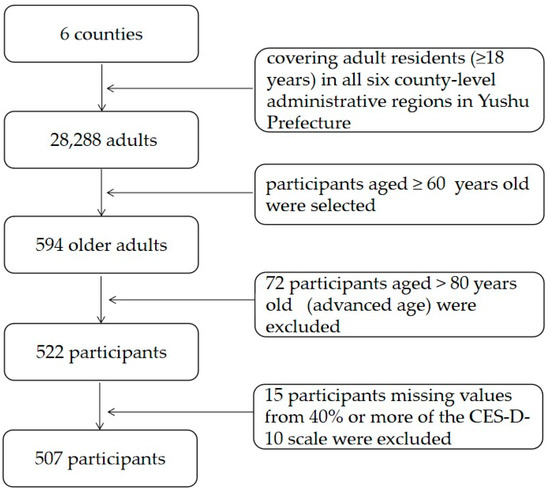
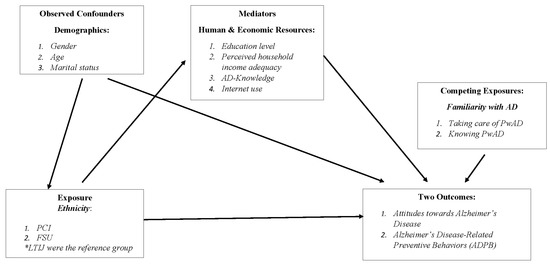
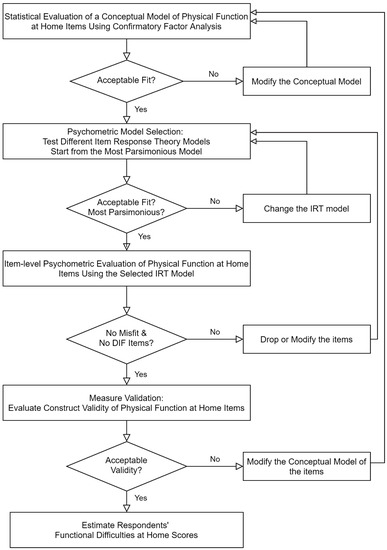
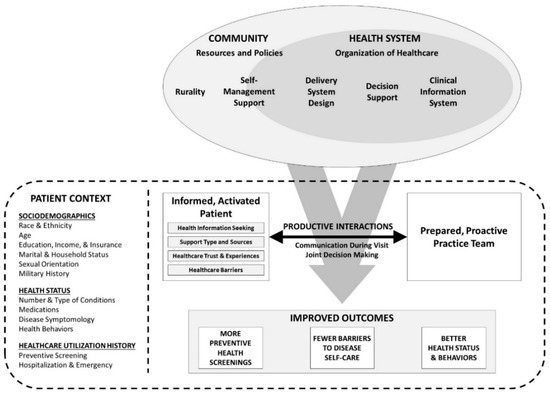
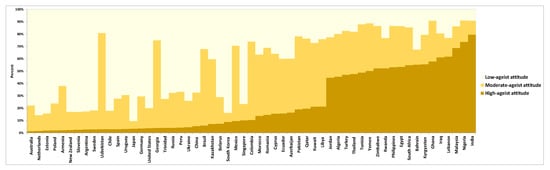
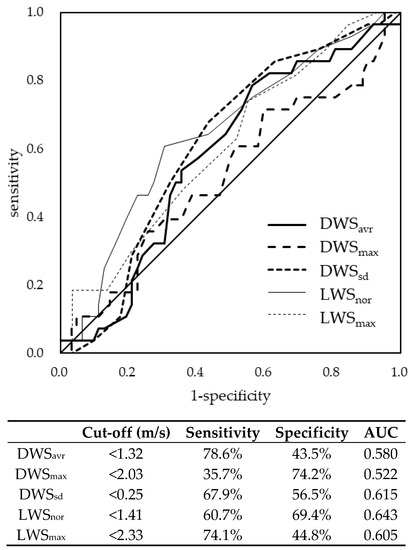
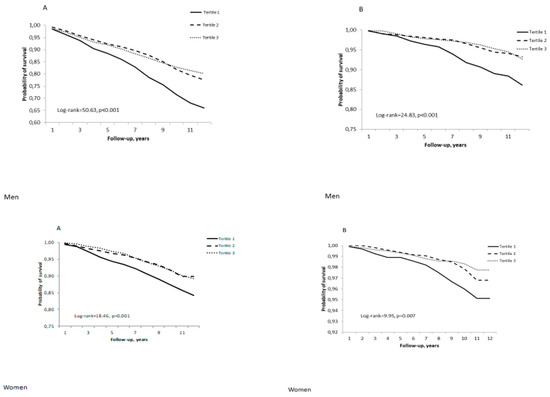
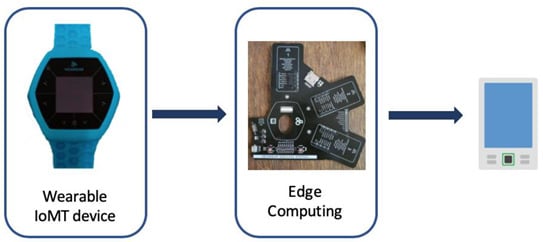
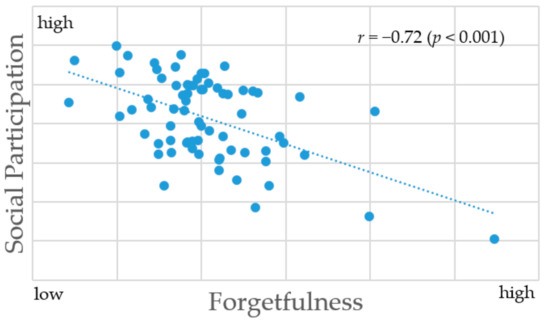
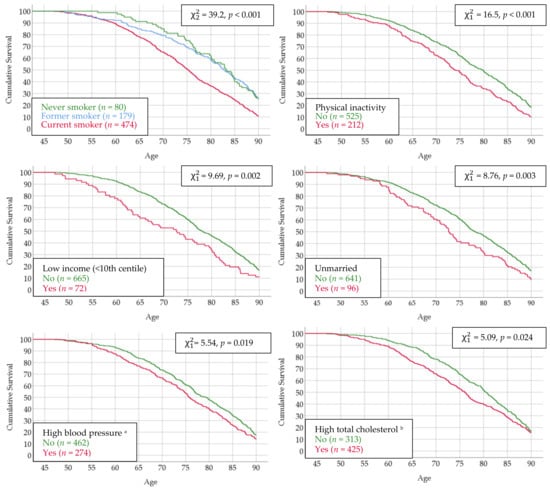
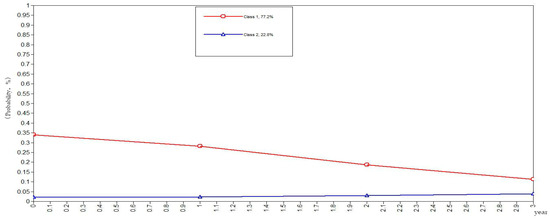
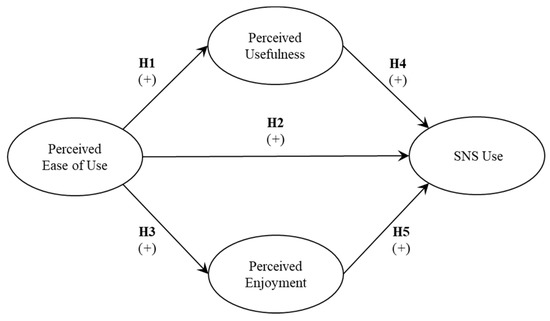
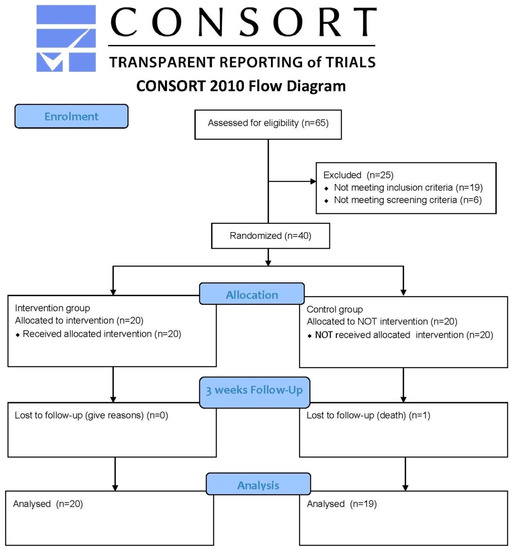
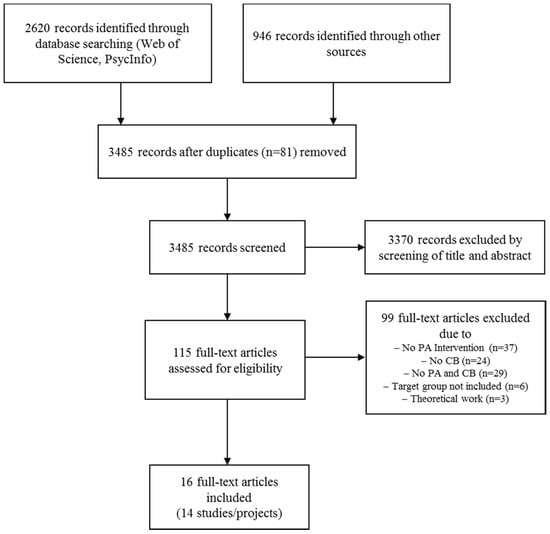
Aging and Public Health
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601). This collection belongs to the section "Global Health".
Viewed by 589521Editors
3. Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, Texas A&M School of Public Health, College Station, TX 77843, USA
Interests: health risk assessment across the life course; program evaluation; evidence-based programming; measurement
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
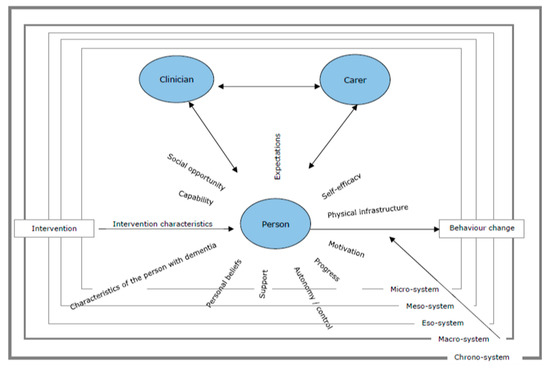
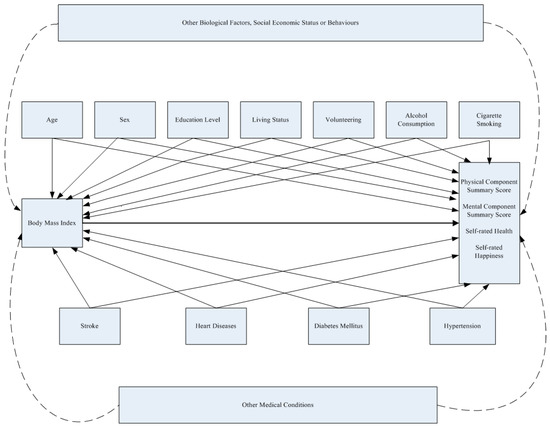
With the world-wide growth of the older adult population, there is increased concern about the impact of aging-related consequences on health and healthcare utilization. While individuals can encounter many problems as they age, two of the most pressing issues facing older adults are falls and chronic disease. The direct and indirect costs of these public health issues are enormous and growing. Many of the known risks for falls are associated with inadequate disease management (e.g., physical activity, medication, communication with healthcare providers), which makes strategies to address these issues highly interrelated. Over the past decade, there has been an emergence of large initiatives to reduce the burden of falls and chronic conditions that draw upon evidence-based programs (EBP) and practices in community, clinical, and industry settings. Often these efforts are translational in nature and integrate technology. Additional research is needed to document the reach and effectiveness of these interventions and advance their implementation, dissemination, and sustainability.
This Topical Collection features a spectrum of articles about health among older adults. Articles being solicited include those that address: (1) health-related risk factors; (2) physical, mental, and social aspects of health and well-being; (3) interventions and programs influencing health status, functioning, and quality of life; and (4) strategies to engage older adults in healthy behaviors, enhance the delivery of EBP, develop infrastructure and networks to support healthy aging.
This Topical Collection will advance healthy aging by contributing to what is known about health risk among older adults and opportunities to promote population health and aging. Further, this Topical Collection will inform practice, policy, and research needed to develop and nurture systems of support for evidence-based programs and strategies.
Prof. Dr. Matthew Lee Smith
Prof. Dr. Marcia G. Ory
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Aging
- Public health
- Behavioral intervention
- Fall prevention
- Physical activity
- Mental health
- Medication management
- Aging-in-place
- Built environment
- Technology
- Translational research
- Dissemination
- Implementation
- Evidence-based programs
- Quality of life
- Chronic disease management