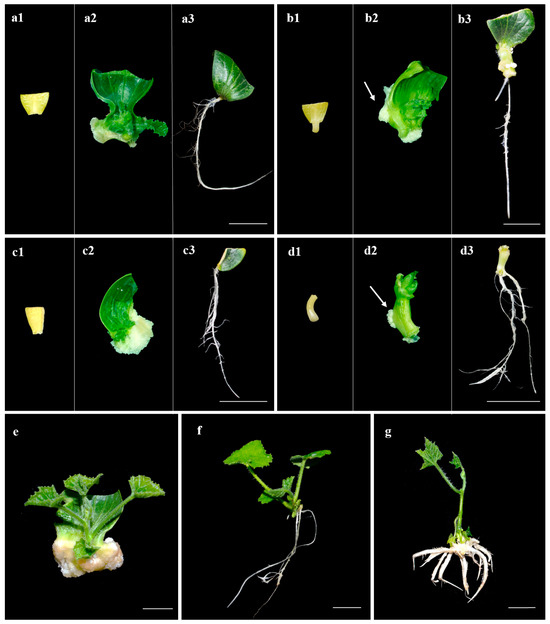
Application of Tissue Culture to Horticulture
A topical collection in Horticulturae (ISSN 2311-7524). This collection belongs to the section "Propagation and Seeds".
Viewed by 65135Editors
Interests: in vitro culture; Food chemistry; anthocyanins
Interests: tissue culture; conservation and propagation of plant biodiversity; plant – fungus interactions in mycorrhizal symbiosis; sustainable cropping systems
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
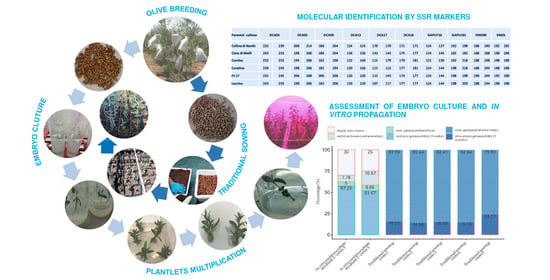
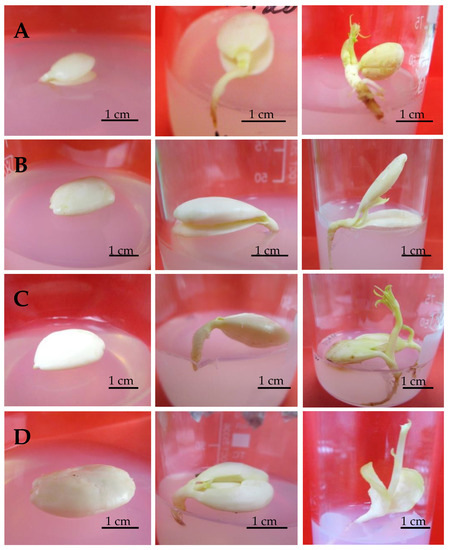
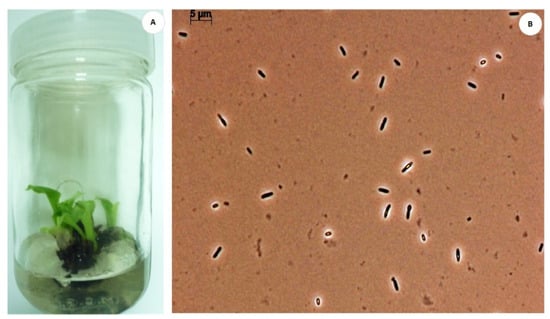
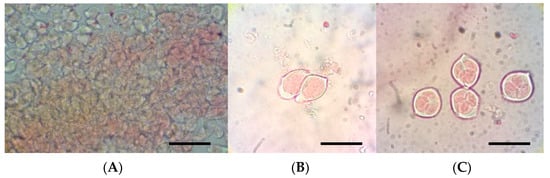
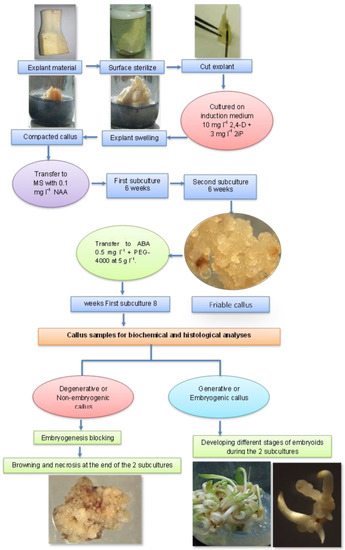
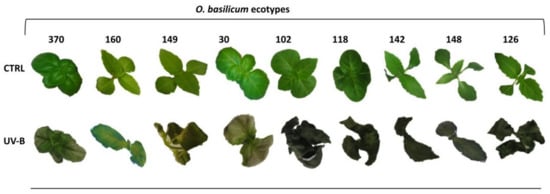
Plant tissue culture is the process of growing plant cells, tissues, or organs isolated from the mother plant, under controlled conditions. Since the early 20th century it has contributed to the progress of basic plant science. In the last twenty years, tissue culture has developed useful biotechnological approaches to agriculture. Particularly, in horticulture, plant tissue culture can offer technologies and methods for micropropagation, disease elimination, germplasm storage, production of secondary metabolites, plant modification and the improvement of fruit, vegetable, ornamental, and medicinal and aromatic plants.
The purpose of this Special Issue on “Application of Tissue Culture to Horticulture” is to present cutting-edge studies, tools, methods, and innovations that have been successful in several fields of tissue culture applied to horticultural crops:
- Clonal propagation;
- Adventitious regeneration/somatic embryogenesis;
- Disease-free plant production;
- Genetic improvement through tissue culture of horticultural crops;
- Production of phytochemicals by in vitro cultures;
- Germplasm conservation of horticultural crops.
Dr. Federica Blando
Dr. Claudia Ruta
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Horticulturae is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Micropropagation
- Plant regeneration
- Plant conservation
- Genetic improvement
- High-quality healthy plant
- Bioactive compounds