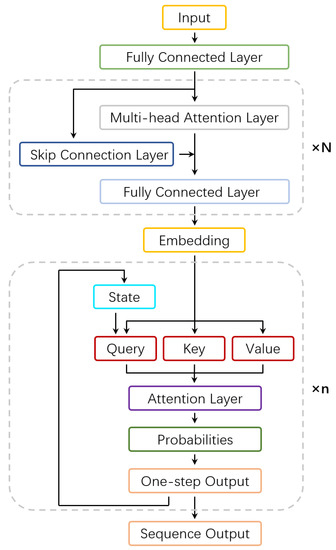
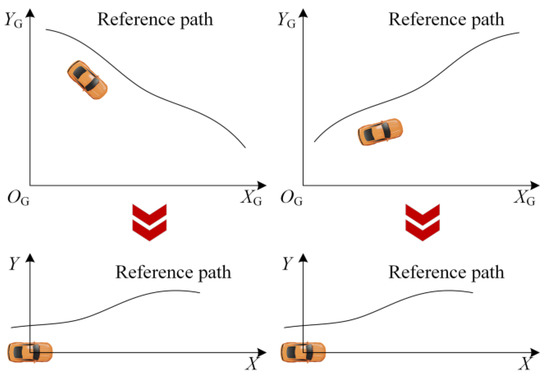
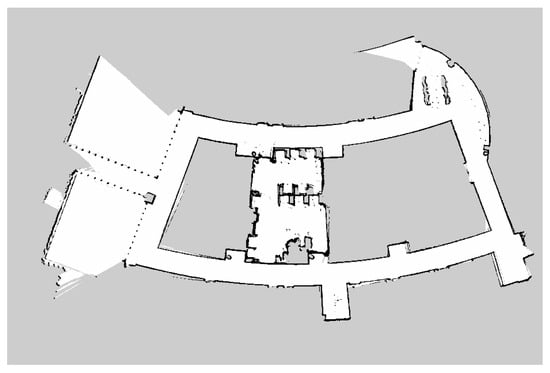
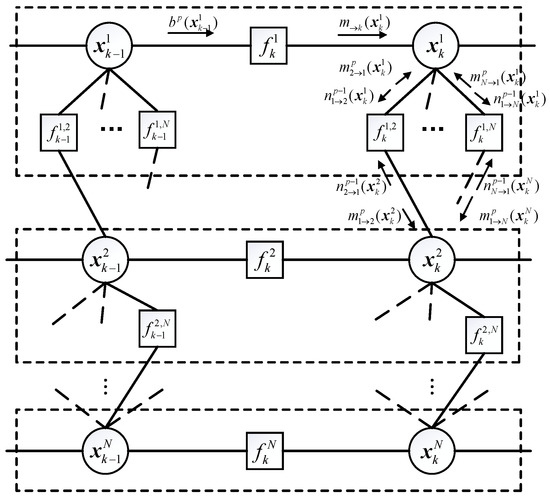
Advance Technologies of Navigation for Intelligent Vehicles
A topical collection in Electronics (ISSN 2079-9292). This collection belongs to the section "Electrical and Autonomous Vehicles".
Viewed by 42398Editors
Interests: unmanned systems; information fusion; distributed control; navigation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: unmanned systems; cooperative control; digital twins
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Intelligent vehicles have become an area of intense research within the robotics and control community, wherein unmanned ground/aerial/underwater vehicles have covered a wide range of applications from the civil domain to the military domain, such as logistics, mine detection, building and environment monitoring, intruder detection and attacking, etc. In recent years, swarms or networks of such autonomous robots are emerging as a disruptive technology to enable highly reconfigurable, on-demand, distributed intelligent vehicles with a high impact in many areas of science, technology, and society. In any application, networked and cooperative vehicles are expected to be more capable than a single large vehicle, offering significantly enhanced flexibility (adaptability, scalability, and maintainability) and robustness (reliability, survivability, and fault tolerance).
Autonomous navigation is one of the supporting pillars for realizing the abovementioned intelligent applications of intelligent vehicles. To date, efforts in this study have been continuously increasing, but many problems remain to be explored, discovered, and solved. The primary purpose of this Special Issue is to explore and display the latest achievements of theory and practice related to the advance technologies of navigation for intelligent vehicles. The areas of interest include but are not limited to:
- Overview of intelligent vehicles;
- Signal processing methods and sensor modules for intelligent vehicles;
- Autonomous navigation in GPS-denied environments;
- Multi-sensor target localization and tracking;
- Autonomous decision making for game and cooperation;
- Cooperative path planning and re-planning for homogeneous/nonhomogeneous vehicles;
- Synchronization for large-scale networks of intelligent vehicles;
- Learning-based and bio-inspired control for complex tasks;
- Distributed optimization and parallel decision making;
- Fault tolerance and robustness in disturbed and uncertain environments;
- Artificial intelligence in swarm cooperative control;
- Deep learning for resource-constrained embedded vision sensor applications;
- Event-driven control strategies for silent and camouflaged intelligent vehicles.
Dr. Jinwen Hu
Prof. Wei Meng
Dr. Shenghai Yuan
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Electronics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- unmanned vehicle
- autonomous navigation
- autonomous control
- network control
- distributed control
- information fusion
- path planning
- formation control
- collision avoidance
- target localization and tracking
- task planning