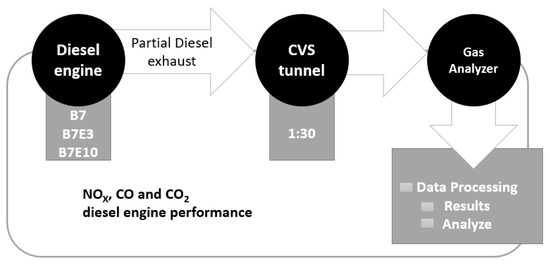
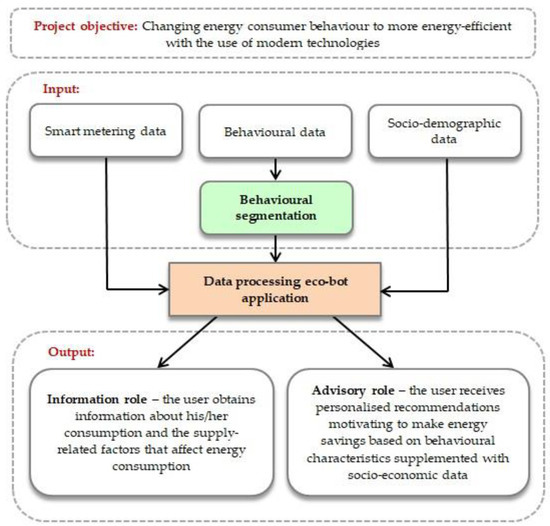
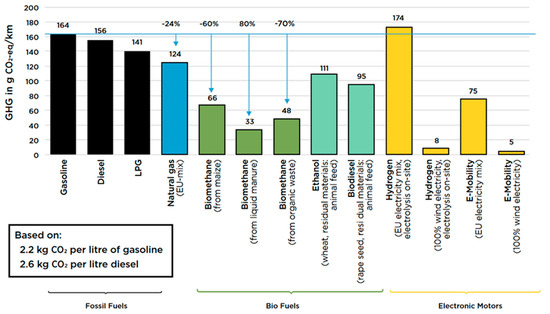
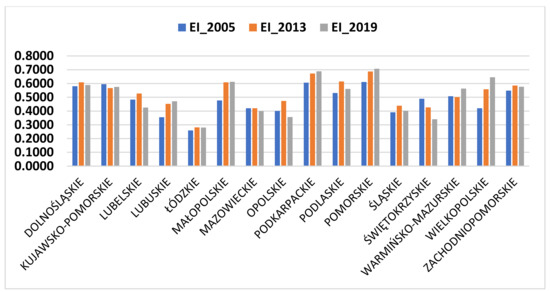
Feature Papers in Energy, Environment and Well-Being
A topical collection in Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This collection belongs to the section "B: Energy and Environment".
Viewed by 335293Editors
Interests: applied physics; ecophysics; environmental monitoring and accounting; vibro-acoustics; environmental science and cultural heritage applications; environment; health and well-being
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: environmental impact assessment; environmental analysis; sustainability; environment; sustainable development; biodiversity; ecology; conservation biology; environmental management; conservation.
2. State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control, School of Environment, Beijing Normal University, No. 19 Xinjiekouwai Street, Beijing 100875, China
Interests: life cycle assessment; energy–exergy–emergy; environmental impact assessment; circular economy; urban metabolism and sustainability; food and water security; disparity in access to energy sources; large efforts invested in energy and resource efficiency, prosperous way down, and environmental integrity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear colleagues,
The Guest Editors are inviting submissions for a Special Issue that addresses radically innovative scenarios and frameworks to assess the interplay of energy, environment, and societal well-being. This is especially needed for the present condition of world societies that have shown their fragility in regards to pollution and pollution-favored disasters and diseases (the last of which has been the coronavirus pandemic). In particular, we are seeking feature papers that consider the following:
(a) Energy is a fundamental resource for societal and economic metabolisms; not only we need energy, but we clearly need to address crucial questions about its use (energy to do what?) and appropriate management (top-down vs bottom-up energy policy making).
(b) Not all energies have the same quality and environmental costs: extraction, processing, use, turnover time, land and water demand. This makes energy planning a challenge, much beyond the achieved or achievable technological progress. We cannot disregard that different energy sources (either renewable or nonrenewable) have pros and cons, in that their use affects the environment and life quality to different but not negligible extents. This is especially true considering CO2 emissions, the hard co-existence of birds and wind turbines, and the impacts of large dams on water availability to farming, among other claimed constraints and trade-offs. Furthermore, a new kind of energy scarcity is occurring, not due to limited abundance, but increasingly due to environmental constraints and trade-offs, to unequal availability worldwide and market prices. The latter also affects the spread of renewables and energy efficiency efforts and programs.
(c) Achieving sustainable economies and shared well-being calls for urgent re-framing of the energy problem towards a balanced mix of different solutions, including technological improvement, use of energy resources consistent with their thermodynamic properties, a selection of environmentally friendly sources and carriers, suitable approaches to monitoring of impacts, efficiency measures with rebound control, life-style equity and reduction of energy poverty, decrease of wasteful habits, recognition of environmental limits in a limited planet, and careful management of the energy-water-food-environment nexus. A deeper understanding of these crucial aspects including ways to address them in our production and consumption patterns may help us develop qualitative growth and sustainable lifestyles, beyond the illusion of unlimited energy availability and technological fix.
Dr. Marco Casazza
Dr. Pedro L. Lomas
Prof. Dr. Sergio Ulgiati
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- energy and environmental constraints and trade-offs
- sustainable energy use
- energy-water-food-environment nexus
- energy quality
- energy poverty
- energy price
- energy and well-being
- energy accounting and management