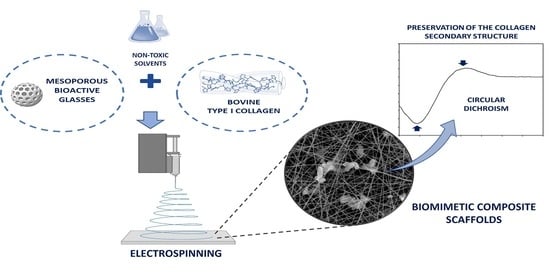
Biomimetic Scaffolds Obtained by Electrospinning of Collagen-Based Materials: Strategies to Hinder the Protein Denaturation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Collagen-Based Materials for Electrospinning
2.2. Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.3. Rheology
2.4. Electrospinning Tests
2.5. Scaffold Characterisation
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX)
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment and Electrospinning of Different Collagen Formulations
3.2. Assessment of the Preservation of the Supramolecular Structure of Collagen
3.3. Electrospinning of Composite Scaffolds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.D.L.; Ganguly, D.; Zuidema, J.M.; Cardinal, T.J.; Ziemba, A.M.; Kearns, K.R.; McCarthy, S.M.; Thompson, D.M.; Ramanath, G.; Borca-Tasciuc, D.-A.; et al. Injectable, Magnetically Orienting Electrospun Fiber Conduits for Neuron Guidance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 11, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadpoor, A.A.; Malda, J. Additive Manufacturing of Biomaterials, Tissues, and Organs. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, F.; Ebert, R.; Ignatius, A.; Matsushita, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Groll, J.; Walles, H. Bone tissue engineering in osteoporosis. Maturitas 2013, 75, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacki, J.; Mizuno, S. Collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.; Woodruff, M.; Epari, D.; Steck, R.; Glatt, V.; Dickinson, I.C.; Choong, P.; Schuetz, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. Bone Regeneration Based on Tissue Engineering Conceptions—A 21st Century Perspective. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 216–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghassemi, T.; Shahroodi, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.H.; Mousavian, A.; Movaffagh, J.; Moradi, A. Current Concepts in Scaffolding for Bone Tissue Engineering. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 6, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frantz, C.; Stewart, K.M.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alford, A.I.; Kozloff, K.M.; Hankenson, K.D. Extracellular matrix networks in bone remodeling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 65, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, K. The development of collagen based composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Duarte, A.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeugolis, D.; Khew, S.T.; Yew, E.S.; Ekaputra, A.K.; Tong, Y.W.; Yung, L.-Y.L.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Sheppard, C.; Raghunath, M. Electro-spinning of pure collagen nano-fibres—Just an expensive way to make gelatin? Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2293–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Sousa, S.R.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Moroni, L.; Monteiro, F. A biocomposite of collagen nanofibers and nanohydroxyapatite for bone regeneration. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sell, S.; McClure, M.J.; Garg, K.; Wolfe, P.S.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen/biopolymers for regenerative medicine and cardiovascular tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, A.; Gualandi, C.; Panseri, S.; Montesi, M.; Marcacci, M.; Focarete, M.L.; Bigi, A. Comparative performance of collagen nanofibers electrospun from different solvents and stabilized by different crosslinkers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.; Schauer, C.L. A Review: Electrospinning of Biopolymer Nanofibers and their Applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, L.; Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y. Collagen Tissue Engineering: Development of Novel Biomaterials and Applications. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, K.S.; Jeong, L.; Lee, G.; Seo, B.-M.; Park, Y.J.; Hong, S.-D.; Roh, S.; Cho, J.J.; Park, W.H.; Min, B.-M. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers: Effects on the behavior of normal human keratinocytes and early-stage wound healing. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Arnoult, O.; Smith, M.E.; Wnek, G.E. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofiber Scaffolds from Benign Solvents. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, D. Greener synthesis of electrospun collagen / hydroxyapatite composite fibers with an excellent microstructure for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3203–3215. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Zhang, S.; Roscioli, N.; Yang, Y. Water-stable electrospun collagen fibers from a non-toxic solvent and crosslinking system. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 101, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Grande, D.; Jesús, V.-G.L.; Manuel, C.-B.J.; Ricardo, V.-G.; Daniel, G. Electrospinning as a Powerful Technique for Biomedical Applications: A Critically Selected Survey. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 27, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.-H.; Lee, E.-J.; Wang, P.; Kim, H.-E. Collagen/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3055–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Relevance of their porous structure compared to that of classical bioglasses. Biomed. Glasses 2015, 1, doi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccini, A.R.; Erol, M.; Stark, W.J.; Mohn, D.; Hong, Z.; Mano, J.F. Polymer/bioactive glass nanocomposites for biomedical applications: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorilli, S.; Pontremoli, C.; Montalbano, G.; Vitale-brovarone, C. Hybrid formulations based on mesoporous bioactive glasses/polymeric phases for the desig of bone scaffolds and delivery platforms. In Bioactive Glasses—Properties, Composition and Recent Applications; Arcos, D., Vallet-Regi, M., Eds.; NOVA: Nagoya, Japan, 2020; p. 412. ISBN 9781631172557. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, F.-Y.; Lu, M.-R.; Weng, R.-C.; Lin, H.-M. Hierarchically biomimetic scaffold of a collagen–mesoporous bioactive glass nanofiber composite for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 25007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontremoli, C.; Boffito, M.; Fiorilli, S.; Laurano, R.; Torchio, A.; Bari, A.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Ciardelli, G.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Hybrid injectable platforms for the in situ delivery of therapeutic ions from mesoporous glasses. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilli, S.; Molino, G.; Pontremoli, C.; Iviglia, G.; Torre, E.; Cassinelli, C.; Morra, M.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. The Incorporation of Strontium to Improve Bone-Regeneration Ability of Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses. Materials 2018, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Noriega, A.; Arcos, D.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Sakamoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Vallet-Regí, M. Ordered Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Structure characteristics, drug/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration application. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarker, B.; Hum, J.; Nazhat, S.N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Combining Collagen and Bioactive Glasses for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2015, 4, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fiqi, A.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.-J.; Kim, H.-W. Collagen hydrogels incorporated with surface-aminated mesoporous nanobioactive glass: Improvement of physicochemical stability and mechanical properties is effective for hard tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9508–9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, G.; Fiorilli, S.; Caneschi, A.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Type I Collagen and Strontium-Containing Mesoporous Glass Particles as Hybrid Material for 3D Printing of Bone-Like Materials. Materials 2018, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montalbano, G.; Borciani, G.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Cerqueni, G.; Licini, C.; Banche-Niclot, F.; Janner, D.; Sola, S.; Fiorilli, S.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M.; et al. Collagen Hybrid Formulations for the 3D Printing of Nanostructured Bone Scaffolds: An Optimized Genipin-Crosslinking Strategy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Teng, W.K.; Chan, B.P.; Chew, S.Y. Photochemical crosslinked electrospun collagen nanofibers: Synthesis, characterization and neural stem cell interactions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 95, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorilli, S.; Pagani, M.; Boggio, E.; Gigliotti, C.; Dianzani, C.; Gauthier, R.; Pontremoli, C.; Montalbano, G.; Dianzani, U.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Sr-Containing Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses Bio-Functionalized with Recombinant ICOS-Fc: An In Vitro Study. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, P.; Naseem, R.; Corvaglia, I.; Montalbano, G.; Pontremoli, C.; Azevedo, A.; Quadros, P.; Gentile, P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Dalgarno, K.; et al. Processing of Sr2+ Containing Poly L-Lactic Acid-Based Hybrid Composites for Additive Manufacturing of Bone Scaffolds. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baino, F.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Bioactive glass-based materials with hierarchical porosity for medical applications: Review of recent advances. Acta Biomater. 2016, 42, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Benjakul, S.; Nalinanon, S. Compositional and physicochemical characteristics of acid solubilized collagen extracted from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket (Aluterus monoceros). Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material | Amide A (cm−1) | Amide B (cm−1) | Amide I (cm−1) | Amide II (cm−1) | Amide III (cm−1) | Si-O-Si (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOV-COL (non-treated) | 3305 | 2922 | 1628 | 1548 | 1237 | - |
| 25%BOV-COL SCAFFOLDS | 3288 | 2930 | 1640 | 1540 | 1239 | - |
| 25%BOV-COL/5%MBG_SG SCAFFOLDS | 3288 | 2932 | 1643 | 1544 | 1231 | 1082 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalbano, G.; Tomasina, C.; Fiorilli, S.; Camarero-Espinosa, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Moroni, L. Biomimetic Scaffolds Obtained by Electrospinning of Collagen-Based Materials: Strategies to Hinder the Protein Denaturation. Materials 2021, 14, 4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164360
Montalbano G, Tomasina C, Fiorilli S, Camarero-Espinosa S, Vitale-Brovarone C, Moroni L. Biomimetic Scaffolds Obtained by Electrospinning of Collagen-Based Materials: Strategies to Hinder the Protein Denaturation. Materials. 2021; 14(16):4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164360
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalbano, Giorgia, Clarissa Tomasina, Sonia Fiorilli, Sandra Camarero-Espinosa, Chiara Vitale-Brovarone, and Lorenzo Moroni. 2021. "Biomimetic Scaffolds Obtained by Electrospinning of Collagen-Based Materials: Strategies to Hinder the Protein Denaturation" Materials 14, no. 16: 4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164360
APA StyleMontalbano, G., Tomasina, C., Fiorilli, S., Camarero-Espinosa, S., Vitale-Brovarone, C., & Moroni, L. (2021). Biomimetic Scaffolds Obtained by Electrospinning of Collagen-Based Materials: Strategies to Hinder the Protein Denaturation. Materials, 14(16), 4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164360