Collection for the International Association for Landscape Ecology (IALE)
A topical collection in Land (ISSN 2073-445X). This collection belongs to the section "Landscape Ecology".
Viewed by 21100
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Weiqi Zhou
Prof. Dr. Weiqi Zhou
 Prof. Dr. Weiqi Zhou
Prof. Dr. Weiqi Zhou
grade
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
State Key Laboratory of Urban and Regional Ecology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 10085, China
Interests: urban ecology; remote sensing; urban greenspace; spatial pattern; urban heat island; landscape ecology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Since 2017, the International Association for Landscape Ecology (IALE) has been affiliated with Land. A new Collection has been created to collate all submissions from IALE members. The topics could cover, but are not limited to:
- 3DLM – 3D landscape metrics;
- Biocultural landscape;
- Biodiversity and ecosystem service assessments;
- Food and water security;
- Forest landscape ecology;
- Historical landscape ecology;
- Landscape planning;
- Outreach and policy;
- Spatial analysis of organisms in the environment;
- Urban and peri-urban governance;
- Pattern–process–scale relationships of landscapes;
- Landscape connectivity and fragmentation;
- Scale and scaling;
- Spatial analysis and landscape modeling;
- Landscape history and legacy effects;
- Landscape and climate change interactions;
- Ecosystem services in changing landscapes;
- Landscape sustainability;
- Remote sensing of landscape.
As part of this collaboration, all members of the IALE will receive a 10% discount on the article processing charge (APC) when submitting articles to Land. Please choose IALE as your institution when submitting papers to this Collection.
The IALE is the worldwide organization for landscape ecologists. The primary mission is to promote global collaborations among their various chapters and with international policymakers. They also serve as a platform for discussion and interactions across disciplines.
Prof. Dr. Weiqi Zhou
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Land is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (10 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Macrophyte and Ecosystem Service Changes in Shallow Eutrophic Coastal Waters Using Remote Sensing Methods
by
Johanna Schumacher, David Horn, Gabriela Escobar-Sánchez, Greta Markfort, Gerald Schernewski and Mario von Weber
Viewed by 436
Abstract
Knowledge of the structure and spatial distribution of coastal water habitats is crucial for understanding coastal water systems. However, spatial habitat data are largely lacking, hampering ecological and ecosystem service assessments as required by EU policies. Mapping the structure, spatial distribution, and temporal
[...] Read more.
Knowledge of the structure and spatial distribution of coastal water habitats is crucial for understanding coastal water systems. However, spatial habitat data are largely lacking, hampering ecological and ecosystem service assessments as required by EU policies. Mapping the structure, spatial distribution, and temporal dynamics of macrophytes is a particular challenge. In this study, we combined long-term macrophyte data with remote sensing methods (i.e., aerial and underwater drones, as well as SENTINEL-2 data) to assess their potential for spatial macrophyte monitoring and habitat-based ecosystem service assessments, in which ecosystem services were linked to habitats using the expert-based Baltic Ecosystem Service Potential Matrix. Greifswald Bay in the German Baltic Sea served as the case study for this research. Our aerial drone detected macrophytes up to a depth of 3 m that could be integrated into the existing macrophyte monitoring scheme of the Water Framework Directive. Reliable data from SENTINEL-2 were only obtained in optically shallow waters and could therefore only be used as proxy indicators to assess changes at a water body level. Despite the uncertainties and inaccuracies of the SENTINEL-2-based macrophyte maps, they were crucial for filling data gaps and enabled a spatially differentiated ecosystem service assessment for Greifswald Bay. However, we have shown that the commonly used matrix approach does not allow for the assessment of spatiotemporal changes at the water body level and is thus not suitable for supporting coastal and marine policy implementation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Towards Biocultural Conservation of Chilean Palm Landscapes: Expanding Perspectives from Historical Ecology
by
Constanza Urresty-Vargas, Emilia Catalán, Jorge Razeto and Fausto O. Sarmiento
Viewed by 546
Abstract
The Chilean palm (
Jubaea chilensis) is an endangered and culturally important species from central Chile. We studied the Ocoa palm landscape (OPL), which is currently part of a protected area that harbors the largest Chilean palm population where local peasant practices
[...] Read more.
The Chilean palm (
Jubaea chilensis) is an endangered and culturally important species from central Chile. We studied the Ocoa palm landscape (OPL), which is currently part of a protected area that harbors the largest Chilean palm population where local peasant practices have been excluded and conflict with biodiversity conservation strategies. We explored how human–landscape relationships over time have shaped present conditions and the implications for biocultural conservation. Methods included a review of archaeobotanical and historical records, and a qualitative study focused on local peasants’ perspectives. We reported the uses of
J. chilensis and the OPL since pre-Hispanic times. For the last 400 years, these uses have involved important differences between landowners and local peasants in terms of power dynamics, access to the land, and intensity of use. The current palm landscape structure directly responds to past human activities, such as palm felling and agriculture. Also, we explain peasant practices linked to the OPL as ways of resisting cultural homogenization and marginalization associated with reductive conservation approaches and other presses and pulses. Chilean palm conservation can be improved by considering ecological legacies to inform future conservation strategies and adding a biocultural approach that respectfully integrates local peasant knowledge systems and worldviews.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Water, Ecosystem Services, and Urban Green Spaces in the Anthropocene
by
Marianna Olivadese and Maria Luisa Dindo
Viewed by 1288
Abstract
As urban centers worldwide face the escalating impacts of climate change, rapid urbanization, and increasing water scarcity, the need for sustainable water management practices to enhance urban resilience in the Anthropocene has become critical. This study explores how ancient water management practices—including Roman
[...] Read more.
As urban centers worldwide face the escalating impacts of climate change, rapid urbanization, and increasing water scarcity, the need for sustainable water management practices to enhance urban resilience in the Anthropocene has become critical. This study explores how ancient water management practices—including Roman aqueducts, Maya rainwater harvesting systems, and ancient Chinese flood control techniques—can be adapted to address contemporary water challenges in modern cities. We evaluate these historical practices through a lens of contemporary environmental pressures, including climate change, urbanization, and resource scarcity. By integrating ancient methods with modern technologies, we propose adaptive solutions to enhance urban water resilience. Case studies from five cities (Singapore, Copenhagen, Mexico City, Los Angeles, and Philadelphia) illustrate how modern green infrastructure, inspired by ancient techniques, is being successfully implemented to manage stormwater, mitigate urban flooding, and improve water conservation. By integrating historical practices with modern technologies—such as advanced filtration systems and water recycling—these cities are enhancing their water resilience and sustainability. The findings suggest that urban planners can draw valuable lessons from historical systems to design adaptive, climate-resilient cities that balance human needs with ecological sustainability. This paper concludes with actionable recommendations for future urban planning, emphasizing the importance of decentralized water systems, nature-based solutions, and community engagement to ensure sustainable urban water management in the Anthropocene.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Dynamic Changes in Vegetation Net Primary Productivity and Its Driving Factors in the Two Regions North and South of the Hu Huanyong Line in China
by
Weimin Liu, Dengming Yan, Zhilei Yu, Zening Wu, Huiliang Wang, Jie Yang, Simin Liu and Tianye Wang
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1178
Abstract
Human activities and global environmental changes have transformed terrestrial ecosystems, notably increasing vegetation greenness in China. However, this greening is less effective across the Hu Huanyong Line (Hu Line). This study analyzes dynamic changes and driving factors of nine vegetation net primary productivities
[...] Read more.
Human activities and global environmental changes have transformed terrestrial ecosystems, notably increasing vegetation greenness in China. However, this greening is less effective across the Hu Huanyong Line (Hu Line). This study analyzes dynamic changes and driving factors of nine vegetation net primary productivities (NPPs) in regions divided by the Hu Line using remote sensing data, trend analysis, and the Geodetector model. Findings reveal that from 2001 to 2022, 38.22% of regional vegetation NPP in China increased, especially in the Loess Plateau, Sichuan Basin, and Northeast Plains, while 2.39% decreased, primarily in the southeastern region and southern Tibet. Grasslands contributed 39.71% to NPP north of the Hu Line, and cultivated vegetation contributed 50.58% south. The driving explanatory power of factors on vegetation NPP on the north side of the Hu Line is generally greater than that on the south side. Natural factors primarily drive NPP changes, with human activities having less impact. Combined factors, particularly climate and elevation, significantly enhance the driving explanatory power (
q, 0–1). The joint effects of elevation and precipitation on grassland NPP dynamics (
q = 0.602) are notable. GDP’s influence on broadleaf forests north of the Hu Line (
q = 0.404) is significant. Grasslands respond strongly to land use changes and population density, with a combined effect of
q = 0.535. Shrubs, alpine vegetation, and meadows show minimal response to individual factors (
q < 0.2). These findings offer insights for devising ecological protection measures tailored to local conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Integration of Acceptability Analyses into an Adaptive Landscape Co-Design and Management Approach—The Acceptability and Landscape Design Cycle (ALDC)
by
Maria Busse, Jana Zscheischler, Nico Heitepriem and Rosemarie Siebert
Viewed by 1457
Abstract
Acceptability analyses of place–based innovations provide crucial in-depth knowledge (e.g., perceptions and values on landscapes) for the social–ecological transformation of landscapes. However, previous acceptability analyses often neglected complex and ongoing processes. We argue that, for the design of a sustainability-oriented transformation and to
[...] Read more.
Acceptability analyses of place–based innovations provide crucial in-depth knowledge (e.g., perceptions and values on landscapes) for the social–ecological transformation of landscapes. However, previous acceptability analyses often neglected complex and ongoing processes. We argue that, for the design of a sustainability-oriented transformation and to address spatial and temporal dynamics in landscapes, an operational heuristic is needed; one that integrates acceptability analyses into an adaptive landscape co-design and management approach. Therefore, this conceptual–empirical paper introduces the concept of the ‘acceptability and landscape design cycle’ (ALDC), which is based on findings from various transdisciplinary innovation processes in the Spreewald region (Germany). It is composed of four iterative phases: (1) defining the preconditions for acceptability analysis, (2) conducting the acceptability analysis, (3) integrating the results into the landscape development strategy, and (4) re-designing and refining it. We illustrate the application of these phases using a case study of the cultural landscape in Spreewald. The paper provides practical implementation guidelines of the ALDC and contributes to a better understanding of the dynamics of acceptability decisions regarding the transformation processes of landscapes. Furthermore, it can advance the understanding of how co-evolution of socio-ecological systems occurs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
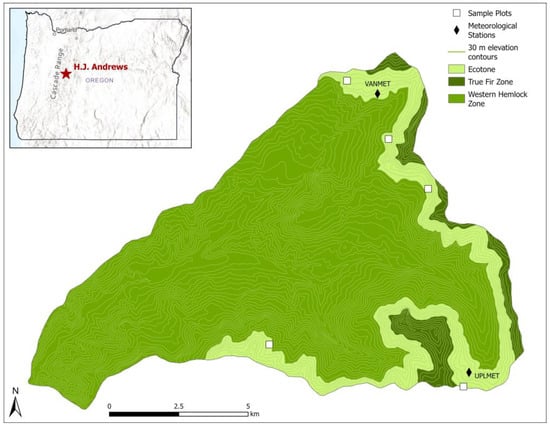
A 20-Year Ecotone Study of Pacific Northwest Mountain Forest Vulnerability to Changing Snow Conditions
by
Todd R. Lookingbill, Jack DuPuy, Ellery Jacobs, Matteo Gonzalez and Tihomir S. Kostadinov
Viewed by 1609
Abstract
(1) Background: Global climate change is expected to significantly alter growing conditions along mountain gradients. Landscape ecological patterns are likely to shift significantly as species attempt to adapt to these changes. We evaluated the extent to which spatial (elevation and canopy cover) and
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Global climate change is expected to significantly alter growing conditions along mountain gradients. Landscape ecological patterns are likely to shift significantly as species attempt to adapt to these changes. We evaluated the extent to which spatial (elevation and canopy cover) and temporal (decadal trend and El Niño–Southern Oscillation/Pacific Decadal Oscillation) factors impact seasonal snowmelt and forest community dynamics in the Western Hemlock–True Fir ecotone region of the Oregon Western Cascades, USA. (2) Methods:
Tsuga heterophylla and
Abies amabilis seedling locations were mapped three times over 20 years (2002–2022) on five sample transects strategically placed to cross the ecotone. Additionally, daily ground temperature readings were collected over 10 years for the five transects using 123 data loggers to estimate below-canopy snow metrics. (3) Results: Based on validation using time-lapse cameras, the data loggers proved highly reliable for estimating snow cover. The method reported fewer days of snow cover as compared to meteorological station-based snow products for the region, emphasizing the importance of direct under-canopy field observations of snow. Snow season variability was most significantly impacted temporally by cyclical ENSO/PDO climate patterns and spatially by differences in canopy cover within the ecotone. The associated seedling analysis identified clear sorting of species by elevation within the ecotone but reflected a lack of a long-term trend, as species dominance in the seedling strata did not significantly shift along the elevation gradient over the 20-year study. (4) Conclusions: The data logger-based approach provided estimates of snow cover at ecologically significant locations and fine enough spatial resolutions to allow for the study of forest regeneration dynamics. The results highlight the importance of long-term, understory snow measurements and the influence of climatic oscillations in understanding the vulnerability of mountain areas to the changing climate.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
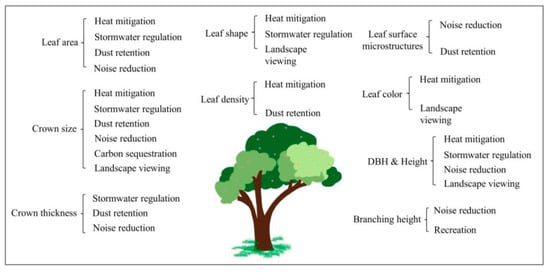
Influence of Urban Tree Traits on Their Ecosystem Services: A Literature Review
by
Danchen Liang and Ganlin Huang
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4883
Abstract
Trees in cities are vital to the health of the urban ecosystem and residents’ wellbeing. Besides providing habitats, trees provide food via fruits and young leaves, reduce temperature, and enrich landscape aesthetics with spring flowers and autumn foliage. The generation and supply of
[...] Read more.
Trees in cities are vital to the health of the urban ecosystem and residents’ wellbeing. Besides providing habitats, trees provide food via fruits and young leaves, reduce temperature, and enrich landscape aesthetics with spring flowers and autumn foliage. The generation and supply of these ecosystem services are closely related to their traits, such as the size of the canopy and the sparseness of the leaves, which directly affect their ability to shade and cool. Studies focusing on ecosystem services often consider green space as a whole, and some distinguish the difference between trees and grass. Relatively fewer studies examined the influence of tree traits on the supply of ecosystem services. Understanding the association among species, traits, and ecosystem services would be helpful in generating actionable knowledge for urban tree planting. However, these studies are often scattered under different research topics. To this end, we reviewed and summarized studies on the relationship between urban tree species/traits and ecosystem services according to provision, regulation, and cultural service types. Based on 45 publications, we found that leaf area, crown size, diameter at breast height, tree height, and leaf shape may influence various ecosystem services. We presented a preliminary framework of “trait- service” and argued that with the help of such a framework, future research should generate actionable knowledge for practitioners to identify potential tree species for selection according to desired services.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
From Productive Landscape to Agritouristic Landscape? The Evidence of an Agricultural Heritage System—Zhejiang Huzhou Mulberry-Dyke and Fish-Pond System
by
Ran Zhou, Lu Huang, Ke Wang and Wenhao Hu
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2508
Abstract
Agricultural Heritage Systems exhibit multiple functions of agricultural production, ecological protection, and invaluable cultures and landscapes. The mulberry-dyke and fish-pond system is an important agricultural heritage. The Nanxun District of Huzhou, China is currently the area with the most complete and largest mulberry
[...] Read more.
Agricultural Heritage Systems exhibit multiple functions of agricultural production, ecological protection, and invaluable cultures and landscapes. The mulberry-dyke and fish-pond system is an important agricultural heritage. The Nanxun District of Huzhou, China is currently the area with the most complete and largest mulberry dykes and fish ponds in the world. In the past thirty years, with changes in labor force distribution and consumer demand, the production function of mulberry dyke and fish ponds has been challenged, and the production landscape as the carrier of farming culture has been threatened. Studying the spatial characteristics and optimization of mulberry dykes and fish ponds is of great significance to the sustainable development of the regional economy, culture, and environment. This study analyzes the spatial and temporal pattern evolution of mulberry dyke and fish ponds in Nanxun District since 1975. Based on the evaluation of the environmental carrying capacity of fish ponds, and according to the development goals of agricultural heritage inheritance and “planting and breeding balance”, the Future Land Use Simulation model is adopted to optimize the study area. The results show the following findings: (1) From 1975 to 2019, fish ponds and construction land increased significantly, mulberry fields and paddy fields decreased significantly, the scale of mulberry dykes and fish ponds decreased significantly, and the proportion of mulberry dykes and fish ponds was seriously unbalanced; (2) The overall scale of fish-pond breeding in Nanxun District is too large, and the proportion of farming and breeding needs to be adjusted; (3) In view of economic growth, cultural inheritance, and environmental protection, this paper simulates the spatial layout of mulberry dykes and fish ponds in 2035, and divides mulberry dykes and fish ponds in Nanxun District into a display area and an industrial development area. The display area restores the traditional mulberry dykes and fish ponds to the greatest extent. The industrial development zone maximizes the economic benefits of agriculture on the basis of “balancing planting and breeding”. Overall, this study provides a reference for protecting Huzhou mulberry-dyke and fish-pond agricultural heritage, optimizing agricultural production space, balancing human–environment relationship, and promoting regional sustainable development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
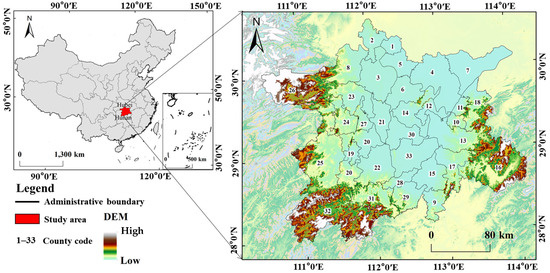
A Framework to Identify Priority Areas for Restoration: Integrating Human Demand and Ecosystem Services in Dongting Lake Eco-Economic Zone, China
by
Yanping Zhao, Jing Luo, Tao Li, Jian Chen, Yi Mi and Kuan Wang
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2100
Abstract
The identification of priority restoration areas (PRAs) for ecosystems is a critical step in establishing restoration programs. Because the majority of existing studies focused on improving the ecosystem supply, the PRAs selected are likely to be remote from human demand, and the restoration
[...] Read more.
The identification of priority restoration areas (PRAs) for ecosystems is a critical step in establishing restoration programs. Because the majority of existing studies focused on improving the ecosystem supply, the PRAs selected are likely to be remote from human demand, and the restoration benefits will not flow to humans. To fill this gap, we constructed an improved framework integrating the ecological restoration projects’ cost and benefits as indicators for choosing PRAs. Then, we identified PRAs for each ecosystem service (ES) with Marxan, and ranked the restoration priority grades according to the superimposed value of PRAs for each ES. Finally, we adjusted the restoration priority grades based on human demand and the concentration of those areas, and chose PRAs with a high ES supply and demand. This framework was applied to the Dongting Lake Eco-Economic Zone, one of China’s most significant ecological restoration project sites. The results indicated that the areas with “high”-, “sub-high”-, and “low”-grade PRAs, based only on the increase in the ES supply, were equal to 82, 410, and 1696 km
2, respectively. After considering human demand, the PRAs moved continuously towards places with a high human demand; high-priority areas grew to reach 144 km
2, while low-priority areas decreased to 1498 km
2. The upgrade of the proposed framework for the identification of PRAs can contribute to increasing human well-being, while also serving as a support tool for environmental restoration management.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
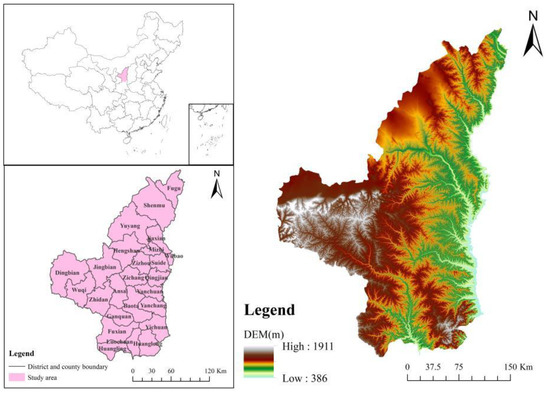
Pattern and Trend of Ecosystem Service Value in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi
by
Yonghua Zhao, Lei Zhang, Xia Jia, Qi Mu, Lei Han, Zhao Liu, Peng Zhang and Ming Zhao
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2160
Abstract
The ecosystem service value (ESV) is a critical metric for assessing the construction and protection of the environment. The research into the ESV pattern and the future development trend in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi is important for the conservation of water
[...] Read more.
The ecosystem service value (ESV) is a critical metric for assessing the construction and protection of the environment. The research into the ESV pattern and the future development trend in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi is important for the conservation of water and soil and the enhancement of the natural environment in the region. In this study, the variations and distribution patterns of the ESV in the study area from 2000 to 2020 were analyzed, the influence of various natural and social factors on the ESV was quantified, the weight of each factor was analyzed and evaluated using the entropy weighting method, and, finally, a prediction was made regarding how the ESV will develop going forward in this area. The results show that (1) the ESV showed a decreasing trend from 2000 to 2020, with the highest value for soil conservation and the lowest value for food production. Among the 25 districts and counties, Suide County had the lowest ESV per unit area, whereas Huanglong County had the highest. (2) The global positive correlation was clearly visible in the ESV. According to local spatial autocorrelation analysis, the area had a “high-high” agglomeration area in the south and a “low-low” agglomeration area in the middle and north. (3) Among the various influencing factors, population density had the highest weight and the distance from roads had the lowest weight. The impact status of the area generally showed a lighter impact in the southern region and a heavier impact in the northern region. (4) In 2030, the total ESV is predicted to be CNY 4343.6 million in the study area, CNY 39 million lower than that in 2020.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures