Databases, Nutrition and Human Health
A special issue of Nutrients (ISSN 2072-6643). This special issue belongs to the section "Nutrition and Public Health".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (25 October 2024) | Viewed by 12795
Special Issue Editors
Interests: food composition tables/databases; community nutrition; social environment; feeding behavior; geographic information systems; dietary assessment methods; sports nutrition
Interests: nutrimetabolomics; biomarkers; food metabolome databases; food metabolome; metabotypes; Mediterranean diet; dietary patterns; intervariability; cardiovascular diseases; age-related diseases; intestinal microbiota
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
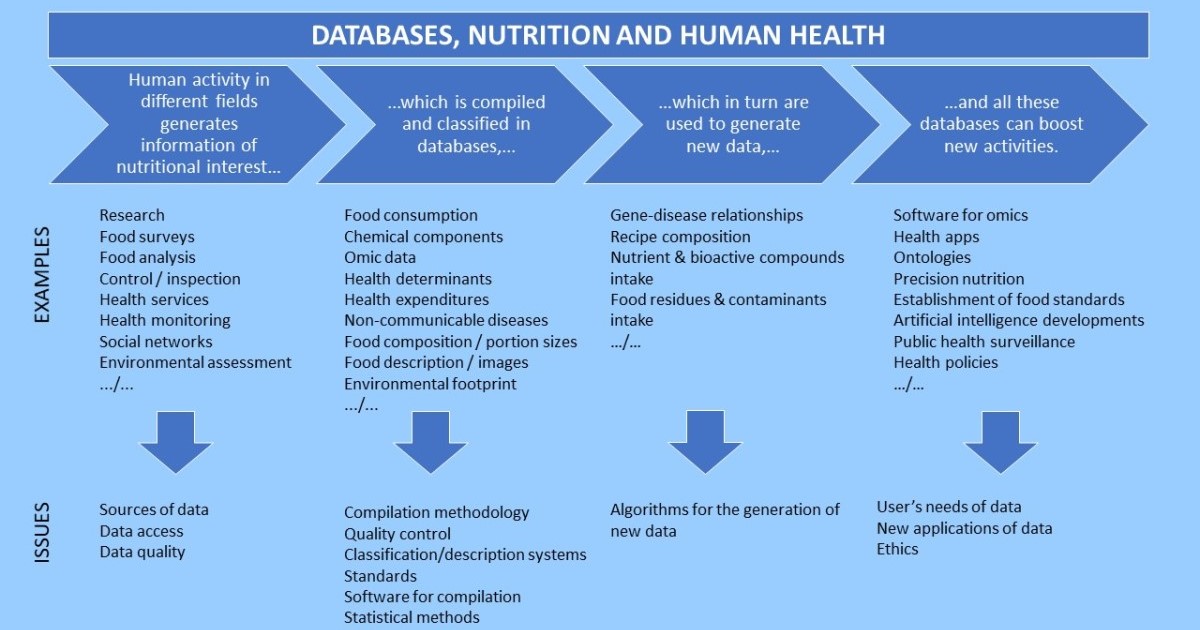
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Almost from the very beginnings of nutrition science, databases (in printed or electronic format) have been a fundamental tool in nutrition research, and in the evaluation and dietary planning of individuals and populations. This includes a wide range of databases, such as food composition databases, descriptor databases for use in standardized and structured languages to describe foods, food allergen databases, food intake databases, and even databases for decision-making in food safety and nutrition policies. The importance of databases has increased in recent decades due to the development of computing and big data analysis. Taking advantage of these advances, omics disciplines such as genomics or metabolomics have emerged, which also have their application in the field of nutrition and require specialized databases. Developments in fields such as semantic Web or artificial intelligence are likely to further increase the importance of high-quality and comprehensive databases. As examples, databases of metabolites detected in the human organism from dietary components, databases of descriptors used in ontologies (well-defined vocabularies with terms connected by logical relationships) and databases of recipes used in computational gastronomy have recently been developed.
The aim of this Special Issue is to provide a broad overview of the applications of databases in nutrition, their development methodologies, as well as the quality requirements they must meet.
Prof. Dr. Andreu Farran-Codina
Dr. Mireia Urpi-Sarda
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Nutrients is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- databases
- food composition data
- omics sciences
- public health
- computing
- nutrition
- ontologies
- artificial intelligence
- big data
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue polices can be found here.






