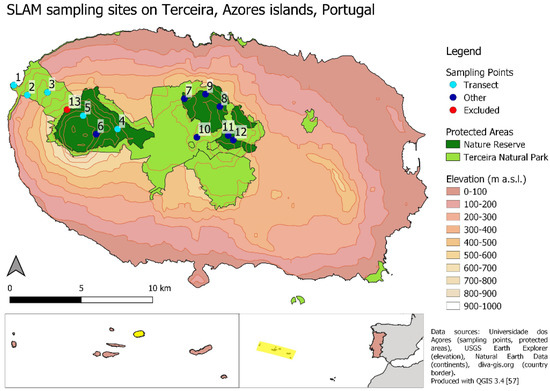
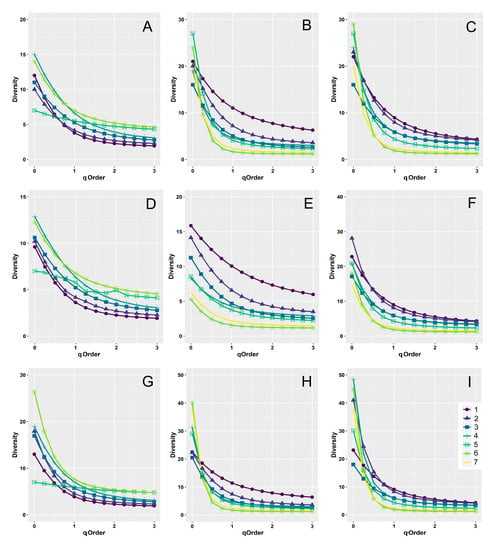
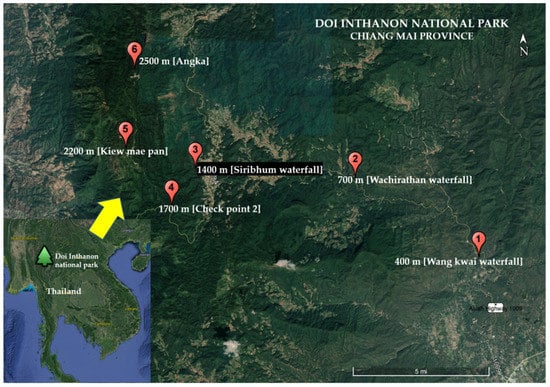
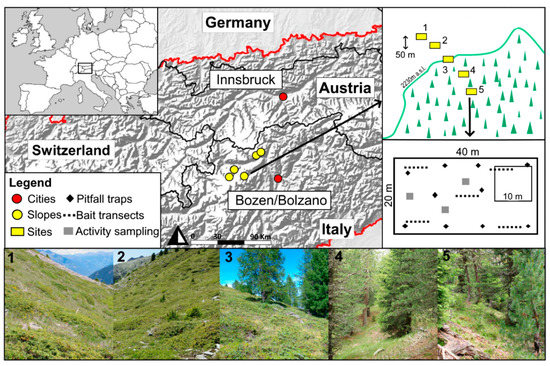
Insects in Mountain Ecosystems
A topical collection in Insects (ISSN 2075-4450). This collection belongs to the section "Insect Ecology, Diversity and Conservation".
Viewed by 100117Editors
Interests: species diversity; alpine ecology; climate change; carabid beetles
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: insect ecology; alpine ecology; high-altitude habitats
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The broad-scale features of mountain ecosystems are tied to the morphology of the relief because temperature variation with elevation is one of the main factors driving the adaptation of living organisms to mountain environments. Moreover the same elevation gradient at different latitudes and accompanied by local abiotic features, e.g., bedrock, soil, and climate, may trigger a particular set of evolution drivers, leading to the colonization of restricted mountain ranges by peculiar biota.
These and other features make mountains the ideal place to study altitude-for-latitude ecosystem variations, or even altitude-for-succession (i.e., time) gradients. Vegetation and soil layers are dominated by complex communities of invertebrates, even in the extreme environments of high altitudes, where the last chance of survival is given to species contracting their geographical range as a consequence of climate change.
Studies of mountain insects have focused on several subjects, including abundance relationships among species as well as zoogeography, phenotypic plasticity, man-made disturbance.
This Topical Collection will broadly address studies on insects in mountain ecosystems across all relevant disciplines, and, in this context, submissions in the form of reviews and original basic or applied research are welcome.
Dr. Roberto Pizzolotto
Dr. Mauro Gobbi
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Insects is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- mountain ecosystems
- extreme environments
- zoogeography
- altitudinal gradient