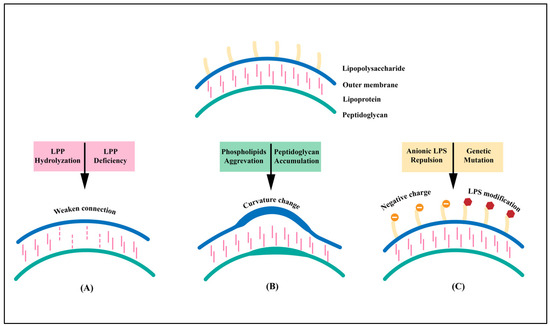
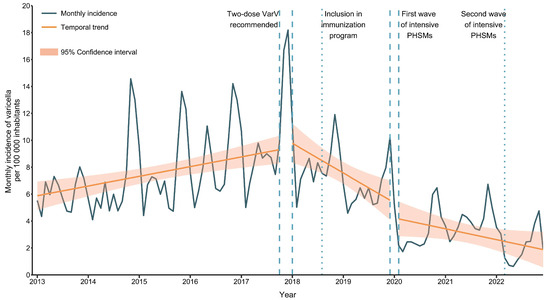
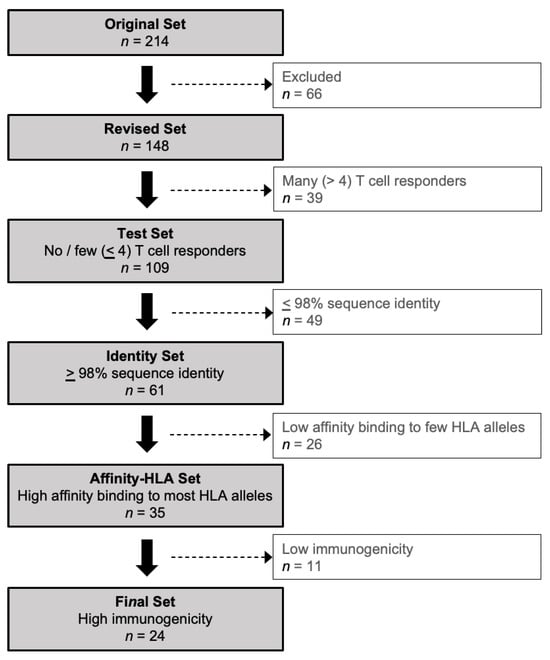
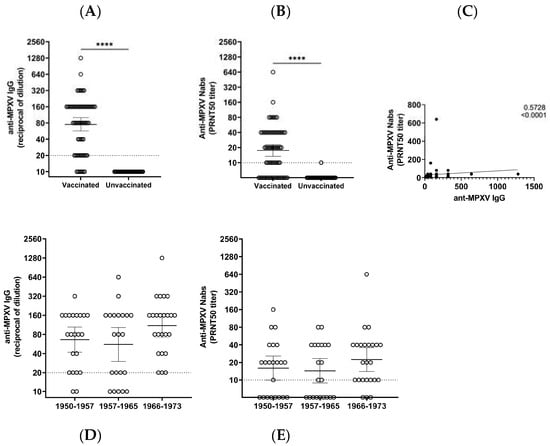
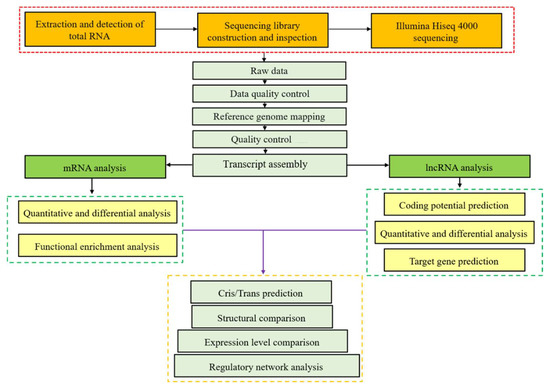
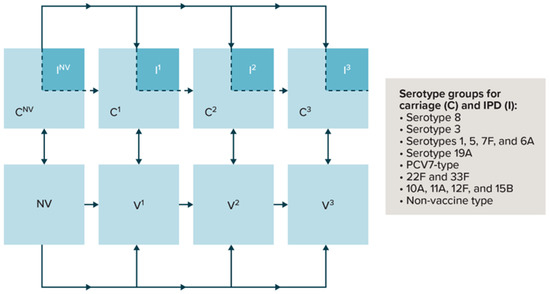
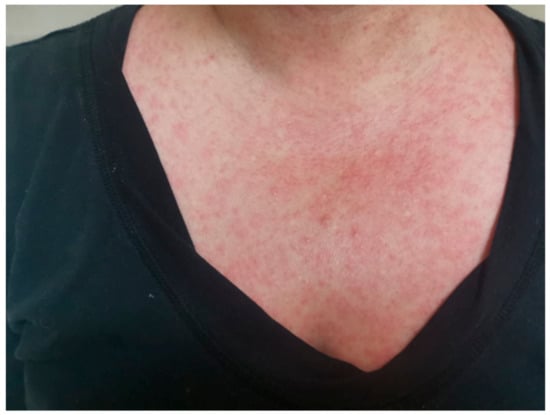
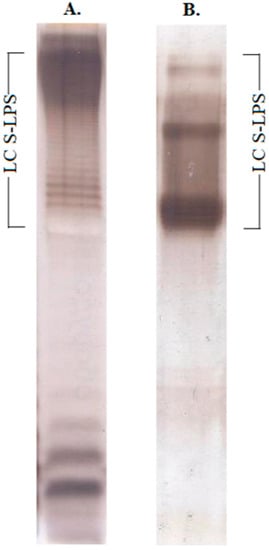
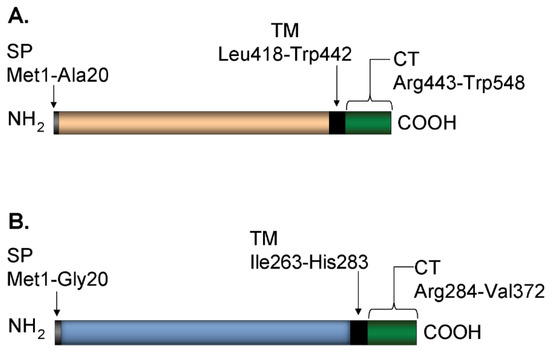
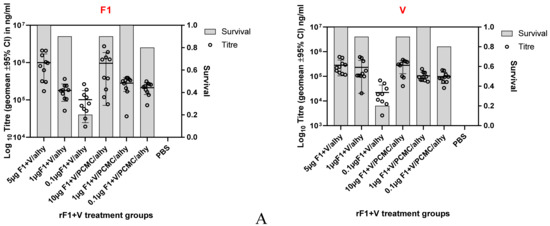
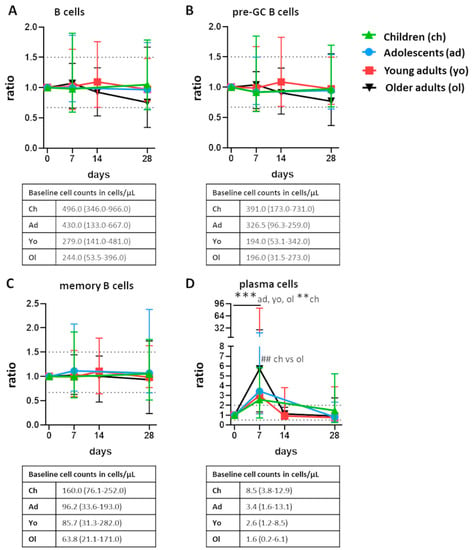
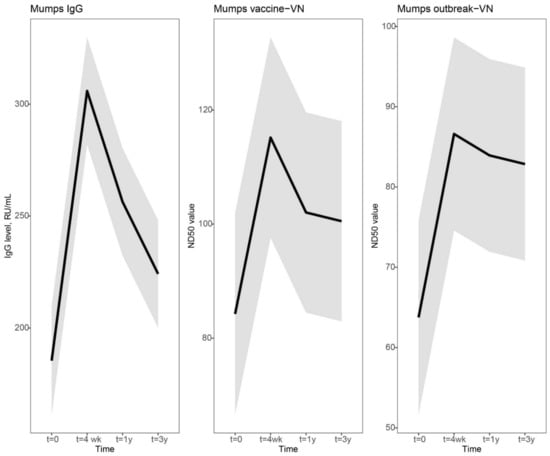
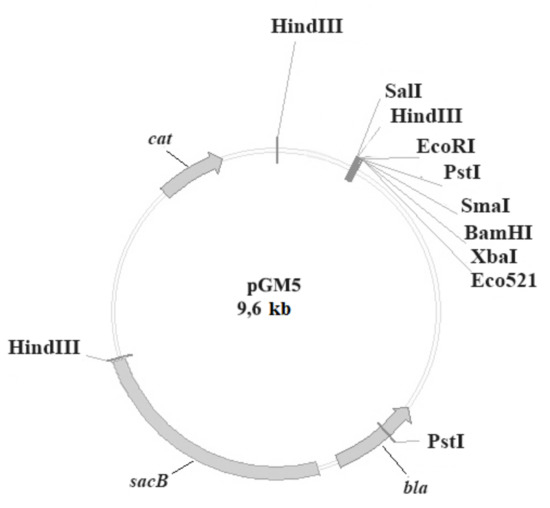
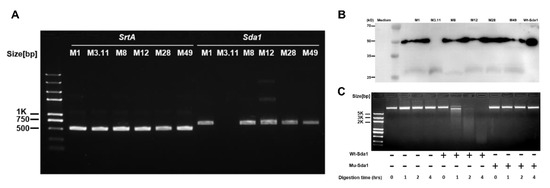
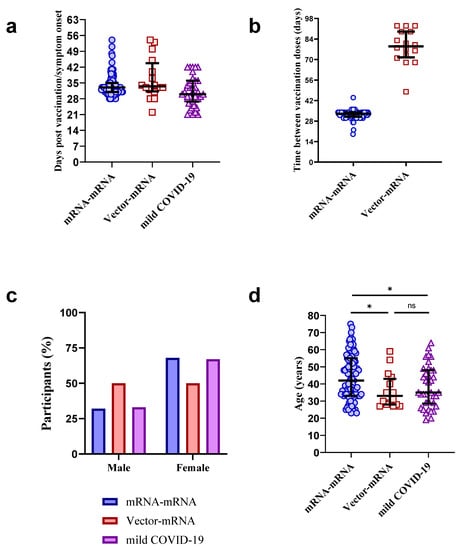
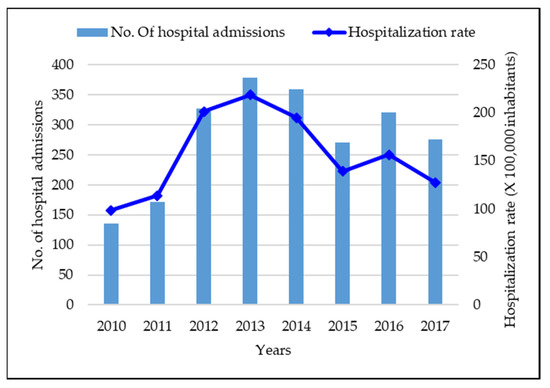
Vaccines against Infectious Diseases
A topical collection in Vaccines (ISSN 2076-393X). This collection belongs to the section "Vaccines against Tropical and other Infectious Diseases".
Viewed by 117644Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We are launching a collection on vaccines against infectious disease, in which we propose to cover aspects of vaccine design, development , formulation, clinical trial and deployment. Despite advances in global healthcare, there is still a clear need for more vaccines against infectious disease, underlined in the past year or more by the coronavirus pandemic. In this series, we will invite a broad range of papers to cover the following topics:
- Vaccines to counter anti-microbial resistance
- Vaccines to eradicate endemic disease-opportunities and challenges
- Vaccines to prevent zoonotic transmission-targeting the animal reservoir
- Vaccine platforms-advantages and disadvantages
- Clinical trial design for reactive and preventive vaccination
- Vaccine deployment in outbreak settings-lessons learned
- Advances in vaccine formulation and adjuvantisation
- WHO pre-qualification of vaccines-creating a Target Product Profile
- Clinical view on routinisation of vaccines
- How do we prepare for vaccines against the as yet unknown?
Dr. E.Diane Williamson
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Vaccines is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- clinical trial
- vaccine
- formulation
- platform
- endemic disease
- outbreak
- preventive
- reactive
- vaccination