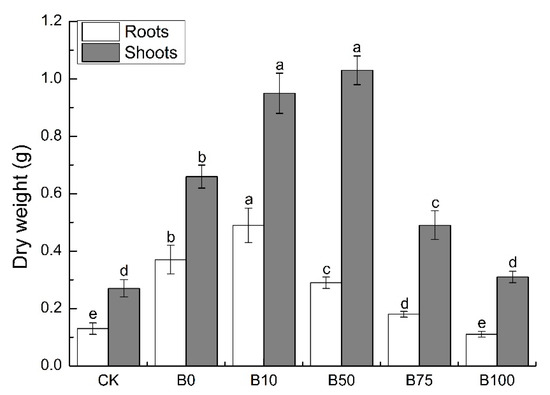
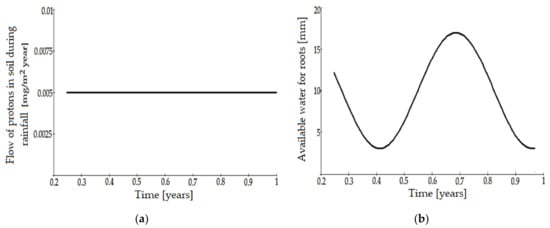
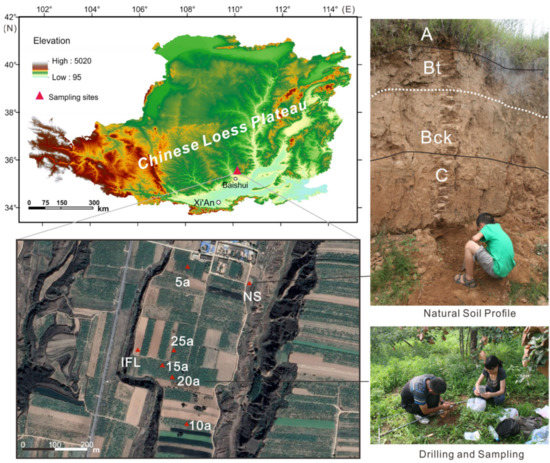
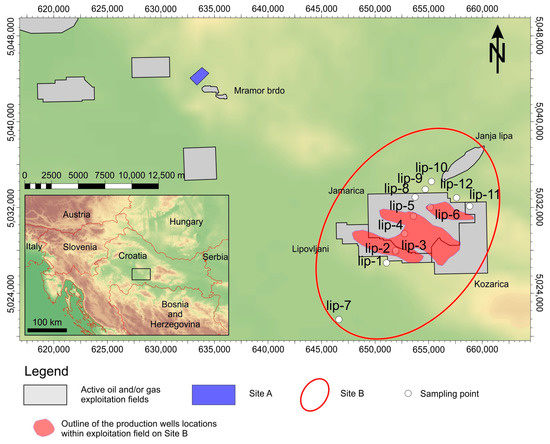
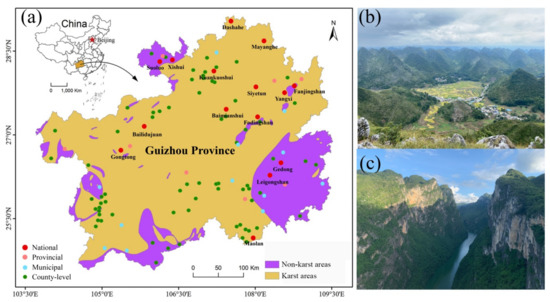
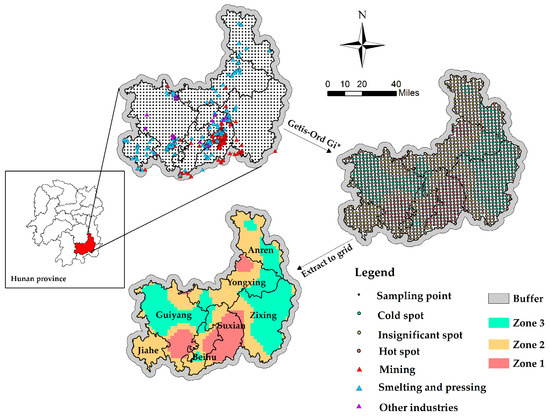
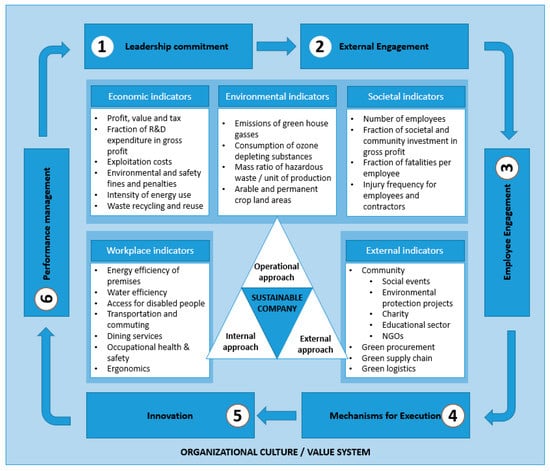
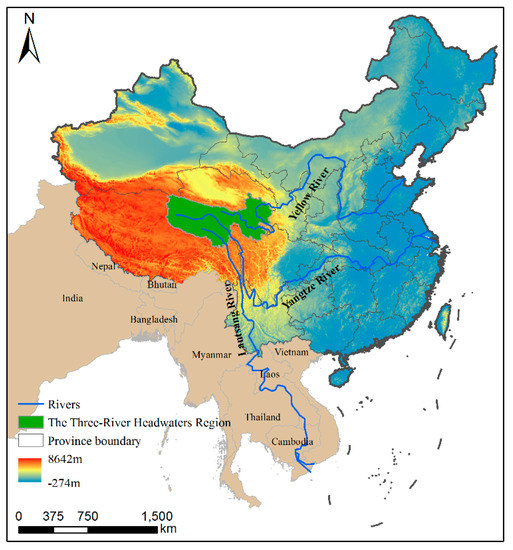
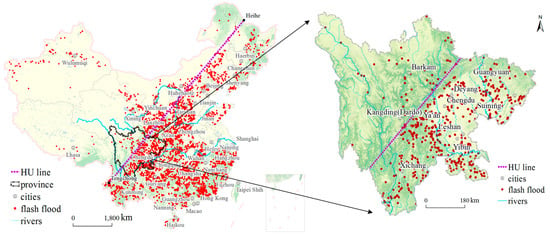
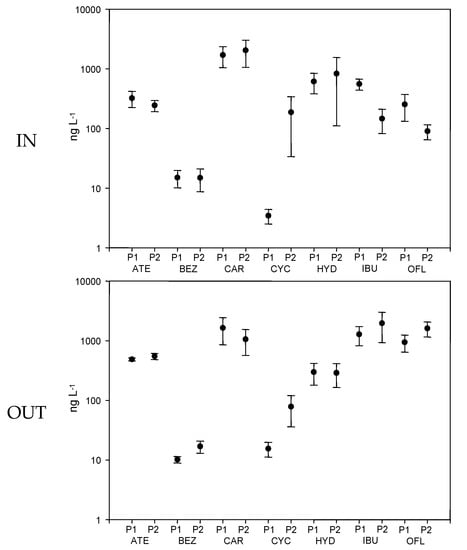
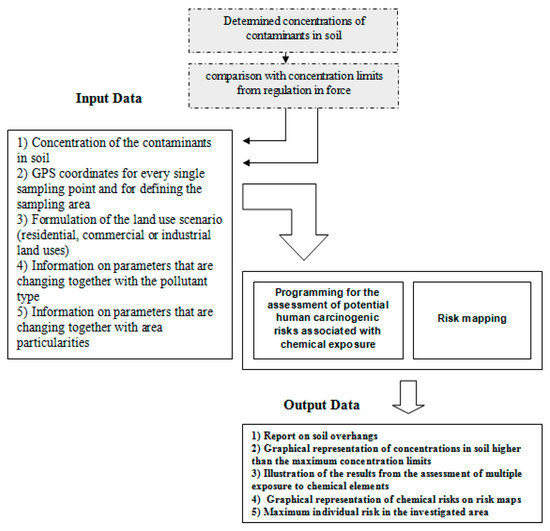
Risk Assessment and Management
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Sustainability and Applications".
Viewed by 307156Editors
Interests: management; human resources management; occupational health and safety management; production systems engineering; ergonomics; circular economy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: resources; renewable energy; environmental sustainability; circular economy; waste management; air pollution; microplastics; sewage sludge management; human health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Risk is defined as the chance of harmful effects to human health or to ecological systems resulting from exposure to an environmental stressor. Risk assessment encompasses three pillars; environmental concerns, social/cultural development, and economic dimensions in the built environment. The second pillar concerns risk assessment and also education. In order to enlarge the impact of this Special Issue, the authors are asked to submit works not only on risk assessment but also on risk management. Risk assessment allows defining priorities of intervention in many cases of concern. Risk management can integrate the previous item with the analysis of solutions aimed to protect human health from many pathways of human exposure. In particular, but not exclusively, these pathways can concern water, air, waste, sites to be remediated. The interest of this collection towards these pathways is related to the non-negligible effects on human health that can be found in spite to the compliance of regulations on environmental management. Safety and Health at Work is a topic that can focus on a particular aspect of risk. The purpose of this Special Issue is to enhance the knowledge of scientists, scholars, engineers, economists and graduate students on present ongoing research activities in order to exchange research ideas in the area of risk assessment and management. The Guest Editors will select high quality research to proceed with blind peer reviews. Reviewers will be selected among researchers active in the field, whose works are present in international databases.
Dr. Elena Cristina Rada
Prof. Dr. Lucian-Ionel Cioca
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Ecological Risk Assessment
- Economic Risk Assessment
- Environmental Risk Assessment
- Human Health Risk Assessment
- Safety and Health at Work
- Risk Management
- Risk Communication
- Risk Assessment Education