Management, Environment, Energy and Sustainability under a Circular Economy
A topical collection in Resources (ISSN 2079-9276).
Viewed by 256172Editors
Interests: environmental sustainability; energy efficiency; environmental management; motor fuels; petroleum refining
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: resources; renewable energy; environmental sustainability; circular economy; waste management; air pollution; microplastics; sewage sludge management; human health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
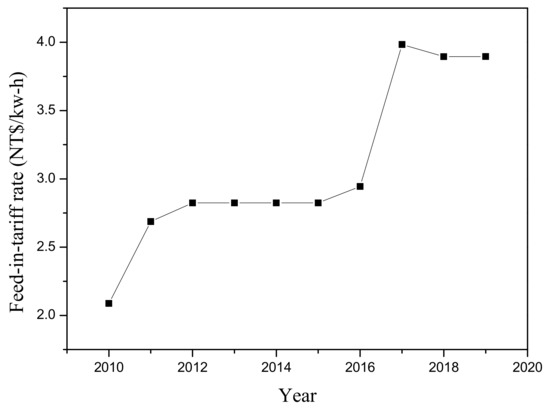
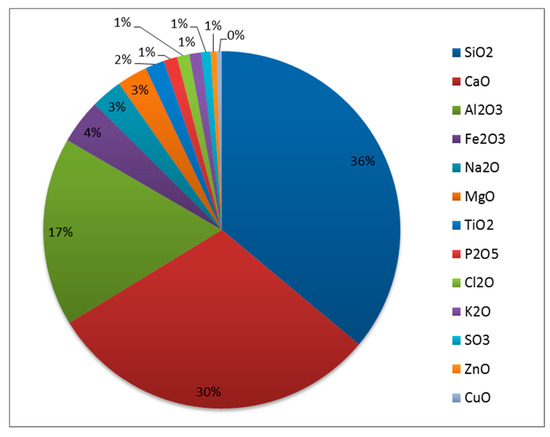
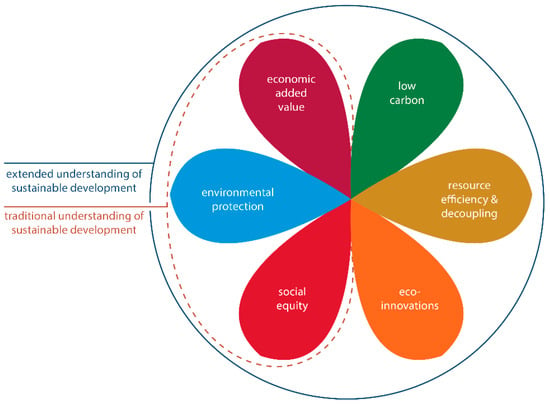
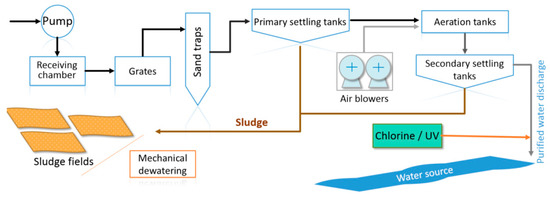
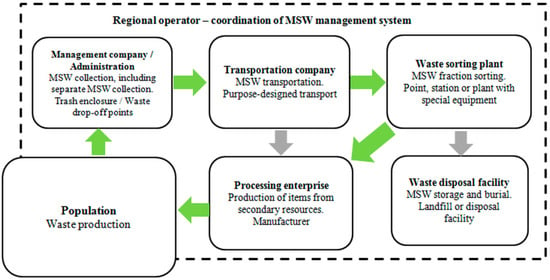
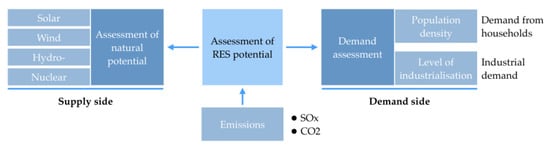
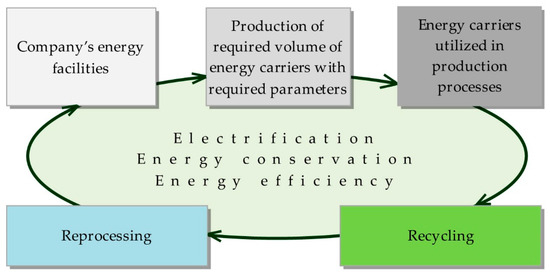
The linear economic model, based on a sequential approach 'take-make-consume-throw away', cannot be acceptable in a society oriented to environmental sustainability. The required change of vision comes from the concept of circular economy: here, products and their materials are valued as much as possible, reducing waste generation to a minimum. As consequence reusing, repairing and recycling grow in importance. Innovation can play a strategic role. Energy recovery from waste should become secondary compared to material recovery, assuming that economic sustainability must be always guaranteed. What used to be managed as a waste can be turned into a resource, reducing the pressure on the environment. An example of the consequences of the adoption of the circular economy concept can be seen in the sector of biogas: The conventional approach for its valorisation is based on the co-generation of electricity and heat thanks to its combustion in an engine coupled with an alternator; the circular economy criteria are moving the biogas sector towards the upgrading of biogas to biomethane and the recovery of CO2 for industrial uses, from the generated off-gas. The circular economy, built on technical and social innovations, necessitates taking into account regional priorities, and assumes, on the one hand, the increased energy and material efficiency of technological processes, including those using conventional fuels and energy, and a raise in the competitiveness of alternative fuels and energy on the other hand. It is necessary to address the challenges of required optimisation for various energy and materials alternatives, and to indicate innovative solutions for industrial and transportation development. The new political and social consequences are an important aspect of the transition to a circular economy, which requires the increase in efficiency for management systems on the basis of an interdisciplinary approach. This calls for a new methodology of education for managers able to work in unstable conditions of increased risks and accelerating changes. In general, the effects of this new vision are on company strategies, citizens’ behavior and public management. The aim of this Topical Collection is to contribute to the evolution of the concept of circular economy from all the above-mentioned points of view.
Prof. Dr. Elena Magaril
Dr. Elena Rada
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Resources is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Circular Economy
- Citizens behavior
- Environmental Sustainability
- Efficiency
- Energy recovery
- Innovation
- Management Systems
- Recycling
- Renewable Energy
- Reuse
- Sustainable Technologies
- Waste management