Mastitis in Dairy Ruminants
A topical collection in Pathogens (ISSN 2076-0817). This collection belongs to the section "Bacterial Pathogens".
Viewed by 91853Editors
Interests: small ruminant health management; diseases of small ruminants; welfare of small ruminants; veterinary infectious diseases
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
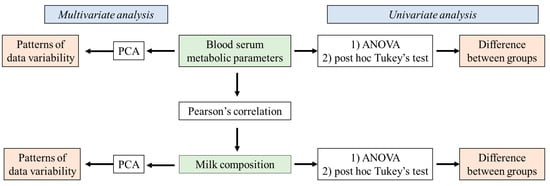
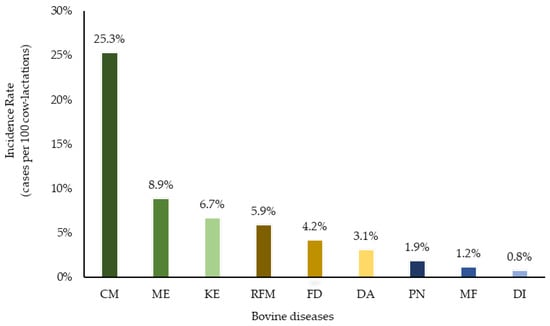
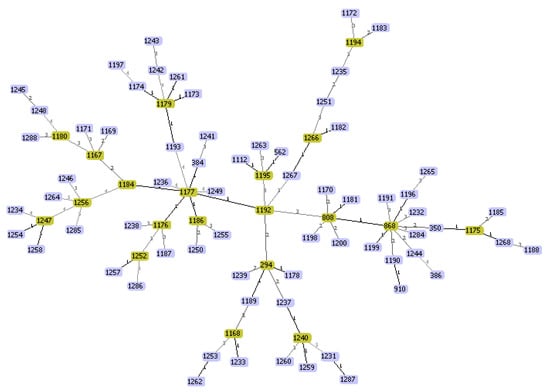
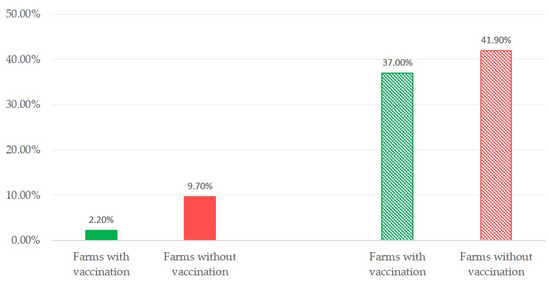
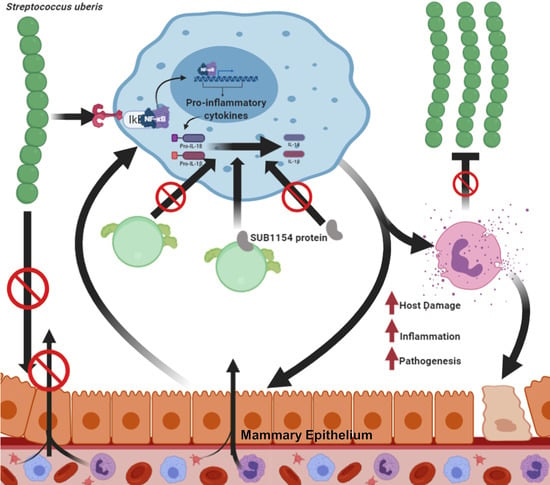
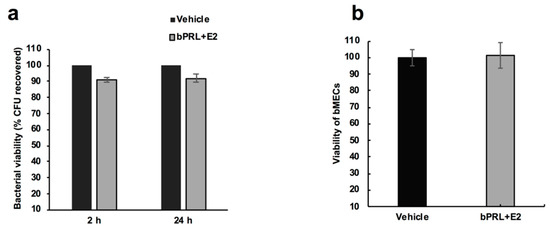
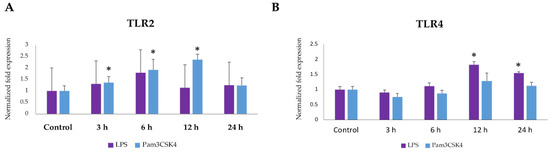
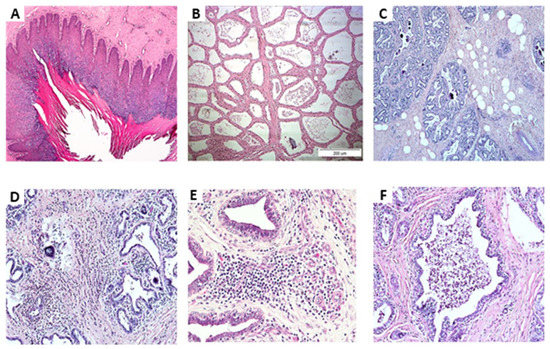
Mastitis, which occurs as the result of intramammary infections by various bacteria, is an important disease of dairy ruminants. It is responsible for significant financial problems in cattle, sheep, goat and buffalo farms and it also adversely hampers the welfare of the affected animals; further, the mastitis causal bacteria have are significant public health hazards. The collection will cover all aspects of mastitis: aetiology (including bacterial studies), welfare, epidemiology, pathogenesis, control, zoonotic aspects. The collection will comprise systematic and opinionated reviews, as well as original manuscripts describing field, laboratory or animal experimental work.
Prof. Dr. George Fthenakis
Dr. Maria Filippa Addis
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pathogens is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- mastitis
- dairy ruminants
- cattle
- sheep
- goat
- buffalo
- aetiology
- pathogenesis
- control