Neuroprotection Mediated by Natural Products and Their Chemical Derivatives
(Closed)
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The protection of nerve cells from acute and chronic damage continues to be an area of significant research efforts, attracting scientists from a diverse range of fields, including neuroscience, pharmacology, and medicinal chemistry among several others. With the ultimate goal to generate intervention strategies that slow or even reverse structural and functional degeneration of neurons, neuroprotection as a research field, and a potential clinical implementation, has profound relevance to numerous medical fields, such as neurology, ophthalmology, and endocrinology, where effective therapies are lacking and urgently needed.
Neuroprotection research has been directly or indirectly influenced and motivated by research on natural products due to a large body of literature indicating medical uses of natural products as alternative, complementary, or novel treatment options for diseases involving the structural and functional degeneration or even the loss of nerve cells. These research efforts are characteristic of how clinical practice, basic, and translational research inform each other, and how such interactions can result in novel therapeutic strategies of high clinical relevance. Recent methodological advances in synthetic and medicinal chemistry, mass spectrometry, proteomics, drug target discovery, and drug development have generated renewed interest in neuroprotection, mediated by natural products and their chemical derivatives.
Therefore, this Topical Collection invites manuscript submissions, namely research and review papers, targeting the gamut of methodological and scientific innovation in this field. Of specific interest to this Topical Collection are papers focused on the discovery and mechanistic characterization of novel drug targets, signaling pathways, and mechanisms of action of natural products and their derivatives as they are relevant for neuroprotection. These contributions can be general and broad in their applicability to a range of conditions affecting neurons, or highly focused on specific research models related to nerve cell damage, impairment or death or directly on clinical studies of diseases, disorders, or trauma affecting the nervous system.
Prof. Dr. Lucian Hritcu
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Keywords
- drug targets of natural products and their derivatives for neuroprotection
- natural products and their derivatives as neuroprotectants for the treatment of disorders of the central nervous system and the retina
- identification of signaling pathways of natural products and their derivatives for neuroprotection
- mechanisms of action of natural products and their derivatives for neuroprotection
- development and assessment of derivatives of natural products for neuroprotection
- Novel technologies and methods for the development and assessment of natural products and their derivatives for neuroprotection
Published Papers (30 papers)
Open AccessReview
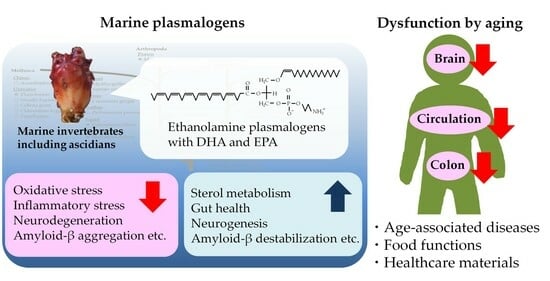
Marine Plasmalogens: A Gift from the Sea with Benefits for Age-Associated Diseases
by
Shinji Yamashita, Taiki Miyazawa, Ohki Higuchi, Mikio Kinoshita and Teruo Miyazawa
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 8579
Abstract
Aging increases oxidative and inflammatory stress caused by a reduction in metabolism and clearance, thus leading to the development of age-associated diseases. The quality of our daily diet and exercise is important for the prevention of these diseases. Marine resources contain various valuable
[...] Read more.
Aging increases oxidative and inflammatory stress caused by a reduction in metabolism and clearance, thus leading to the development of age-associated diseases. The quality of our daily diet and exercise is important for the prevention of these diseases. Marine resources contain various valuable nutrients, and unique glycerophospholipid plasmalogens are found abundantly in some marine invertebrates, including ascidians. One of the major classes, the ethanolamine class (PlsEtn), exists in a high ratio to phospholipids in the brain and blood, while decreased levels have been reported in patients with age-associated diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease. Animal studies have shown that the administration of marine PlsEtn prepared from marine invertebrates improved PlsEtn levels in the body and alleviated inflammation. Animal and human studies have reported that marine PlsEtn ameliorates cognitive impairment. In this review, we highlight the biological significance, relationships with age-associated diseases, food functions, and healthcare materials of plasmalogens based on recent knowledge and discuss the contribution of marine plasmalogens to health maintenance in aging.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
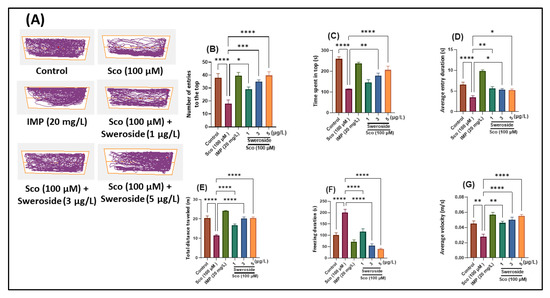
Sweroside Ameliorated Memory Deficits in Scopolamine-Induced Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model: Involvement of Cholinergic System and Brain Oxidative Stress
by
Ion Brinza, Mohamed A. El Raey, Walaa El-Kashak, Omayma A. Eldahshan and Lucian Hritcu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2474
Abstract
Sweroside is a secoiridoid glycoside and belongs to a large group of naturally occurring monoterpenes with glucose sugar attached to C-1 in the pyran ring. Sweroside can promote different biological activities such as antifungal, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, gastroprotective, sedative and antitumor, antioxidant, and neuroprotective
[...] Read more.
Sweroside is a secoiridoid glycoside and belongs to a large group of naturally occurring monoterpenes with glucose sugar attached to C-1 in the pyran ring. Sweroside can promote different biological activities such as antifungal, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, gastroprotective, sedative and antitumor, antioxidant, and neuroprotective activities. Zebrafish were given sweroside (12.79, 8.35, and 13.95 nM) by immersion once daily for 8 days, along with scopolamine (Sco, 100 μM) 30 min before the initiation of the behavioral testing to cause anxiety and memory loss. Employing the novel tank diving test (NTT), the Y-maze, and the novel object recognition test (NOR), anxiety-like reactions and memory-related behaviors were assessed. The following seven groups (
n = 10 animals per group) were used: control, Sco (100 μM), sweroside treatment (2.79, 8.35, and 13.95 nM), galantamine (GAL, 2.71 μM as the positive control in Y-maze and NOR tests), and imipramine (IMP, 63.11 μM as the positive control in NTT test). Acetylcholinesterase activity (AChE) and the antioxidant condition of the brains were also evaluated. The structure of sweroside isolated from
Schenkia spicata was identified. Treatment with sweroside significantly improved the Sco-induced decrease of the cholinergic system activity and brain oxidative stress. These results suggest that sweroside exerts a significant effect on anxiety and cognitive impairment, driven in part by the modulation of the cholinergic system activity and brain antioxidant action.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
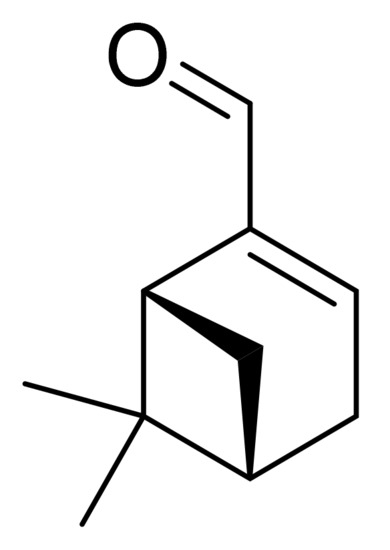
New Myrtenal–Adamantane Conjugates Alleviate Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia in Rat Model
by
Stela Dragomanova, Maria Lazarova, Aldar Munkuev, Evgeniy Suslov, Konstantin Volcho, Nariman Salakhutdinov, Amina Bibi, Jóhannes Reynisson, Elina Tzvetanova, Albena Alexandrova, Almira Georgieva, Diamara Uzunova, Miroslava Stefanova, Reni Kalfin and Lyubka Tancheva
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2685
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease associated with memory impairment and other central nervous system (CNS) symptoms. Two myrtenal–adamantane conjugates (MACs) showed excellent CNS potential against Alzheimer’s models. Adamantane is a common pharmacophore for drug design, and myrtenal (M) demonstrated neuroprotective effects
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease associated with memory impairment and other central nervous system (CNS) symptoms. Two myrtenal–adamantane conjugates (MACs) showed excellent CNS potential against Alzheimer’s models. Adamantane is a common pharmacophore for drug design, and myrtenal (M) demonstrated neuroprotective effects in our previous studies. The aim of this study is to evaluate the MACs’ neuroprotective properties in dementia. Methods: Scopolamine (Scop) was applied intraperitoneally in Wistar rats for 11 days, simultaneously with MACs or M as a referent, respectively. Brain acetylcholine esterase (AChE) activity, noradrenaline and serotonin levels, and oxidative brain status determination followed behavioral tests on memory abilities. Molecular descriptors and docking analyses for AChE activity center affinity were performed. Results: M derivatives have favorable physicochemical parameters to enter the CNS. Both MACs restored memory damaged by Scop, showing significant AChE-inhibitory activity in the cortex, in contrast to M, supported by the modeling analysis. Moderate antioxidant properties were manifested by glutathione elevation and catalase activity modulation. MACs also altered noradrenaline and serotonin content in the hippocampus. Conclusion: For the first time, neuroprotective properties of two MACs in a rat dementia model were observed. They were stronger than the natural M effects, which makes the substances promising candidates for AD treatment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
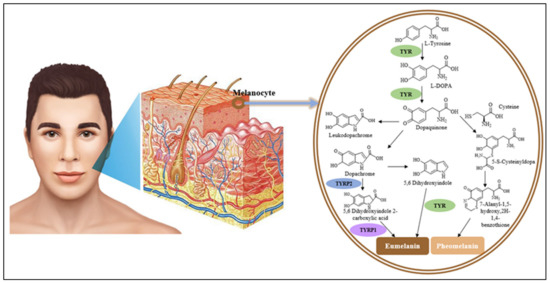
Insights on the Inhibitory Power of Flavonoids on Tyrosinase Activity: A Survey from 2016 to 2021
by
Heba A. S. El-Nashar, Mariam I. Gamal El-Din, Lucian Hritcu and Omayma A. Eldahshan
Cited by 73 | Viewed by 5681
Abstract
Tyrosinase is a multifunctional copper-containing oxidase enzyme that initiates melanin synthesis in humans. Excessive accumulation of melanin pigments or the overexpression of tyrosinase may result in skin-related disorders such as aging spots, wrinkles, melasma, freckles, lentigo, ephelides, nevus, browning and melanoma. Nature expresses
[...] Read more.
Tyrosinase is a multifunctional copper-containing oxidase enzyme that initiates melanin synthesis in humans. Excessive accumulation of melanin pigments or the overexpression of tyrosinase may result in skin-related disorders such as aging spots, wrinkles, melasma, freckles, lentigo, ephelides, nevus, browning and melanoma. Nature expresses itself through the plants as a source of phytochemicals with diverse biological properties. Among these bioactive compounds, flavonoids represent a huge natural class with different categories such as flavones, flavonols, isoflavones, flavan-3-ols, flavanones and chalcones that display antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitor activities with a diversity of mechanistic approaches. In this review, we explore the role of novel or known flavonoids isolated from different plant species and their participation as tyrosinase inhibitors reported in the last five years from 2016 to 2021. We also discuss the mechanistic approaches through the different studies carried out on these compounds, including in vitro, in vivo and in silico computational research. Information was obtained from Google Scholar, PubMed, and Science Direct. We hope that the updated comprehensive data presented in this review will help researchers to develop new safe, efficacious, and effective drug or skin care products for the prevention of and/or protection against skin-aging disorders.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (Lamiaceae) Essential Oil Prevents Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in the Scopolamine Zebrafish Model
by
Luminita Capatina, Edoardo Marco Napoli, Giuseppe Ruberto and Lucian Hritcu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3327
Abstract
Origanum vulgare ssp.
hirtum has been used as medicinal herbs promoting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective activities. We investigated the protective effects and the mechanism of
O. vulgare ssp.
hirtum essential oil (OEO) on cognitive impairment and brain oxidative stress in a scopolamine
[...] Read more.
Origanum vulgare ssp.
hirtum has been used as medicinal herbs promoting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective activities. We investigated the protective effects and the mechanism of
O. vulgare ssp.
hirtum essential oil (OEO) on cognitive impairment and brain oxidative stress in a scopolamine (Sco)-induced zebrafish (
Danio rerio) model of cognitive impairment. Our results show that exposure to Sco (100 µM) leads to anxiety, spatial memory, and response to novelty dysfunctions, whereas the administration of OEO (25, 150, and 300 µL/L, once daily for 13 days) reduced anxiety-like behavior and improved cognitive ability, which was confirmed by behavioral tests, such as the novel tank-diving test (NTT), Y-maze test, and novel object recognition test (NOR) in zebrafish. Additionally, Sco-induced brain oxidative stress and increasing of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity were attenuated by the administration of OEO. The gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses were used to elucidate the OEO composition, comprising thymol (38.82%),
p-cymene (20.28%), and γ-terpinene (19.58%) as the main identified components. These findings suggest the ability of OEO to revert the Sco-induced cognitive deficits by restoring the cholinergic system activity and brain antioxidant status. Thus, OEO could be used as perspective sources of bioactive compounds, displaying valuable biological activities, with potential pharmaceutical applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Anti-Amyloidogenic Effects of Asarone Derivatives From Perilla frutescens Leaves Against Beta-Amyloid Aggregation and Nitric Oxide Production
by
Jae Eun Lee, Nayeon Kim, Ji Yun Yeo, Dae-Gun Seo, Sunggun Kim, Jae-Sun Lee, Kwang Woo Hwang and So-Young Park
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3756
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative brain disorder associated with loss of memory and cognitive function. Beta-amyloid (Aβ) aggregates, in particular, are known to be highly neurotoxic and lead to neurodegeneration. Therefore, blockade or reduction of Aβ aggregation is a promising therapeutic
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative brain disorder associated with loss of memory and cognitive function. Beta-amyloid (Aβ) aggregates, in particular, are known to be highly neurotoxic and lead to neurodegeneration. Therefore, blockade or reduction of Aβ aggregation is a promising therapeutic approach in AD. We have previously reported an inhibitory effect of the methanol extract of
Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton (Lamiaceae) and its hexane fraction on Aβ aggregation. Here, the hexane fraction of
P. frutescens was subjected to diverse column chromatography based on activity-guided isolation methodology. This approach identified five asarone derivatives including 2,3-dimethoxy-5-(1
E)-1-propen-1-yl-phenol (
1), β-asarone (
2), 3-(2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-(2
E)-2-propen-1-ol (
3), asaronealdehyde (
4), and α-asarone (
5). All five asarone derivatives efficiently reduced the aggregation of Aβ and disaggregated preformed Aβ aggregates in a dose-dependent manner as determined by a Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence assay. Furthermore, asarone derivatives protected PC12 cells from Aβ aggregate-induced toxicity by reducing the aggregation of Aβ, and significantly reduced NO production from LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Taken together, these results suggest that asarone derivatives derived from
P. frutescens are neuroprotective and have the prophylactic and therapeutic potential in AD.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Varying Concentrations of Docosahexaenoic Acid on Amyloid Beta (1–42) Aggregation: An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
by
Brenda Yasie Lee, Simon James Attwood, Stephen Turnbull and Zoya Leonenko
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 4361
Abstract
Healthcare has advanced significantly, bringing with it longer life expectancies and a growing population of elders who suffer from dementia, specifically Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide has been implicated in the cause of AD, where the peptides undergo a conformational
[...] Read more.
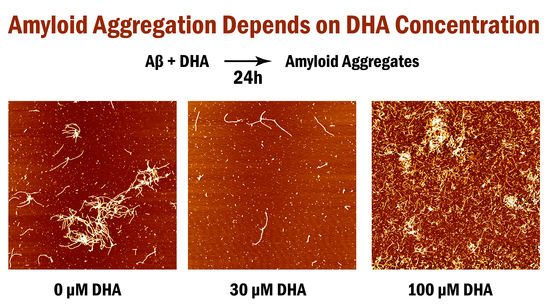
Healthcare has advanced significantly, bringing with it longer life expectancies and a growing population of elders who suffer from dementia, specifically Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide has been implicated in the cause of AD, where the peptides undergo a conformational change and form neurotoxic amyloid oligomers which cause neuronal cell death. While AD has no cure, preventative measures are being designed to either slow down or stop the progression of this neurodegenerative disease. One of these measures involves dietary supplements with polyunsaturated fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). This omega-3 fatty acid is a key component of brain development and has been suggested to reduce the progression of cognitive decline. However, different studies have yielded different results as to whether DHA has positive, negative, or no effects on Aβ fibril formation. We believe that these discrepancies can be explained with varying concentrations of DHA. Here, we test the inhibitory effect of different concentrations of DHA on amyloid fibril formation using atomic force microscopy. Our results show that DHA has a strong inhibitory effect on Aβ
1–42 fibril formation at lower concentrations (50% reduction in fibril length) than higher concentrations above its critical micelle concentration (70% increase in fibril length and three times the length of those at lower concentrations). We provide evidence that various concentrations of DHA can play a role in the inhibitory effects of amyloid fibril formation in vitro and help explain the discrepancies observed in previous studies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Nutritional Regulators of Bcl-xL in the Brain
by
Han-A Park, Katheryn Broman, Allison Stumpf, Sara Kazyak and Elizabeth A. Jonas
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 5302
Abstract
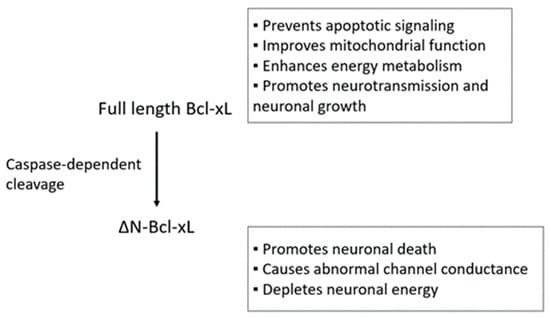
B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) is an anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein found in the mitochondrial membrane. Bcl-xL is reported to support normal brain development and protects neurons against toxic stimulation during pathological process via its roles in regulation of mitochondrial functions. Despite promising evidence showing
[...] Read more.
B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) is an anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein found in the mitochondrial membrane. Bcl-xL is reported to support normal brain development and protects neurons against toxic stimulation during pathological process via its roles in regulation of mitochondrial functions. Despite promising evidence showing neuroprotective properties of Bcl-xL, commonly applied molecular approaches such as genetic manipulation may not be readily applicable for human subjects. Therefore, findings at the bench may be slow to be translated into treatments for disease. Currently, there is no FDA approved application that specifically targets Bcl-xL and treats brain-associated pathology in humans. In this review, we will discuss naturally occurring nutrients that may exhibit regulatory effects on Bcl-xL expression or activity, thus potentially providing affordable, readily-applicable, easy, and safe strategies to protect the brain.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Neuroprotection Comparison of Rosmarinic Acid and Carnosic Acid in Primary Cultures of Cerebellar Granule Neurons
by
Faten Taram, Elizabeth Ignowski, Nathan Duval and Daniel A. Linseman
Cited by 37 | Viewed by 5813
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons in specific regions of the brain and/or spinal cord. Neuronal cell loss typically occurs by either apoptotic or necrotic mechanisms. Oxidative stress
[...] Read more.
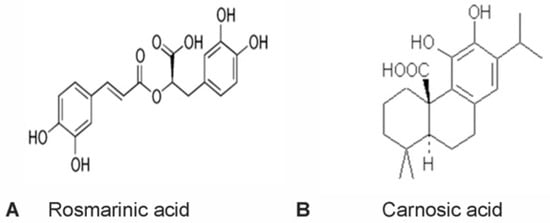
Neurodegenerative disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons in specific regions of the brain and/or spinal cord. Neuronal cell loss typically occurs by either apoptotic or necrotic mechanisms. Oxidative stress and nitrosative stress, along with excitotoxicity and caspase activation, have all been implicated as major underlying causes of neuronal cell death. Diverse nutraceuticals (bioactive compounds found in common foods) have been shown to have neuroprotective effects in a variety of in vitro and in vivo disease models. In the current study, we compared the neuroprotective effects of two polyphenolic compounds, rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid, which are both found at substantial concentrations in the herb rosemary. The capacity of these compounds to rescue primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) from a variety of stressors was investigated. Both polyphenols significantly reduced CGN death induced by the nitric oxide donor, sodium nitroprusside (nitrosative stress). Rosmarinic acid uniquely protected CGNs from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, while only carnosic acid rescued CGNs from caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by removal of depolarizing extracellular potassium (5K apoptotic condition). Finally, we found that carnosic acid protects CGNs from 5K-induced apoptosis by activating a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pro-survival pathway. The shared and unique neuroprotective effects of these two compounds against diverse modes of neuronal cell death suggest that future preclinical studies should explore the potential complementary effects of these rosemary polyphenols on neurodegenerative disease progression.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
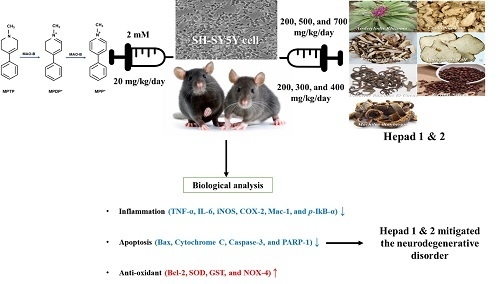
Mitigation Effects of a Novel Herbal Medicine, Hepad, on Neuroinflammation, Neuroapoptosis, and Neuro-Oxidation
by
Da Hye Song, Gyeong-Ji Kim, Kwon Jai Lee, Jae Soo Shin, Dong-Hee Kim, Byung-Jun Park and Jeung Hee An
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3771
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD), a common adult-onset neurodegenerative disorder with complex pathological mechanisms, is characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons. The present study demonstrated that the herbal medicines Hepad 1 and 2 protected against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in C57BL/6 mice and
[...] Read more.
Parkinson’s disease (PD), a common adult-onset neurodegenerative disorder with complex pathological mechanisms, is characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons. The present study demonstrated that the herbal medicines Hepad 1 and 2 protected against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in C57BL/6 mice and SH-SY5Y cells. Hepad 1 and 2 remarkably alleviated the enhanced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, macrophage-1, and phosphorylated iκB-α) and apoptotic signals (Bcl-2-associated X protein, caspase-3, and poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase-1). Additionally, Hepad reduced MPTP-induced oxidative damage by increasing the expression of anti-oxidant defense enzymes (superoxide dismutase and glutathione S-transferase) and downregulating the levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4. This study also showed that the neuroprotective effects of Hepad include anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-oxidative properties, in addition to activation of the protein kinase B, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways. Furthermore, oral administration of Hepad 1 and 2 attenuated the death of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive substantia nigra neurons that was induced by 20 mg/kg MPTP. Therefore, our results suggest that Hepad 1 and 2 are useful for treating PD and other disorders associated with neuro-inflammatory, neuro-apoptotic, and neuro-oxidative damage.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
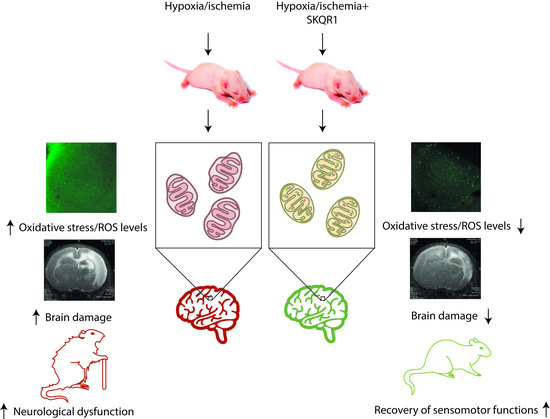
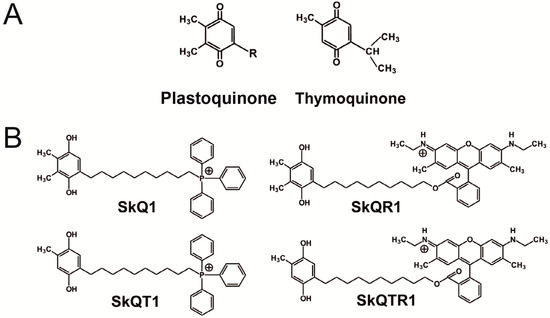
Neuroprotective Effects of Mitochondria-Targeted Plastoquinone in a Rat Model of Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury
by
Denis N. Silachev, Egor Y. Plotnikov, Irina B. Pevzner, Ljubava D. Zorova, Anastasia V. Balakireva, Mikhail V. Gulyaev, Yury A. Pirogov, Vladimir P. Skulachev and Dmitry B. Zorov
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 5441
Abstract
Neonatal hypoxia–ischemia is one of the main causes of mortality and disability of newborns. To study the mechanisms of neonatal brain cell damage, we used a model of neonatal hypoxia–ischemia in seven-day-old rats, by annealing of the common carotid artery with subsequent hypoxia
[...] Read more.
Neonatal hypoxia–ischemia is one of the main causes of mortality and disability of newborns. To study the mechanisms of neonatal brain cell damage, we used a model of neonatal hypoxia–ischemia in seven-day-old rats, by annealing of the common carotid artery with subsequent hypoxia of 8% oxygen. We demonstrate that neonatal hypoxia–ischemia causes mitochondrial dysfunction associated with high production of reactive oxygen species, which leads to oxidative stress. Targeted delivery of antioxidants to the mitochondria can be an effective therapeutic approach to treat the deleterious effects of brain hypoxia–ischemia. We explored the neuroprotective properties of the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQR1, which is the conjugate of a plant plastoquinone and a penetrating cation, rhodamine 19. Being introduced before or immediately after hypoxia–ischemia, SkQR1 affords neuroprotection as judged by the diminished brain damage and recovery of long-term neurological functions. Using vital sections of the brain, SkQR1 has been shown to reduce the development of oxidative stress. Thus, the mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant derived from plant plastoquinone can effectively protect the brain of newborns both in pre-ischemic and post-stroke conditions, making it a promising candidate for further clinical studies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Therapeutic Potentials of Microalgae in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
by
Tosin A. Olasehinde, Ademola O. Olaniran and Anthony I. Okoh
Cited by 95 | Viewed by 11481
Abstract
Current research is geared towards the discovery of new compounds with strong neuroprotective potential and few or no side effects compared to synthetic drugs. This review focuses on the potentials of extracts and biologically active compounds derived from microalgal biomass for the treatment
[...] Read more.
Current research is geared towards the discovery of new compounds with strong neuroprotective potential and few or no side effects compared to synthetic drugs. This review focuses on the potentials of extracts and biologically active compounds derived from microalgal biomass for the treatment and management of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Microalgal research has gained much attention recently due to its contribution to the production of renewable fuels and the ability of alga cells to produce several secondary metabolites such as carotenoids, polyphenols, sterols, polyunsaturated fatty acids and polysaccharides. These compounds exhibit several pharmacological activities and possess neuroprotective potential. The pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) involves complex mechanisms that are associated with oxidative stress, cholinergic dysfunction, neuronal damage, protein misfolding and aggregation. The antioxidant, anticholinesterase activities as well as the inhibitory effects of some bioactive compounds from microalgae extracts on β-amyloid aggregation and neuronal death are discussed extensively. Phytochemical compounds from microalgae are used as pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals and food supplements, and may possess neuroprotective potentials that are relevant to the management and/or treatment of AD.
Full article
Open AccessReview
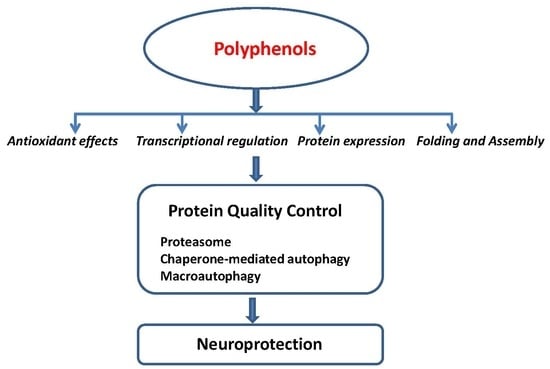
The Effect of Polyphenols on Protein Degradation Pathways: Implications for Neuroprotection
by
Parvana Hajieva
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 9279
Abstract
Human neurodegenerative diseases are accompanied by accumulation of heavily oxidized and aggregated proteins. However, the exact molecular reason is not fully elucidated yet. Insufficient cellular protein quality control is thought to play an important role in accumulating covalently oxidized misfolded proteins. Pharmacologically active
[...] Read more.
Human neurodegenerative diseases are accompanied by accumulation of heavily oxidized and aggregated proteins. However, the exact molecular reason is not fully elucidated yet. Insufficient cellular protein quality control is thought to play an important role in accumulating covalently oxidized misfolded proteins. Pharmacologically active polyphenols and their derivatives exhibit potential for preventive and therapeutic purposes against protein aggregation during neurodegeneration. Although these compounds act on various biochemical pathways, their role in stabilizing the protein degradation machinery at different stages may be an attractive therapeutical strategy to halt the accumulation of misfolded proteins. This review evaluates and discusses the existing scientific literature on the effect of polyphenols on three major protein degradation pathways: chaperone-mediated autophagy, the proteasome and macroautophagy. The results of these studies demonstrate that phenolic compounds are able to influence the major protein degradation pathways at different levels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessShort Note
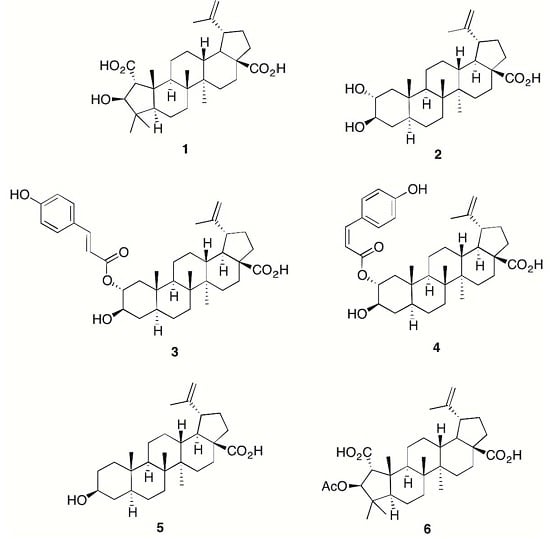
Anti-Inflammatory Chemical Profiling of the Australian Rainforest Tree Alphitonia petriei (Rhamnaceae)
by
Ritesh Raju, Dhanushka Gunawardena, Most Afia Ahktar, Mitchell Low, Paul Reddell and Gerald Münch
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 7131
Abstract
Chronic inflammation is an important pathological condition in many human diseases, and due to the side effects of the currently used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, discovery of novel anti-inflammatory drugs is of general interest. Anti-inflammatory activity guided compound isolation from the plant
Alphitonia petriei
[...] Read more.
Chronic inflammation is an important pathological condition in many human diseases, and due to the side effects of the currently used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, discovery of novel anti-inflammatory drugs is of general interest. Anti-inflammatory activity guided compound isolation from the plant
Alphitonia petriei led to the isolation of the known plant sterols emmolic acid (
1), alphitolic acid (
2),
trans- and
cis-coumaroyl esters of alphitolic acid (
3 and
4) and betulinic acid (
5). A detailed spectroscopic analysis led to the structure elucidation of the alphitolic acid derivatives (
1–
5), and the semi-synthetic emmolic acid acetate (
6). When tested in LPS (Lipopolysaccharides) + IFN-γ (Interferon gamma) activated RAW 264.7 macrophages, all compounds except (
1) exhibited potent anti-inflammatory activity (IC
50 values as low as 1.7 μM) in terms of downregulation of NO and TNF-α production, but also demonstrated some considerable cytotoxicity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
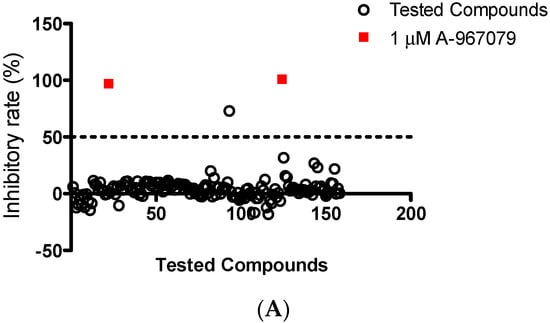
Cardamonin, a Novel Antagonist of hTRPA1 Cation Channel, Reveals Therapeutic Mechanism of Pathological Pain
by
Shifeng Wang, Chenxi Zhai, Yanling Zhang, Yangyang Yu, Yuxin Zhang, Lianghui Ma, Shiyou Li and Yanjiang Qiao
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 7387
Abstract
The increasing demand for safe and effective treatments of chronic pain has promoted the investigation of novel analgesic drugs. Some herbals have been known to be able to relieve pain, while the chemical basis and target involved in this process remained to be
[...] Read more.
The increasing demand for safe and effective treatments of chronic pain has promoted the investigation of novel analgesic drugs. Some herbals have been known to be able to relieve pain, while the chemical basis and target involved in this process remained to be clarified. The current study aimed to find anti-nociceptive candidates targeting transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1), a receptor that implicates in hyperalgesia and neurogenic inflammation. In the current study, 156 chemicals were tested for blocking HEK293/TRPA1 ion channel by calcium-influx assay. Docking study was conducted to predict the binding modes of hit compound with TRPA1 using Discovery Studio. Cytotoxicity in HEK293 was conducted by Cell Titer-Glo assay. Additionally, cardiotoxicity was assessed via xCELLigence RTCA system. We uncovered that cardamonin selectively blocked TRPA1 activation while did not interact with TRPV1 nor TRPV4 channel. A concentration-dependent inhibitory effect was observed with IC
50 of 454 nM. Docking analysis of cardamonin demonstrated a compatible interaction with A-967079-binding site of TRPA1. Meanwhile, cardamonin did not significantly reduce HEK293 cell viability, nor did it impair cardiomyocyte constriction. Our data suggest that cardamonin is a selective TRPA1 antagonist, providing novel insight into the target of its anti-nociceptive activity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
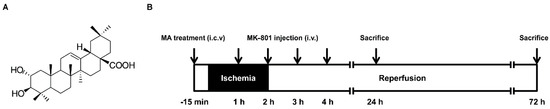
Neuroprotection by Combined Administration with Maslinic Acid, a Natural Product from Olea europaea, and MK-801 in the Cerebral Ischemia Model
by
Yisong Qian, Xuzhen Tang, Teng Guan, Yunman Li and Hongbin Sun
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 6718
Abstract
Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity is a major cause of ischemic brain damage. MK-801 confers neuroprotection by attenuating the activation of the
N-methyl-
d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, but it failed in clinical use due to the short therapeutic window. Here we aim to investigate the
[...] Read more.
Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity is a major cause of ischemic brain damage. MK-801 confers neuroprotection by attenuating the activation of the
N-methyl-
d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, but it failed in clinical use due to the short therapeutic window. Here we aim to investigate the effects of maslinic acid, a natural product from
Olea europaea, on the therapeutic time window and dose range for the neuroprotection of MK-801. Rats were administered with maslinic acid intracerebroventricularly and cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) followed by reperfusion. MK-801 was administered at 1 h, 2 h, 3 h and 4 h after ischemia, respectively. The cerebral infarct volume was determined by 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, neuronal damage was assessed by Haematoxylin Eosin (H&E) staining, and the expression of glial glutamate transporters and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and Western blot post-ischemia. Results showed that the presence of maslinic acid extended the therapeutic time window for MK-801 from 1 h to 3 h. Co-treatment of maslinic acid and MK-801 at a subthreshold dosage obviously induced neuroprotection after ischemia. The combination of these two compounds improved the outcome in ischemic rats. Moreover, maslinic acid treatment promoted the expression of GLT-1 and GFAP post-ischemia. These data suggest that the synergistic effect of maslinic acid on neurological protection might be associated with the improvement of glial function, especially with the increased expression of GLT-1. The combination therapy of maslinic acid and MK-801 may prove to be a potential strategy for treating acute ischemic stroke.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
RETRACTED: The Aminopyridinol Derivative BJ-1201 Protects Murine Hippocampal Cells against Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity via Heme Oxygenase-1
by
Dong-Sung Lee, Tae-Gyu Nam, Byeong-Seon Jeong and Gil-Saeng Jeong
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 6114
|
Retraction
Abstract
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It can cause neuronal cell damage in the context of oxidative stress. BJ-1201 is a derivative of the compound aminopyridinol, which is known for its antioxidant activity. In this study, we examined the effect
[...] Read more.
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It can cause neuronal cell damage in the context of oxidative stress. BJ-1201 is a derivative of the compound aminopyridinol, which is known for its antioxidant activity. In this study, we examined the effect of BJ-1201, a 6-(diphenylamino)-2,4,5-trimethylpyridin-3-ol compound, on neuroprotection in HT22 cells. Our data showed that BJ-1201 can protect HT22 cells against glutamate-induced cell cytotoxicity. In addition, BJ-1201 upregulated heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) to levels comparable to those of the CoPP-treated group. BJ-1201 treatment induced phosphorylation of JNK, but not p38-MAPK or ERK. It also increased the signal in the reporter assay based on β-galactosidase activity driven by the nuclear transcription factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) promoter harboring antioxidant response elements (AREs) and induced the translocation of Nrf2. These results demonstrate that BJ-1201 may be a good therapeutic platform against neurodegenerative diseases induced by oxidative stress.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
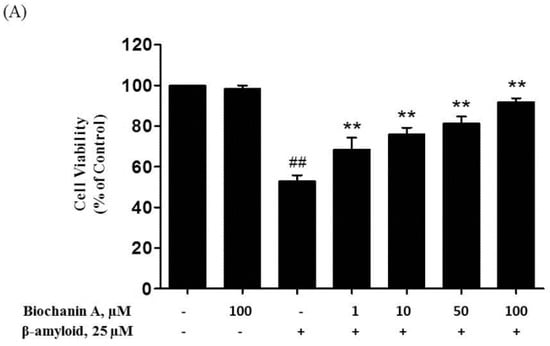
Neuroprotective Effects of Biochanin A against β-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells via a Mitochondrial-Dependent Apoptosis Pathway
by
Ji Wei Tan and Min Kyu Kim
Cited by 62 | Viewed by 8282
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease is considered one of the major neurodegenerative diseases and is characterized by the production of β-amyloid (Aβ) proteins and progressive loss of neurons. Biochanin A, a phytoestrogen compound found mainly in
Trifolium pratense, was used in the present study as
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease is considered one of the major neurodegenerative diseases and is characterized by the production of β-amyloid (Aβ) proteins and progressive loss of neurons. Biochanin A, a phytoestrogen compound found mainly in
Trifolium pratense, was used in the present study as a potential alternative to estrogen replacement therapy via the investigation of its neuroprotective effects against Aβ
25–35-induced toxicity, as well as of its potential mechanisms of action in PC12 cells. Exposure of these cells to the Aβ
25–35 protein significantly increased cell viability loss and apoptosis. However, the effects induced by Aβ
25–35 were markedly reversed in the present of biochanin A. Pretreatment with biochanin A attenuated the cytotoxic effect of the Aβ
25–35 protein by decreasing viability loss, LDH release, and caspase activity in cells. Moreover, we found that expression of cytochrome c and Puma were reduced, alongside with the restoration of Bcl-2/Bax and Bcl-xL/Bax ratio in the presence of biochanin A, which led to a decrease in the apoptotic rate. These data demonstrate that mitochondria are involved in the protective effect of biochanin A against Aβ
25–35 and that this drug attenuated Aβ
25–35-induced PC12 cell injury and apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction. Thus, biochanin A might raise a possibility as a potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease and other related neurodegenerative diseases.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
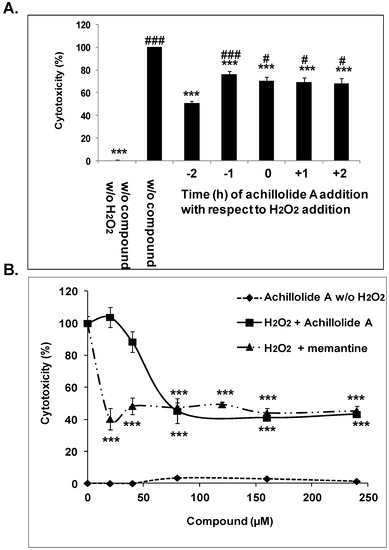
Achillolide A Protects Astrocytes against Oxidative Stress by Reducing Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species and Interfering with Cell Signaling
by
Anat Elmann, Alona Telerman, Hilla Erlank, Rivka Ofir, Yoel Kashman and Elie Beit-Yannai
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 5942
Abstract
Achillolide A is a natural sesquiterpene lactone that we have previously shown can inhibit microglial activation. In this study we present evidence for its beneficial effects on astrocytes under oxidative stress, a situation relevant to neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries. Viability of brain
[...] Read more.
Achillolide A is a natural sesquiterpene lactone that we have previously shown can inhibit microglial activation. In this study we present evidence for its beneficial effects on astrocytes under oxidative stress, a situation relevant to neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries. Viability of brain astrocytes (primary cultures) was determined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity, intracellular ROS levels were detected using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate,
in vitro antioxidant activity was measured by differential pulse voltammetry, and protein phosphorylation was determined using specific ELISA kits. We have found that achillolide A prevented the H
2O
2-induced death of astrocytes, and attenuated the induced intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These activities could be attributed to the inhibition of the H
2O
2-induced phosphorylation of MAP/ERK kinase 1 (MEK1) and p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), and to the antioxidant activity of achillolide A, but not to H
2O
2 scavenging. This is the first study that demonstrates its protective effects on brain astrocytes, and its ability to interfere with MAPK activation. We propose that achillolide A deserves further evaluation for its potential to be developed as a drug for the prevention/treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries where oxidative stress is part of the pathophysiology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
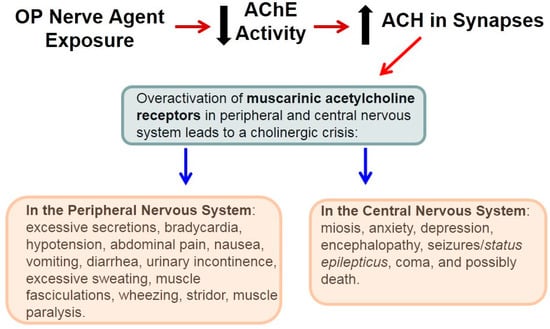
α-Linolenic Acid, A Nutraceutical with Pleiotropic Properties That Targets Endogenous Neuroprotective Pathways to Protect against Organophosphate Nerve Agent-Induced Neuropathology
by
Tetsade Piermartiri, Hongna Pan, Taiza H. Figueiredo and Ann M. Marini
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 9809
Abstract
α-Linolenic acid (ALA) is a nutraceutical found in vegetable products such as flax and walnuts. The pleiotropic properties of ALA target endogenous neuroprotective and neurorestorative pathways in brain and involve the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a
[...] Read more.
α-Linolenic acid (ALA) is a nutraceutical found in vegetable products such as flax and walnuts. The pleiotropic properties of ALA target endogenous neuroprotective and neurorestorative pathways in brain and involve the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a major neuroprotective protein in brain, and downstream signaling pathways likely mediated via activation of TrkB, the cognate receptor of BDNF. In this review, we discuss possible mechanisms of ALA efficacy against the highly toxic OP nerve agent soman. Organophosphate (OP) nerve agents are highly toxic chemical warfare agents and a threat to military and civilian populations. Once considered only for battlefield use, these agents are now used by terrorists to inflict mass casualties. OP nerve agents inhibit the critical enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) that rapidly leads to a cholinergic crisis involving multiple organs.
Status epilepticus results from the excessive accumulation of synaptic acetylcholine which in turn leads to the overactivation of muscarinic receptors; prolonged seizures cause the neuropathology and long-term consequences in survivors. Current countermeasures mitigate symptoms and signs as well as reduce brain damage, but must be given within minutes after exposure to OP nerve agents supporting interest in newer and more effective therapies. The pleiotropic properties of ALA result in a coordinated molecular and cellular program to restore neuronal networks and improve cognitive function in soman-exposed animals. Collectively, ALA should be brought to the clinic to treat the long-term consequences of nerve agents in survivors. ALA may be an effective therapy for other acute and chronic neurodegenerative disorders.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
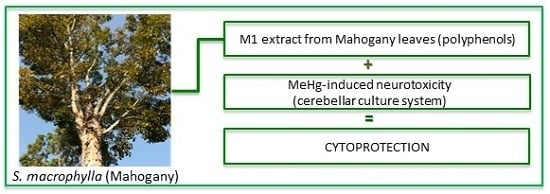
In Vitro Cytoprotective Effects and Antioxidant Capacity of Phenolic Compounds from the Leaves of Swietenia macrophylla
by
Sônia Pamplona, Paulo Sá, Dielly Lopes, Edmar Costa, Elizabeth Yamada, Consuelo E Silva, Mara Arruda, Jesus Souza and Milton Da Silva
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 7719
Abstract
Swietenia macrophylla (mahogany) is a highly valued timber species, whereas the leaves are considered to be waste product. A total of 27 phenolic compounds were identified in aqueous extracts from mahogany leaves by comparing retention times and mass spectra data with those of
[...] Read more.
Swietenia macrophylla (mahogany) is a highly valued timber species, whereas the leaves are considered to be waste product. A total of 27 phenolic compounds were identified in aqueous extracts from mahogany leaves by comparing retention times and mass spectra data with those of authentic standards using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Polyphenols play an important role in plants as defense mechanisms against pests and pathogens and have potent antioxidant properties. In terms of health applications, interest has increased considerably in naturally occurring antioxidant sources, since they can retard the progress of many important neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. The antioxidant capacities of two aqueous extracts, M1 (decoction) and M2 (infusion), were measured using TEAC and Folin-Ciocalteau methods. Additionally, M1 was used in order to investigate its potential cytoprotective effects on an
in vitro model of neurodegeneration, by using primary cerebellar cultures exposed to methyl mercury (MeHg). Under experimental sub-chronic conditions (72 h), concomitant exposure of the same cultures to MeHg and M1 extract resulted in a statistically significant increase in cell viability in all three concentrations tested (10, 50 and 100 μg/mL), strongly suggesting that due to its high content of antioxidant compounds, the M1 extract provides significant cytoprotection against the MeHg-induced in vitro neurotoxicity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
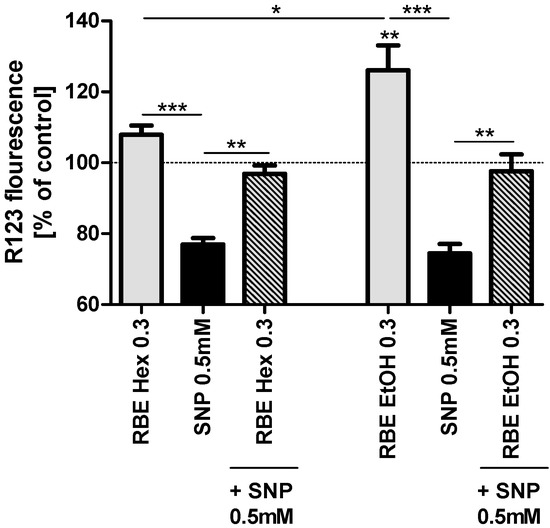
Beneficial Effects of Ethanolic and Hexanic Rice Bran Extract on Mitochondrial Function in PC12 Cells and the Search for Bioactive Components
by
Stephanie Hagl, Dirk Berressem, Bastian Bruns, Nadine Sus, Jan Frank and Gunter P. Eckert
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 6979
Abstract
Mitochondria are involved in the aging processes that ultimately lead to neurodegeneration and the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). A healthy lifestyle, including a diet rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, represents one strategy to protect the brain and to prevent neurodegeneration. We recently
[...] Read more.
Mitochondria are involved in the aging processes that ultimately lead to neurodegeneration and the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). A healthy lifestyle, including a diet rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, represents one strategy to protect the brain and to prevent neurodegeneration. We recently reported that a stabilized hexanic rice bran extract (RBE) rich in vitamin E and polyphenols (but unsuitable for human consumption) has beneficial effects on mitochondrial function in vitro and in vivo (doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.06.008, 10.3233/JAD-132084). To enable the use of RBE as food additive, a stabilized ethanolic extract has been produced. Here, we compare the vitamin E profiles of both extracts and their effects on mitochondrial function (ATP concentrations, mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial respiration and mitochondrial biogenesis) in PC12 cells. We found that vitamin E contents and the effects of both RBE on mitochondrial function were similar. Furthermore, we aimed to identify components responsible for the mitochondria-protective effects of RBE, but could not achieve a conclusive result. α-Tocotrienol and possibly also γ-tocotrienol, α-tocopherol and δ-tocopherol might be involved, but hitherto unknown components of RBE or a synergistic effect of various components might also play a role in mediating RBE’s beneficial effects on mitochondrial function.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
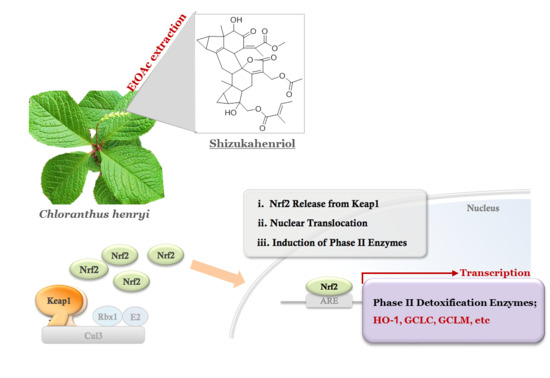
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of a Natural Compound, Shizukahenriol, through Nrf2 Activation
by
Jong-Hyun Park, Ji Won Choi, Eun Ji Ju, Ae Nim Pae and Ki Duk Park
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 7987
Abstract
Imbalance in the antioxidant defense system leads to detrimental consequences, such as neurological disorders. The Nrf2 signaling is known as a main pathway involved in cellular defense system. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that regulates oxidative stress response by inducing expression of various
[...] Read more.
Imbalance in the antioxidant defense system leads to detrimental consequences, such as neurological disorders. The Nrf2 signaling is known as a main pathway involved in cellular defense system. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that regulates oxidative stress response by inducing expression of various antioxidant enzyme genes. In this study, we screened several pure natural compounds for Nrf2 activator. Among them, shizukahenriol (SZH), isolated from
Chloranthus henryi, activated Nrf2, and induced expression of the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant enzymes HO-1, GCLC, and GCLM in BV-2 microglial cells. This natural compound was also effective in suppressing production of inflammatory molecules NO, TNF-α, and inhibition of NF-κB p65 translocation to the nucleus in a dose-dependent manner. We also examined whether SZH rescued the microglial cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death. Pretreatment with SZH dose-dependently attenuated H
2O
2-induced cytotoxicity in BV-2 microglial cells. These results suggested SZH as a potential neuroprotective agent for neurological disorders.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Neuroprotective Effects of Mitochondria-Targeted Plastoquinone and Thymoquinone in a Rat Model of Brain Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
by
Denis N. Silachev, Egor Y. Plotnikov, Ljubava D. Zorova, Irina B. Pevzner, Natalia V. Sumbatyan, Galina A. Korshunova, Mikhail V. Gulyaev, Yury A. Pirogov, Vladimir P. Skulachev and Dmitry B. Zorov
Cited by 55 | Viewed by 7882
Abstract
We explored the neuroprotective properties of natural plant-derived antioxidants plastoquinone and thymoquinone (2-demethylplastoquinone derivative) modified to be specifically accumulated in mitochondria. The modification was performed through chemical conjugation of the quinones with penetrating cations: Rhodamine 19 or tetraphenylphosphonium. Neuroprotective properties were evaluated in
[...] Read more.
We explored the neuroprotective properties of natural plant-derived antioxidants plastoquinone and thymoquinone (2-demethylplastoquinone derivative) modified to be specifically accumulated in mitochondria. The modification was performed through chemical conjugation of the quinones with penetrating cations: Rhodamine 19 or tetraphenylphosphonium. Neuroprotective properties were evaluated in a model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. We demonstrate that the mitochondria-targeted compounds, introduced immediately after reperfusion, possess various neuroprotective potencies as judged by the lower brain damage and higher neurological status. Plastoquinone derivatives conjugated with rhodamine were the most efficient, and the least efficiency was shown by antioxidants conjugated with tetraphenylphosphonium. Antioxidants were administered intraperitoneally or intranasally with the latter demonstrating a high level of penetration into the brain tissue. The therapeutic effects of both ways of administration were similar. Long-term administration of antioxidants in low doses reduced the neurological deficit, but had no effect on the volume of brain damage. At present, cationic decylrhodamine derivatives of plastoquinone appear to be the most promising anti-ischemic mitochondria-targeted drugs of the quinone family. We suggest these antioxidants could be potentially used for a stroke treatment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
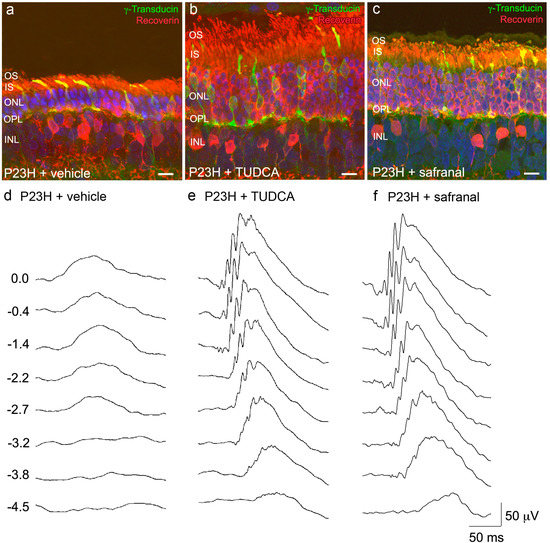
Natural Compounds from Saffron and Bear Bile Prevent Vision Loss and Retinal Degeneration
by
Laura Fernández-Sánchez, Pedro Lax, Agustina Noailles, Antonia Angulo, Victoria Maneu and Nicolás Cuenca
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 8855
Abstract
All retinal disorders, regardless of their aetiology, involve the activation of oxidative stress and apoptosis pathways. The administration of neuroprotective factors is crucial in all phases of the pathology, even when vision has been completely lost. The retina is one of the most
[...] Read more.
All retinal disorders, regardless of their aetiology, involve the activation of oxidative stress and apoptosis pathways. The administration of neuroprotective factors is crucial in all phases of the pathology, even when vision has been completely lost. The retina is one of the most susceptible tissues to reactive oxygen species damage. On the other hand, proper development and functioning of the retina requires a precise balance between the processes of proliferation, differentiation and programmed cell death. The life-or-death decision seems to be the result of a complex balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic signals. It has been recently shown the efficacy of natural products to slow retinal degenerative process through different pathways. In this review, we assess the neuroprotective effect of two compounds used in the ancient pharmacopoeia. On one hand, it has been demonstrated that administration of the saffron constituent safranal to P23H rats, an animal model of retinitis pigmentosa, preserves photoreceptor morphology and number, the capillary network and the visual response. On the other hand, it has been shown that systemic administration of tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), the major component of bear bile, to P23H rats preserves cone and rod structure and function, together with their contact with postsynaptic neurons. The neuroprotective effects of safranal and TUDCA make these compounds potentially useful for therapeutic applications in retinal degenerative diseases.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
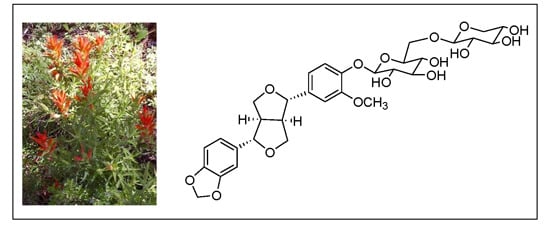
A New Furofuran Lignan Diglycoside and Other Secondary Metabolites from the Antidepressant Extract of Castilleja tenuiflora Benth
by
Maribel Herrera-Ruiz, Ricardo López-Rodríguez, Gabriela Trejo-Tapia, Blanca Eda Domínguez-Mendoza, Manases González-Cortazar, Jaime Tortoriello and Alejandro Zamilpa
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6901
Abstract
Castilleja tenuiflora has been used for the treatment of several Central Nervous System (CNS) diseases. Herein we report the antidepressant activity of the methanol extract from the leaves of this medicinal plant. The oral administration of MeOH extract (500 mg/kg) induced a significant
[...] Read more.
Castilleja tenuiflora has been used for the treatment of several Central Nervous System (CNS) diseases. Herein we report the antidepressant activity of the methanol extract from the leaves of this medicinal plant. The oral administration of MeOH extract (500 mg/kg) induced a significant (
p < 0.05) decrement of the immobility parameter on Forced Swimming Test (FST) and an increment in the latency and duration of the hypnosis, induced by administration of sodium pentobarbital (Pbi, 40 mg/kg,
i.p.). Chemical analysis of this antidepressant extract allowed the isolation of (+)-piperitol-4-
O-xylopyranosyl-(1→6)-
O-glucopyranoside. This new furofuran lignan diglycoside was named tenuifloroside (
1) and its complete chemical structure elucidation on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR spectra analysis of the natural compound
1 and its peracetylated derivative
1a is described. This compound was found together with two flavones—apigenin and luteolin 5-methyl ether—a phenylethanoid—verbascoside—and three iridoids—geniposide, caryoptoside and aucubin. All these compounds were purified by successive normal and reverse phase column chromatography. Tenuifloroside, caryoptoside and luteolin 5-methyl ether were isolated from
Castilleja genus for the first time. These findings demonstrate that
C. tenuiflora methanol extract has beneficial effect on depressive behaviors, and the knowledge of its chemical constitution allows us to propose a new standardized treatment for future investigations of this species in depressive illness.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
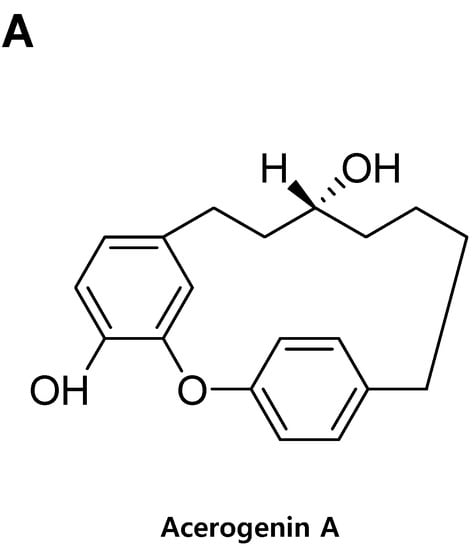
Acerogenin A from Acer nikoense Maxim Prevents Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Cell Death through Nrf2-Mediated Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in Mouse Hippocampal HT22 Cell Line
by
Dong-Sung Lee, Byung-Yoon Cha, Je-Tae Woo, Youn-Chul Kim and Jun-Hyeog Jang
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 7364
Abstract
Oxidative cell damage contributes to neuronal degeneration in many central nervous system (CNS) diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and ischemia. Inducible heme oxygenase (HO)-1 acts against oxidants that are thought to play a key role in the pathogenesis of neuronal diseases.
[...] Read more.
Oxidative cell damage contributes to neuronal degeneration in many central nervous system (CNS) diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and ischemia. Inducible heme oxygenase (HO)-1 acts against oxidants that are thought to play a key role in the pathogenesis of neuronal diseases. The stem bark of
Acer nikoense Maxim (Aceraceae) is indigenous to Japan; it has been used in folk medicine as a treatment of hepatic disorders and eye diseases. Acerogenin A, a natural compound isolated from Japanese folk medicine
A. nikoense, showed neuroprotective effects and reactive oxygen species (ROS) reduction on glutamate-induced neurotoxicity by inducing the expression of HO-1 in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Furthermore, acerogenin A caused the nuclear accumulation of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. In this study, we demonstrated that acerogenin A effectively prevents glutamate-induced oxidative damage, and HO-1 induction via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2 pathways appears to play a key role in the protection of HT22 cells. Therefore, this study implies that the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway represents a biological target and that acerogenin A might be a candidate for the prevention of neurodegeneration.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Riluzole as a Neuroprotective Drug for Spinal Cord Injury: From Bench to Bedside
by
Narihito Nagoshi, Hiroaki Nakashima and Michael G. Fehlings
Cited by 102 | Viewed by 25518
Abstract
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a devastating event resulting in permanent loss of neurological function. To date, effective therapies for SCI have not been established. With recent progress in neurobiology, however, there is hope that drug administration could improve outcomes after SCI. Riluzole
[...] Read more.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a devastating event resulting in permanent loss of neurological function. To date, effective therapies for SCI have not been established. With recent progress in neurobiology, however, there is hope that drug administration could improve outcomes after SCI. Riluzole is a benzothiazole anticonvulsant with neuroprotective effects. It has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a safe and well-tolerated treatment for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The mechanism of action of riluzole involves the inhibition of pathologic glutamatergic transmission in synapses of neurons via sodium channel blockade. There is convincing evidence that riluzole diminishes neurological tissue destruction and promotes functional recovery in animal SCI models. Based on these results, a phase I/IIa clinical trial with riluzole was conducted for patients with SCI between 2010 and 2011. This trial demonstrated significant improvement in neurological outcomes and showed it to be a safe drug with no serious adverse effects. Currently, an international, multi-center clinical trial (Riluzole in Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study: RISCIS) in phase II/III is in progress with riluzole for patients with SCI (clinicaltrials.gov, registration number NCT01597518). This article reviews the pharmacology and neuroprotective mechanisms of riluzole, and focuses on existing preclinical evidence, and emerging clinical data in the treatment of SCI.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Flavonoids from Sideritis Species: Human Monoamine Oxidase (hMAO) Inhibitory Activities, Molecular Docking Studies and Crystal Structure of Xanthomicrol
by
Fatma Pinar Turkmenoglu, İpek Baysal, Samiye Ciftci-Yabanoglu, Kemal Yelekci, Hamdi Temel, Salih Paşa, Nurten Ezer, İhsan Çalış and Gulberk Ucar
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 8912
Abstract
The inhibitory effects of flavonoids on monoamine oxidases (MAOs) have attracted great interest since alterations in monoaminergic transmission are reported to be related to neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases and psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety, thus MAOs may
[...] Read more.
The inhibitory effects of flavonoids on monoamine oxidases (MAOs) have attracted great interest since alterations in monoaminergic transmission are reported to be related to neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases and psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety, thus MAOs may be considered as targets for the treatment of these multi-factorial diseases. In the present study, four
Sideritis flavonoids, xanthomicrol (
1), isoscutellarein 7-
O-[6'''-
O-acetyl-β-D-allopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside (
2), isoscutellarein 7-
O-[6'''-
O-acetyl-β-D-allopyranosyl-(1→2)]-6''-
O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (
3) and salvigenin (
4) were docked computationally into the active site of the human monoamine oxidase isoforms (hMAO-A and hMAO-B) and were also investigated for their hMAO inhibitory potencies using recombinant hMAO isoenzymes. The flavonoids inhibited hMAO-A selectively and reversibly in a competitive mode. Salvigenin (
4) was found to be the most potent hMAO-A inhibitor, while xanthomicrol (
1) appeared as the most selective hMAO-A inhibitor. The computationally obtained results were in good agreement with the corresponding experimental values. In addition, the x-ray structure of xanthomicrol (
1) has been shown. The current work warrants further preclinical studies to assess the potential of xanthomicrol (
1) and salvigenin (
4) as new selective and reversible hMAO-A inhibitors for the treatment of depression and anxiety.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
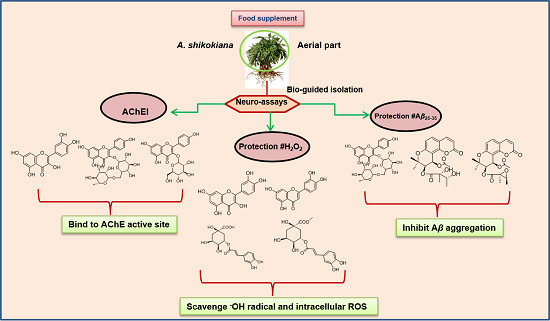
In Vitro Neuroprotective Activities of Compounds from Angelica shikokiana Makino
by
Amira Mira, Shuntaro Yamashita, Yoshinori Katakura and Kuniyoshi Shimizu
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 9337
Abstract
Angelica shikokiana is widely marketed in Japan as a dietary food supplement. With a focus on neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, the aerial part was extracted and through bio-guided fractionation, fifteen compounds [α-glutinol, β-amyrin, kaempferol, luteolin, quercetin, kaempferol-3-
O-glucoside, kaempferol-3-
O
[...] Read more.
Angelica shikokiana is widely marketed in Japan as a dietary food supplement. With a focus on neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, the aerial part was extracted and through bio-guided fractionation, fifteen compounds [α-glutinol, β-amyrin, kaempferol, luteolin, quercetin, kaempferol-3-
O-glucoside, kaempferol-3-
O-rutinoside, methyl chlorogenate, chlorogenic acid, hyuganin E, 5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furaldehyde, β-sitosterol-3-O-glucoside, adenosine (isolated for the first time from
A. shikokiana), isoepoxypteryxin and isopteryxin] were isolated. Isolated compounds were evaluated for
in vitro neuroprotection using acetylcholine esterase inhibitory, protection against hydrogen peroxide and amyloid β peptide (Aβ
25-35)-induced neurotoxicity in neuro-2A cells, scavenging of hydroxyl radicals and intracellular reactive oxygen species and thioflavin T assays. Quercetin showed the strongest AChE inhibition (IC
50 value = 35.5 µM) through binding to His-440 and Tyr-70 residues at the catalytic and anionic sites of acetylcholine esterase, respectively. Chlorogenic acid, its methyl ester, quercetin and luteolin could significantly protect neuro-2A cells against H
2O
2-induced neurotoxicity and scavenge hydroxyl radical and intracellular reactive oxygen species. Kaempferol-3-
O-rutinoiside, hyuganin E and isoepoxypteryxin significantly decreased Aβ
25-35-induced neurotoxicity and Th-T fluorescence. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report about neuroprotection of hyuganin E and isoepoxypteryxin against Aβ
25-35-induced neurotoxicity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Myrtenal-Adamantane Conjugates' Effects in Experimental Rat Neurodegeneration Model
Authors: Dragomanova S.1,2; Lazarova M.1; Munkuev A.3; Suslov E.3; Volcho K.3; Salakhutdinov N.3; Bibi A. 4; Reynisson J.4; Tzvetanova E.1; Alexandrova A.1; Georgieva A.1; Uzunova D.1; Kalfin R.1; Tancheva L.1
Affiliation: 1 – Department of Biological Effects of Natural and Synthetic Substances, Institute of Neurobiology, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Acad. G. Bonchev St., Block 23, Sofia 1113, Bulgaria.; 2 – Department of Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmacotherapy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical University, Varna 9002, Bulgaria; 3 – Russian Academy of Sciences, Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Novosibirsk Institute of Organic Chemistry, Lavrentiev av., 9, Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia; 4 - School of Pharmacy and Bioengineering, Keele University, Hornbeam Building, Staffordshire, ST5 5BG, United Kingdom