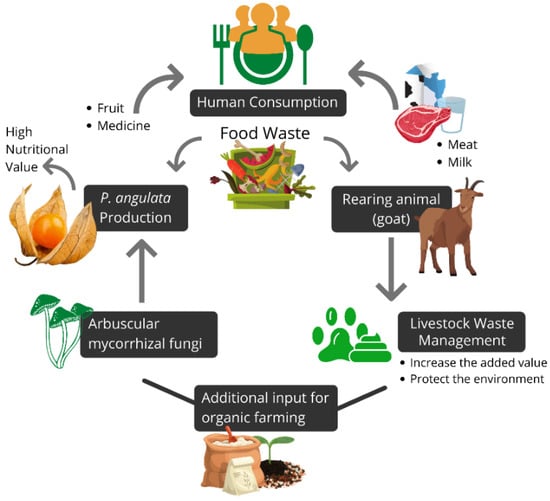
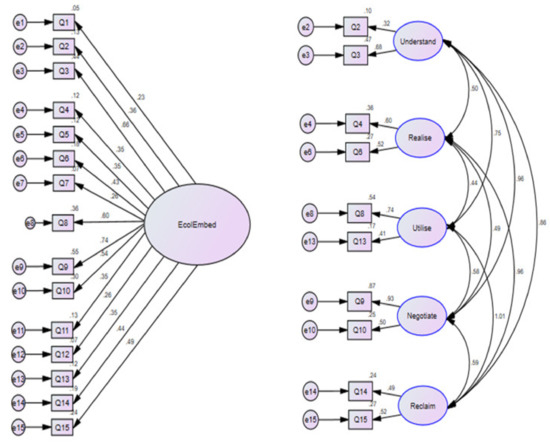
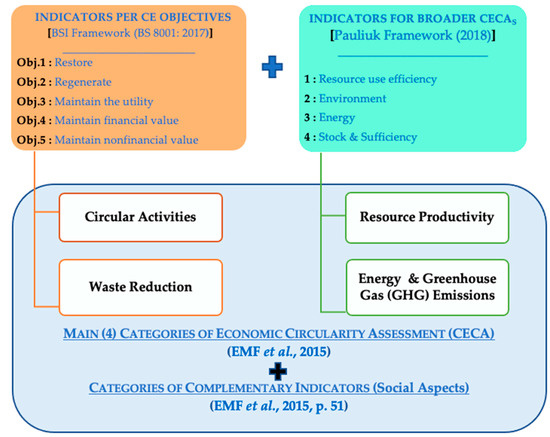
Circular Economy and Sustainable Strategies
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Sustainability and Applications".
Viewed by 296425Editors
Interests: environmental pollution; circular economy; waste and wastewater management; human health; renewable energy; interdisciplinary approaches for environmental management; air quality; environmental sustainability
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: management; human resources management; occupational health and safety management; production systems engineering; ergonomics; circular economy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
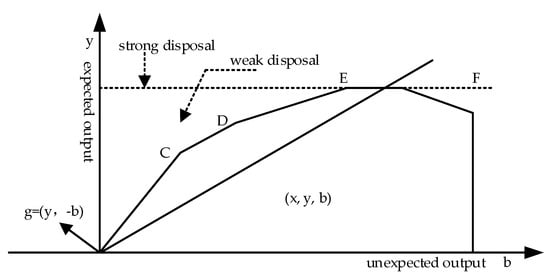
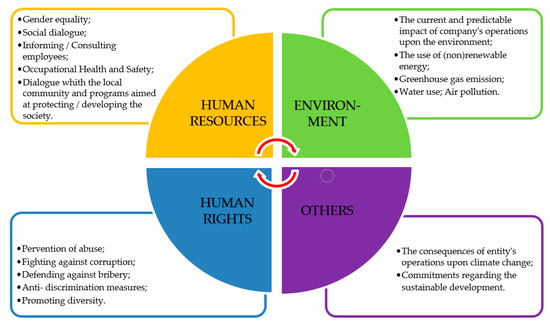
The Circular Economy and the Sustainable Strategies are the most significant issues in all projects and proposals in many sectors. The closing the loop approach is constantly gaining importance and is beginning to be asked at all the levels. The 9R (Responsibility, React, Reduce, Reuse, Re-design, Repair, Recover, Recycle and Rot) development strategy will help to retain materials and products in the economy for as long as possible, saving primary reserves.
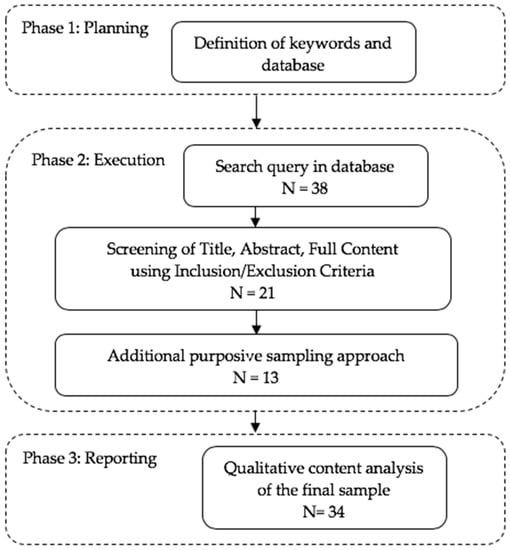
The focus of this Special Issue on “Circular Economy and Sustainable Strategies” aims to collect up-to-date research articles that explore, examine and make proposals for a better world, taking into account the environment, human health, as well as the economic benefits. This Special Issue will incorporate articles that examine current policies, qualitative and quantitative measurements in the materials treatment sector and use/reuse, techno-economical aspects, multi-criteria systems for consuming, and closing the loop strategies. Papers on innovative developments, the environment, human health and the economy, reviews and case studies are also welcome.
The Guest Editors will select high quality research papers to proceed with blind peer reviews. Reviewers will be selected among researchers active in the field, whose works are present in international databases.
Within the framework described above, this Special Issue invites authors to contribute in the following fields (keywords):
- Circular Economy Indicators;
- Circular Economy Strategies;
- Trash to Treasure;
- Life-Cycle-Assessment;
- Business Model for Circular Economy and Sustainability;
- Circular, Green and Bio-Economy;
- Consuming Strategies and Economic Optimization;
- Health, Safety, Environment and Management;
- Closing the Loop Strategies.
Dr. Elena Cristina Rada
Prof. Dr. Lucian-Ionel Cioca
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.