Tools, Approaches and Modeling in Sustainable Supply Chain Management
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Chi-Jie Lu
Prof. Dr. Chi-Jie Lu
 Prof. Dr. Chi-Jie Lu
Prof. Dr. Chi-Jie Lu
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Information Management, Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City 24205, Taiwan
Interests: machine learning and its applications; medical/healthcare informatics; time-series data analysis; supply chain management; quality management
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Sustainable supply chain management involves environmentally, financially, and socially viable practices of the overall supply chain operation and aims to develop actions that make the supply chain more sustainable, while ensuring effectiveness and efficiency. All kinds of supply chains can be optimized using sustainable tools, approaches, and modeling. This Special Issue seeks high-quality works focusing on state-of-the-art/potential tools and approaches in enabling the development of sustainable supply chain management. Topics include but are not limited to the following:
- Carbon emissions technology
- Corporate social responsibility of supply chains
- Data mining/machine learning approaches in sustainable supply chains
- Demand management
- Environmental impact assessment in supply chains
- Inventory management
- Internet of Things in sustainable supply chains
- Modelling for sustainable transportation and logistics
- Reverse logistics and circular economy
- Sustainable manufacturing
- Supply chain technology and impact on sustainability
- Sustainability in small and medium enterprises
- Sustainability assessment and resilience analysis of critical infrastructures
Prof. Dr. Chih-Te Yang
Prof. Dr. Chi-Jie Lu
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Processes is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Carbon emissions
- Circular economy
- Green supply chains
- Inventory
- Logistics
- Machine learning
- Sustainability
- Supply chain management
- Sustainable production
Published Papers (21 papers)
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceArticle
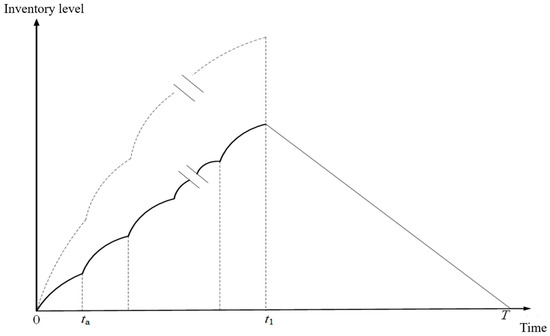
Research on an Optimal Maintenance and Inventory Model Based on Carbon Tax Policy
by
Wei-Jen Chen, Chi-Jie Lu, Pei-Ti Hsu and Chih-Te Yang
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1581
Abstract
The equipment in a factory will gradually deteriorate during production, leading to the production of defective products. Without appropriate maintenance, the defect rate will increase over time. Consequently, the production cost will rise, the inventory quality will be affected, the profit will decrease,
[...] Read more.
The equipment in a factory will gradually deteriorate during production, leading to the production of defective products. Without appropriate maintenance, the defect rate will increase over time. Consequently, the production cost will rise, the inventory quality will be affected, the profit will decrease, and the risk of carbon emissions will increase, leading to more customer complaints and damaging the corporate image. In addition to focusing on preventive maintenance to ensure the quality of products, companies should also take carbon emissions into consideration. Furthermore, the frequency of maintenance must be carefully considered, as both carbon emissions and maintenance costs will increase if the frequency is too high; conversely, if the maintenance frequency is too low or non-existent, the defect rate may increase cumulatively, or production may be suspended due to equipment failure. Therefore, this research explores preventive maintenance and inventory management issues within an imperfect production system and develops an extended economic production quantity model that incorporates defective products as well as taking carbon tax and preventive maintenance into consideration. The main purpose is to determine the optimal maintenance frequency, production, and replenishment cycle length, so as to maximize the total profit under the carbon tax policy. This study demonstrates a computing process with relatively impractical product data based on the actual business situation of a disposable diaper manufacturer. Furthermore, a sensitivity analysis is implemented to the model parameters in the proposed model. The managemental insights are illustrated based on the results of theoretical analysis to provide a reference to policy makers during decision making, hence, to secure the sustainability and green transitions of corporates. The results of this study not only help to reduce environmental impact but can also improve the competitiveness and sustainable development of enterprises.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
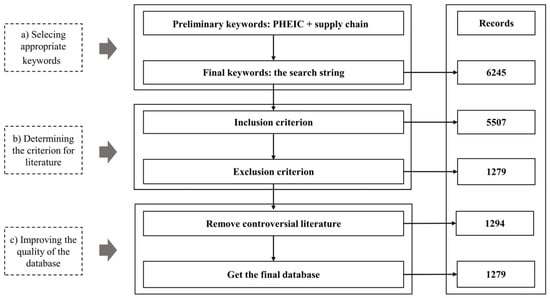
Supply Chain Management during a Public Health Emergency of International Concern: A Bibliometric and Content Analysis
by
Jianli Luo, Minmin Huang, Yanhu Bai and Jia Li
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3246
Abstract
A public health emergency of international concern, such as a pandemic, disrupts the normal operation of the global supply chain, which necessitates in-depth research on supply chain management. In this paper, we used bibliometric and content analysis to provide a systematic analysis of
[...] Read more.
A public health emergency of international concern, such as a pandemic, disrupts the normal operation of the global supply chain, which necessitates in-depth research on supply chain management. In this paper, we used bibliometric and content analysis to provide a systematic analysis of the supply chain industry from this background. The descriptive analysis provides insights into the publication growth trajectory, in terms of the contributing authors, countries, and subject categories, which presents an intuitive display of previous research. In addition, the existing research mainly covers three dimensions of supply chain disruption, strategies, and sustainability, which can be clustered into supply chain disruption, disruption recovery, reconfiguration, digital intelligence, optimization, and sustainability. By revisiting the supply chain industry, we explored the transformation of its characteristics in the pandemic, covering themes ranging from expansion to contraction, from traditional to digital intelligence, and from fragile to sustainability, which suggests potential research directions for future studies. This contributes to the further research of supply chain management during the pandemic and provides supply chain managers with a practical approach for dealing with supply chain disruption risks and improving supply chain sustainability in this context.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
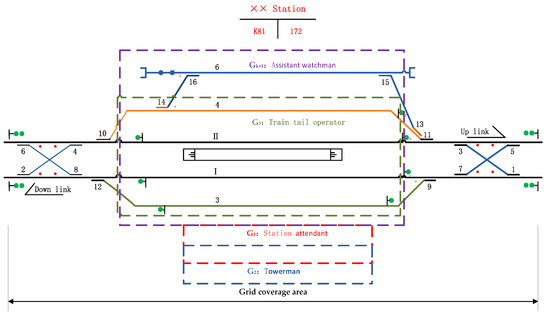
Analysis of Grid Response Strategies for the Safety Behavior Risk Events of Transportation System Based on System Dynamics—“the Assistant Watchman Does Not Appear as Required”
by
Huafeng Zhang, Changmao Qi and Mingyuan Ma
Viewed by 3333
Abstract
Employees are the most important and dynamic elements in the railway transportation system. How to achieve accurate control of inertial violation of “key person, key matter, key period”, and formulate more personalized risk response strategy is a thorny problem that faced by safety
[...] Read more.
Employees are the most important and dynamic elements in the railway transportation system. How to achieve accurate control of inertial violation of “key person, key matter, key period”, and formulate more personalized risk response strategy is a thorny problem that faced by safety managers. The existing risk response usually takes control measures from the perspective of the system as a whole, ignoring the heterogeneity of risk, and the selection of response strategies only considers the target risks to be dealt with, ignoring the secondary risks that may occur in the process of risk response, or the residual risks formed by changing the existing risk, coupled with the lack of quantitative evaluation of risk response effect, resulting in poor risk response effect. By introducing the grid theory and taking the risk event of “the assistant watchman does not appear as required” at Huangyangcheng station of Shenshuo Railway as an example, this study constructs a grid response model of the assistant watchman risk events based on system dynamics. Through the grid division, the model accurately locates and classifies the assistant watchman on duty. Then, during the system dynamics simulation process, the hazard factor is regarded as a bridge, and the traditional virtual boundary of system simulation is transformed into accurate grid definition. By improving the response strategy of safety behavior risk event of the assistant watchman on duty in cell grid and using Vensim-PLE software for personalized simulation, the intervention of “the assistant watchman does not appear as required” risk event is transformed from qualitative analysis to dynamic quantitative mathematical model, so as to realize the personalized response simulation analysis of employees in the grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
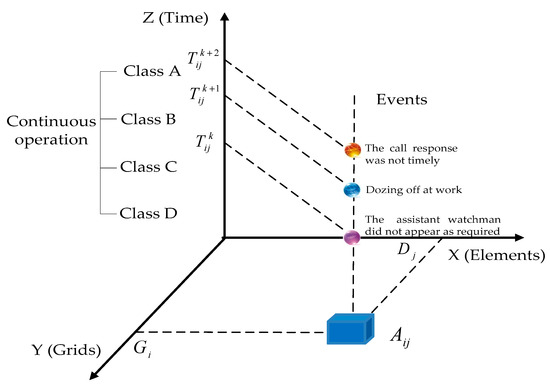
Grid-Based Employee Safety Behavior Risk Assessment of the Train Operation Department
by
Huafeng Zhang, Changmao Qi and Mingyuan Ma
Viewed by 1737
Abstract
In the train operation department, the most important and dynamic factor is that the department employees are involved in all areas. Realizing the dynamic control of “key person, key event, and key period” to fundamentally curb employee inertia violation is a significant issue
[...] Read more.
In the train operation department, the most important and dynamic factor is that the department employees are involved in all areas. Realizing the dynamic control of “key person, key event, and key period” to fundamentally curb employee inertia violation is a significant issue that needs to be solved on the railway site. The traditional “probability–severity” two-dimensional risk assessment model is carried out from the perspective of the system, ignoring the spatiotemporal risk characteristics of the individual, and a large amount of hazard factor data generated in the operation process is not applied in the risk assessment process. As a result, safety behavior risk practice lacks pertinence, accuracy, and individuation. This study proposes a safety behavior risk assessment model based on the grid management and hazard factor assignment function to improve the traditional two-dimensional risk matrix. By introducing spatial location variables, the method accurately locates and classifies the site staff and organizes the disorder and lack of associated risk data with regard to time and space. With a focus on the hazard factor, the induced intensity is proposed for the first time and considered as the input of probability calculation to innovate the traditional “probability–severity” risk matrix. Finally, the methodology is applied to the risk event assessment of “the assistant watchman doesn’t appear as required” scenario in the Huangyangcheng station of Shenshuo Railway, and the evaluation results realize the personalized evaluation of the risk event in different cell grids.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
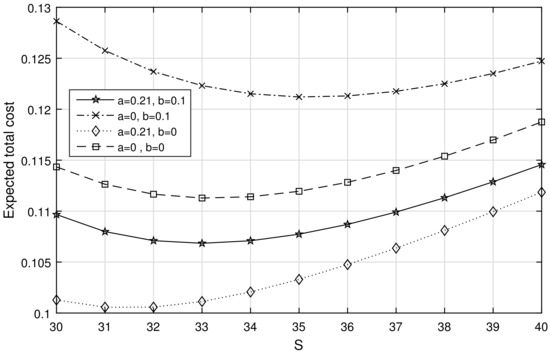
Analysis of Stock-Dependent Arrival Process in a Retrial Stochastic Inventory System with Server Vacation
by
C. Sugapriya, M. Nithya, K. Jeganathan, N. Anbazhagan, Gyanendra Prasad Joshi, Eunmok Yang and Suseok Seo
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2718
Abstract
The present study deals with the stock-dependent Markovian demand of a retrial queueing system with a single server and multiple server vacation. The items are restocked under a continuous review
ordering policy. When there is no item in
[...] Read more.
The present study deals with the stock-dependent Markovian demand of a retrial queueing system with a single server and multiple server vacation. The items are restocked under a continuous review
ordering policy. When there is no item in the system, the server goes on vacation. Further, any arrival demand permits entry into an infinite orbit whenever the server is on vacation. In the Matrix geometric approach with the Neuts-Rao truncation technique, the steady-state joint distribution of the number of customers in orbit, the server status, and the inventory level is obtained. Under the steady-state conditions, some significant system performance measures, including the long-run total cost rate, are derived, and the Laplace-Stieltjes transform is also used to investigate the waiting time distribution. According to various considerations of uncontrollable parameters and costs, the merits of the proposed model, especially the important characteristics of the system with stock dependency over non-stock dependency, are explored. Ultimately, the important facts and ideas behind this model are given in conclusion.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Prediction Process of the Remaining Useful Life of Electric Vehicle Battery Using Real-World Data
by
Xu Wang, Jian Li, Ben-Chang Shia, Yi-Wei Kao, Chieh-Wen Ho and Mingchih Chen
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3431
Abstract
In modern society, environmental sustainability is always a top priority, and thus electric vehicles (EVs) equipped with lithium-ion batteries are becoming more and more popular. As a key component of EVs, the remaining useful life of battery directly affects the demand of the
[...] Read more.
In modern society, environmental sustainability is always a top priority, and thus electric vehicles (EVs) equipped with lithium-ion batteries are becoming more and more popular. As a key component of EVs, the remaining useful life of battery directly affects the demand of the EV supply chain. Accurate prediction of the remaining useful life (RUL) benefits not only EV users but also the battery inventory management. There are many existing methods to predict RUL based on state of health (SOH), but few of them are suitable for real-world data. There are several difficulties: (1) battery capacity is not easy to obtain in the real world; (2) most of these methods use the individual data for each battery, and the computing processes are difficult to perform in the cloud; (3) there is a lack of approaches for real-time SOH estimating and RUL predicting. This paper adopts several statistical methods to perform the prediction and compars the results of different models on experimental data (NASA dataset). Then, real-world data were implemented for an online process of RUL prediction. The main finding of this research is that the required CPU time was short enough to meet the daily usage after the real-world data was implemented for an online process of RUL prediction. The feasibility and precision of the prediction model can help to support the frequency control in power systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
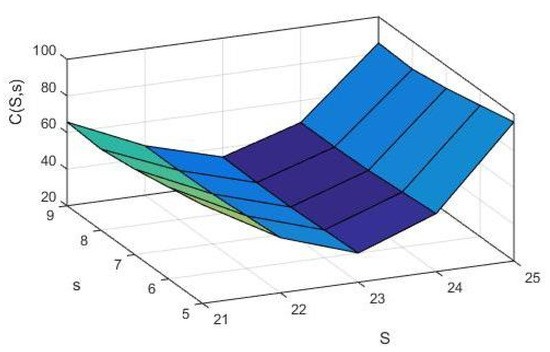
Steady State Analysis of Impulse Customers and Cancellation Policy in Queueing-Inventory System
by
V. Vinitha, N. Anbazhagan, S. Amutha, K. Jeganathan, Gyanendra Prasad Joshi, Woong Cho and Suseok Seo
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2420
Abstract
This article discusses the queueing-inventory model with a cancellation policy and two classes of customers. The two classes of customers are named ordinary and impulse customers. A customer who does not plan to buy the product when entering the system is called an
[...] Read more.
This article discusses the queueing-inventory model with a cancellation policy and two classes of customers. The two classes of customers are named ordinary and impulse customers. A customer who does not plan to buy the product when entering the system is called an impulse customer. Suppose the customer enters into the system to buy the product with a plan is called ordinary customer. The system consists of a pool of finite waiting areas of size N and maximum S items in the inventory. The ordinary customer can move to the pooled place if they find that the inventory is empty under the Bernoulli schedule. In such a situation, impulse customers are not allowed to enter into the pooled place. Additionally, the pooled customers buy the product whenever they find positive inventory. If the inventory level falls to s, the replenishment of Q items is to be replaced immediately under the (s, Q) ordering principle. Both arrival streams occur according to the independent Markovian arrival process (MAP), and lead time follows an exponential distribution. In addition, the system allows the cancellation of the purchased item only when there exist fewer than S items in the inventory. Here, the time between two successive cancellations of the purchased item is assumed to be exponentially distributed. The Gaver algorithm is used to obtain the stationary probability vector of the system in the steady-state. Further, the necessary numerical interpretations are investigated to enhance the proposed model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
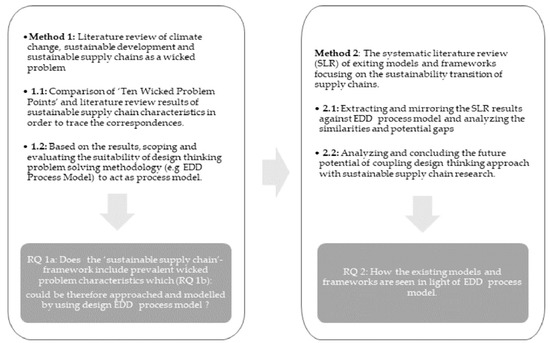
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Approaching Sustainability Transition in Supply Chains as a Wicked Problem: Systematic Literature Review in Light of the Evolved Double Diamond Design Process Model
by
Harri Pyykkö, Mari Suoheimo and Stefan Walter
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 7655
Abstract
Transition from the status quo to more sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) practices is a highly complex and non-linear process with multiple drivers, but also obstacles, on the way. The impending strict regulatory framework, particularly in terms of the environmental dimensions of sustainability
[...] Read more.
Transition from the status quo to more sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) practices is a highly complex and non-linear process with multiple drivers, but also obstacles, on the way. The impending strict regulatory framework, particularly in terms of the environmental dimensions of sustainability development (SD), is single-handedly opening the door to rapid and potentially disruptive change. The research literature on SSCM has increased exponentially over the last decade to meet the mounting demand for information on how to tackle often conflicting sustainability-related requirements while satisfying all internal and external stakeholders. Due to the continuously evolving and
wicked nature of SSCM, a limited number of scholars have approached the issue with design thinking problem solving methodologies (DTPSMs). The results of a systematic literature review (SLR) were mirrored with the Evolved Double Diamond (EDD) design process model to formulate a design thinking overview and trace potential research gaps of selected frameworks and models regarding the sustainability transition (ST) of supply chains (SCs). The research results demonstrate that modelling the ST in SC as a wicked problem can contribute to the creation of more structured and novel SSCM models and frameworks, which take into deeper consideration the evolving nature of the issue and improve facilitation practices of stakeholder engagement.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Optimization Framework for Low-Carbon Oriented Integrated Energy System Management in Commercial Building under Electric Vehicle Demand Response
by
Zesen Wang, Xin Li, Yu Li, Tianqi Zhao, Xue Xia and Hanzhi Zhang
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2610
Abstract
As the carbon emissions of commercial buildings are attracting considerable attention, the integrated energy system (IES) has become a promising low-carbon method in response. In this paper, an optimization framework for low-carbon oriented integrated energy system management under electric vehicles (EV) demand response
[...] Read more.
As the carbon emissions of commercial buildings are attracting considerable attention, the integrated energy system (IES) has become a promising low-carbon method in response. In this paper, an optimization framework for low-carbon oriented integrated energy system management under electric vehicles (EV) demand response is proposed. After analyzing the charging behavior, EV charging demand is simulated. Then, the low-carbon integrated energy system model is proposed with the optimization framework considering carbon reduction. Subsequently the objective function containing carbon emission is obtained for the whole operation optimization. The results of the studied case show that the optimization framework proposed can reduce the carbon emission greatly as well as moderate economic cost, which declined because of the revenue from charging demand response. In general, the optimization of low-carbon oriented IES in commercial buildings is feasible.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Dynamic Sales Price Control Model for Exclusive Exquisite Products within a Time Interval
by
Po-Yu Chen
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1998
Abstract
When information regarding the effective evaluation of the value of exquisite products is lacking, the market demand function for such products at a given time point is affected by the diffusion of historical transaction price information before the time point. This is because
[...] Read more.
When information regarding the effective evaluation of the value of exquisite products is lacking, the market demand function for such products at a given time point is affected by the diffusion of historical transaction price information before the time point. This is because historical transaction prices play an active role in influencing the internal reference price (IRP) of customers, and the continuous diffusion of historical transaction price information leads to the continuous correction, adjustment, and updating of customers’ IRPs. Given the varying rates of such information diffusion, the speed at which customers adjust their IRPs also varies across individuals and contexts. By considering the exponential distribution of potential customers’ IRPs as an example to establish the dynamic demand function that considers the effect of historical transaction prices, this paper discusses the effect of different information diffusion rates on the demand function at a time point. On the basis of this demand function, a sales price control model that maximizes the discounted profitability for businesses in the patent term of an exquisite product is then constructed to provide businesses with an operation method to cultivate prices and increase profits.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Demand Forecasting for Multichannel Fashion Retailers by Integrating Clustering and Machine Learning Algorithms
by
I-Fei Chen and Chi-Jie Lu
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 7599
Abstract
In today’s rapidly changing and highly competitive industrial environment, a new and emerging business model—fast fashion—has started a revolution in the apparel industry. Due to the lack of historical data, constantly changing fashion trends, and product demand uncertainty, accurate demand forecasting is an
[...] Read more.
In today’s rapidly changing and highly competitive industrial environment, a new and emerging business model—fast fashion—has started a revolution in the apparel industry. Due to the lack of historical data, constantly changing fashion trends, and product demand uncertainty, accurate demand forecasting is an important and challenging task in the fashion industry. This study integrates k-means clustering (KM), extreme learning machines (ELMs), and support vector regression (SVR) to construct cluster-based KM-ELM and KM-SVR models for demand forecasting in the fashion industry using empirical demand data of physical and virtual channels of a case company to examine the applicability of proposed forecasting models. The research results showed that both the KM-ELM and KM-SVR models are superior to the simple ELM and SVR models. They have higher prediction accuracy, indicating that the integration of clustering analysis can help improve predictions. In addition, the KM-ELM model produces satisfactory results when performing demand forecasting on retailers both with and without physical stores. Compared with other prediction models, it can be the most suitable demand forecasting method for the fashion industry.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
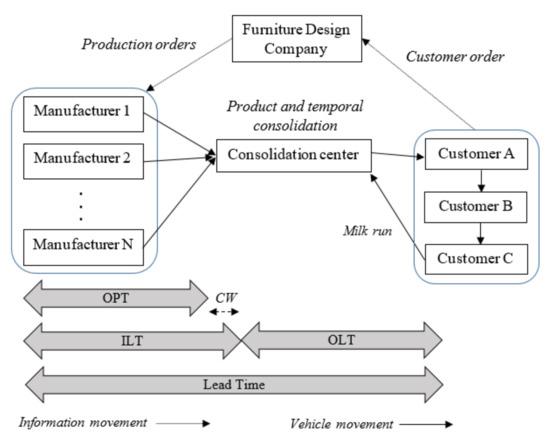
Modeling Freight Consolidation in a Make-to-Order Supply Chain: A Simulation Approach
by
Mohammed Alnahhal, Diane Ahrens and Bashir Salah
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4293
Abstract
Shipment consolidation is one of main initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions and transportation cost. It reduces the number of shipments per customer and reduces transportation costs by using larger shipments. This paper investigates the temporal consolidation process in a central consolidation center in
[...] Read more.
Shipment consolidation is one of main initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions and transportation cost. It reduces the number of shipments per customer and reduces transportation costs by using larger shipments. This paper investigates the temporal consolidation process in a central consolidation center in a make-to-order supply chain. This research was motivated by a case study of a design furniture company that has many suppliers and customers in large parts of Europe. Simulation was used to check the effect of a new and a special time-based temporal consolidation on the response time in outbound logistics. A soft delivery deadline that is less than the average lead time was used because of the long lead time. Arena Software was used to model the supply chain in order to find the best circumstances to use consolidation. Results showed that temporal consolidation could be more effective when order preparation time is with larger variability. The useful waiting is more when there is at least one order every four days. A formula that approximates the percent of reduced shipments was found. Furthermore, many shipments can be reduced without severely affecting the average response time. The value of the study is that it investigates consolidation problems in a high-mix low-volume environment that was overlooked by previous research.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceArticle
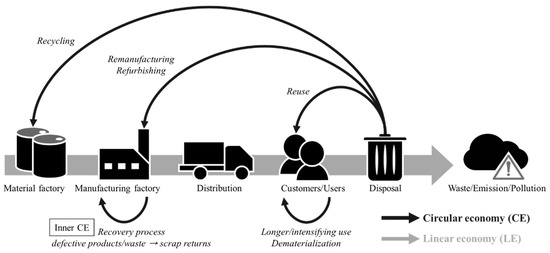
An Imperfect Production–Inventory Model with Mixed Materials Containing Scrap Returns Based on a Circular Economy
by
Rung-Hung Su, Ming-Wei Weng, Chih-Te Yang and Hsin-Ting Li
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3020
Abstract
The implementation of scrap recovery activities has been shown to improve the financial performance of many firms, and this kind of circular economy (CE) is particularly evident in industries with green manufacturing (GM). In this paper, we consider an imperfect multiple-stage production system
[...] Read more.
The implementation of scrap recovery activities has been shown to improve the financial performance of many firms, and this kind of circular economy (CE) is particularly evident in industries with green manufacturing (GM). In this paper, we consider an imperfect multiple-stage production system that manufactures paired products made from mixed materials containing scrap returns, in which the scrap returns are converted from defective products. The feed rates of scrap returns for two products are different, and the product with the higher feed rate is placed in the second order of the process to avoid unlimited accumulation of scrap returns. The proposed problem is formulated as a joint economic order quantity (EOQ) and economic production quantity (EPQ) model aimed at cost minimization. The decision variables of the proposed model include the production run time of two products, order quantity of new material, and the extent of investment in converted equipment. We also prove that the optimal solution exists uniquely and provide an algorithm for the computation of the optimal solution. Finally, a numerical example involving the pulp and paper manufacturing industry is provided to illustrate the solution process, and the results of its sensitivity analysis are also presented to show some managerial implications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
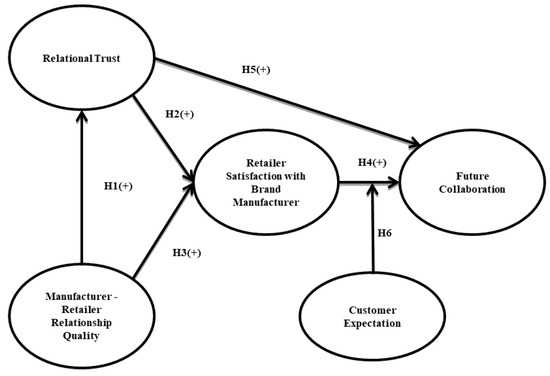
The Influence of Relationship Quality between Manufacturer and Retailer on Future Collaboration—A Case Study of Customer Electronic Product Channel in Taiwan
by
Shui-Lien Chen, Hao-Hsiang Tsao and Yung-Hsin Lee
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2770
Abstract
This study explores the collaboration between upstream manufacturer brands and first-line retailers in Taiwan’s 3C product market, which is influenced by several factors. Both parties are motivated by profit and thus, strive for mutual cooperation in the business environment. Whether influencing factors exist
[...] Read more.
This study explores the collaboration between upstream manufacturer brands and first-line retailers in Taiwan’s 3C product market, which is influenced by several factors. Both parties are motivated by profit and thus, strive for mutual cooperation in the business environment. Whether influencing factors exist between the retailer and manufacturer is a crucial issue. This study investigates 308 customer electronics retailers in Taiwan. Focusing on relationship quality, relational trust, and retailer satisfaction with the brand, we explore the possibility of future collaboration between retailers and manufacturer brands. The study results indicate the relationship quality between retailers and manufacturers has a significant impact on the relationship of trust. Both the relationship quality between retailers and manufacturers and the relational trust between the retailers and manufacturers have significant impacts on the retailer’s satisfaction with the manufacturer. Retailer satisfaction has a direct impact on the future collaboration between retailers and manufacturers. Compared with customers with high expectations, customers with low expectations have a higher effect on the relationship between retailer satisfaction with the brand manufacturer and the future collaboration between retailers and manufacturers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
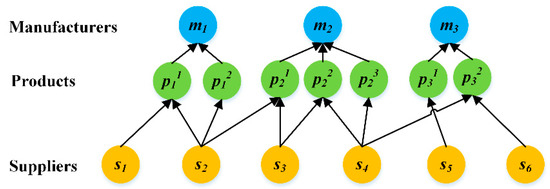
Enhanced Variable Neighborhood Search-Based Recovery Supplier Selection for Post-Disruption Supply Networks
by
Yuting Chen, Ping Lou and Wen Jiang
Viewed by 1982
Abstract
With the increasing reliance on global sourcing and the growth in the likelihood of disruptive incidents, today’s supply networks are more prone to unexpected natural and man-made disruptive events. In order to alleviate the losses caused by these disruptive events, when a large-scale
[...] Read more.
With the increasing reliance on global sourcing and the growth in the likelihood of disruptive incidents, today’s supply networks are more prone to unexpected natural and man-made disruptive events. In order to alleviate the losses caused by these disruptive events, when a large-scale event disrupts multiple suppliers simultaneously, a single or several critical suppliers should be selected from the disrupted ones to assist them to recover their production as soon as possible. The selection of these recovery suppliers is of great importance in the recovery process of the entire supply network. Thus, this paper proposes a recovery supplier selection method from the view of the supply network structure. Firstly, a tripartite graph-based supply model is proposed to depict a two-stage supply network, which consists of multiple manufacturers and suppliers as well as the diverse product supply-demand interdependence connecting them. To measure the impacts caused by supplier disruptions and to evaluate the effectiveness of recovery supplier decisions, two supply network performance metrics reflecting product supply availability are also given. Then, the recovery supplier selection problem is described as a combinatorial optimization problem. To solve this problem, a heuristic algorithm, with enhanced variable neighborhood search (EVNS) is designed based on the general framework of a variable neighborhood search. Finally, experiments based on a real-world supply network are conducted. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method is applicable and effective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
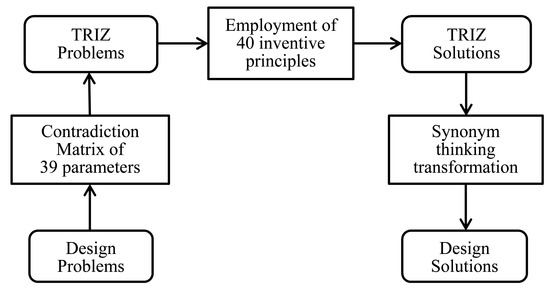
Implementing TRIZ with Supply Chain Management in New Product Development for Small and Medium Enterprises
by
Yun-Sheng Lin and Mingchih Chen
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4694
Abstract
Due to the impact of globalization, the competition between enterprises has become fierce and led the supply chains of many industries to be reorganized. One of the consequences is that the operation of many small and medium enterprises (SMs) had become very difficult.
[...] Read more.
Due to the impact of globalization, the competition between enterprises has become fierce and led the supply chains of many industries to be reorganized. One of the consequences is that the operation of many small and medium enterprises (SMs) had become very difficult. Hence, many of SMEs in Taiwan have gone bankrupt and some of them have moved to other places where they have lower production costs, in order to survive; this not only hollowed out the industries but also disconnected the supply chains in their mother countries. Because Taiwan’s SMEs are generally poor in innovation, this study explored the implementation of the theory of inventive problem-solving (TRIZ) with alignment of new product development (NPD) and supply chain management (SCM) to strengthen the innovation and productivity of new products, so that SMEs can refer to its use to aid sustainable business operation. We considered an SME in Taiwan as a case to study and investigate the strategies that it employed to achieve survival and sustainability. By examining the practical applications of the NPD of the case company, which was based on the TRIZ and NPD SCM alignment, we found that value-added products may be created despite unfavorable industry environments, by implementing and coordinating the TRIZ and three product-related variables, namely innovating, modularity, and variety. This study explored practical alternatives for SMEs to develop various value-added products that meet customers’ changing requirements and succeed in competitive markets to achieve a sustainable business operation. Considering SMEs are crucially important to the economic equality and development of countries and that SMEs may only survive for a short time when operating in changing supply chain environments, this study can be used as a reference for the management of SMEs and future academic research in related fields.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
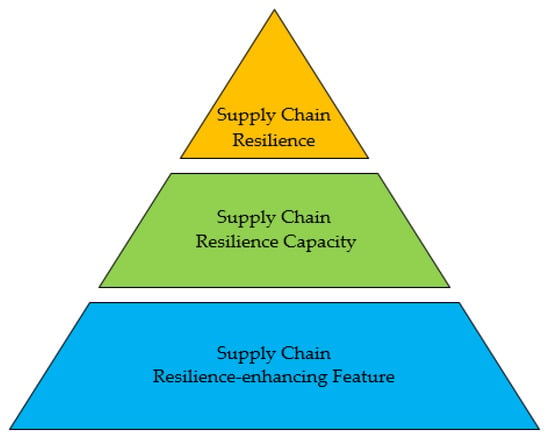
Resilience-Enhancing Solution to Mitigate Risk for Sustainable Supply Chain—An Empirical Study of Elevator Manufacturing
by
Chih-Hung Hsu, Ru-Yue Yu, An-Yuan Chang, Wen-Hong Chung and Wan-Ling Liu
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 11286
Abstract
As the complexity of supply chains increases, the enhancement of resilience for mitigating sustainable disruption risks in supply chains is an important issue. Quality function deployment (QFD) has been successfully applied in many domains to solve multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) problems. However, research on
[...] Read more.
As the complexity of supply chains increases, the enhancement of resilience for mitigating sustainable disruption risks in supply chains is an important issue. Quality function deployment (QFD) has been successfully applied in many domains to solve multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) problems. However, research on developing two houses of quality to connect sustainable supply chain disruption risks, resilience capacities, and resilience-enhancing features in elevator manufacturing supply chains by using the MCDM approach is lacking. This study aims to develop a framework for exploring useful decision-making by integrating the MCDM approach and QFD. By applying the framework, supply chain resilience can be improved by identifying the major sustainable risks and the key resilience to mitigate these risks. Important managerial insights and practical implications are obtained from the framework implementation in a case study of the elevator manufacturing industry. To strengthen resilience and thus mitigate key risks, the most urgent tasks are to connect the working site and the backstage to enhance product development and design and to share real-time job information. When these features are strengthened, agility, capacity, and visibility can be improved. Finally, unexpected events lead to changes in supplier delivery dates, and factors such as typhoon and lack of critical capacities/skilled employees with the greatest impact can be alleviated. This framework will provide an effective and pragmatic approach for constructing sustainable supply chain risk resilience in the elevator manufacturing industry.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
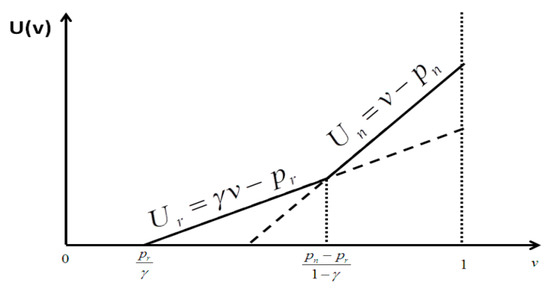
Optimal Channel Structure for Remanufacturing under Cap-and-Trade Regulation
by
Ying Teng and Binggang Feng
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2481
Abstract
In recent years, carbon cap-and-trade has been promoted by many national governments aiming to limit, or cap, total carbon dioxide emissions. Such a mechanism impacts manufacturers’ remanufacturing decisions, as it increases the cost of carbon emissions. The current literature has recognized the importance
[...] Read more.
In recent years, carbon cap-and-trade has been promoted by many national governments aiming to limit, or cap, total carbon dioxide emissions. Such a mechanism impacts manufacturers’ remanufacturing decisions, as it increases the cost of carbon emissions. The current literature has recognized the importance of carbon cap-and-trade regulations; however, little attention has been paid to what effect such regulations have on manufacturer’s remanufacturing with the flexibility to engage it in-house or outsource it to third-party remanufacturers. To fill this gap, we develop two theoretical models that, under the carbon cap-and-trade mechanism, allow the manufacturer to engage in remanufacturing operations in-house (Model H) or outsource them to an independent remanufacturer (Model R). The primary goal of this paper is to understand what effects carbon cap-and-trade regulations have on green supply chain management when producing new and remanufactured products. In particular, we find that although the manufacturer has a higher incentive to reduce the carbon emissions per remanufactured unit in Model H, the total carbon emissions may be higher than the value in Model R, because the sales volume effect dominates in that case. As such, our analysis suggests that environmental groups and agencies should not only take effective measures to stimulate the incentive of reducing the carbon emissions per unit but must also take care regarding the supply chain structure to limit the volume effect.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
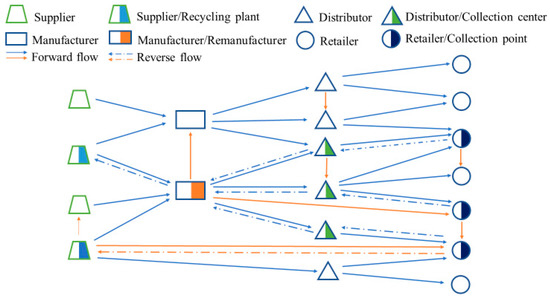
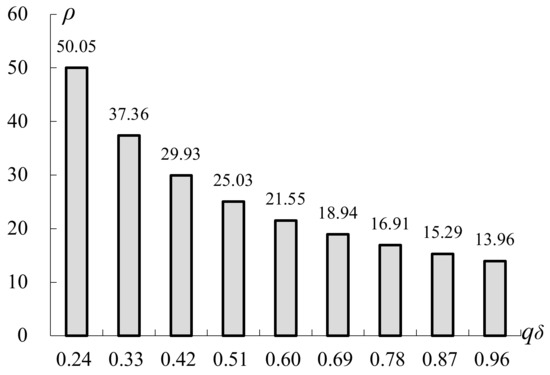
Building Robust Closed-Loop Supply Networks against Malicious Attacks
by
Ding-Shan Deng, Wei Long, Yan-Yan Li and Xiao-Qiu Shi
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2267
Abstract
With recent industrial upgrades, it is essential to transform the current forward supply networks (FSNs) into closed-loop supply networks (CLSNs), which are formed by the integration of forward and reverse logistics. The method chosen in this paper for building reverse logistics is to
[...] Read more.
With recent industrial upgrades, it is essential to transform the current forward supply networks (FSNs) into closed-loop supply networks (CLSNs), which are formed by the integration of forward and reverse logistics. The method chosen in this paper for building reverse logistics is to add additional functions to the existing forward logistics. This process can be regarded as adding reverse edges to the original directed edges in an FSN. Due to the limitation of funds and the demand for reverse flow, we suppose that a limited number of reverse edges can be built in a CLSN. To determine the transformation schemes with excellent robustness against malicious attacks, this paper proposes a multi-population evolutionary algorithm with novel operators to optimize the robustness of the CLSN, and this algorithm is abbreviated as MPEA-RSN. Then, both the generated and realistic SNs are taken as examples to validate the effectiveness of MPEA-RSN. The simulation results show that the index
R, introduced to evaluate the robustness of CLSNs, can be improved by more than 95%, and this indicates that (1) the different schemes for adding reverse routes to an FSN can lead to different robustness values, and (2) the robustness of the transformed CLSN to malicious attacks can be significantly improved after optimization by MPEA-RSN. When an FSN is to be transformed into a CLSN, this paper can provide a frame of reference for building a CLSN that is robust to malicious attacks from a network structural perspective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Quality Inspection Plan for Imperfect Production System with Assembly Configuration
by
Jyh-Wen Ho
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1842
Abstract
In this study, the model concerning a negative binomial sampling inspection plan is proposed and applied to an imperfect production system with assemble-to-order configuration, where the production system is subject to a Weibull deteriorating process and is operated under an in-control or an
[...] Read more.
In this study, the model concerning a negative binomial sampling inspection plan is proposed and applied to an imperfect production system with assemble-to-order configuration, where the production system is subject to a Weibull deteriorating process and is operated under an in-control or an out-of-control state. The proposed model of this study contributes to developing an approach which can effectively integrate the considerations of the production system status, the defective rate, the working efficiency of employees, and the market demands with an aim to determine the optimal number of conforming items for inspection with minimum total cost, and the results can be practically applied to the assembly of products in various industries, especially for the prevalent Industry 4.0 in manufacturing.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
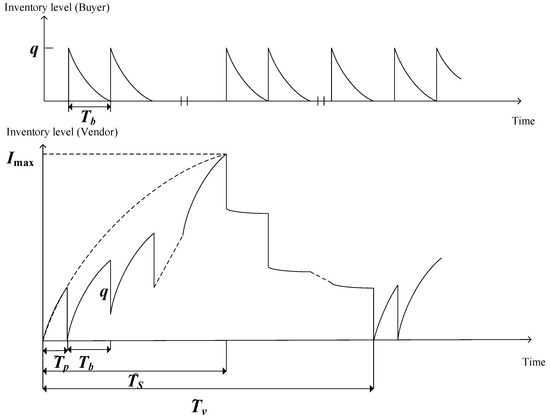
Sustainable Production–Inventory Model in Technical Cooperation on Investment to Reduce Carbon Emissions
by
JiaLiang Pan, Chui-Yu Chiu, Kun-Shan Wu, Hsiu-Feng Yen and Yen-Wen Wang
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 2697
Abstract
Carbon cap-and-trade and carbon offsets are common and important carbon emission reduction policies in many countries. In addition, carbon emissions from business activities can be effectively reduced through specific capital investments in green technologies. Nevertheless, such capital investments are costly and not all
[...] Read more.
Carbon cap-and-trade and carbon offsets are common and important carbon emission reduction policies in many countries. In addition, carbon emissions from business activities can be effectively reduced through specific capital investments in green technologies. Nevertheless, such capital investments are costly and not all enterprises can afford these investments. Therefore, if all members of a supply chain agree to share the investments in the facilities, the supply chain can reduce carbon emissions and generate more profit. Under carbon cap-and-trade and carbon tax policies, this study proposes a production–inventory model in which the buyer and vendor in the integrated supply chain agree to co-invest funds to reduce carbon emissions. We planned to integrate production, delivery, replenishment, and technology to reduce carbon emissions so as to maximize the total profit of the supply chain system. Several examples are simulated and the sensitivity analysis of the main parameters is carried out. The optimal solutions and joint total profit under various carbon emission policies are also compared. The future carbon emission control trend is expected to enable companies to share risks by co-investing and developing sustainable supply chains.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures