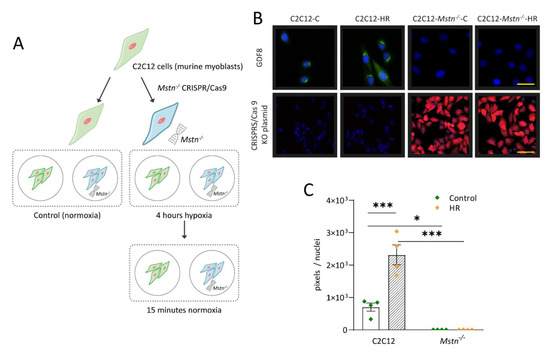
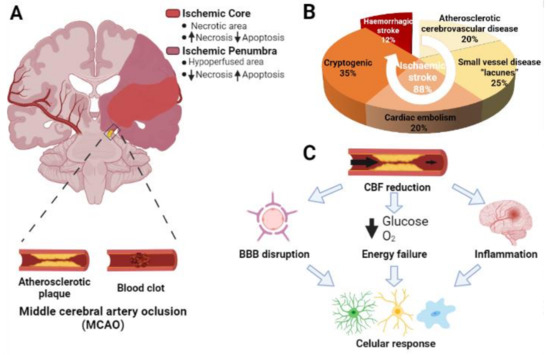
Ischemic disorders are a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, and affect multiple organs, including the heart, brain, kidney and the gut, among others. Several conditions, such as acute coronary syndrome, sepsis, thromboembolism, organ transplantation or limb injury, may produce tissue hypoperfusion and ischemia. The treatment of choice for patients suffering from tissue ischemia is the immediate restoration of blood flow. However, and despite the correct and rapid application of blood flow restoration techniques, reperfusion protocols do not prevent the occurrence of extensive cell death and tissue necrosis in a significant fraction of patients. This is, in part, due to the fact that blood flow restoration can itself cause a paradoxical exacerbation of injury, a phenomenon termed reperfusion injury. Importantly, reperfusion injury can be prevented by treatments applied at the onset of reflow, which presents a promising therapeutic opportunity. However, the protective effect of most of these treatments has not been confirmed in clinical trials. Therefore, it is essential to increase our knowledge on the pathophysiology of ischemia-reperfusion injury, to be able to propose new therapeutic approaches specifically addressed to mitigate it.
This Topical Collection aims to summarize the current knowledge on the molecular and cellular mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury, to explore tissue specific differences, and to identify potential therapeutic strategies capable of reducing cell death and dysfunction that could, eventually, be applied to patients.
We look forward to your contributions.
Dr. Antonio Rodríguez-Sinovas
Dr. Marisol Ruiz-Meana
Dr. Javier Inserte
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- reperfusion injury
- ischemia
- infarct
- stroke
- conditioning
- cardioprotection
- mitochondria
- heart
- kidney
- brain
- gut
- limb