Journal Description
Vibration
Vibration
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of vibration science and engineering, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 29.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
1.9 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.0 (2023)
Latest Articles
Soil–Structure Interaction and Damping by the Soil—Effects of Foundation Groups, Foundation Flexibility, Soil Stiffness and Layers
Vibration 2025, 8(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8010005 (registering DOI) - 31 Jan 2025
Abstract
In many tasks of railway vibration, the structure, that is, the track, a bridge, and a nearby building and its floors, is coupled to the soil, and the soil–structure interaction and the damping by the soil should be included in the analysis to
[...] Read more.
In many tasks of railway vibration, the structure, that is, the track, a bridge, and a nearby building and its floors, is coupled to the soil, and the soil–structure interaction and the damping by the soil should be included in the analysis to obtain realistic resonance frequencies and amplitudes. The stiffness and damping of a variety of foundations is calculated by an indirect boundary element method which uses fundamental solutions, is meshless, uses collocation points on the boundary, and solves the singularity by an appropriate averaging over a part of the surface. The boundary element method is coupled with the finite element method in the case of flexible foundations such as beams, plates, piles, and railway tracks. The results, the frequency-dependent stiffness and damping of single and groups of rigid foundations on homogeneous and layered soil and the amplitude and phase of the dynamic compliance of flexible foundations, show that the simple constant stiffness and damping values of a rigid footing on homogeneous soil are often misleading and do not represent well the reality. The damping may be higher in some special cases, but, in most cases, the damping is lower than expected from the simple theory. Some applications and measurements demonstrate the importance of the correct damping by the soil.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Experiment-Based Design of Stirling Cryocooler Compressor Using Response-Controlled Testing
by
Suna Güçyılmaz Çetin, Taylan Karaağaçlı and Ahmet H. Ertas
Vibration 2025, 8(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8010004 - 30 Jan 2025
Abstract
Flexure-based Stirling cryocooler compressors are a critical technology in providing cryogenic temperatures in various advanced engineering fields, such as aerospace, defense, and medical imaging. The most challenging problem in the design of this type of compressor is achieving a precise alignment that preserves
[...] Read more.
Flexure-based Stirling cryocooler compressors are a critical technology in providing cryogenic temperatures in various advanced engineering fields, such as aerospace, defense, and medical imaging. The most challenging problem in the design of this type of compressor is achieving a precise alignment that preserves small gaps between the components moving relative to each other and avoids severe friction and wear. This paper introduces a novel experimental procedure for designing Stirling cryocooler compressors, leveraging a recently developed nonlinear experimental modal analysis method known as response-controlled stepped-sine testing (RCT). The alignment in a compressor prototype was significantly improved in light of a series of RCT with base excitation. The enhanced compressor design was subsequently validated though a series of constant-current tests, which confirmed the elimination of the sticking/locking phenomenon observed in the initial design. Furthermore, an indirect harmonic force surface (HFS)-based approach proposed for weakly nonlinear systems was extended to identify the high and nonlinear damping (up to a 65% hysteretic modal damping ratio) observed in the enhanced compressor design due to excessive friction. As another contribution, it was shown that the extrapolation of the HFS gives accurate results in the prediction of the nonlinear modal parameters at response levels where no experimental data are available. In light of these findings, it was concluded that the enhanced design needs further design modifications to further decrease the friction and wear between the moving parts. Overall, this study provides valuable insights for designing cryocooler compressors, with implications for aerospace and medical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vibration Damping)
►▼
Show Figures
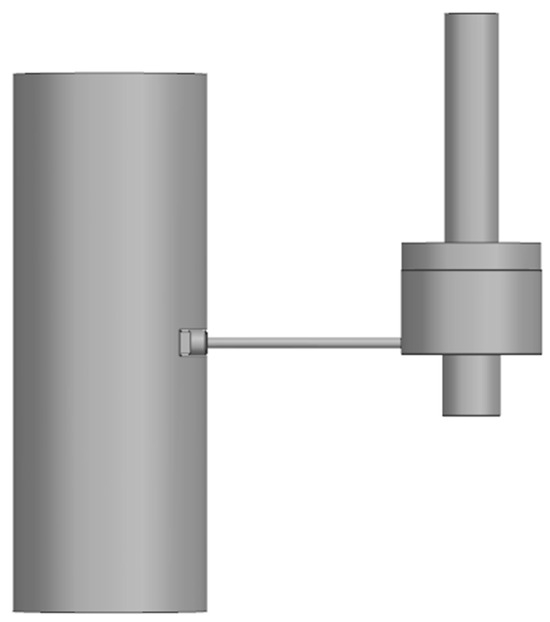
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Methodology for Designing Vibration Devices with Asymmetric Oscillations and a Given Value of the Asymmetry of the Driving Force
by
Mihail D. Gerasimov, Nickolai S. Lubimyi, Andrey A. Polshin, Boris S. Chetverikov and Anastasia Chetverikova
Vibration 2025, 8(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8010003 - 15 Jan 2025
Abstract
In mechanical engineering, the building industry, and many other branches of industry, vibration machines are widely used, in which circular and directed oscillations predominate in the form of movement of the working equipment. This article examines methods for generating asymmetric oscillations, which are
[...] Read more.
In mechanical engineering, the building industry, and many other branches of industry, vibration machines are widely used, in which circular and directed oscillations predominate in the form of movement of the working equipment. This article examines methods for generating asymmetric oscillations, which are estimated by a numerical parameter, namely by the coefficient of asymmetry of the magnitude of the driving force when changing the direction of action in a directed motion within each period of oscillations. It is shown that for generating asymmetric mechanical vibrations, vibration devices are used, consisting of vibrators of directed vibrations, called stages. These stages form the total asymmetric driving force. The behavior of the total driving force of asymmetric vibrations and the working equipment of the vibration machine are described by analytical equations, which represent certain laws of motion of the mechanical system. This article presents a numerical analysis of methods for obtaining laws of motion for a two-stage, three-stage, and four-stage vibration device with asymmetric oscillations. An analysis of the methodology for obtaining a generalized law of motion for a vibration device with asymmetric oscillations is performed based on the application of polyharmonic oscillation synthesis methods. It is shown that the method of forming the total driving force of a vibration device based on the coefficients of the terms of the Fourier series has limited capabilities. This article develops, substantiates, and presents a generalized method for calculating and designing a vibration device with asymmetric oscillations by the value of the total driving force and a given value of the asymmetry coefficient in a wide range of rational designs of vibration machines. The proposed method is accompanied by a numerical example for a vibration device with an asymmetry coefficient of the total driving force equal to 10.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nonlinear Vibration of Mechanical Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
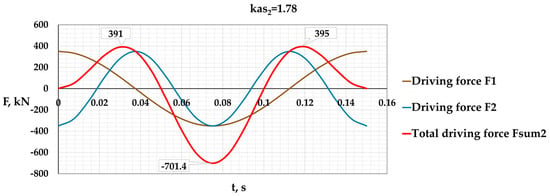
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Homogenization Method in Free Vibration of Multi-Material Auxetic Metamaterials
by
Kadir Gunaydin, Orhan Gülcan and Aykut Tamer
Vibration 2025, 8(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8010002 - 13 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Different additive manufacturing modalities enable the production of multi-material components which can be used in a wide range of industrial applications. The prediction of the mechanical properties of these components via finite element modelling rather than through testing is critical in terms of
[...] Read more.
Different additive manufacturing modalities enable the production of multi-material components which can be used in a wide range of industrial applications. The prediction of the mechanical properties of these components via finite element modelling rather than through testing is critical in terms of cost and time. However, due to the higher computational time spent on the modelling of lattice structures, different methods have been investigated to accurately predict mechanical properties. For this purpose, this study proposes the use of a homogenization method in the two most common types of multi-material lattices: honeycomb and re-entrant auxetics. Modal analyses were performed, and the first six mode shapes were extracted from explicit and implicit models. The results were compared in terms of mode shapes and natural frequencies. The results showed that homogenization can be successfully applied to multi-material honeycomb and re-entrant auxetic lattices without compromising the accuracy. It was shown that the implicit models predict the natural frequencies with an error range of less than 6.5% when compared with the explicit models in all of the mode shapes for both honeycomb and re-entrant auxetic lattices. The Modal Assurance Criteria, which is an indication of the degree of similarity between the mode shapes of explicit and implicit models, was found to be higher than 0.996, indicating very high similarity.
Full article
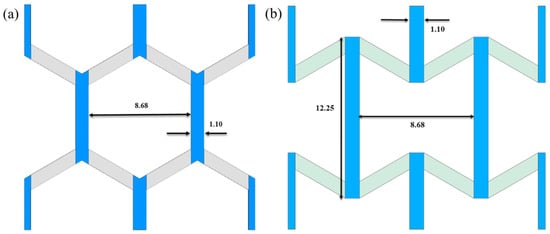
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parameter Estimation of Nonlinear Structural Systems Using Bayesian Filtering Methods
by
Kalil Erazo
Vibration 2025, 8(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8010001 - 31 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper examines the performance of Bayesian filtering system identification in the context of nonlinear structural and mechanical systems. The objective is to assess the accuracy and limitations of the four most well-established filtering-based parameter estimation methods: the extended Kalman filter, the unscented
[...] Read more.
This paper examines the performance of Bayesian filtering system identification in the context of nonlinear structural and mechanical systems. The objective is to assess the accuracy and limitations of the four most well-established filtering-based parameter estimation methods: the extended Kalman filter, the unscented Kalman filter, the ensemble Kalman filter, and the particle filter. The four methods are applied to estimate the parameters and the response of benchmark dynamical systems used in structural mechanics, including a Duffing oscillator, a hysteretic Bouc–Wen oscillator, and a hysteretic Bouc–Wen chain system. Based on the performance, accuracy, and computational efficiency of the methods under different operating conditions, it is concluded that the unscented Kalman filter is the most effective filtering system identification method for the systems considered, with the other filters showing large estimation errors or divergence, high computational cost, and/or curse of dimensionality as the dimension of the system and the number of uncertain parameters increased.
Full article
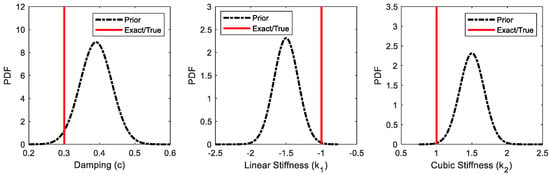
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mitigating Motion Sickness by Anticipatory Cues
by
Anna J. C. Reuten, Jelte E. Bos, Marieke H. Martens, Jessica Rausch and Jeroen B. J. Smeets
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1266-1278; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040065 - 21 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Car passengers suffer much more from motion sickness compared to car drivers, presumably because drivers can better anticipate the car’s motions. Visual and auditory cues that announce upcoming motions have been demonstrated to mitigate motion sickness. In automated vehicles, vibrotactile cues might be
[...] Read more.
Car passengers suffer much more from motion sickness compared to car drivers, presumably because drivers can better anticipate the car’s motions. Visual and auditory cues that announce upcoming motions have been demonstrated to mitigate motion sickness. In automated vehicles, vibrotactile cues might be more desirable. However, prior studies provided mixed evidence regarding their effectiveness. In this study, we directly compared the effectiveness of anticipatory auditory and vibrotactile cues. We determined their effectiveness by examining self-reported motion sickness from anticipatory sessions with auditory or vibrotactile cues announcing the onset and direction of upcoming motion relative to a control session. Our preregistered analysis did not show a significant difference in mitigation between the cues but also no significant overall effect. As this lack of an effect may be due to limited statistical power, we performed an internal meta-analysis. This analysis demonstrated a small overall effect of anticipatory cues. We conclude that it is worthwhile to investigate how their effectiveness can be enhanced.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stress Distribution and Transverse Vibration of Flywheel Within Linear Elastic Range
by
Desejo Filipeson Sozinando, Kgotso Koketso Leema, Vhahangwele Colleen Sigonde, Bernard Xavier Tchomeni and Alfayo Anyika Alugongo
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1248-1265; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040064 - 13 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Flywheels have been largely used in rotating machine engines to save inertial energy and to limit speed fluctuations. A stress distribution problem is created due to the centrifugal forces that are formed when the flywheel is spinning around, which leads to different levels
[...] Read more.
Flywheels have been largely used in rotating machine engines to save inertial energy and to limit speed fluctuations. A stress distribution problem is created due to the centrifugal forces that are formed when the flywheel is spinning around, which leads to different levels of pressure and decompression inside its structure. Lack of balance leads to high energy losses through various mechanisms, which deteriorate both the flywheel’s expectancy and their ability to rotate at high speeds. Deviation in the design of flywheels from their optimum performance can cause instability issues and even a catastrophic failure during operation. This paper aims to analytically examine the stress distribution of radial and tangential directions along the flywheel structure within a linear elastic range. The eigenvalues and eigenvectors, which are representative of free vibrational features, were extracted by applying finite element analysis (FEA). Natural frequencies and their corresponding vibrating mode shapes and mass participation factors were identified. Furthermore, Kirchhoff–Love plate theory was employed to model the transverse vibration of the system. A general solution for the radial component of the equation of flywheel motion was derived with the help of the Bessel function. The results show certain modes of vibration identified as particularly influential in specific directions. Advanced time-frequency analysis techniques, including but not limited to continuous wavelet transform (CWT) and Hilbert–Huang transform (HHT), were applied to extract transverse vibration features of the flywheel system. It was also found that using CWT, low-frequency vibrations contribute to the majority of the energy in the extracted signal spectrum, while HHT exposes the high-frequency components of vibration that may cause significant structural damage if not addressed in time.
Full article
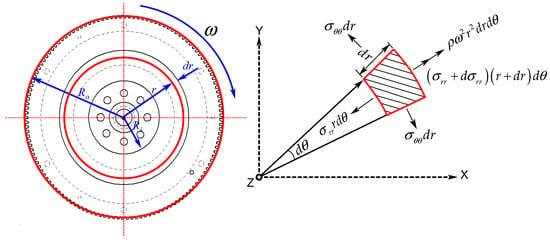
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Theoretical and Experimental Vibration Generation in a Coaxial Pulse-Tube Cryocooler
by
Hongyan Wei, Yulan Li, Yuqiang Xun and Huaqiang Zhong
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1226-1247; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040063 - 11 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The microphonic noise induced by the vibration from cryocoolers has been found to cause energy resolution degradation in vibration-sensitive instruments. In this paper, theoretical and experimental research on the vibration generation mechanism of an aerospace-grade coaxial pulse-tube cryocooler (CPTC) is presented. Accordingly, suggestions
[...] Read more.
The microphonic noise induced by the vibration from cryocoolers has been found to cause energy resolution degradation in vibration-sensitive instruments. In this paper, theoretical and experimental research on the vibration generation mechanism of an aerospace-grade coaxial pulse-tube cryocooler (CPTC) is presented. Accordingly, suggestions for suppressing the vibration of the pulse-tube cryocooler are provided. A vibration model for the Oxford-type dual-opposed linear compressor is established, and the mechanism of vibration induced by the compressor is theoretically analyzed. A numerical simulation indicates that deviations in the compressor’s inductance coefficient, electromagnetic force coefficient, and flexure spring stiffness coefficient significantly affect the axial vibration of the compressor. The theoretical and experimental studies show that the high-order harmonic vibrations of the compressor are determined by both the resonance of the flexure springs and the high-order harmonics of the driving power supply. Through experiments and simulations, it is revealed that the dynamic gas pressure only induces vibration axially at the cold tip, while the radial vibration at the cold tip is determined by the heat head ‘s vibration and the structural response characteristics of the cold finger.
Full article
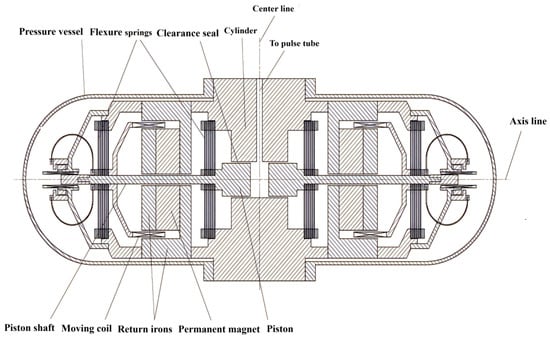
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Displacement Transmissibility and Bifurcation Behavior in Nonlinear Systems with Friction and Nonlinear Spring
by
Deog Jae Hur and Sung Chul Hong
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1210-1225; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040062 - 3 Dec 2024
Abstract
In this paper, a nonlinear vibration system with friction and linear and nonlinear springs is modeled and analyzed. The analysis examined how the combination of nonlinear variables affects the displacement of the system using the slowly varying amplitude and phase (SVAP) method. The
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a nonlinear vibration system with friction and linear and nonlinear springs is modeled and analyzed. The analysis examined how the combination of nonlinear variables affects the displacement of the system using the slowly varying amplitude and phase (SVAP) method. The break-loose frequency at which relative motion begins was obtained as a function of the friction ratio, and it was found that the displacement transmissibility differed depending on the change in design parameters. The displacement transmissibility response showed a unique phenomenon in which bifurcation occurred in the front resonant branch before the maximum response point when the linear damping coefficient was small and the friction coefficient was large, and the displacement transfer curve was separated at a specific parameter value. This phenomenon can be divided into three parameter zones considering the bifurcation pattern and stability of the displacement transmissibility curve. In addition, a 3-D spatial zone of dimensionless parameters was presented, which can predict stability during the design process, along with the drawing method and procedure. This can be conveniently utilized in the process of setting the parameters of the isolators considering the stability of the response during the design. In the analysis and design process of vibration isolators with friction damping, this study has important implications for practical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nonlinear Vibration of Mechanical Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
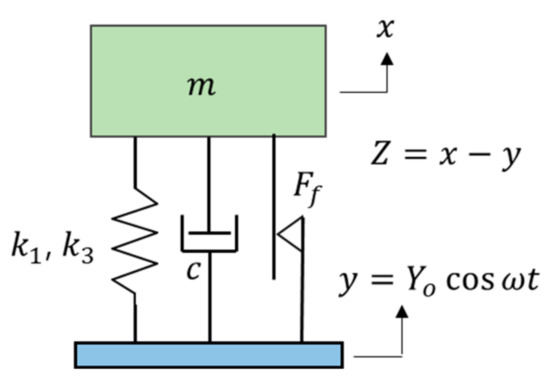
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Seismic Response of Hybrid Concrete/Steel Structures Equipped with the Seesaw System
by
George A. Papagiannopoulos, Panagiota S. Katsimpini and George D. Hatzigeorgiou
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1190-1209; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040061 - 1 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research investigates the seismic performance of structures equipped with the seesaw system in relation to conventional structures within two- and five-storey mixed concrete and steel buildings. Through time history analysis, the study assesses structural responses to severe ground motion accelerograms, taking into
[...] Read more.
This research investigates the seismic performance of structures equipped with the seesaw system in relation to conventional structures within two- and five-storey mixed concrete and steel buildings. Through time history analysis, the study assesses structural responses to severe ground motion accelerograms, taking into account both fixed-base conditions and soil–structure interaction (SSI) scenarios. The focus is on essential performance indicators such as maximum and residual displacements, inter-storey drift ratios, and floor accelerations. By comparing the structures with the seesaw system with bare structures, the research seeks to quantify the benefits of this novel design in mitigating seismic effects. A significant component of this study is the examination of various seismic incidence angles, specifically 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°. This extensive approach facilitates a comprehensive evaluation of structural behavior under diverse directional loadings, thereby capturing a wide range of potential seismic responses. The analysis of these different incidence angles is vital for understanding how the orientation of structural elements, particularly steel columns in the mixed system, affects the seismic performance of the building. Additionally, incorporating SSI effects yields a more precise depiction of structural behavior during earthquakes, considering the impact of soil flexibility on the overall system response.
Full article
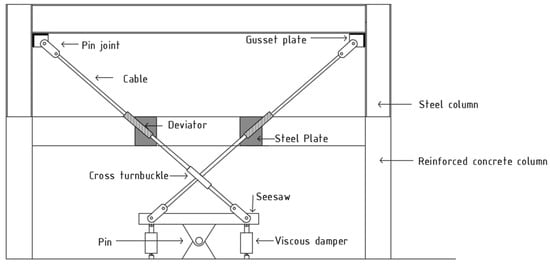
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stirred Not Shaken: A Longitudinal Pilot Study of Head Kinematics and Cognitive Changes in Horseracing
by
Emma Edwards, Bert Bond, Timothy P. Holsgrove, Jerry Hill, Ryan Baker and Genevieve K. R. Williams
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1171-1189; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040060 - 27 Nov 2024
Abstract
The purpose of this longitudinal pilot study was to add to the body of research relating to head kinematics/vibration in sport and their potential to cause short-term alterations in brain function. In horseracing, due to the horse’s movement, repeated low-level accelerations are transmitted
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this longitudinal pilot study was to add to the body of research relating to head kinematics/vibration in sport and their potential to cause short-term alterations in brain function. In horseracing, due to the horse’s movement, repeated low-level accelerations are transmitted to the jockey’s head. To measure this, professional jockeys (2 male, 2 female) wore an inertial measurement unit (IMU) to record their head kinematics while riding out. In addition, a short battery of tests (Stroop, Trail Making Test B, choice reaction time, manual dexterity, and visual function) was completed immediately before and after riding. Pre- and post-outcome measures from the cognitive test battery were compared using descriptive statistics. The average head kinematics measured across all jockeys and days were at a low level: resultant linear acceleration peak = 5.82 ± 1.08 g, mean = 1.02 ± 0.01 g; resultant rotational velocity peak = 10.37 ± 3.23 rad/s, mean = 0.85 ± 0.15 rad/s; and resultant rotational acceleration peak = 1495 ± 532.75 rad/s2, mean = 86.58 ± 15.54 rad/s2. The duration of an acceleration event was on average 127.04 ± 17.22 ms for linear accelerations and 89.42 ± 19.74 ms for rotational accelerations. This was longer than those noted in many impact and non-impact sports. Jockeys experienced high counts of linear and rotational head accelerations above 3 g and 400 rad/s2, which are considered normal daily living levels (average 300 linear and 445 rotational accelerations per hour of riding). No measurable decline in executive function or dexterity was found after riding; however, a deterioration in visual function (near point convergence and accommodation) was seen. This work lays the foundation for future large-scale research to monitor the head kinematics of riders, measure the effects and understand variables that might influence them.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vibrations in Sports)
►▼
Show Figures
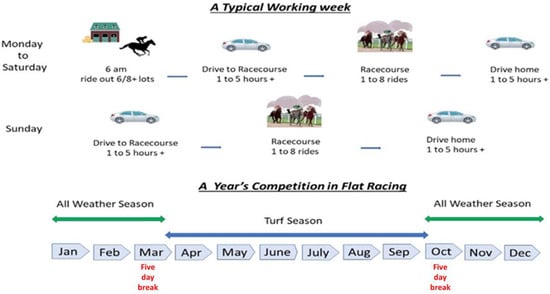
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Non-Linear Dynamic Analysis of Timber Frame Structure with Bolted-Fastener Connections
by
Thomas Catterou, Yann Sousseau, Sidi Mohammed Elachachi, Myriam Chaplain and Carole Faye
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1156-1170; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040059 - 26 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Understanding the dynamics of timber structures is essential for the timber structural engineering field, where it is necessary to build predictive numerical models and digital twins. Three similar-sized representative post-beam bracing frames with wood–metal assemblies were tested. Experimental modal analysis gave some indication
[...] Read more.
Understanding the dynamics of timber structures is essential for the timber structural engineering field, where it is necessary to build predictive numerical models and digital twins. Three similar-sized representative post-beam bracing frames with wood–metal assemblies were tested. Experimental modal analysis gave some indication of the non-linear behaviour of the structure. Then, the frame was submitted to a logarithmic sine sweep, which highlighted some specificities of the non-linear modes: dependence on the sweep direction and amplitude, jump, etc. These phenomena can be explained by friction and shocks in the assemblies. An accurate model of these non-linearities could lead to resilient and more earthquake-resistant timber structures, as the equivalent damping of a non-linear structure is way lower than for a linear one.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Novel Nonlinear Suspension Based on Concept of Origami Metastructures: Theoretical and Experimental Investigations
by
Antonio Zippo, Giovanni Iarriccio, Moslem Molaie and Francesco Pellicano
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1126-1155; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040058 - 22 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents a comprehensive investigation of an innovative mechanical system inspired by recent advancements in metamaterials; more specifically, the work is focused on origami-type structures due to their intriguing mechanical properties. Originating from specific fields such as aerospace for their lightweight and
[...] Read more.
This study presents a comprehensive investigation of an innovative mechanical system inspired by recent advancements in metamaterials; more specifically, the work is focused on origami-type structures due to their intriguing mechanical properties. Originating from specific fields such as aerospace for their lightweight and foldable characteristics, origami mechanical devices exhibit unique nonlinear stiffness; in particular, when suitably designed, they show Quasi-Zero Stiffness (QZS) characteristics within a specific working range. The QZS property, aligned with the High Static Low Dynamic (HSLD) stiffness concept, suggests promising applications such as a low-frequency mechanical passive vibration isolator. The study explores the vibration isolation characteristics of origami-type suspensions, with a particular emphasis on their potential application as low-frequency passive vibration isolators. The Kresling Origami Module (KOM) has been selected for its compactness and compatibility with 3D printers. A detailed analysis using 3D CAD, Finite Element Analysis, and experimental testing has been carried out. The investigation includes the analysis of the influence of geometric parameters on the nonlinear force–displacement curve. Multibody simulations validate the low-frequency isolation properties within the QZS region, as well as disparities in dynamic properties beyond the QZS range. The study underscores the transformative potential of origami-type metamaterials in enhancing low-frequency vibration isolation technology. It also highlights challenges related to material properties and loading mass variations, providing valuable insights for future developments in this promising field.
Full article
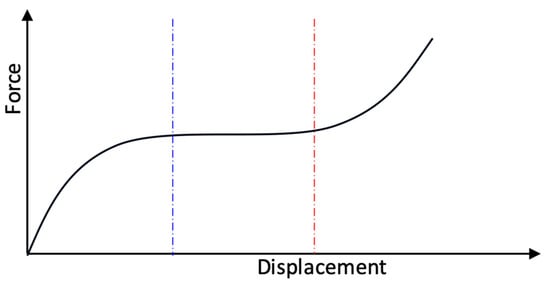
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Vibration-Based Diagnostics of Non-Ceramic Insulators: Characterization of Signals
by
Dániel Balogh, Richárd Cselkó and Gergely Márk Csányi
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1111-1125; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040057 - 18 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents an experimental method for testing composite insulators based on vibration testing. The method used investigated the propagation, signal shape, and distortion of excited mechanical waves under the influence of defects. The aim of the method was to identify defects in
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an experimental method for testing composite insulators based on vibration testing. The method used investigated the propagation, signal shape, and distortion of excited mechanical waves under the influence of defects. The aim of the method was to identify defects in the core of a composite insulator that cannot be economically detected by currently available diagnostic methods in field conditions. Therefore, this experiment aimed to distinguish between the mechanical waves’ characteristics of damaged and intact insulators using inexpensive tools. This article seeks to provide a basis for mechanical vibration diagnostics of composite insulators by demonstrating that damage to the core can result in a perceptible difference in the characteristics of mechanical waves when testing within the frequency range of audible sound.
Full article
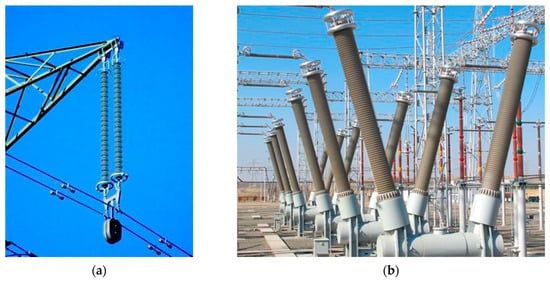
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Investigation of the Nonlinear Drill String Dynamics Under Stick–Slip Vibration
by
Mohammad Javad Moharrami, Hodjat Shiri and Clóvis de Arruda Martins
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1086-1110; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040056 - 15 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the influence of rotary table velocity, weight-on-bit, and viscous damping on the drill string stick–slip vibration. The analysis allows for studying the qualitative and quantitative variation of the dynamic response of the drill pipes and drill
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the influence of rotary table velocity, weight-on-bit, and viscous damping on the drill string stick–slip vibration. The analysis allows for studying the qualitative and quantitative variation of the dynamic response of the drill pipes and drill collars/bit. To achieve this goal, a robust and practical finite element (FE) model of the full-scaled drill string was developed based on a velocity-weakening formulation of the nonlinear bit–rock interaction. A detailed investigation of damping parameters was carried out. The performance of the developed model was verified through comparisons with a lumped-parameter model and a field test example. Parametric studies on the stick–slip response of the entire drill string under different field operational conditions were conducted. The dynamical time series of the system response were analyzed in terms of the phase planes, response spectra, and descriptive statistics of the drill pipes and drill collars. The findings of the study revealed that for a realistic drill string geometry, the angular velocity (i.e., mean, peak-to-peak amplitude, and standard deviation) and dominant frequency of self-excited torsional stick–slip oscillations along the drill pipes and drill collars/bit are mainly governed by the rotary table velocity. Furthermore, it was shown that the contribution of higher harmonics in the torsional stick–slip response of the drill pipes is more substantial than the drill collars/bit.
Full article
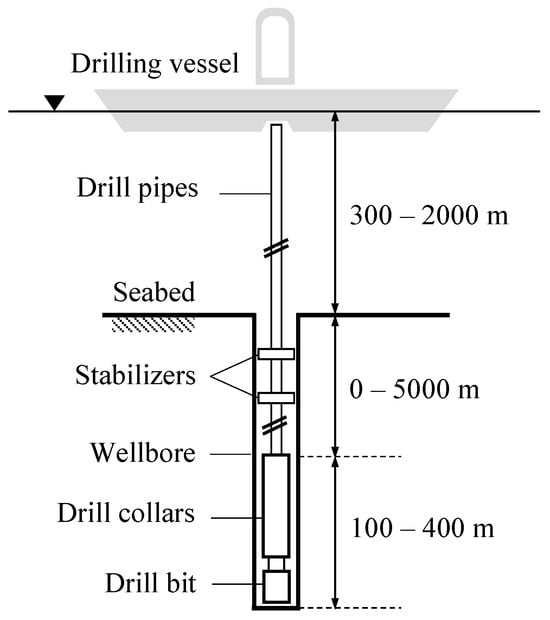
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modular Modeling of a Half-Vehicle System Using Generalized Receptance Coupling and Frequency-Based Substructuring (GRCFBS)
by
Behzad Hamedi and Saied Taheri
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1063-1085; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040055 - 11 Nov 2024
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents an advanced modular modeling approach for vertical vibration analysis of dynamic systems using the Generalized Receptance Coupling and Frequency-Based Substructuring (GRCFBS) method. The focus is on a four-DoF half-vehicle model comprising three key subsystems: front suspension, rear suspension, and the
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an advanced modular modeling approach for vertical vibration analysis of dynamic systems using the Generalized Receptance Coupling and Frequency-Based Substructuring (GRCFBS) method. The focus is on a four-DoF half-vehicle model comprising three key subsystems: front suspension, rear suspension, and the vehicle’s trimmed body. The proposed technique is designed to predict dynamic responses in reconfigurable systems across various applications, including automotive, robotics, mechanical machinery, and aerospace structures. By coupling the receptance matrices (FRFs) of individual vehicle modules, the overall system receptance matrix is efficiently derived in a disassembled configuration. Two generalized coupling methods, originally developed by Jetmundsen and D.D. Klerk, are employed to determine the complete vehicle’s receptance matrix from its subsystems. Validation is achieved by comparing the results with established methods, such as direct solution and modal analysis, demonstrating high accuracy and reliability for complex dynamic systems. This modular approach allows for the creation of reduced-order models focused on key measurement points without the need for detailed system representation. The method offers significant advantages in early-stage vehicle development, providing critical insights into system vibration behavior.
Full article
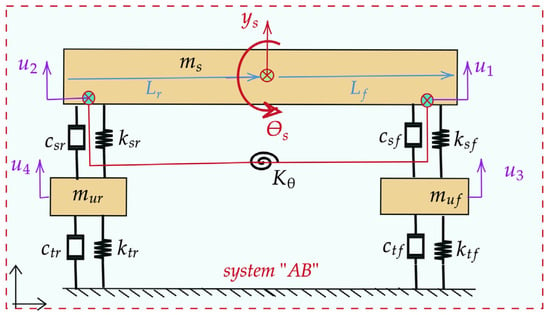
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Vibration Signal Analysis for Intelligent Rotating Machinery Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Comprehensive Systematic Literature Review
by
Ikram Bagri, Karim Tahiry, Aziz Hraiba, Achraf Touil and Ahmed Mousrij
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 1013-1062; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040054 - 31 Oct 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Many industrial processes, from manufacturing to food processing, incorporate rotating elements as principal components in their production chain. Failure of these components often leads to costly downtime and potential safety risks, further emphasizing the importance of monitoring their health state. Vibration signal analysis
[...] Read more.
Many industrial processes, from manufacturing to food processing, incorporate rotating elements as principal components in their production chain. Failure of these components often leads to costly downtime and potential safety risks, further emphasizing the importance of monitoring their health state. Vibration signal analysis is now a common approach for this purpose, as it provides useful information related to the dynamic behavior of machines. This research aimed to conduct a comprehensive examination of the current methodologies employed in the stages of vibration signal analysis, which encompass preprocessing, processing, and post-processing phases, ultimately leading to the application of Artificial Intelligence-based diagnostics and prognostics. An extensive search was conducted in various databases, including ScienceDirect, IEEE, MDPI, Springer, and Google Scholar, from 2020 to early 2024 following the PRISMA guidelines. Articles that aligned with at least one of the targeted topics cited above and provided unique methods and explicit results qualified for retention, while those that were redundant or did not meet the established inclusion criteria were excluded. Subsequently, 270 articles were selected from an initial pool of 338. The review results highlighted several deficiencies in the preprocessing step and the experimental validation, with implementation rates of 15.41% and 10.15%, respectively, in the selected prototype studies. Examination of the processing phase revealed that time scale decomposition methods have become essential for accurate analysis of vibration signals, as they facilitate the extraction of complex information that remains obscured in the original, undecomposed signals. Combining such methods with time–frequency analysis methods was shown to be an ideal combination for information extraction. In the context of fault detection, support vector machines (SVMs), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, k-nearest neighbors (KNN), and random forests have been identified as the five most frequently employed algorithms. Meanwhile, transformer-based models are emerging as a promising venue for the prediction of RUL values, along with data transformation. Given the conclusions drawn, future researchers are urged to investigate the interpretability and integration of the diagnosis and prognosis models developed with the aim of applying them in real-time industrial contexts. Furthermore, there is a need for experimental studies to disclose the preprocessing details for datasets and the operational conditions of the machinery, thereby improving the data reproducibility. Another area that warrants further investigation is differentiation of the various types of fault information present in vibration signals obtained from bearings, as the defect information from the overall system is embedded within these signals.
Full article
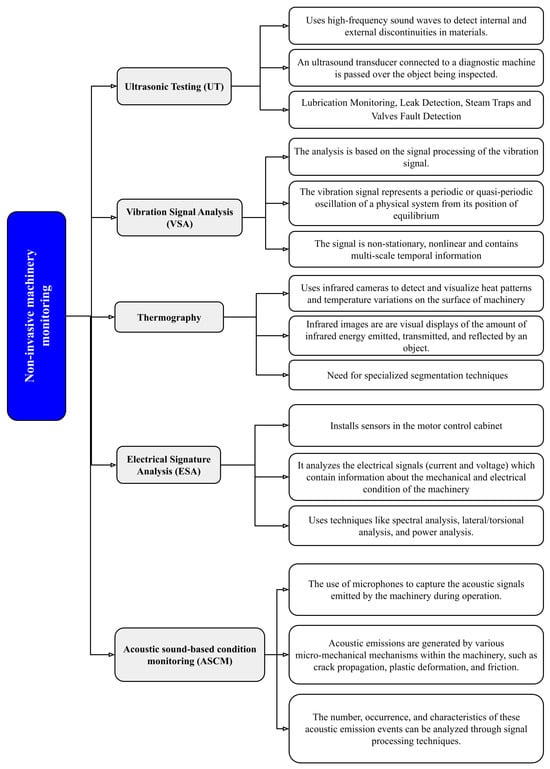
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Active Vibration Control Performance Comparison Based on Middle Pedestal Stiffness Using a Mobility Model and the Narrowband Fx-LMS Technique
by
Anmok Jeong, Kyuchul Jung, Youngcheol Park, Junyeong Heo and Hakjun Lee
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 999-1012; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040053 - 29 Oct 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Vibrations generated from equipment mounted on ships radiate into the water and affect covert operation capabilities. Accordingly, various studies are being conducted to reduce vibration transmitted from mounted equipment. In this study, a system consisting of mounting equipment, a 3-axis active mount, a
[...] Read more.
Vibrations generated from equipment mounted on ships radiate into the water and affect covert operation capabilities. Accordingly, various studies are being conducted to reduce vibration transmitted from mounted equipment. In this study, a system consisting of mounting equipment, a 3-axis active mount, a middle pedestal, and a lower mount of the middle pedestal was modeled using a finite element analysis program, and a mobility model was constructed by calculating the frequency response function between the positions required for analysis. The error signal (primary path) obtained using the mobility model and the response at the operating point by the control force of the actuator (secondary path) are applied to the narrowband Fx-LMS algorithm for vibration control, and the control performance was compared. Through coupling analysis of the middle pedestal, the control influence according to the rigidity of the middle pedestal was analyzed. As a result of the control simulation, the time required for vibration control was controlled approximately 6 times faster in the model, with increased stiffness of the middle pedestal, and the vibration reduction performance was predicted to improve by a minimum of 0.9 dB and a maximum of 13.3 dB. Through this study, a simulation model that can provide a guide for the design of the middle pedestal of a ship was obtained, and it is expected that it can be utilized for a preliminary design review before manufacturing the middle pedestal of a ship.
Full article
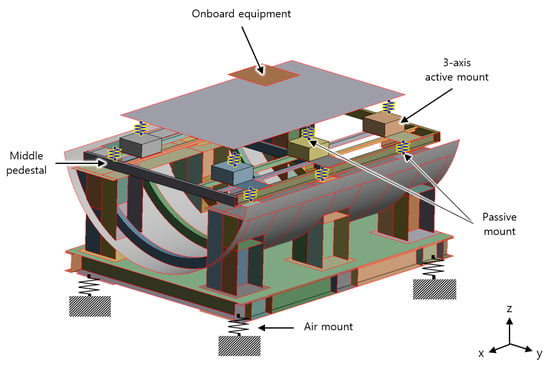
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unidirectional Flow Through Time-Dependent Cross-Sectional Areas of a Compliant Tube and a Valve: A Nonlinear Model
by
Christos Manopoulos, Sokrates Tsangaris, Christina Georgantopoulou and Dimitrios Mathioulakis
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 987-998; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040052 - 29 Oct 2024
Abstract
This work investigates the conditions for net flow generation by a straight tube with a cross-sectional area harmonically varying in time that connects two tanks—a problem that is mainly found in the design of impedance pumps. By assuming a quasi-one-dimensional flow and applying
[...] Read more.
This work investigates the conditions for net flow generation by a straight tube with a cross-sectional area harmonically varying in time that connects two tanks—a problem that is mainly found in the design of impedance pumps. By assuming a quasi-one-dimensional flow and applying continuity and momentum equations, a first-order differential equation with respect to the flow rate is derived and presented for the first time, including a nonlinear term that is responsible for net flow rate generation. Namely, the net flow rate is found to be nonzero (as is the nonlinear term) if the cross-sectional areas of the two tanks are unequal and one of them is smaller than that of the straight tube. In this case, the flow is directed from the smaller to the larger tank and the net flow rate increases with the frequency of the tube’s cross-sectional area variation. In contrast, when the tanks’ cross-sections are equal, the net flow is generated only if a valve is installed, e.g., at one end of the tube, due to the large asymmetries imposed in the hydraulic losses with respect to the tube mid-length. Compared with constant valve opening, the net flow rate is augmented significantly if the valve opening is time-dependent. By employing the same equation, the flow rate of an intra-aortic counter-pulsating balloon pump is also examined, in which the valve (representing the aortic valve) opens during the shrinkage of the tube, and it is shown that the net flow rate increases with the frequency and amplitude of the tube’s cross-sectional area. Conclusively, the harmonic oscillation in time of a tube’s wall can cause unidirectional flow only if asymmetric losses are present with respect to its mid-length.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nonlinear Vibration of Mechanical Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
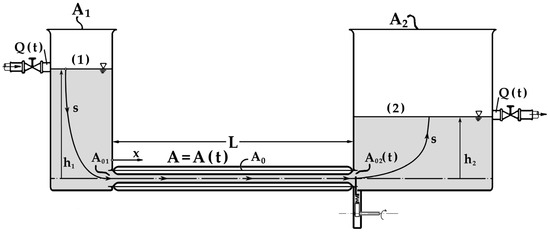
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Mechanical Fault Identification Method for On-Load Tap Changers Based on Hybrid Time—Frequency Graphs of Vibration Signals and DSCNN-SVM with Small Sample Sizes
by
Yanhui Shi, Yanjun Ruan, Liangchuang Li, Bo Zhang, Yichao Huang, Mao Xia, Kaiwen Yuan, Zhao Luo and Sizhao Lu
Vibration 2024, 7(4), 970-986; https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration7040051 - 28 Oct 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In engineering applications, the accuracy of on-load tap changer (OLTC) mechanical fault identification methods based on vibration signals is constrained by the quantity and quality of the samples. Therefore, a novel small-sample-size OLTC mechanical fault identification method incorporating short-time Fourier transform (STFT), synchrosqueezed
[...] Read more.
In engineering applications, the accuracy of on-load tap changer (OLTC) mechanical fault identification methods based on vibration signals is constrained by the quantity and quality of the samples. Therefore, a novel small-sample-size OLTC mechanical fault identification method incorporating short-time Fourier transform (STFT), synchrosqueezed wavelet transform (SWT), a dual-stream convolutional neural network (DSCNN), and support vector machine (SVM) is proposed. Firstly, the one-dimensional time-series vibration signals are transformed using STFT and SWT to obtain time–frequency graphs. STFT time–frequency graphs capture the global features of the OLTC vibration signals, while SWT time–frequency graphs capture the local features of the OLTC vibration signals. Secondly, these time–frequency graphs are input into the CNN to extract key features. In the fusion layer, the feature vectors from the STFT and SWT graphs are combined to form a fusion vector that encompasses both global and local time–frequency features. Finally, the softmax classifier of the traditional CNN is replaced with an SVM classifier, and the fusion vector is input into this classifier. Compared to the traditional fault identification methods, the proposed method demonstrates higher identification accuracy and stronger generalization ability under the conditions of small sample sizes and noise interference.
Full article
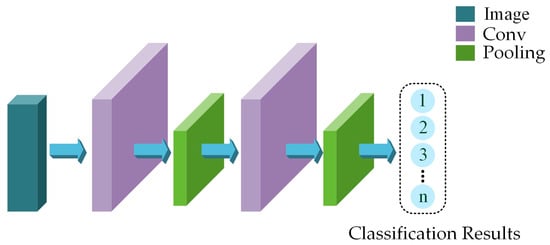
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Vibration
Whole-Body Vibration and Hand-Arm Vibration Related to ISO-TC108-SC4 Published Standards
Guest Editors: Setsuo Maeda, Marco TarabiniDeadline: 31 March 2025
Special Issue in
Vibration
Nonlinear Vibration of Mechanical Systems
Guest Editors: Francesco Pellicano, Yuri Mikhlin, Konstantin Avramov, Antonio ZippoDeadline: 15 June 2025
Special Issue in
Vibration
Machine Learning Applications to Vibration Problems
Guest Editor: Maria ChierichettiDeadline: 20 July 2025
Special Issue in
Vibration
Railway Dynamics and Ground-Borne Vibrations
Guest Editors: Aires Colaço, Hassan Liravi, Pedro Alves CostaDeadline: 20 September 2025









