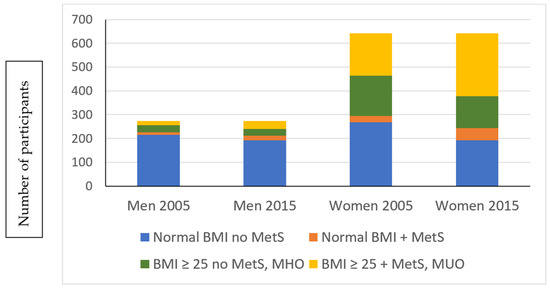
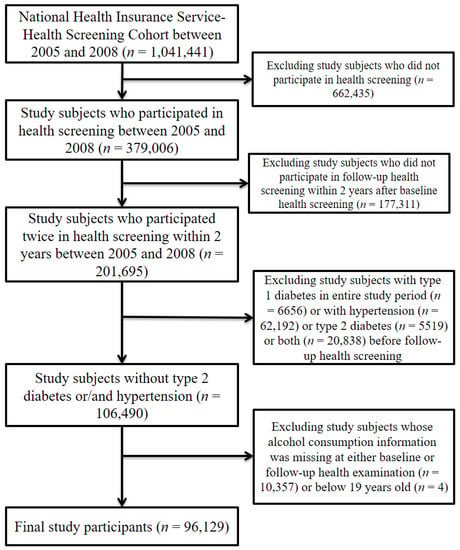
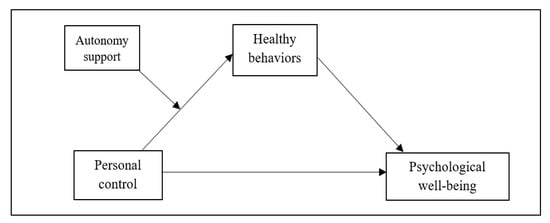
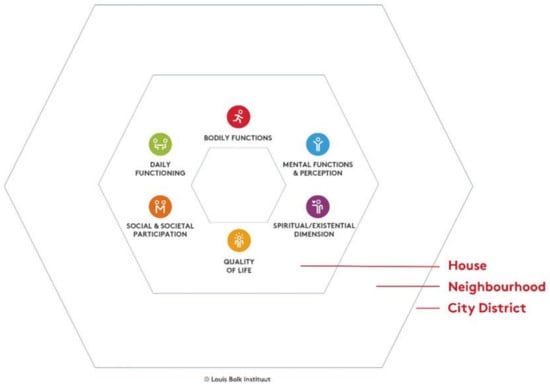
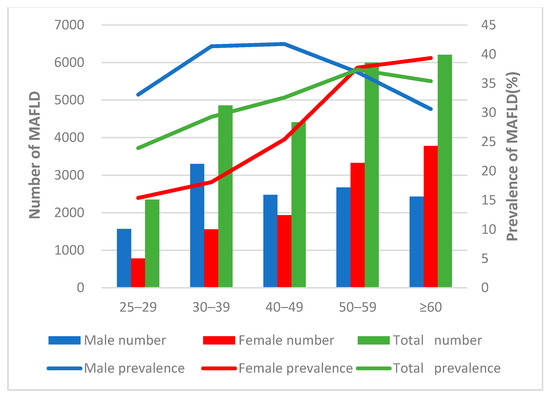
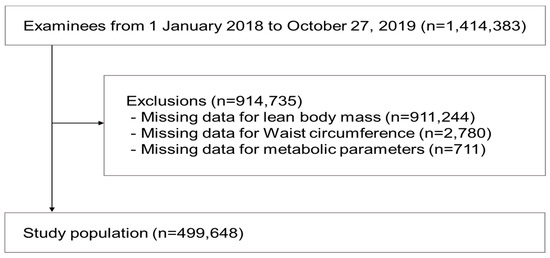
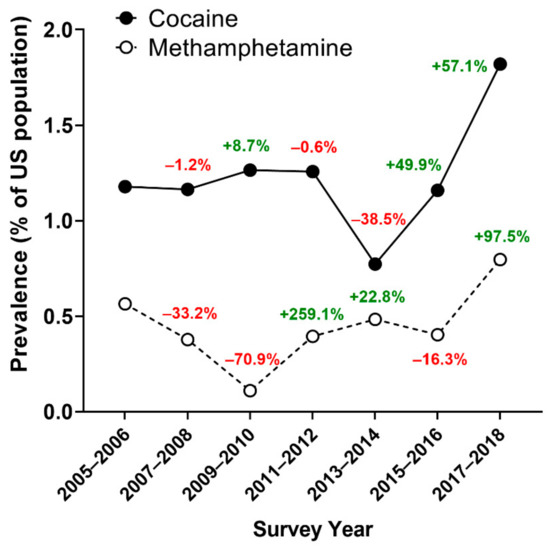
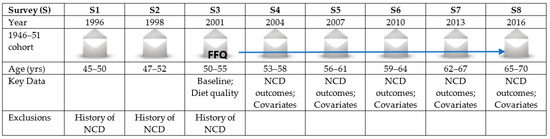
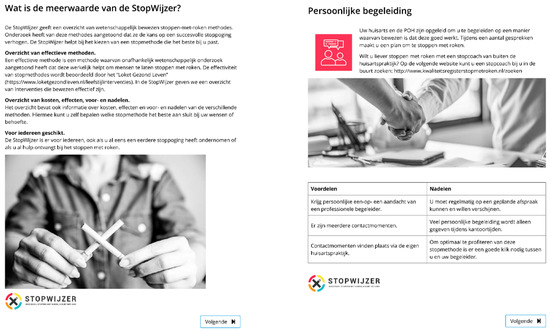
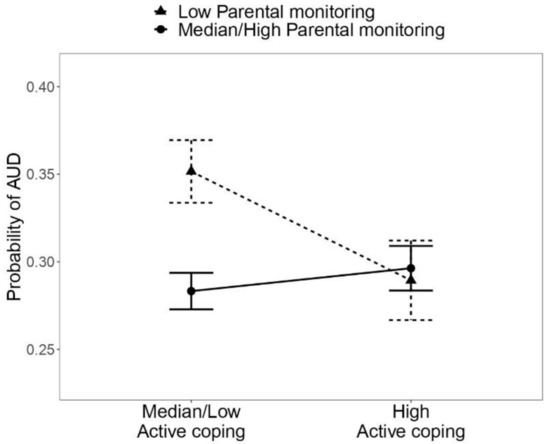
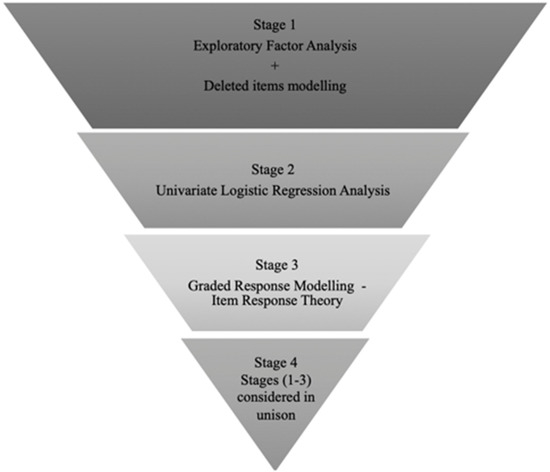
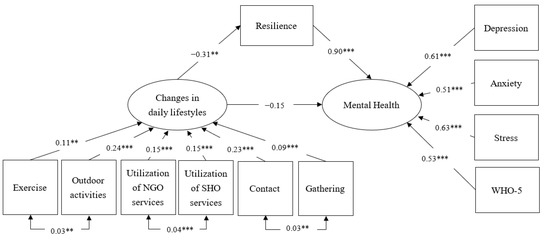
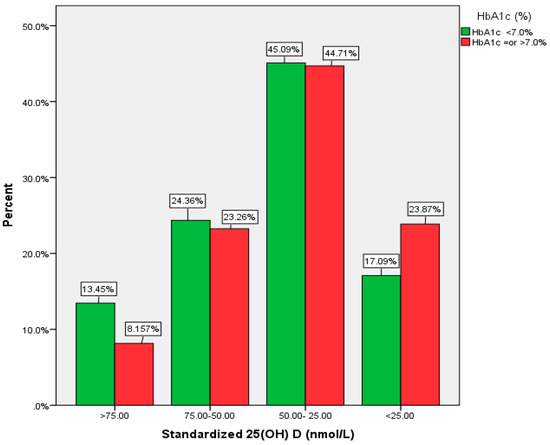
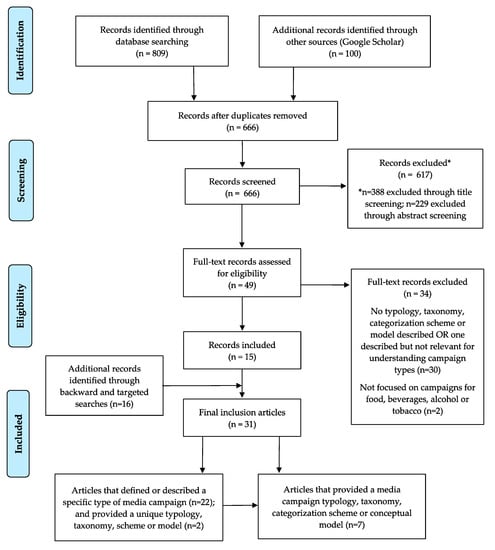
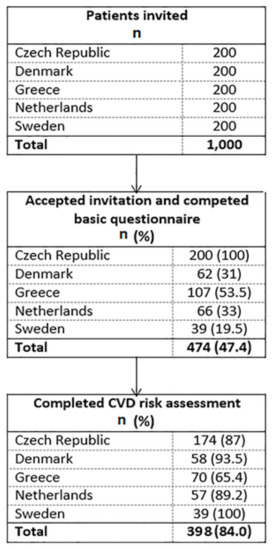
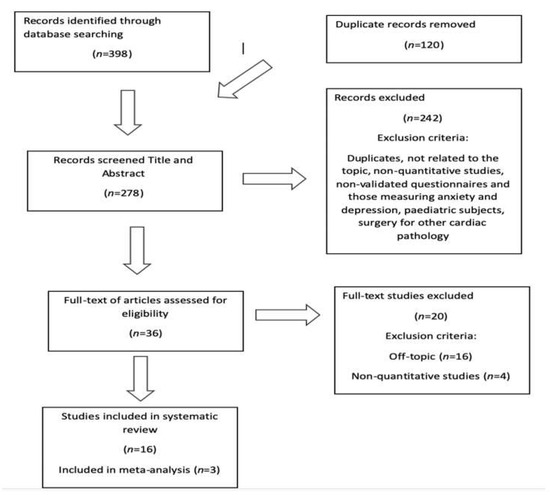
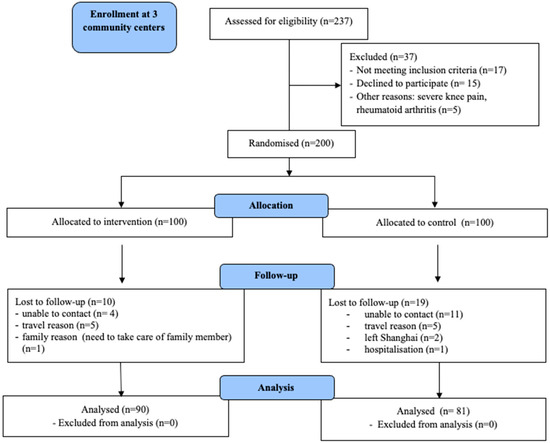
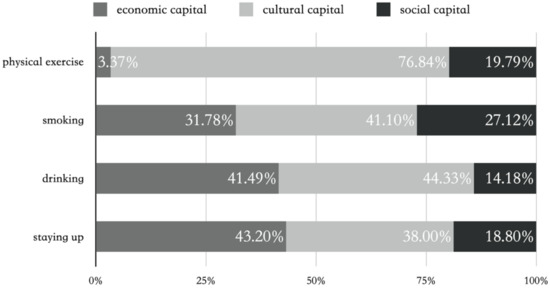
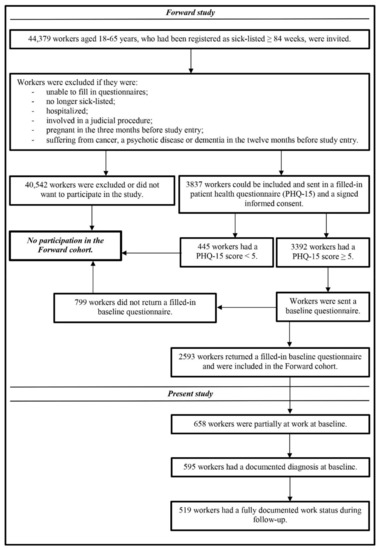
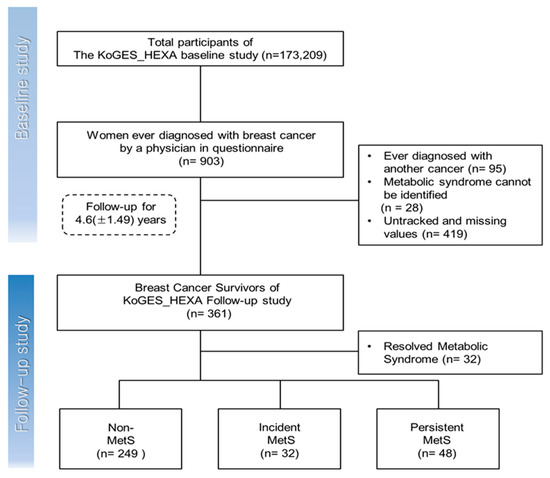
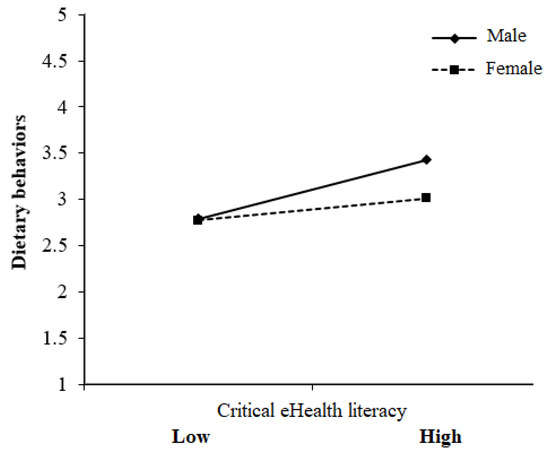
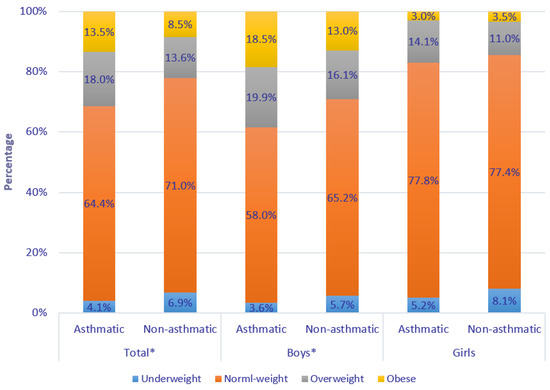
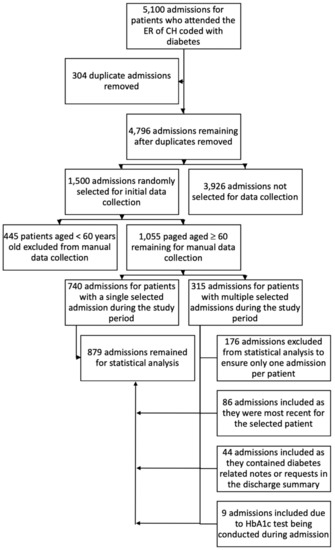
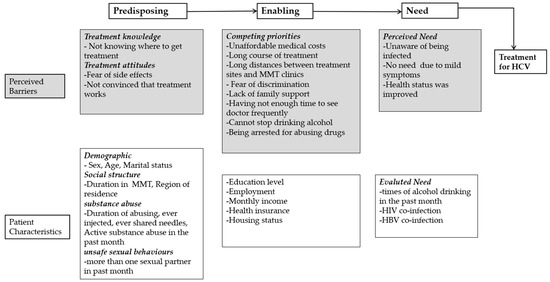
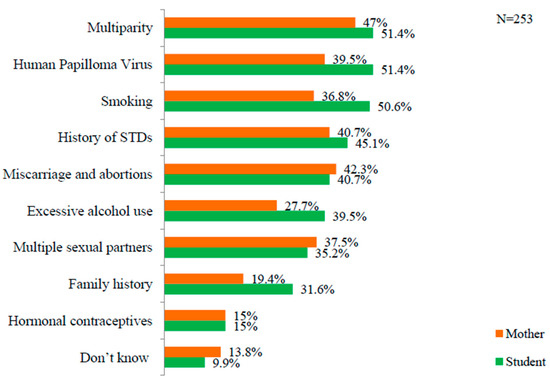
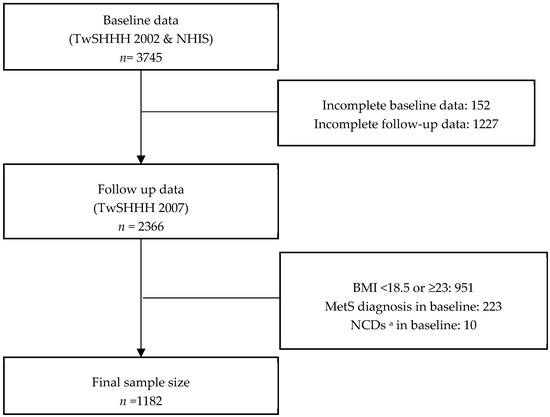
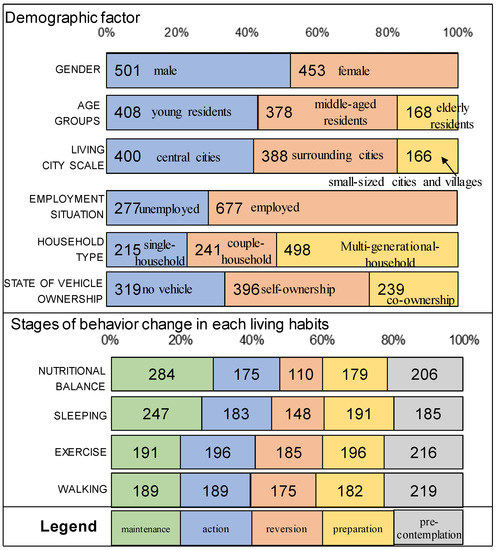
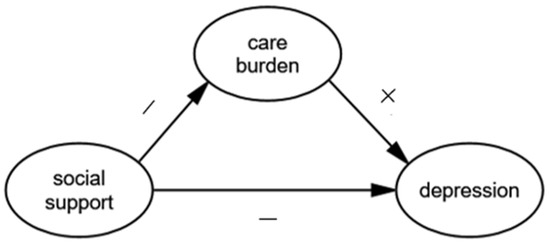
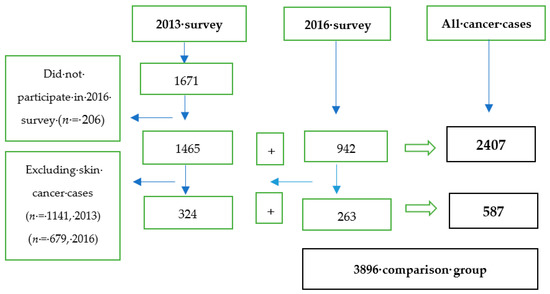
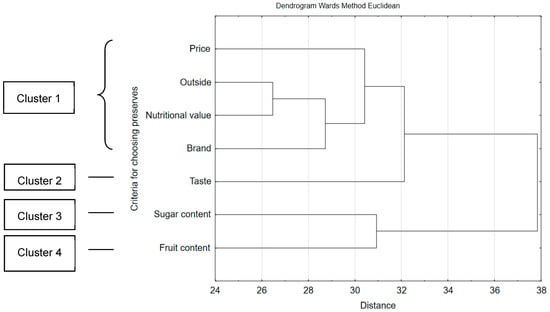
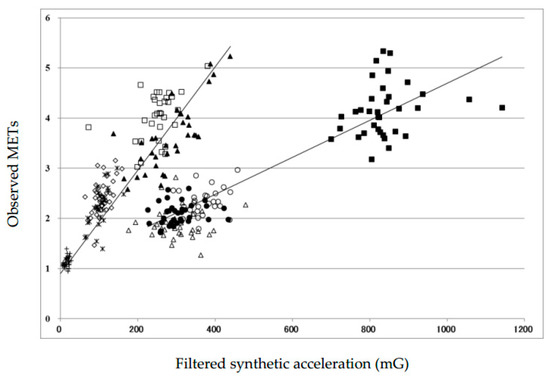
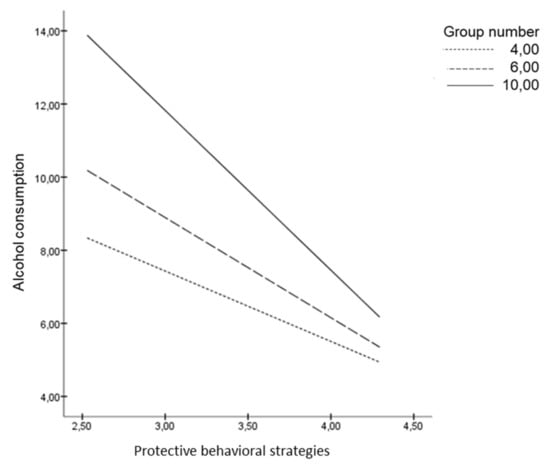
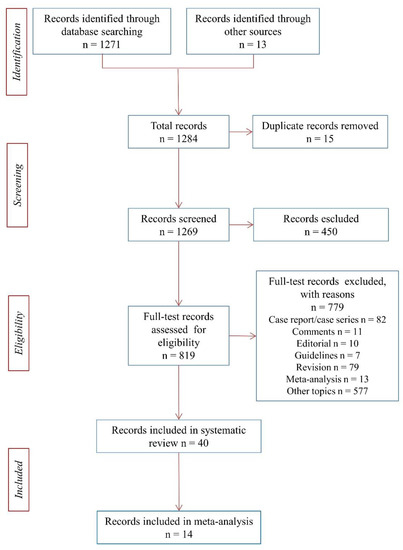
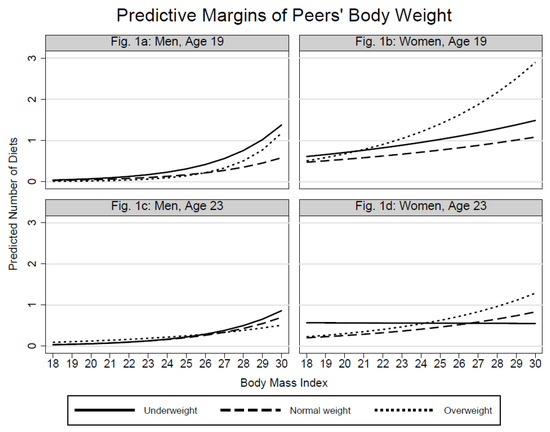
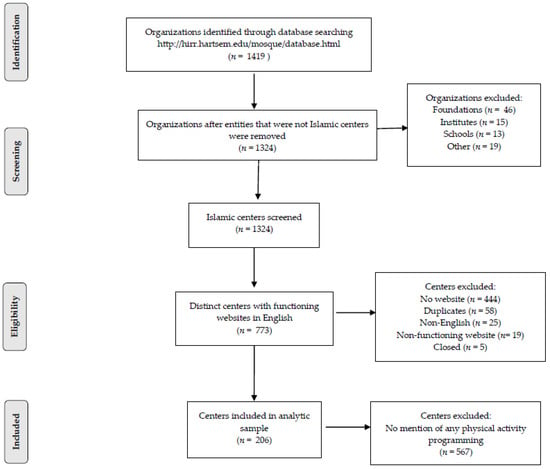
Health Behaviors, Risk Factors, NCDs and Health Promotion
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601). This collection belongs to the section "Behavioral and Mental Health".
Viewed by 457076Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
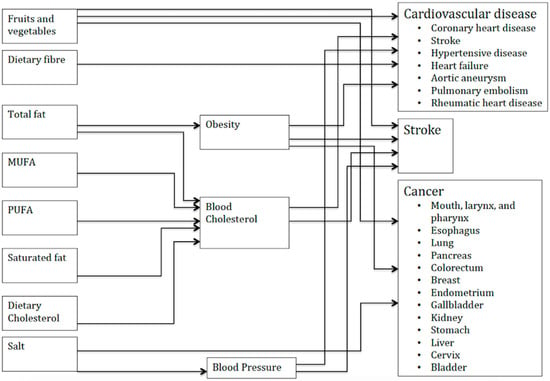
As clearly shown in the literature and remarked by international organizations, Non Communicable Diseases (NCDs) account for 70 to more than 90% of deaths in almost any country in the world, and, even more, for years of living with disability. As pointed out in the recent report “TIME TO DELIVER” of the WHO Independent High-Level Commission on Noncommunicable Diseases, action is needed at all levels to increase global health and avoid premature mortality. Despite the fact that this need has been shared globally, not only by WHO but also in the UN General Assembly Declarations (2011), little improvements have been seen in this field, and the shared global targets, such as a 25% reduction in premature NCD mortality by 2025, seem too far to reach.
Much undergoing research is studying the relationship between risk factors at individual and community level and NCDs, as well as trying to identify “what works” in reducing the risk factors’ prevalence. Smoking, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, and alcohol are the main areas of action and study, together with some other more specific fields.
This Topical Collection is open to the subject area of health behaviors, risk factors, and NCDs, with a specific interest in the analysis of public health actions and health promotion programs. The keywords listed below provide an outline of some of the possible areas of interest.
Prof. Dr. Stefano Campostrini
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Risk factors
- Risk factors and NCDs among specific populations (migrants, etc.)
- Health behaviors
- Health promotion
- Evaluation
- Surveillance
- Premature mortality
- NCDs and primary care
- Universal care
- Smoking
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Alcohol
- Obesity