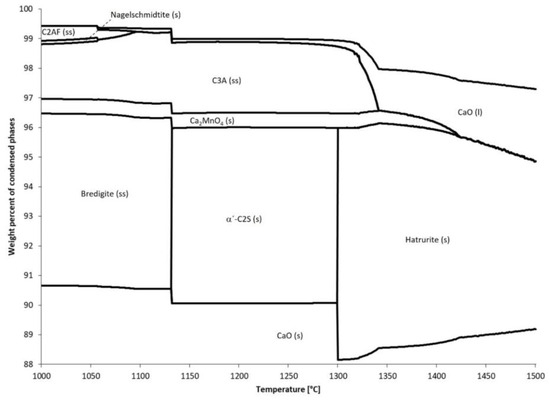
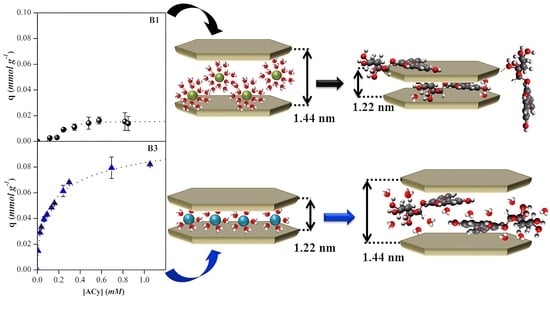
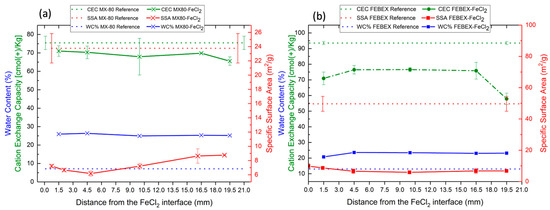
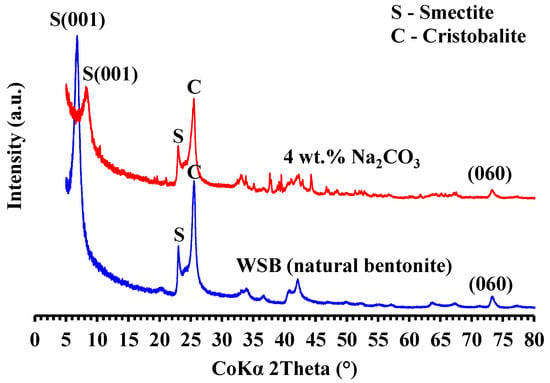
Clays and Other Industrial Mineral Materials
A topical collection in Minerals (ISSN 2075-163X). This collection belongs to the section "Clays and Engineered Mineral Materials".
Viewed by 35210Editors
Interests: geology and geochemistry of clays; special clays applications; sepiolite–palygorskite; bentonite; talc–kerolite; clays and health; mineral characterization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: kaolin; smectite group of minerals; sepiolite; palygorskite; pelotherapy; advanced, clay-based materials; pharmaceutical uses of adsorption processes; new technologies
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: raw materials characterization; industrial minerals in environmental applications; economic geology; green geochemistry; mineralogy; cementitious and construction materials; industrial clays; fillers–filters–absorbents; microporous raw materials; marine aggregates; raw materials policy; mine waste reuse; environmental impacts; ecosystems; geoarchaeology; natural heritage
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
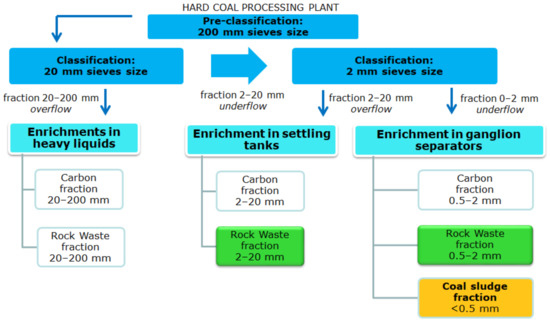
Industrial minerals form an exceptionally varied group of raw materials that cover virtually all needs of modern human life, although their presence is often invisible. Industrial minerals can be defined as those minerals that, due to their physical and/or chemical properties, are used in industrial processes. From a compositional point of view, industrial mineral materials include both silicates (e.g., zeolites and clays) and nonsilicates (e.g., chromite and barite). No doubt, it can be said that clay minerals and clays, whether in their natural state or modified, are outstanding materials in the field of industrial mineral materials. They are abundant, relatively cheap to obtain, and mostly friendly from an industrial and health viewpoint.
Clay is a textural term referring to natural rock, sediment, and/or alteration products mainly made up of very fine-grained clay mineral phyllosilicates. Clay minerals, whether natural or synthetic, show economically interesting physical and chemical properties directly related to their structure and composition. Both the layer charge and small particle size of the clay minerals give place to suitable properties such as plasticity, sorption, rheology, and ion exchange, among others.
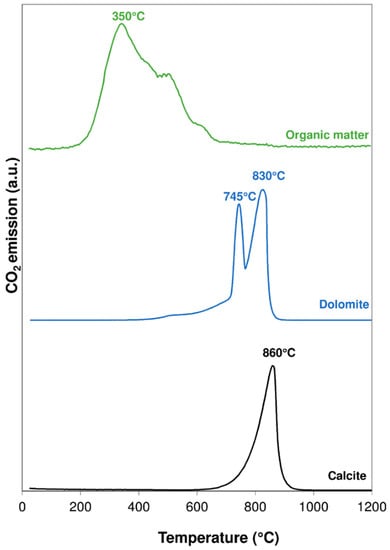
Taking into account their origin, clay minerals can be detrital and authigenic. Detrital clay minerals are inherited and thus reflect the sediment source (provenance). Authigenic clay minerals are, in a broad sense, “formed or generated in place”, whether related to soil processes, sedimentary deposition or diagenesis; in addition, authigenic clays are also formed under low-grade metamorphic conditions and/or the influence of hydrothermal events.
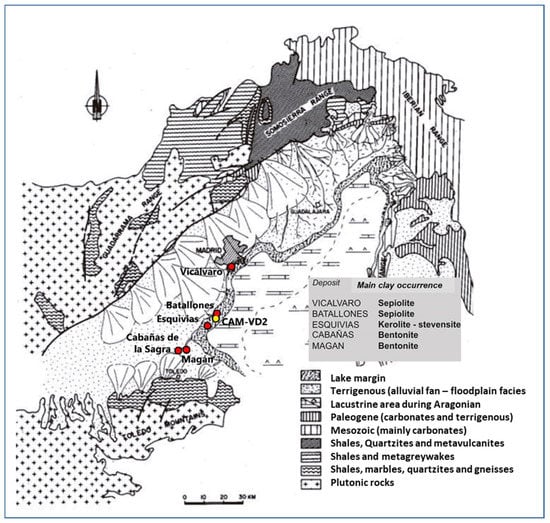
When they are classified as industrial minerals, a distinction is made between common clays, which usually consist of an association of several clay minerals, and special clays, which are typically formed of just one clay mineral and include kaolin, bentonite, sepiolite and palygorskite.
This collection aims to cover several broad objectives. It will be focused mainly on the study of industrial clays and clay minerals, but it also will deal with other industrial minerals. Approaches to these industrial mineral materials can be focused on: 1) geology, 2) mineralogy and geochemistry, 3) mineral genesis, 4) physical and physicochemical properties, 5) industrial and environmental applications, and 6) methods for their characterization.
We look forward to your submissions.
Prof. Dr. Manuel Pozo Rodríguez
Prof. Dr. Francisco Franco
Prof. Dr. Michael G. Stamatakis
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Minerals is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Clays
- Clay minerals
- Industrial mineral materials
- Geology
- Mineralogy
- Geochemistry
- Genesis
- Properties
- Applications
- Common clays
- Special clays
- Bentonite
- Kaolin and related clays
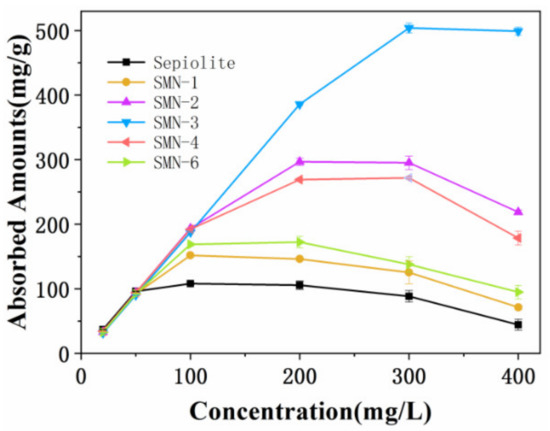
- Sepiolite
- Palygorskite