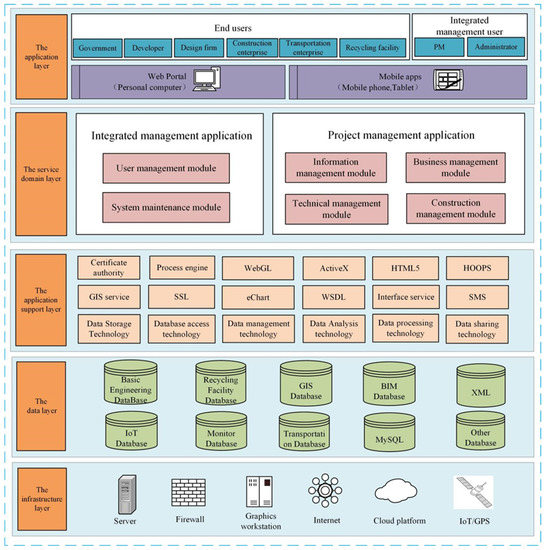
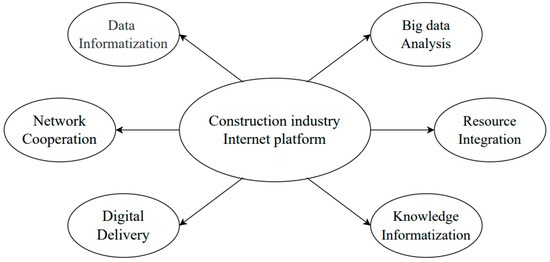
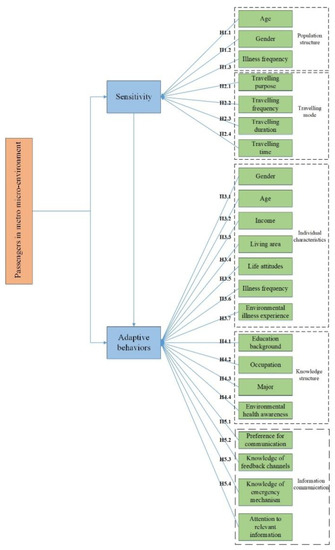
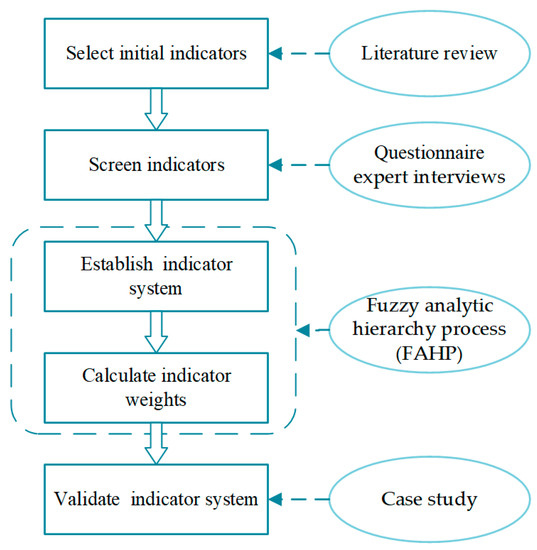
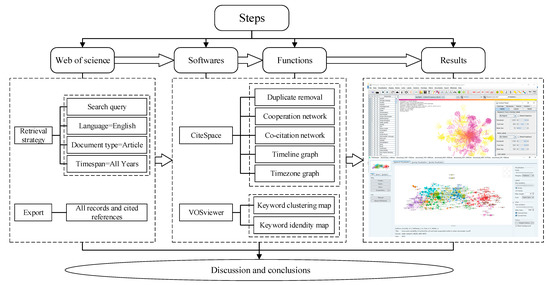
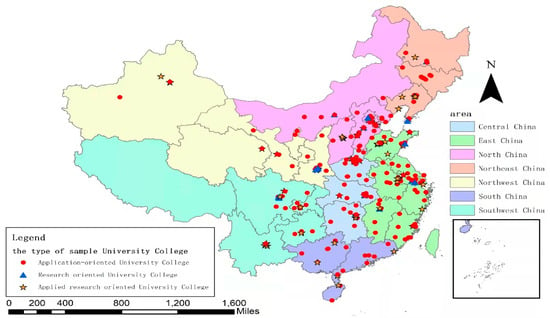
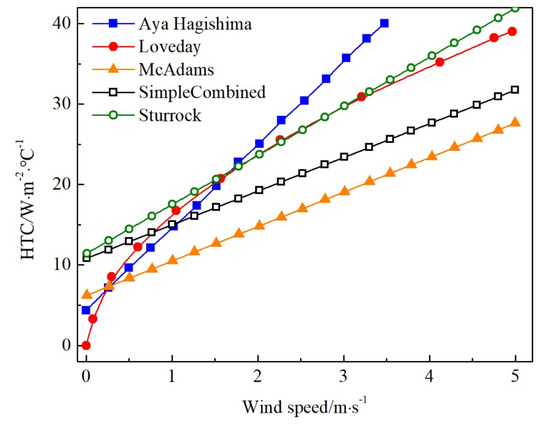
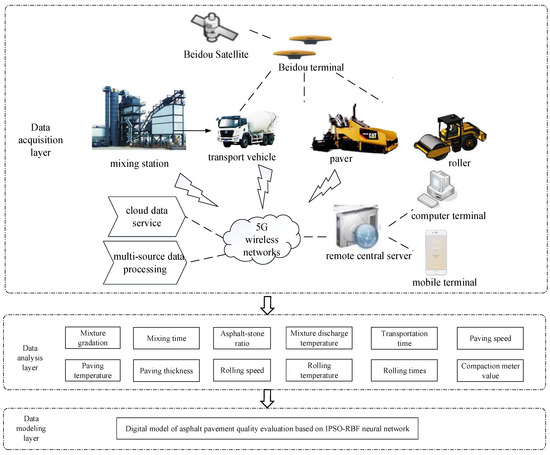
Buildings, Infrastructure and SDGs 2030
A topical collection in Buildings (ISSN 2075-5309). This collection belongs to the section "Building Energy, Physics, Environment, and Systems".
Viewed by 184684
Editors
Interests: strategies of urban infrastructure investment; risk management and disaster prevention; urban governance and sustainable development; energy conservation and climate adaptation; green building and carbon mitigation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: construction and demolition waste recycling; green building; energy policy; stakeholder engagement; competitiveness; housing quality; smart construction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: neural sensors; neuromanagement in engineering; engineering management; public acceptance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: building sustainability based on smart technologies (construction waste management, green building, LCA, prefabricated building, BIM); sustainable urbanization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In 2015, all Member States of the United Nations adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which set 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to end poverty, protect the planet, and improve the lives and prospects of everyone, everywhere by 2030. The buildings and infrastructure are directly related to the achievement of some SDGs, such as clean water and sanitation (SDG 6), affordable and clean energy (SDG 7), industry, innovation, and infrastructure (SDG 9), and sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11), and they also play an essential role in underpinning the other SDGs in education, health, and economic growth. Therefore, achieving sustainable development of buildings and infrastructure is critical to guiding the economic, social, and environmentally sustainable transformation of cities. Moreover, given the globally negative impact caused by the outbreak of COVID-19, the investments, construction, and operation of sustainable buildings and infrastructures have become fundamental conditions for countries to respond to COVID-19.
As such, this Topical Collection aims to explore the influence features and pathways of buildings and infrastructure on the achievement of 2030 SDGs, and to propose the directions, strategies, and solutions for cities to improve the sustainability of buildings and infrastructures.
We welcome original research including—but not limited to—the following topics and themes:
- Buildings, infrastructures, and urban environment;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and urban resilience;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and energies;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and climate responses;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and COVID-19 responses;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and health;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and education;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and sustainable development models;
- Buildings, infrastructures, sustainable production, and consumption models;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and promoting equality and justice;
- Buildings, infrastructures, and promoting global partnerships.
Prof. Dr. Tao Wang
Prof. Dr. Jian Zuo
Dr. Hanliang Fu
Dr. Zezhou Wu
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- green building
- infrastructure
- sustainable development goals
- resilient city
- city environment
- COVID-19
- healthy building