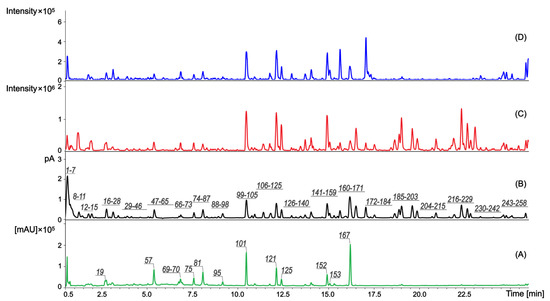
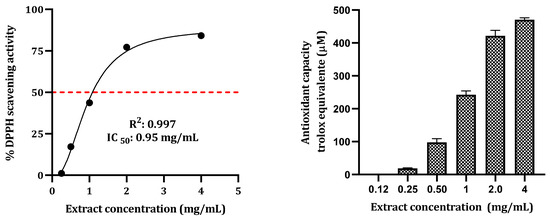
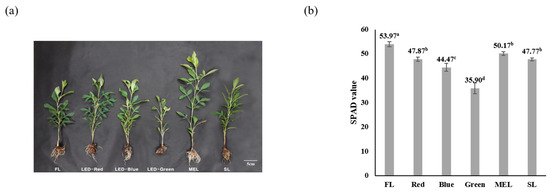
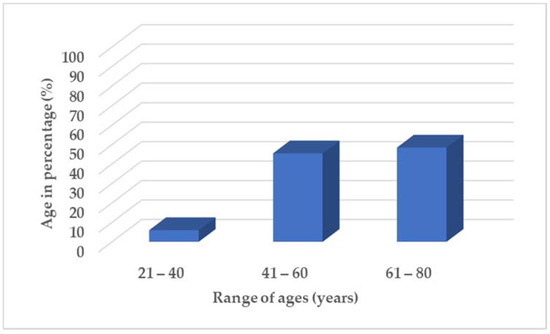
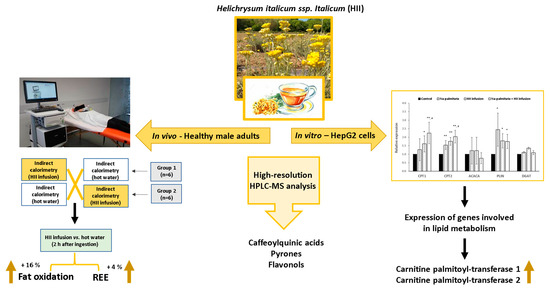
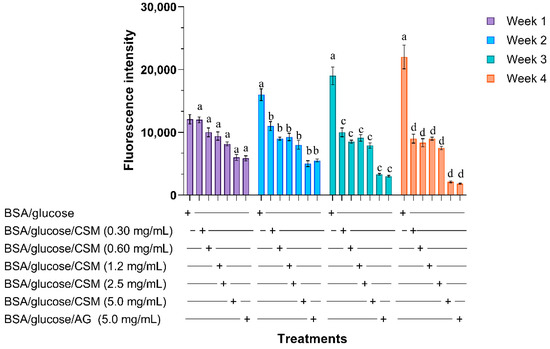
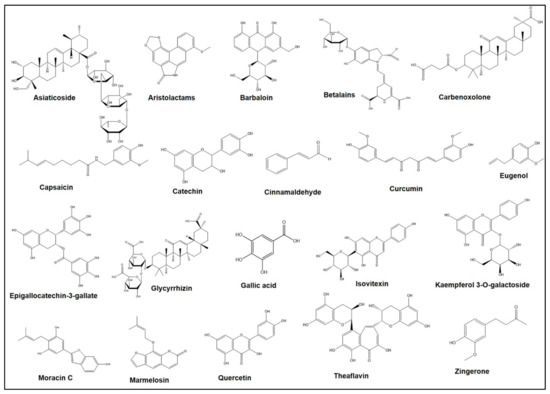
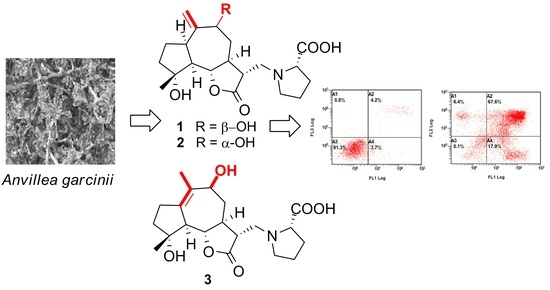
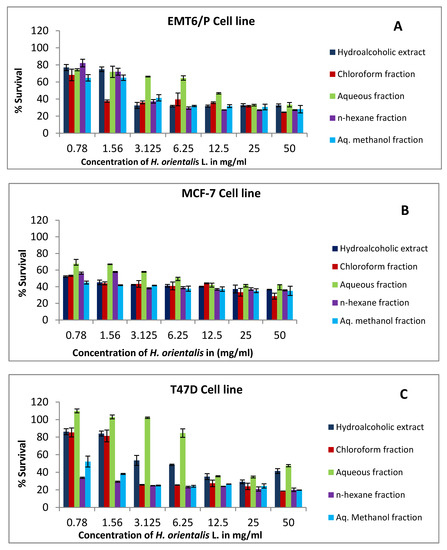
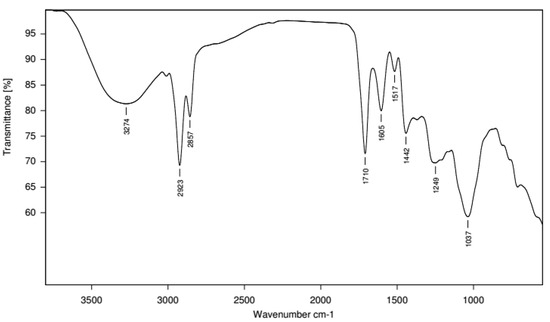
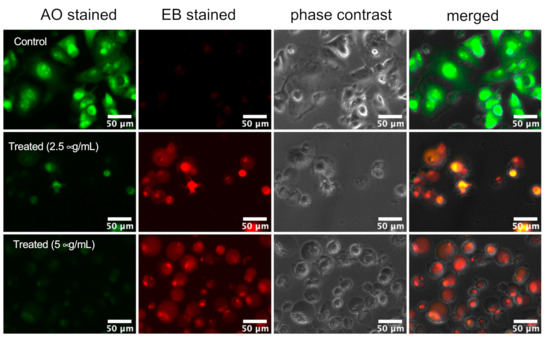
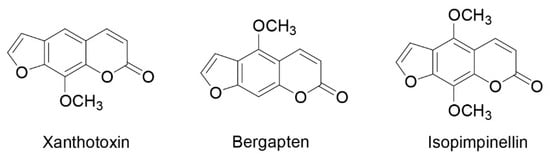
Medicinal Plants: New Advances in Phytochemicals and Their Health Benefits
A topical collection in Plants (ISSN 2223-7747). This collection belongs to the section "Phytochemistry".
Viewed by 109966Editors
Interests: medicinal plants; plant extracts; natural bioactive compounds; essential oils; nutraceuticals; antioxidant activity; antiproliferative activity; anti-inflammatory properties; photocytotoxic compounds
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: secondary metabolite isolation; structural determination; oxidative stress; nutraceuticals; bioactive molecules; cholinesterase inhibitory activity; Alzheimer’s disease; cytotoxic effects
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Medicinal plants have a long history of use all around the world. Knowledge of their induced health benefits has been transmitted over the centuries within human communities and natural products play a pivotal role as a productive source of drug lead compounds.
The development of advanced tools for the qualitative and quantitative assessment of phytochemicals significantly improved phytochemical investigation. On the other hand, empirical data on the biological properties of many plant species have been verified. The potential benefits for human health of different plant raw extracts and their bioactive components, together with their mechanisms of action, have also been elucidated. Nevertheless, medicinal plants still have a hopeful future. Many species have not yet been studied or remain to be more deeply investigated as regards to their chemical constituents and biological properties, not to mention that new fields of application could be also be identified for well-known plant species.
This Topical Collection will focus on more recent studies dealing with the extraction, isolation, and structural elucidation of medicinal plant secondary metabolites, the in vitro or in vivo biological properties, and the potential beneficial effects for human health. Papers focusing on functional foods and nutraceuticals from plant sources will be also taken into account.
Original research articles, reviews, and short communications are welcome.
Dr. Mariangela Marrelli
Dr. Luigi Milella
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Plant extracts
- Phytochemicals
- Bioactive compounds
- Essential oils
- Nutraceuticals
- Antioxidant
- Health promoting
- Chronic diseases
- Neurological diseases