Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
- Vol. 42 (2021)
- Vol. 41 (2021)
- Vol. 40 (2021)
- Vol. 39 (2020)
- Vol. 38 (2020)
- Vol. 37 (2020)
- Vol. 36 (2020)
- Vol. 35 (2020)
- Vol. 34 (2019)
- Vol. 33 (2019)
- Vol. 32 (2019)
- Vol. 31 (2019)
- Vol. 30 (2019)
- Vol. 29 (2018)
- Vol. 28 (2018)
- Vol. 27 (2018)
- Vol. 26 (2018)
- Vol. 25 (2018)
- Vol. 24 (2017)
- Vol. 23 (2017)
- Vol. 22 (2017)
- Vol. 21 (2017)
- Vol. 20 (2016)
- Vol. 19 (2016)
- Vol. 18 (2016)
- Vol. 17 (2015)
- Vol. 16 (2014)
- Vol. 15 (2013)
- Vol. 14 (2012)
- Vol. 13 (2011)
- Vol. 12 (2010)
- Vol. 11 (2009)
- Vol. 10 (2008)
- Vol. 9 (2007)
- Vol. 8 (2006)
- Vol. 7 (2005)
- Vol. 6 (2004)
- Vol. 5 (2003)
- Vol. 4 (2002)
- Vol. 3 (2001)
- Vol. 2 (2000)
- Vol. 1 (1999)
Need Help?
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol., Volume 45, Issue 8 (August 2023) – 48 articles
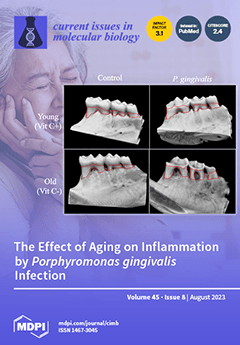
Cover Story (view full-size image):
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease driven by periodontal pathogens such as Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis), and its prevalence increases with age. This study aims to investigate the effects of aging on inflammation in P. gingivalis-infected macrophages, and on alveolar bone loss in a P. gingivalis-induced periodontitis mice model. The cytotoxicity and various cytokine levels of P. gingivalis were higher in old cells than in young cells. Furthermore, the activations of inflammasome components for interleukin (IL)-1β production by P. gingivalis infection were greater in old cells. Bone loss was significantly greater in P. gingivalis-infected aged mice than in young mice. This study enhances the understanding of periodontal inflammatory response in the elderly. View this paper
- Issues are regarded as officially published after their release is announced to the table of contents alert mailing list.
- You may sign up for e-mail alerts to receive table of contents of newly released issues.
- PDF is the official format for papers published in both, html and pdf forms. To view the papers in pdf format, click on the "PDF Full-text" link, and use the free Adobe Reader to open them.
Previous Issue
Next Issue
Issue View Metrics
Multiple requests from the same IP address are counted as one view.