Electrospinning of Fish Gelatin Solution Containing Citric Acid: An Environmentally Friendly Approach to Prepare Crosslinked Gelatin Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
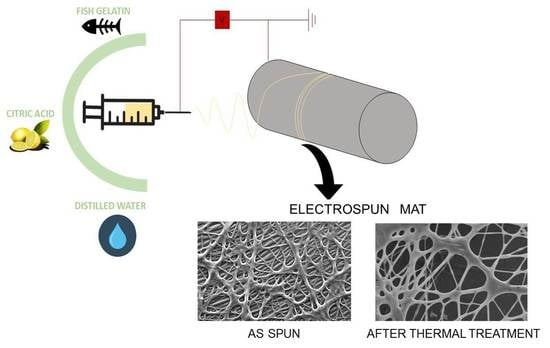
2.2. Preparation of Solutions
2.3. Rheological Assessment of Solutions
2.4. Electrospun Mat Fabrication
2.5. Characterization Methods
2.6. Crosslinking Extent
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrospinning of Fish Gelatin
3.2. Characterization of Fish Gelatin Electrospun Mats
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Encapsulation of curcumin in electrosprayed gelatin microspheres enhances its bioaccessibility and widens its uses in food applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Wang, C. Recent advances in the use of gelatin in biomedical research. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolci, L.S.; Liguori, A.; Panzavolta, S.; Miserocchi, A.; Passerini, N.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Bigi, A.; Albertini, B. Non-equilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma as innovative method to crosslink and enhance mucoadhesion of econazole-loaded gelatin films for buccal drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 163, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, E. Methods for the treatment of collagenous tissues for bioprostheses. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aduba, J.; Hammer, J.A.; Yuan, Q.; Andrew Yeudal, W.; Bowlin, G.L.; Yang, H. Semi-interpenetrating network (sIPN) gelatin nanofiber scaffolds for oral mucosal drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6576–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angarano, M.; Schulz, S.; Fabritius, M.; Vogt, R.; Steinberg, T.; Tomakidi, P.; Friedrich, C.; Mulhaupt, R. Layered gradient nonwovens of in situ crosslinked electrospun collagenous nanofibers used as modular scaffold systems for soft tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mondrinos, M.J.; Gandhi, M.R.; Ko, F.K.; Weiss, A.S.; Lelkes, P.I. Electrospun protein fibers as matrices for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5999–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzavolta, S.; Gioffrè, M.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C.; Foroni, L.; Bigi, A. Electrospun gelatin nanofibers: Optimization of genipin cross-linking to preserve fiber morphology after exposure to water. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Osteochondral defects: Present situation and tissue engineering approaches. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, A.; Bigi, A.; Colombo, V.; Focarete, M.L.; Gherardi, M.; Gualandi, C.; Oleari, M.C.; Panzavolta, S. Atmospheric pressure non-equilibrium plasma as a green tool to crosslink gelatin nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandi, C.; Torricelli, P.; Panzavolta, S.; Pagani, S.; Focarete, M.L.; Bigi, A. An innovative co-axial system to electrospin in situ crosslinked gelatin nanofibers. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratanavaraporn, J.; Rangkupan, R.; Jeeratawatchai, K.; Kanokpanont, S.; Damrongsakkul, S. Influences of physical and chemical crosslinking techniques on electrospun type A and B gelatin fiber mats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.M.; Limab, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishan, A.P.; Nezarati, R.M.; Radzicki, C.M.; Renfro, A.L.; Robinson, J.L.; Whitely, M.E.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. In situ crosslinking of electrospun gelatin for improved fiber morphology retention and tunable degradation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7930–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, B.T. Fabrication and characterization of cross-linked gelatin electro-spun nano-fibers. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agheb, M.; Dinar, M.; Rafienia, M.; Salehi, H. Novel electrospun nanofibers of modified gelatin-tyrosine in cartilage tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sisson, K.; Zhang, C.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Bruce Chase, D.; Rabolt, J.F. Evaluation of cross-linking methods for electrospun gelatin on cell growth and viability. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Padrão, J.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Dourado, F.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Sencadas, V. Thermal and hydrolytic degradation of electrospun fish gelatin membranes. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Ma, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cao, X.; Guo, Y. Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater. Lett. 2015, 140, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.F.; Luo, L.J.; Lai, J.Y.; Hui-Kang Ma, D. Role of solvent-mediated carbodiimide cross-linking in fabrication of electrospun gelatin nanofibrous membranes as ophthalmic biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 17, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, M.H.; Leonard, A.R.; Le Corre-Bordes, D.S.; Hofman, K. Intra-fibrillar citric acid crosslinking of marine collagen electrospun nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Cytocompatible cross-linking of electrospun zein fibers for the development of water-stable tissue engineering scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, N.; Warner, K.; Yang, Y. Low-temperature wet-cross-linking of silk with citric acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 4458–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Zhang, S.; Roscioli, N.; Yang, Y. Water-stable electrospun collagen fibers from a non-toxic solvent and crosslinking system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 2011, 50, 4458–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Taguchi, T.; Kobayashic, H.; Kataoka, K.; Tanaka, J.; Murabayashi, S.; Mitamura, Y. Physicochemical properties of gelatin gels prepared using citric acid derivative. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 24, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafagh, N.; Sabzi, M.; Afshari, M.J. Development of pH-sensitive and antibacterial gelatin/citric acid/Ag nanocomposite hydrogels with potential for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.; Leceta, I.; Etxabide, A.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Cross-linking of fish gelatins to develop sustainable films with enhanced properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 78, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setta, S.; Stephansen, K.; Yarin, L. Solution-blown nanofiber mats from fish sarcoplasmic protein. Polymer 2016, 93, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawłowska, S.; Kowalewski, T.A.; Pierini, F. Fibrous polymer nanomaterials for biomedical applications and their transport by fluids: An overview. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 8421–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Cai, S.; Yang, Y. Ultrafine fibrous gelatin scaffolds with deep cell infiltration mimicking 3D ECMs for soft tissue repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Kamilah, H.; Sudesh, K.; Karim, A.A.; Ariffin, F. Study of electrospun fish gelatin nanofilms from benign organic acids as solvents. Food Packag. Shelf 2019, 19, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erencia, M.; Cano, F.; Tornero, J.A.; Fernandes, M.M.; Tzanov, T.; Macanas, J.; Carrillo, F. Electrospinning of gelatin fibers using solutions with low acetic acid concentration: Effect of solvent composition on both diameter of electrospun fibers and cytotoxicity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabourov, M.; Leblond, J.; Papon, P. Gelation of aqueous gelatin solutions. I. Structural investigation. J. Phys. Fr. 1988, 49, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Eriksson, S.; Uno, H.; Windheuser, J.J. Facilitated Reversible Formation of Amides from Carboxylic Acids in Aqueous Solutions. Intermediate production of acid anhydride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3655–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shen, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y. Low-temperature crosslinking of proteins using non-toxic citric acid in neutral aqueous medium: Mechanism and kinetic study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, A.T.; Balbinot, E.; Weber, C.I.; Tonial, I.B.; Machado-Lunkes, A. Fish Gelatin: Characteristics, Functional Properties, Applications and Future Potentials. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioffrè, M.; Torricelli, P.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K.; Bigi, A. Role of pH on stability and mechanical properties of gelatin films. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2012, 27, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Leceta, I.; Cabezudo, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Sustainable fish gelatin films: From food processing waste to compost. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4626–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, X.M.; Tu, Z.C.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, T.; Man, Z.Z. Effect of ammonium sulfate fractional precipitation on gel strength and characteristics of gelatin from bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthysnobilis) scale. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 36, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniasadi, H.; Ramazani, S.A.A.; Mashayekhan, S. Fabrication and characterization of conductive chitosan/gelatin-based scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Beach, E.S.; Anastas, P.T. Modification of chitosan films with environmentally benign reagents for increased water resistance. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2011, 4, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, C.R.L.; Heleno, S.A.; Fernandes, I.P.M.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Barros, L.; Gonçalves, O.H.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barreiro, M.F. Functionalization of yogurts with Agaricusbisporus extracts encapsulated in spray-dried maltodextrin crosslinked with citric acid. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Amide I Area | 1603–1616 cm−1 (%) | 1634 cm−1 (%) | 1641–1650 cm−1 (%) | 1670–1678 cm−1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FG powder | 20.37 | - | 57.00 | 22.63 |
| FG | 18.75 | 48.73 | 26.54 | 5.98 |
| FG+NaOH | 16.94 | 44.70 | 29.79 | 8.57 |
| FG+NaOH treated at 80 °C | 16.16 | 44.29 | 30.84 | 8.71 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liguori, A.; Uranga, J.; Panzavolta, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K.; Focarete, M.L. Electrospinning of Fish Gelatin Solution Containing Citric Acid: An Environmentally Friendly Approach to Prepare Crosslinked Gelatin Fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172808
Liguori A, Uranga J, Panzavolta S, Guerrero P, de la Caba K, Focarete ML. Electrospinning of Fish Gelatin Solution Containing Citric Acid: An Environmentally Friendly Approach to Prepare Crosslinked Gelatin Fibers. Materials. 2019; 12(17):2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172808
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiguori, Anna, Jone Uranga, Silvia Panzavolta, Pedro Guerrero, Koro de la Caba, and Maria Letizia Focarete. 2019. "Electrospinning of Fish Gelatin Solution Containing Citric Acid: An Environmentally Friendly Approach to Prepare Crosslinked Gelatin Fibers" Materials 12, no. 17: 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172808
APA StyleLiguori, A., Uranga, J., Panzavolta, S., Guerrero, P., de la Caba, K., & Focarete, M. L. (2019). Electrospinning of Fish Gelatin Solution Containing Citric Acid: An Environmentally Friendly Approach to Prepare Crosslinked Gelatin Fibers. Materials, 12(17), 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172808