Sustainable Animal Nutrition and Feeding
A topical collection in Animals (ISSN 2076-2615). This collection belongs to the section "Animal Nutrition".
Viewed by 140355Editor
Interests: sustainable farming; animal production; insects in feed and food; animal nutrition; poultry production; animal welfare
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
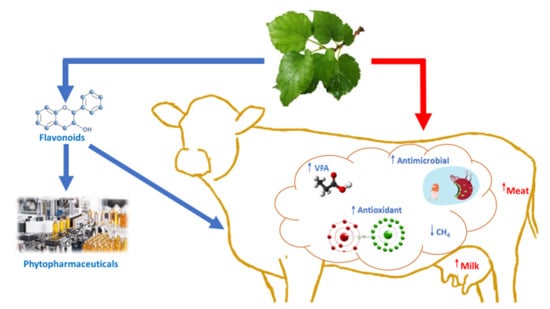
The world’s population is expected to increase by 2 billion persons in the coming 30 years, and by 2050 it will reach 9.7 billion persons from its current size of 7.7 billion persons. To meet the demand of a population of this size for animal products, we need agricultural production systems that are capable of producing more with fewer resources and cause fewer negative externalities. Indeed, the main challenge for animal production over the next few years will be to provide animal products of impeccable sanitary quality at an acceptable economic and environmental cost, i.e., without a negative impact on animal welfare, water resources, agricultural land, forests, biodiversity, and the atmosphere. Feeding of animals is based on the corn–soybean system, which is adopted everywhere and, therefore, very little research has been conducted to develop other alternative systems. Animal feed is thus based on the exploitation of the environment and on the collection of waste from the food industry or primitive human food. The advancements that have been made in the field of nutrition are the result of progress in the fields of physiology, animal husbandry, and animal metabolism. Nevertheless, nutrition remains the central pillar of animal husbandry. There is an urgent need to develop alternative feeding systems based on high-yielding plants, insects, aquatic plants, and fodder leaves, which can also be produced locally. Alternative feed could also be based on human food waste or primitive food from the food industry.
For this Topical Collection, we encourage leading scientists working on sustainable animal nutrition and feeding to submit original research and/or review articles.
Dr. Nassim Moula
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Animals is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- animal production
- alternative protein sources
- fish
- pig
- poultry
- rabbit
- ruminants
- insects
- sustainable feed
- ecological feed
- organic livestock production